Alvin Rajkomar
SDOH-NLI: a Dataset for Inferring Social Determinants of Health from Clinical Notes
Oct 27, 2023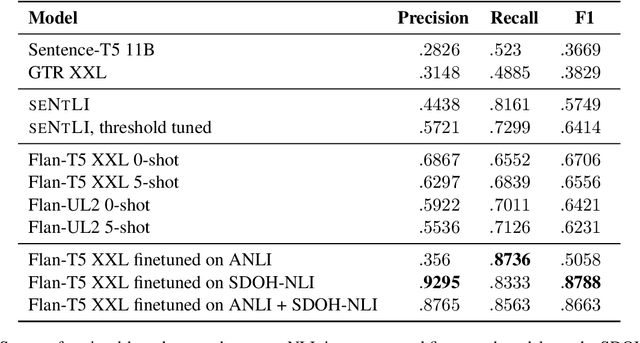
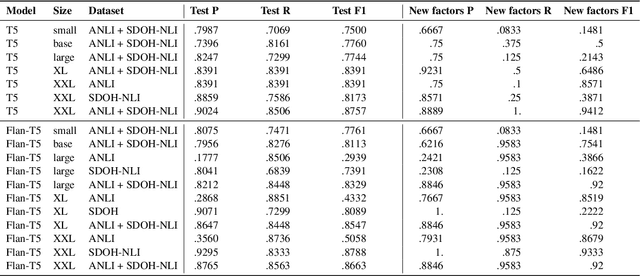
Abstract:Social and behavioral determinants of health (SDOH) play a significant role in shaping health outcomes, and extracting these determinants from clinical notes is a first step to help healthcare providers systematically identify opportunities to provide appropriate care and address disparities. Progress on using NLP methods for this task has been hindered by the lack of high-quality publicly available labeled data, largely due to the privacy and regulatory constraints on the use of real patients' information. This paper introduces a new dataset, SDOH-NLI, that is based on publicly available notes and which we release publicly. We formulate SDOH extraction as a natural language inference (NLI) task, and provide binary textual entailment labels obtained from human raters for a cross product of a set of social history snippets as premises and SDOH factors as hypotheses. Our dataset differs from standard NLI benchmarks in that our premises and hypotheses are obtained independently. We evaluate both "off-the-shelf" entailment models as well as models fine-tuned on our data, and highlight the ways in which our dataset appears more challenging than commonly used NLI datasets.
Large Language Models Encode Clinical Knowledge
Dec 26, 2022Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in natural language understanding and generation, but the quality bar for medical and clinical applications is high. Today, attempts to assess models' clinical knowledge typically rely on automated evaluations on limited benchmarks. There is no standard to evaluate model predictions and reasoning across a breadth of tasks. To address this, we present MultiMedQA, a benchmark combining six existing open question answering datasets spanning professional medical exams, research, and consumer queries; and HealthSearchQA, a new free-response dataset of medical questions searched online. We propose a framework for human evaluation of model answers along multiple axes including factuality, precision, possible harm, and bias. In addition, we evaluate PaLM (a 540-billion parameter LLM) and its instruction-tuned variant, Flan-PaLM, on MultiMedQA. Using a combination of prompting strategies, Flan-PaLM achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on every MultiMedQA multiple-choice dataset (MedQA, MedMCQA, PubMedQA, MMLU clinical topics), including 67.6% accuracy on MedQA (US Medical License Exam questions), surpassing prior state-of-the-art by over 17%. However, human evaluation reveals key gaps in Flan-PaLM responses. To resolve this we introduce instruction prompt tuning, a parameter-efficient approach for aligning LLMs to new domains using a few exemplars. The resulting model, Med-PaLM, performs encouragingly, but remains inferior to clinicians. We show that comprehension, recall of knowledge, and medical reasoning improve with model scale and instruction prompt tuning, suggesting the potential utility of LLMs in medicine. Our human evaluations reveal important limitations of today's models, reinforcing the importance of both evaluation frameworks and method development in creating safe, helpful LLM models for clinical applications.
Modelling EHR timeseries by restricting feature interaction
Nov 14, 2019

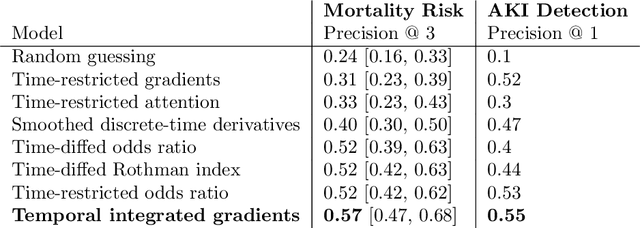
Abstract:Time series data are prevalent in electronic health records, mostly in the form of physiological parameters such as vital signs and lab tests. The patterns of these values may be significant indicators of patients' clinical states and there might be patterns that are unknown to clinicians but are highly predictive of some outcomes. Many of these values are also missing which makes it difficult to apply existing methods like decision trees. We propose a recurrent neural network model that reduces overfitting to noisy observations by limiting interactions between features. We analyze its performance on mortality, ICD-9 and AKI prediction from observational values on the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care III (MIMIC-III) dataset. Our models result in an improvement of 1.1% [p<0.01] in AU-ROC for mortality prediction under the MetaVision subset and 1.0% and 2.2% [p<0.01] respectively for mortality and AKI under the full MIMIC-III dataset compared to existing state-of-the-art interpolation, embedding and decay-based recurrent models.
Improved Patient Classification with Language Model Pretraining Over Clinical Notes
Oct 02, 2019



Abstract:Clinical notes in electronic health records contain highly heterogeneous writing styles, including non-standard terminology or abbreviations. Using these notes in predictive modeling has traditionally required preprocessing (e.g. taking frequent terms or topic modeling) that removes much of the richness of the source data. We propose a pretrained hierarchical recurrent neural network model that parses minimally processed clinical notes in an intuitive fashion, and show that it improves performance for multiple classification tasks on the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care III (MIMIC-III) dataset, improving top-5 recall to 89.7% (increase of 4.8%) for primary diagnosis classification and AUPRC to 35.2% (increase of 2.1%) for multilabel diagnosis classification compared to models that treat the notes as an unordered collection of terms, using no pretraining. We also apply an attribution technique to several examples to identify the words and the nearby context that the model uses to make its prediction, and show the importance of the words' context.
Explaining an increase in predicted risk for clinical alerts
Jul 10, 2019

Abstract:Much work aims to explain a model's prediction on a static input. We consider explanations in a temporal setting where a stateful dynamical model produces a sequence of risk estimates given an input at each time step. When the estimated risk increases, the goal of the explanation is to attribute the increase to a few relevant inputs from the past. While our formal setup and techniques are general, we carry out an in-depth case study in a clinical setting. The goal here is to alert a clinician when a patient's risk of deterioration rises. The clinician then has to decide whether to intervene and adjust the treatment. Given a potentially long sequence of new events since she last saw the patient, a concise explanation helps her to quickly triage the alert. We develop methods to lift static attribution techniques to the dynamical setting, where we identify and address challenges specific to dynamics. We then experimentally assess the utility of different explanations of clinical alerts through expert evaluation.
Scalable and accurate deep learning for electronic health records
May 11, 2018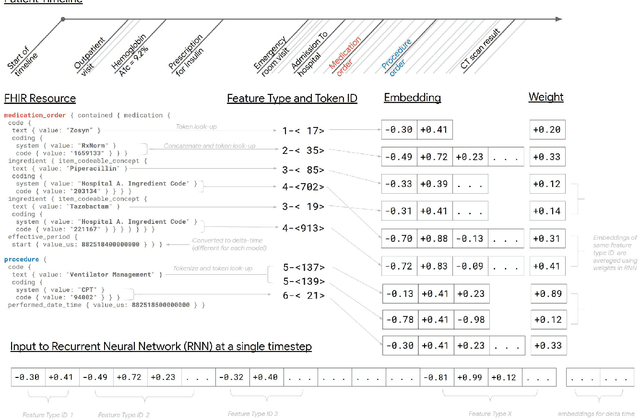
Abstract:Predictive modeling with electronic health record (EHR) data is anticipated to drive personalized medicine and improve healthcare quality. Constructing predictive statistical models typically requires extraction of curated predictor variables from normalized EHR data, a labor-intensive process that discards the vast majority of information in each patient's record. We propose a representation of patients' entire, raw EHR records based on the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) format. We demonstrate that deep learning methods using this representation are capable of accurately predicting multiple medical events from multiple centers without site-specific data harmonization. We validated our approach using de-identified EHR data from two U.S. academic medical centers with 216,221 adult patients hospitalized for at least 24 hours. In the sequential format we propose, this volume of EHR data unrolled into a total of 46,864,534,945 data points, including clinical notes. Deep learning models achieved high accuracy for tasks such as predicting in-hospital mortality (AUROC across sites 0.93-0.94), 30-day unplanned readmission (AUROC 0.75-0.76), prolonged length of stay (AUROC 0.85-0.86), and all of a patient's final discharge diagnoses (frequency-weighted AUROC 0.90). These models outperformed state-of-the-art traditional predictive models in all cases. We also present a case-study of a neural-network attribution system, which illustrates how clinicians can gain some transparency into the predictions. We believe that this approach can be used to create accurate and scalable predictions for a variety of clinical scenarios, complete with explanations that directly highlight evidence in the patient's chart.
* Published version from https://www.nature.com/articles/s41746-018-0029-1
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge