Michael Neunert
Gemini Robotics: Bringing AI into the Physical World
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in large multimodal models have led to the emergence of remarkable generalist capabilities in digital domains, yet their translation to physical agents such as robots remains a significant challenge. This report introduces a new family of AI models purposefully designed for robotics and built upon the foundation of Gemini 2.0. We present Gemini Robotics, an advanced Vision-Language-Action (VLA) generalist model capable of directly controlling robots. Gemini Robotics executes smooth and reactive movements to tackle a wide range of complex manipulation tasks while also being robust to variations in object types and positions, handling unseen environments as well as following diverse, open vocabulary instructions. We show that with additional fine-tuning, Gemini Robotics can be specialized to new capabilities including solving long-horizon, highly dexterous tasks, learning new short-horizon tasks from as few as 100 demonstrations and adapting to completely novel robot embodiments. This is made possible because Gemini Robotics builds on top of the Gemini Robotics-ER model, the second model we introduce in this work. Gemini Robotics-ER (Embodied Reasoning) extends Gemini's multimodal reasoning capabilities into the physical world, with enhanced spatial and temporal understanding. This enables capabilities relevant to robotics including object detection, pointing, trajectory and grasp prediction, as well as multi-view correspondence and 3D bounding box predictions. We show how this novel combination can support a variety of robotics applications. We also discuss and address important safety considerations related to this new class of robotics foundation models. The Gemini Robotics family marks a substantial step towards developing general-purpose robots that realizes AI's potential in the physical world.
Real-World Fluid Directed Rigid Body Control via Deep Reinforcement Learning
Feb 08, 2024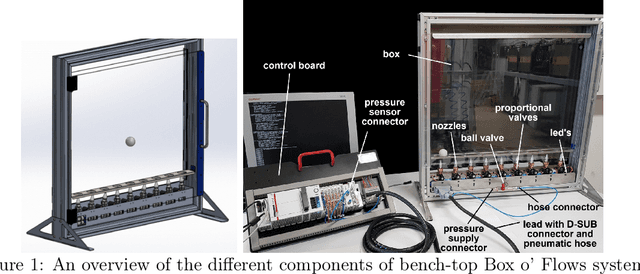
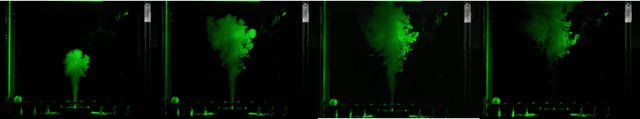
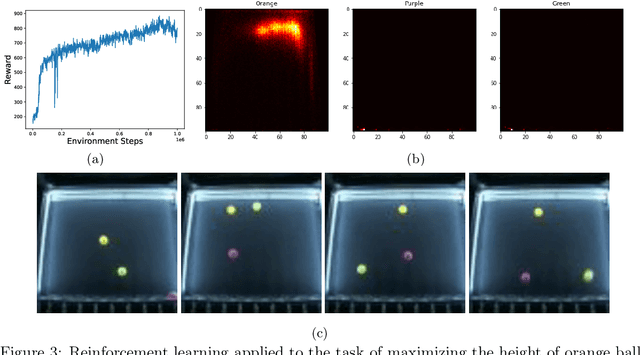
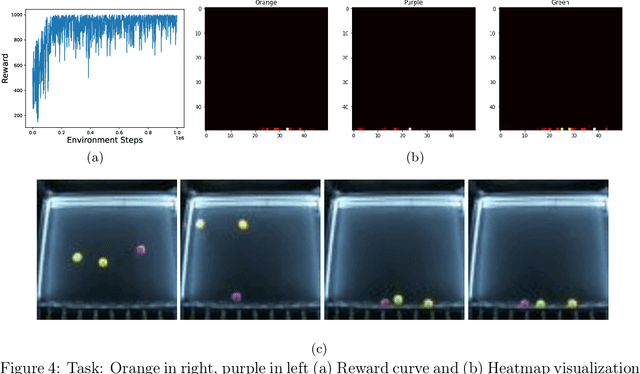
Abstract:Recent advances in real-world applications of reinforcement learning (RL) have relied on the ability to accurately simulate systems at scale. However, domains such as fluid dynamical systems exhibit complex dynamic phenomena that are hard to simulate at high integration rates, limiting the direct application of modern deep RL algorithms to often expensive or safety critical hardware. In this work, we introduce "Box o Flows", a novel benchtop experimental control system for systematically evaluating RL algorithms in dynamic real-world scenarios. We describe the key components of the Box o Flows, and through a series of experiments demonstrate how state-of-the-art model-free RL algorithms can synthesize a variety of complex behaviors via simple reward specifications. Furthermore, we explore the role of offline RL in data-efficient hypothesis testing by reusing past experiences. We believe that the insights gained from this preliminary study and the availability of systems like the Box o Flows support the way forward for developing systematic RL algorithms that can be generally applied to complex, dynamical systems. Supplementary material and videos of experiments are available at https://sites.google.com/view/box-o-flows/home.
Mastering Stacking of Diverse Shapes with Large-Scale Iterative Reinforcement Learning on Real Robots
Dec 18, 2023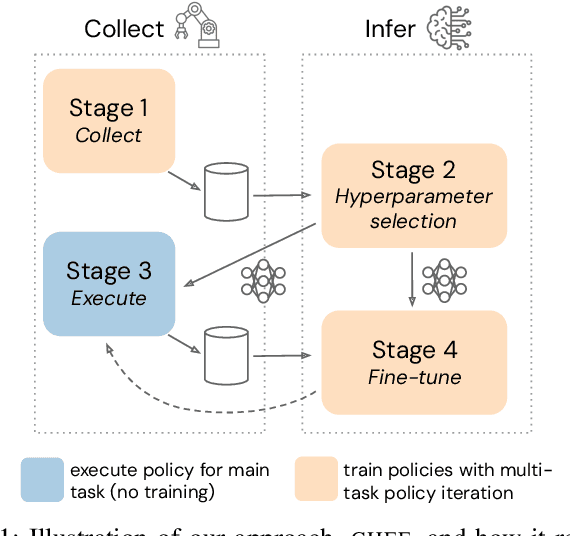
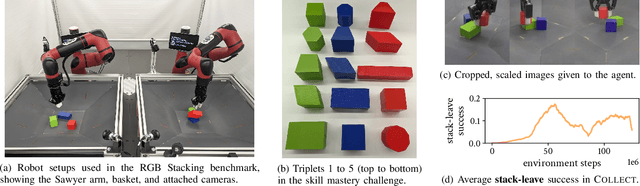
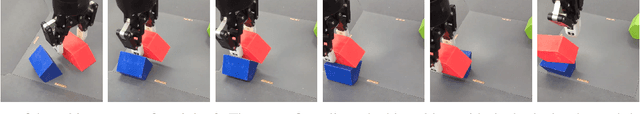
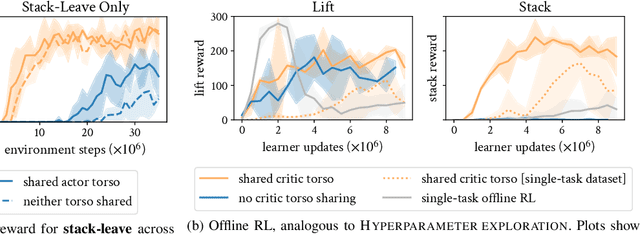
Abstract:Reinforcement learning solely from an agent's self-generated data is often believed to be infeasible for learning on real robots, due to the amount of data needed. However, if done right, agents learning from real data can be surprisingly efficient through re-using previously collected sub-optimal data. In this paper we demonstrate how the increased understanding of off-policy learning methods and their embedding in an iterative online/offline scheme (``collect and infer'') can drastically improve data-efficiency by using all the collected experience, which empowers learning from real robot experience only. Moreover, the resulting policy improves significantly over the state of the art on a recently proposed real robot manipulation benchmark. Our approach learns end-to-end, directly from pixels, and does not rely on additional human domain knowledge such as a simulator or demonstrations.
Towards practical reinforcement learning for tokamak magnetic control
Jul 21, 2023



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has shown promising results for real-time control systems, including the domain of plasma magnetic control. However, there are still significant drawbacks compared to traditional feedback control approaches for magnetic confinement. In this work, we address key drawbacks of the RL method; achieving higher control accuracy for desired plasma properties, reducing the steady-state error, and decreasing the required time to learn new tasks. We build on top of \cite{degrave2022magnetic}, and present algorithmic improvements to the agent architecture and training procedure. We present simulation results that show up to 65\% improvement in shape accuracy, achieve substantial reduction in the long-term bias of the plasma current, and additionally reduce the training time required to learn new tasks by a factor of 3 or more. We present new experiments using the upgraded RL-based controllers on the TCV tokamak, which validate the simulation results achieved, and point the way towards routinely achieving accurate discharges using the RL approach.
Barkour: Benchmarking Animal-level Agility with Quadruped Robots
May 24, 2023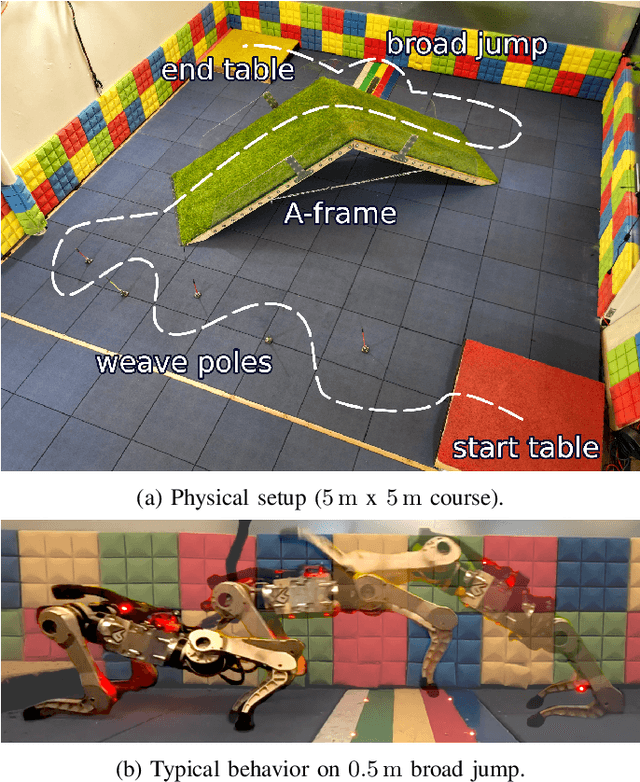
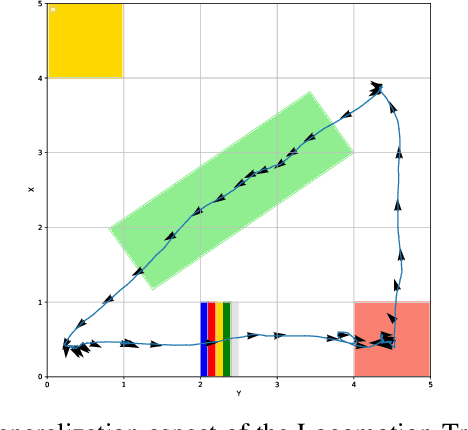
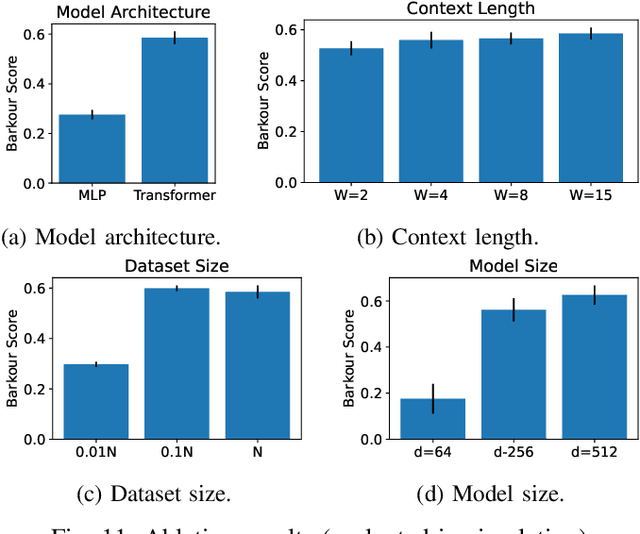

Abstract:Animals have evolved various agile locomotion strategies, such as sprinting, leaping, and jumping. There is a growing interest in developing legged robots that move like their biological counterparts and show various agile skills to navigate complex environments quickly. Despite the interest, the field lacks systematic benchmarks to measure the performance of control policies and hardware in agility. We introduce the Barkour benchmark, an obstacle course to quantify agility for legged robots. Inspired by dog agility competitions, it consists of diverse obstacles and a time based scoring mechanism. This encourages researchers to develop controllers that not only move fast, but do so in a controllable and versatile way. To set strong baselines, we present two methods for tackling the benchmark. In the first approach, we train specialist locomotion skills using on-policy reinforcement learning methods and combine them with a high-level navigation controller. In the second approach, we distill the specialist skills into a Transformer-based generalist locomotion policy, named Locomotion-Transformer, that can handle various terrains and adjust the robot's gait based on the perceived environment and robot states. Using a custom-built quadruped robot, we demonstrate that our method can complete the course at half the speed of a dog. We hope that our work represents a step towards creating controllers that enable robots to reach animal-level agility.
SkillS: Adaptive Skill Sequencing for Efficient Temporally-Extended Exploration
Dec 03, 2022


Abstract:The ability to effectively reuse prior knowledge is a key requirement when building general and flexible Reinforcement Learning (RL) agents. Skill reuse is one of the most common approaches, but current methods have considerable limitations.For example, fine-tuning an existing policy frequently fails, as the policy can degrade rapidly early in training. In a similar vein, distillation of expert behavior can lead to poor results when given sub-optimal experts. We compare several common approaches for skill transfer on multiple domains including changes in task and system dynamics. We identify how existing methods can fail and introduce an alternative approach to mitigate these problems. Our approach learns to sequence existing temporally-extended skills for exploration but learns the final policy directly from the raw experience. This conceptual split enables rapid adaptation and thus efficient data collection but without constraining the final solution.It significantly outperforms many classical methods across a suite of evaluation tasks and we use a broad set of ablations to highlight the importance of differentc omponents of our method.
Imitate and Repurpose: Learning Reusable Robot Movement Skills From Human and Animal Behaviors
Mar 31, 2022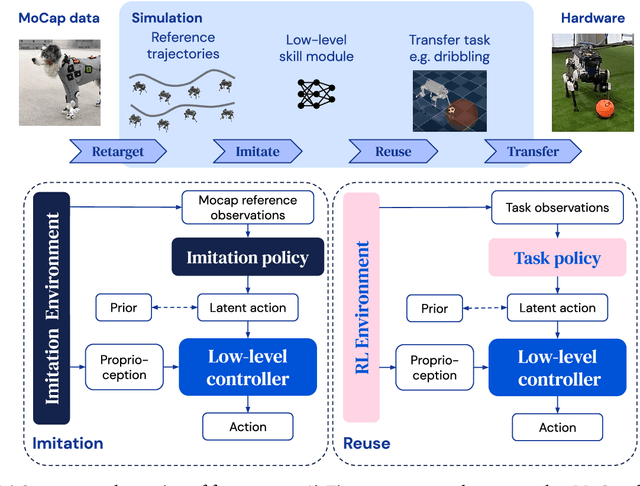
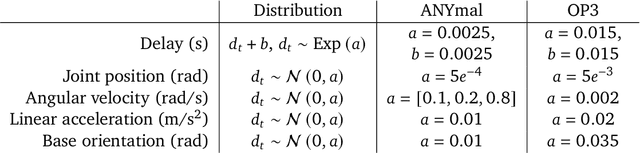
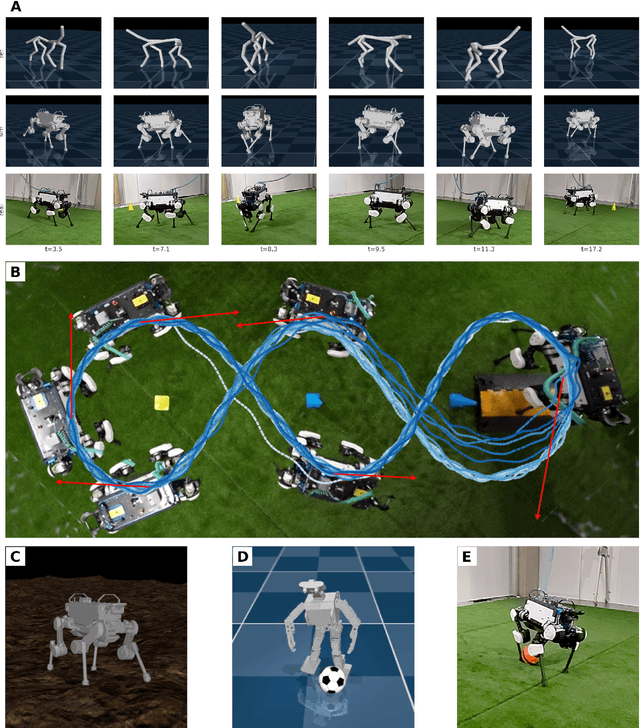
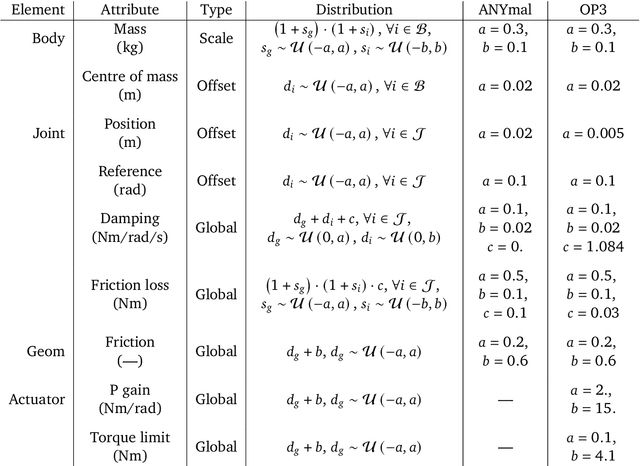
Abstract:We investigate the use of prior knowledge of human and animal movement to learn reusable locomotion skills for real legged robots. Our approach builds upon previous work on imitating human or dog Motion Capture (MoCap) data to learn a movement skill module. Once learned, this skill module can be reused for complex downstream tasks. Importantly, due to the prior imposed by the MoCap data, our approach does not require extensive reward engineering to produce sensible and natural looking behavior at the time of reuse. This makes it easy to create well-regularized, task-oriented controllers that are suitable for deployment on real robots. We demonstrate how our skill module can be used for imitation, and train controllable walking and ball dribbling policies for both the ANYmal quadruped and OP3 humanoid. These policies are then deployed on hardware via zero-shot simulation-to-reality transfer. Accompanying videos are available at https://bit.ly/robot-npmp.
Beyond Pick-and-Place: Tackling Robotic Stacking of Diverse Shapes
Nov 03, 2021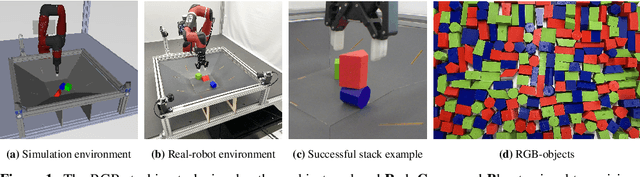
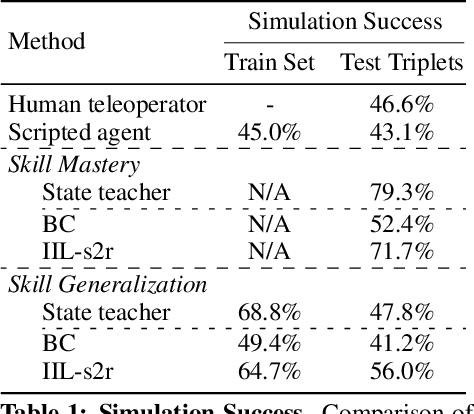
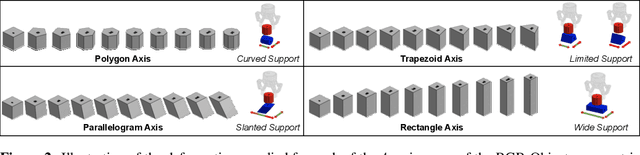
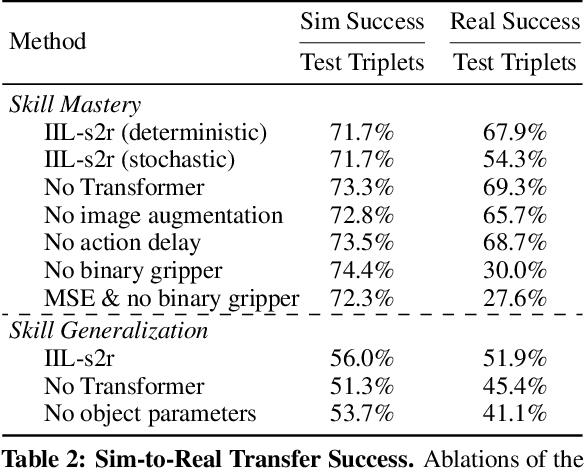
Abstract:We study the problem of robotic stacking with objects of complex geometry. We propose a challenging and diverse set of such objects that was carefully designed to require strategies beyond a simple "pick-and-place" solution. Our method is a reinforcement learning (RL) approach combined with vision-based interactive policy distillation and simulation-to-reality transfer. Our learned policies can efficiently handle multiple object combinations in the real world and exhibit a large variety of stacking skills. In a large experimental study, we investigate what choices matter for learning such general vision-based agents in simulation, and what affects optimal transfer to the real robot. We then leverage data collected by such policies and improve upon them with offline RL. A video and a blog post of our work are provided as supplementary material.
"What, not how": Solving an under-actuated insertion task from scratch
Oct 30, 2020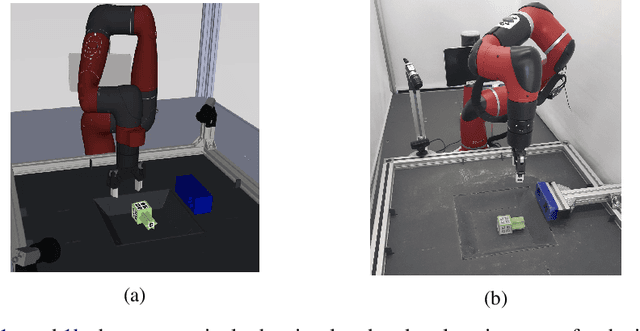

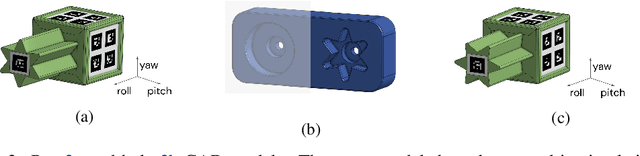
Abstract:Robot manipulation requires a complex set of skills that need to be carefully combined and coordinated to solve a task. Yet, most ReinforcementLearning (RL) approaches in robotics study tasks which actually consist only of a single manipulation skill, such as grasping an object or inserting a pre-grasped object. As a result the skill ('how' to solve the task) but not the actual goal of a complete manipulation ('what' to solve) is specified. In contrast, we study a complex manipulation goal that requires an agent to learn and combine diverse manipulation skills. We propose a challenging, highly under-actuated peg-in-hole task with a free, rotational asymmetrical peg, requiring a broad range of manipulation skills. While correct peg (re-)orientation is a requirement for successful insertion, there is no reward associated with it. Hence an agent needs to understand this pre-condition and learn the skill to fulfil it. The final insertion reward is sparse, allowing freedom in the solution and leading to complex emerging behaviour not envisioned during the task design. We tackle the problem in a multi-task RL framework using Scheduled Auxiliary Control (SAC-X) combined with Regularized Hierarchical Policy Optimization (RHPO) which successfully solves the task in simulation and from scratch on a single robot where data is severely limited.
Towards General and Autonomous Learning of Core Skills: A Case Study in Locomotion
Aug 06, 2020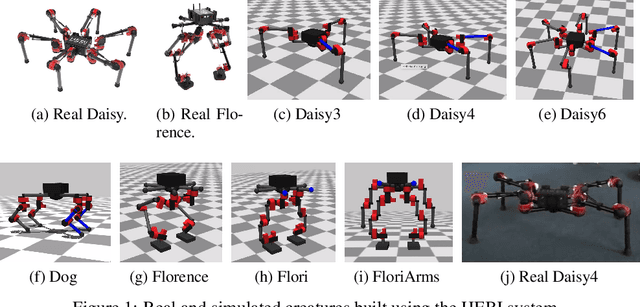
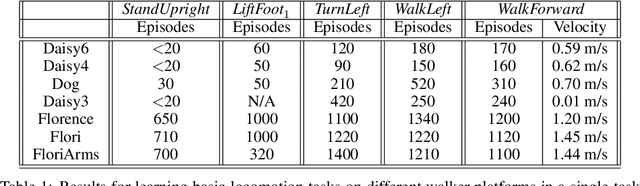
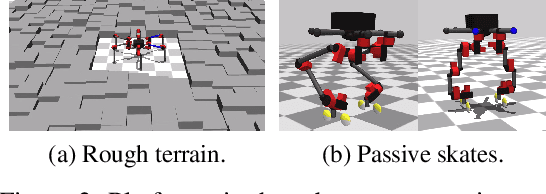

Abstract:Modern Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithms promise to solve difficult motor control problems directly from raw sensory inputs. Their attraction is due in part to the fact that they can represent a general class of methods that allow to learn a solution with a reasonably set reward and minimal prior knowledge, even in situations where it is difficult or expensive for a human expert. For RL to truly make good on this promise, however, we need algorithms and learning setups that can work across a broad range of problems with minimal problem specific adjustments or engineering. In this paper, we study this idea of generality in the locomotion domain. We develop a learning framework that can learn sophisticated locomotion behavior for a wide spectrum of legged robots, such as bipeds, tripeds, quadrupeds and hexapods, including wheeled variants. Our learning framework relies on a data-efficient, off-policy multi-task RL algorithm and a small set of reward functions that are semantically identical across robots. To underline the general applicability of the method, we keep the hyper-parameter settings and reward definitions constant across experiments and rely exclusively on on-board sensing. For nine different types of robots, including a real-world quadruped robot, we demonstrate that the same algorithm can rapidly learn diverse and reusable locomotion skills without any platform specific adjustments or additional instrumentation of the learning setup.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge