Jonas Buchli
Improving cosmological reach of a gravitational wave observatory using Deep Loop Shaping
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:Improved low-frequency sensitivity of gravitational wave observatories would unlock study of intermediate-mass black hole mergers, binary black hole eccentricity, and provide early warnings for multi-messenger observations of binary neutron star mergers. Today's mirror stabilization control injects harmful noise, constituting a major obstacle to sensitivity improvements. We eliminated this noise through Deep Loop Shaping, a reinforcement learning method using frequency domain rewards. We proved our methodology on the LIGO Livingston Observatory (LLO). Our controller reduced control noise in the 10--30Hz band by over 30x, and up to 100x in sub-bands surpassing the design goal motivated by the quantum limit. These results highlight the potential of Deep Loop Shaping to improve current and future GW observatories, and more broadly instrumentation and control systems.
Preference Optimization as Probabilistic Inference
Oct 05, 2024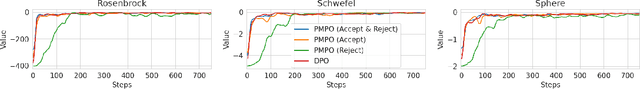
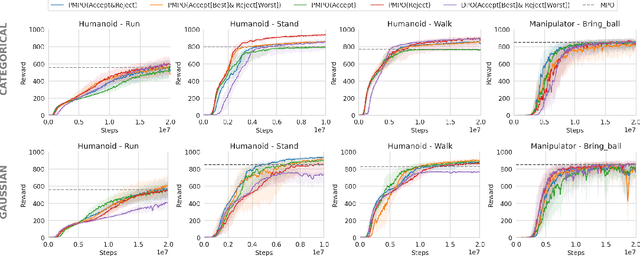
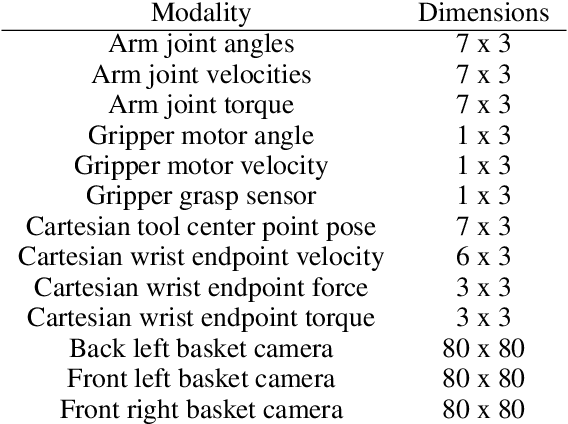
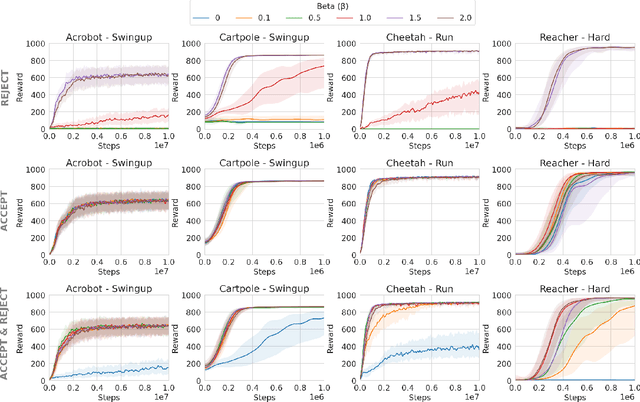
Abstract:Existing preference optimization methods are mainly designed for directly learning from human feedback with the assumption that paired examples (preferred vs. dis-preferred) are available. In contrast, we propose a method that can leverage unpaired preferred or dis-preferred examples, and works even when only one type of feedback (positive or negative) is available. This flexibility allows us to apply it in scenarios with varying forms of feedback and models, including training generative language models based on human feedback as well as training policies for sequential decision-making problems, where learned (value) functions are available. Our approach builds upon the probabilistic framework introduced in (Dayan and Hinton, 1997), which proposes to use expectation-maximization (EM) to directly optimize the probability of preferred outcomes (as opposed to classic expected reward maximization). To obtain a practical algorithm, we identify and address a key limitation in current EM-based methods: when applied to preference optimization, they solely maximize the likelihood of preferred examples, while neglecting dis-preferred samples. We show how one can extend EM algorithms to explicitly incorporate dis-preferred outcomes, leading to a novel, theoretically grounded, preference optimization algorithm that offers an intuitive and versatile way to learn from both positive and negative feedback.
Real-World Fluid Directed Rigid Body Control via Deep Reinforcement Learning
Feb 08, 2024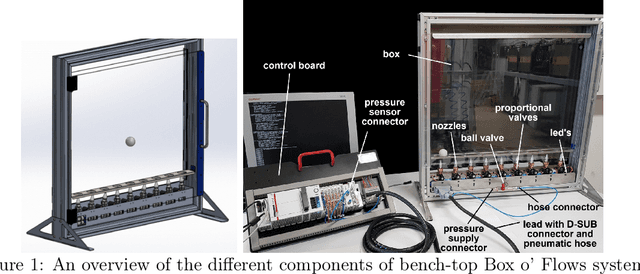
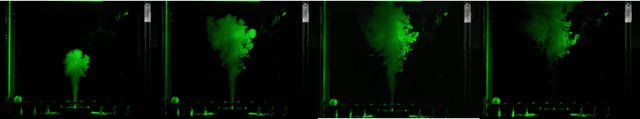
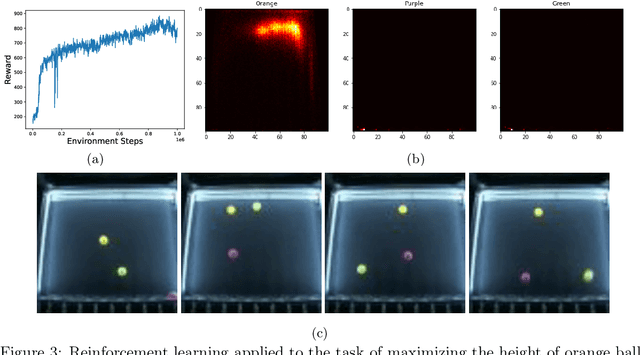
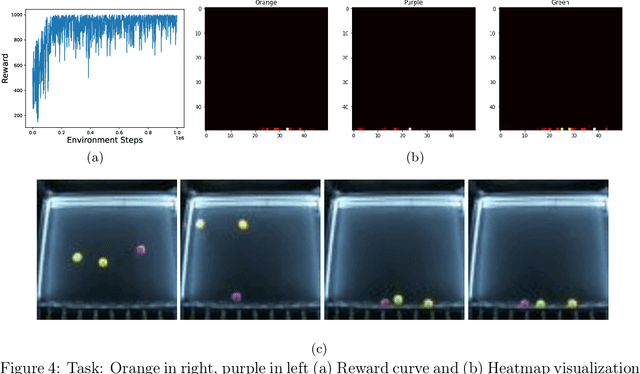
Abstract:Recent advances in real-world applications of reinforcement learning (RL) have relied on the ability to accurately simulate systems at scale. However, domains such as fluid dynamical systems exhibit complex dynamic phenomena that are hard to simulate at high integration rates, limiting the direct application of modern deep RL algorithms to often expensive or safety critical hardware. In this work, we introduce "Box o Flows", a novel benchtop experimental control system for systematically evaluating RL algorithms in dynamic real-world scenarios. We describe the key components of the Box o Flows, and through a series of experiments demonstrate how state-of-the-art model-free RL algorithms can synthesize a variety of complex behaviors via simple reward specifications. Furthermore, we explore the role of offline RL in data-efficient hypothesis testing by reusing past experiences. We believe that the insights gained from this preliminary study and the availability of systems like the Box o Flows support the way forward for developing systematic RL algorithms that can be generally applied to complex, dynamical systems. Supplementary material and videos of experiments are available at https://sites.google.com/view/box-o-flows/home.
Towards practical reinforcement learning for tokamak magnetic control
Jul 21, 2023



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has shown promising results for real-time control systems, including the domain of plasma magnetic control. However, there are still significant drawbacks compared to traditional feedback control approaches for magnetic confinement. In this work, we address key drawbacks of the RL method; achieving higher control accuracy for desired plasma properties, reducing the steady-state error, and decreasing the required time to learn new tasks. We build on top of \cite{degrave2022magnetic}, and present algorithmic improvements to the agent architecture and training procedure. We present simulation results that show up to 65\% improvement in shape accuracy, achieve substantial reduction in the long-term bias of the plasma current, and additionally reduce the training time required to learn new tasks by a factor of 3 or more. We present new experiments using the upgraded RL-based controllers on the TCV tokamak, which validate the simulation results achieved, and point the way towards routinely achieving accurate discharges using the RL approach.
Shaking the foundations: delusions in sequence models for interaction and control
Oct 20, 2021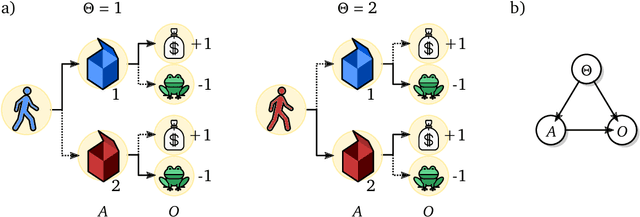
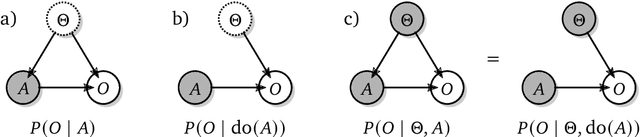
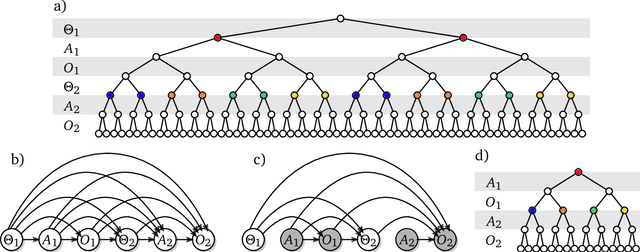
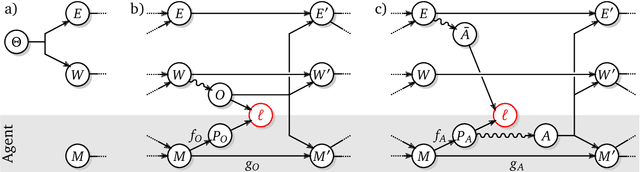
Abstract:The recent phenomenal success of language models has reinvigorated machine learning research, and large sequence models such as transformers are being applied to a variety of domains. One important problem class that has remained relatively elusive however is purposeful adaptive behavior. Currently there is a common perception that sequence models "lack the understanding of the cause and effect of their actions" leading them to draw incorrect inferences due to auto-suggestive delusions. In this report we explain where this mismatch originates, and show that it can be resolved by treating actions as causal interventions. Finally, we show that in supervised learning, one can teach a system to condition or intervene on data by training with factual and counterfactual error signals respectively.
Local Search for Policy Iteration in Continuous Control
Oct 12, 2020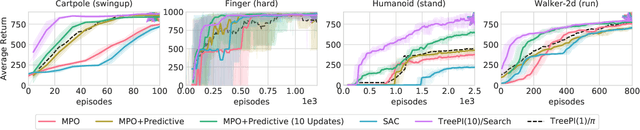
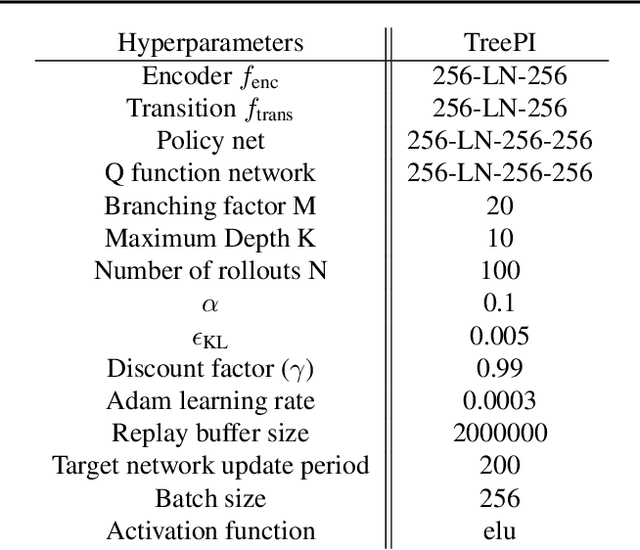
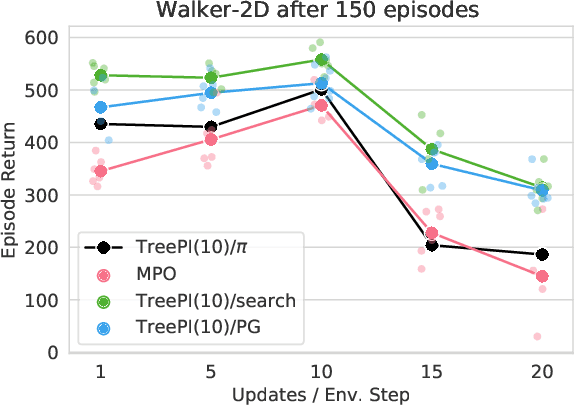
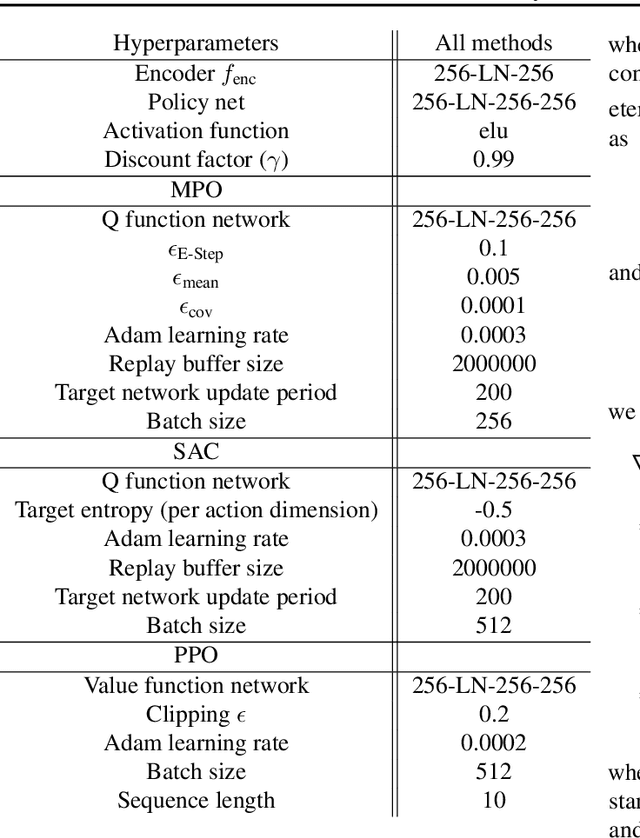
Abstract:We present an algorithm for local, regularized, policy improvement in reinforcement learning (RL) that allows us to formulate model-based and model-free variants in a single framework. Our algorithm can be interpreted as a natural extension of work on KL-regularized RL and introduces a form of tree search for continuous action spaces. We demonstrate that additional computation spent on model-based policy improvement during learning can improve data efficiency, and confirm that model-based policy improvement during action selection can also be beneficial. Quantitatively, our algorithm improves data efficiency on several continuous control benchmarks (when a model is learned in parallel), and it provides significant improvements in wall-clock time in high-dimensional domains (when a ground truth model is available). The unified framework also helps us to better understand the space of model-based and model-free algorithms. In particular, we demonstrate that some benefits attributed to model-based RL can be obtained without a model, simply by utilizing more computation.
Continuous-Discrete Reinforcement Learning for Hybrid Control in Robotics
Jan 02, 2020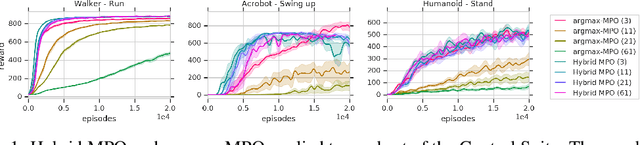
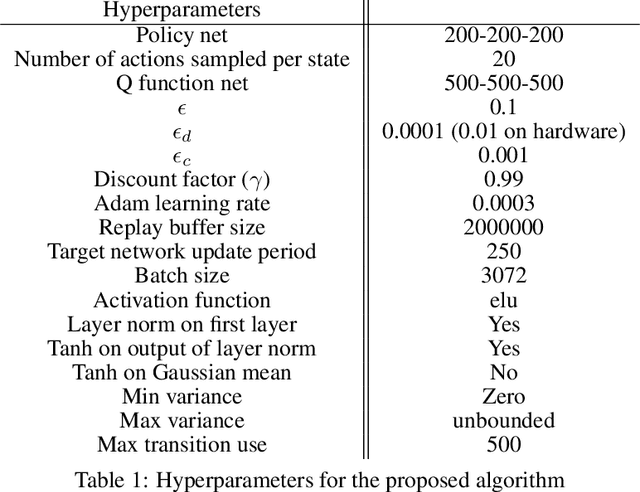
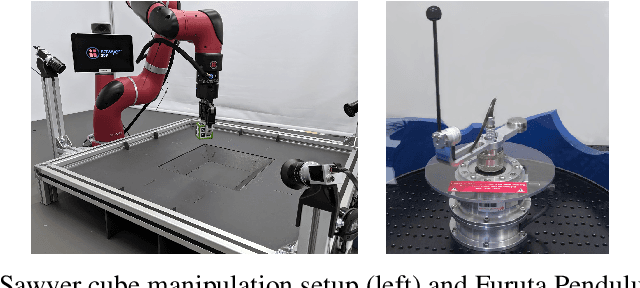

Abstract:Many real-world control problems involve both discrete decision variables - such as the choice of control modes, gear switching or digital outputs - as well as continuous decision variables - such as velocity setpoints, control gains or analogue outputs. However, when defining the corresponding optimal control or reinforcement learning problem, it is commonly approximated with fully continuous or fully discrete action spaces. These simplifications aim at tailoring the problem to a particular algorithm or solver which may only support one type of action space. Alternatively, expert heuristics are used to remove discrete actions from an otherwise continuous space. In contrast, we propose to treat hybrid problems in their 'native' form by solving them with hybrid reinforcement learning, which optimizes for discrete and continuous actions simultaneously. In our experiments, we first demonstrate that the proposed approach efficiently solves such natively hybrid reinforcement learning problems. We then show, both in simulation and on robotic hardware, the benefits of removing possibly imperfect expert-designed heuristics. Lastly, hybrid reinforcement learning encourages us to rethink problem definitions. We propose reformulating control problems, e.g. by adding meta actions, to improve exploration or reduce mechanical wear and tear.
ConFusion: Sensor Fusion for Complex Robotic Systems using Nonlinear Optimization
Mar 01, 2019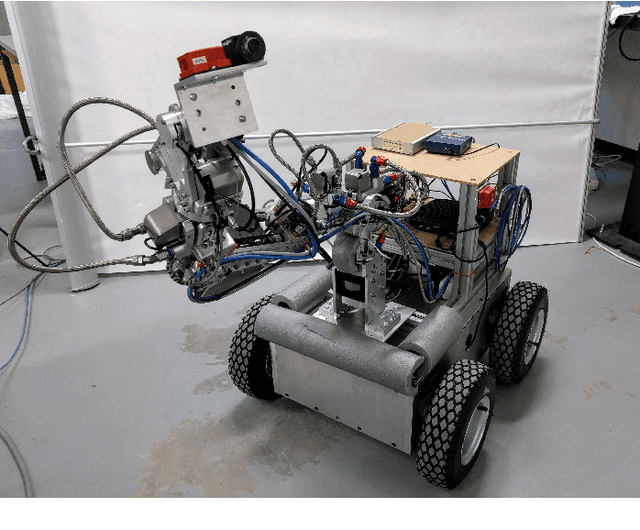
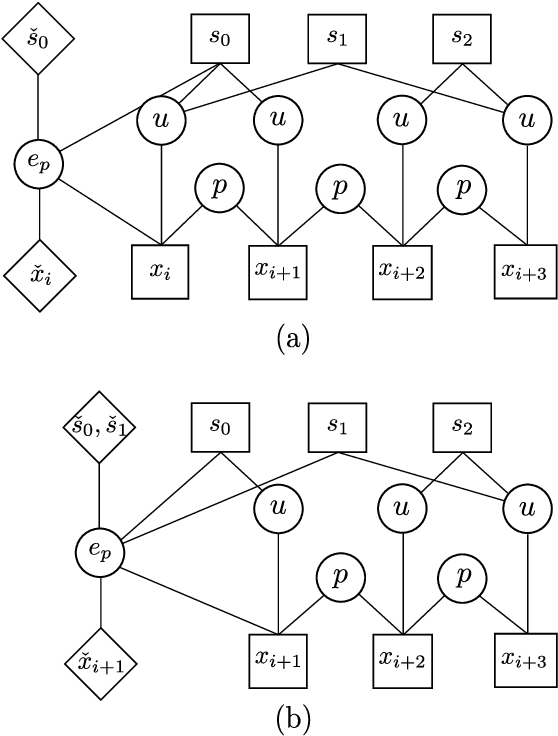
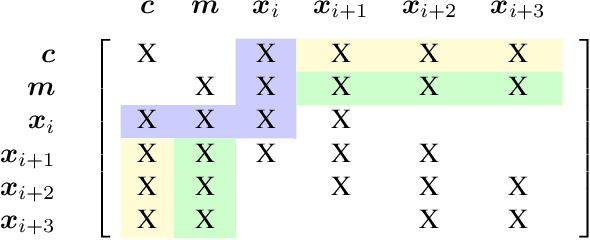
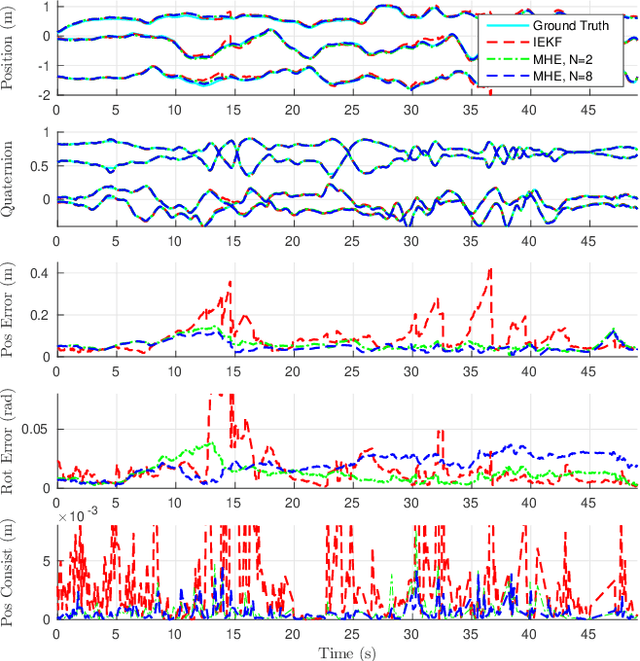
Abstract:We present ConFusion, an open-source package for online sensor fusion for robotic applications. ConFusion is a modular framework for fusing measurements from many heterogeneous sensors within a moving horizon estimator. ConFusion offers greater flexibility in sensor fusion problem design than filtering-based systems and the ability to scale the online estimate quality with the available computing power. We demonstrate its performance in comparison to an iterated extended Kalman filter in visual-inertial tracking, and show its versatility through whole-body sensor fusion on a mobile manipulator.
Value constrained model-free continuous control
Feb 12, 2019



Abstract:The naive application of Reinforcement Learning algorithms to continuous control problems -- such as locomotion and manipulation -- often results in policies which rely on high-amplitude, high-frequency control signals, known colloquially as bang-bang control. Although such solutions may indeed maximize task reward, they can be unsuitable for real world systems. Bang-bang control may lead to increased wear and tear or energy consumption, and tends to excite undesired second-order dynamics. To counteract this issue, multi-objective optimization can be used to simultaneously optimize both the reward and some auxiliary cost that discourages undesired (e.g. high-amplitude) control. In principle, such an approach can yield the sought after, smooth, control policies. It can, however, be hard to find the correct trade-off between cost and return that results in the desired behavior. In this paper we propose a new constraint-based reinforcement learning approach that ensures task success while minimizing one or more auxiliary costs (such as control effort). We employ Lagrangian relaxation to learn both (a) the parameters of a control policy that satisfies the desired constraints and (b) the Lagrangian multipliers for the optimization. Moreover, we demonstrate that we can satisfy constraints either in expectation or in a per-step fashion, and can even learn a single policy that is able to dynamically trade-off between return and cost. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approach using a number of continuous control benchmark tasks, a realistic, energy-optimized quadruped locomotion task, as well as a reaching task on a real robot arm.
Nonlinear disturbance attenuation control of hydraulic robotics
Aug 04, 2018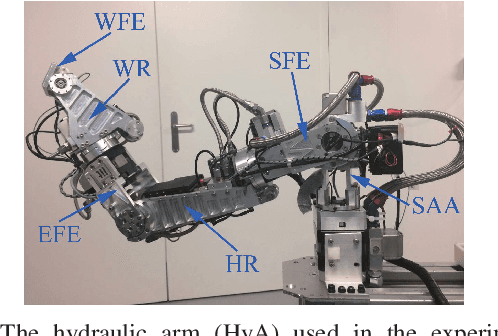
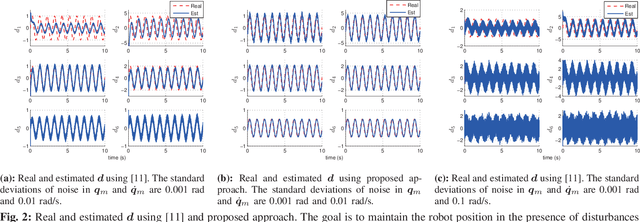
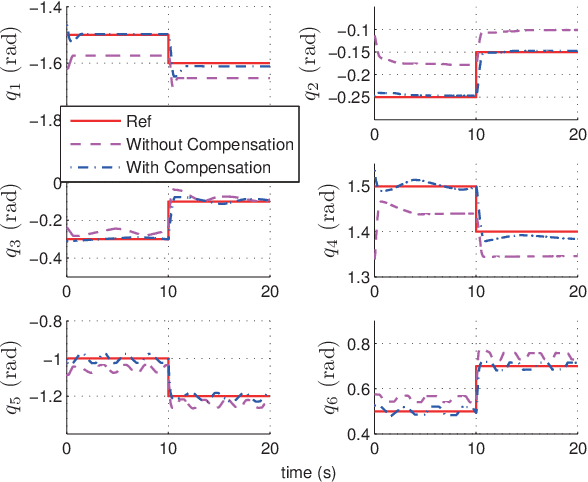
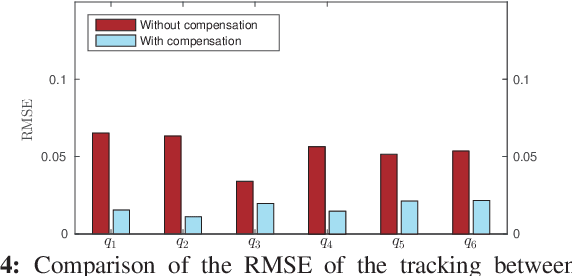
Abstract:This paper presents a novel nonlinear disturbance rejection control for hydraulic robots. This method requires two third-order filters as well as inverse dynamics in order to estimate the disturbances. All the parameters for the third-order filters are pre-defined. The proposed method is nonlinear, which does not require the linearization of the rigid body dynamics. The estimated disturbances are used by the nonlinear controller in order to achieve disturbance attenuation. The performance of the proposed approach is compared with existing approaches. Finally, the tracking performance and robustness of the proposed approach is validated extensively on real hardware by performing different tasks under either internal or both internal and external disturbances. The experimental results demonstrate the robustness and superior tracking performance of the proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge