Pheng Ann Heng
Dual Ensembled Multiagent Q-Learning with Hypernet Regularizer
Feb 04, 2025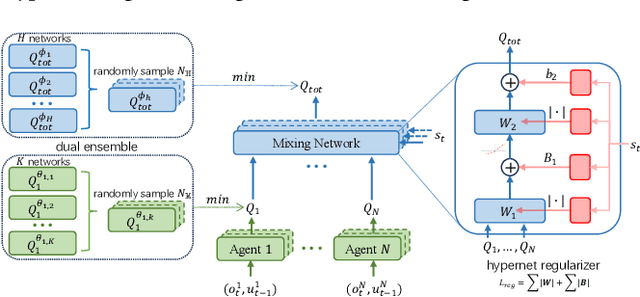
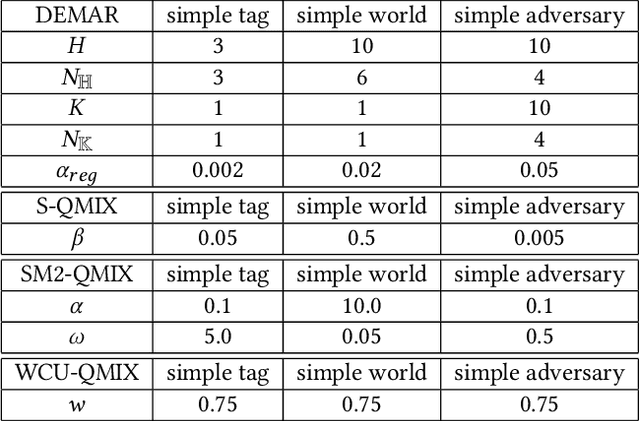
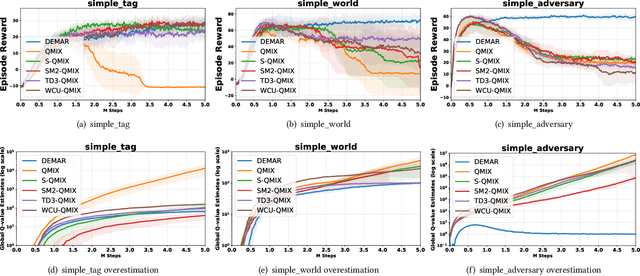
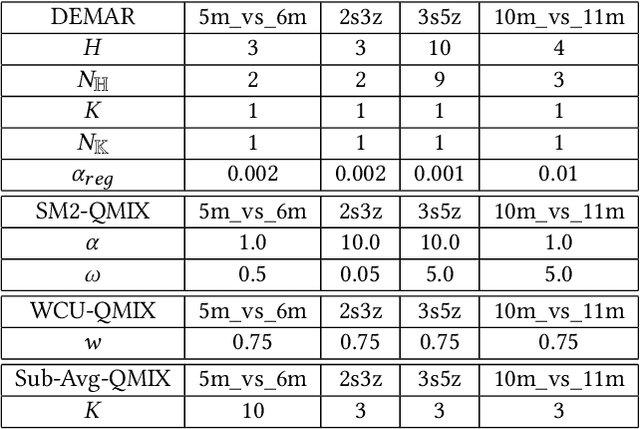
Abstract:Overestimation in single-agent reinforcement learning has been extensively studied. In contrast, overestimation in the multiagent setting has received comparatively little attention although it increases with the number of agents and leads to severe learning instability. Previous works concentrate on reducing overestimation in the estimation process of target Q-value. They ignore the follow-up optimization process of online Q-network, thus making it hard to fully address the complex multiagent overestimation problem. To solve this challenge, in this study, we first establish an iterative estimation-optimization analysis framework for multiagent value-mixing Q-learning. Our analysis reveals that multiagent overestimation not only comes from the computation of target Q-value but also accumulates in the online Q-network's optimization. Motivated by it, we propose the Dual Ensembled Multiagent Q-Learning with Hypernet Regularizer algorithm to tackle multiagent overestimation from two aspects. First, we extend the random ensemble technique into the estimation of target individual and global Q-values to derive a lower update target. Second, we propose a novel hypernet regularizer on hypernetwork weights and biases to constrain the optimization of online global Q-network to prevent overestimation accumulation. Extensive experiments in MPE and SMAC show that the proposed method successfully addresses overestimation across various tasks.
SeaDAG: Semi-autoregressive Diffusion for Conditional Directed Acyclic Graph Generation
Oct 21, 2024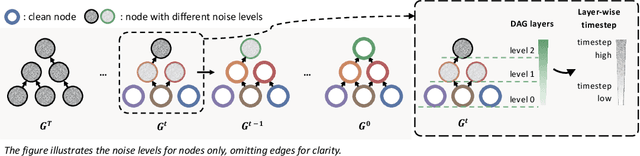
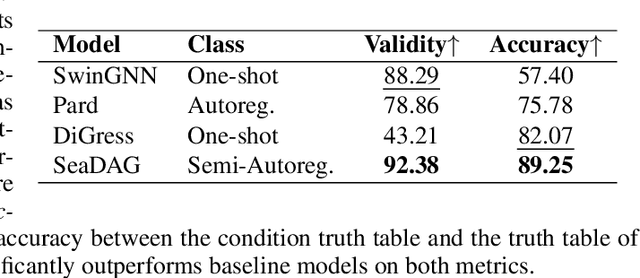
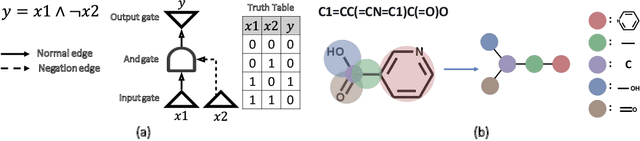
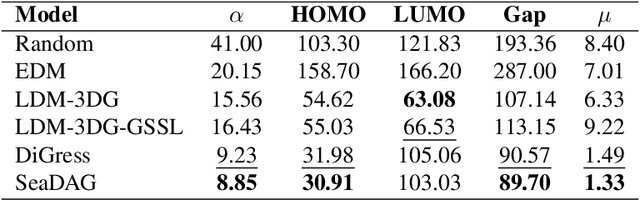
Abstract:We introduce SeaDAG, a semi-autoregressive diffusion model for conditional generation of Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs). Considering their inherent layer-wise structure, we simulate layer-wise autoregressive generation by designing different denoising speed for different layers. Unlike conventional autoregressive generation that lacks a global graph structure view, our method maintains a complete graph structure at each diffusion step, enabling operations such as property control that require the full graph structure. Leveraging this capability, we evaluate the DAG properties during training by employing a graph property decoder. We explicitly train the model to learn graph conditioning with a condition loss, which enhances the diffusion model's capacity to generate graphs that are both realistic and aligned with specified properties. We evaluate our method on two representative conditional DAG generation tasks: (1) circuit generation from truth tables, where precise DAG structures are crucial for realizing circuit functionality, and (2) molecule generation based on quantum properties. Our approach demonstrates promising results, generating high-quality and realistic DAGs that closely align with given conditions.
Unlocking Potential Binders: Multimodal Pretraining DEL-Fusion for Denoising DNA-Encoded Libraries
Sep 07, 2024



Abstract:In the realm of drug discovery, DNA-encoded library (DEL) screening technology has emerged as an efficient method for identifying high-affinity compounds. However, DEL screening faces a significant challenge: noise arising from nonspecific interactions within complex biological systems. Neural networks trained on DEL libraries have been employed to extract compound features, aiming to denoise the data and uncover potential binders to the desired therapeutic target. Nevertheless, the inherent structure of DEL, constrained by the limited diversity of building blocks, impacts the performance of compound encoders. Moreover, existing methods only capture compound features at a single level, further limiting the effectiveness of the denoising strategy. To mitigate these issues, we propose a Multimodal Pretraining DEL-Fusion model (MPDF) that enhances encoder capabilities through pretraining and integrates compound features across various scales. We develop pretraining tasks applying contrastive objectives between different compound representations and their text descriptions, enhancing the compound encoders' ability to acquire generic features. Furthermore, we propose a novel DEL-fusion framework that amalgamates compound information at the atomic, submolecular, and molecular levels, as captured by various compound encoders. The synergy of these innovations equips MPDF with enriched, multi-scale features, enabling comprehensive downstream denoising. Evaluated on three DEL datasets, MPDF demonstrates superior performance in data processing and analysis for validation tasks. Notably, MPDF offers novel insights into identifying high-affinity molecules, paving the way for improved DEL utility in drug discovery.
Unveiling the Generalization Power of Fine-Tuned Large Language Models
Mar 14, 2024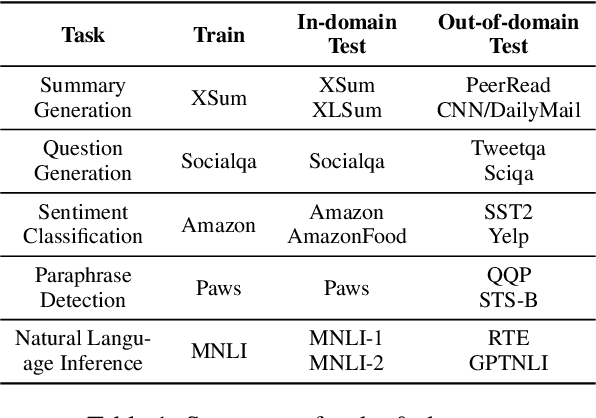
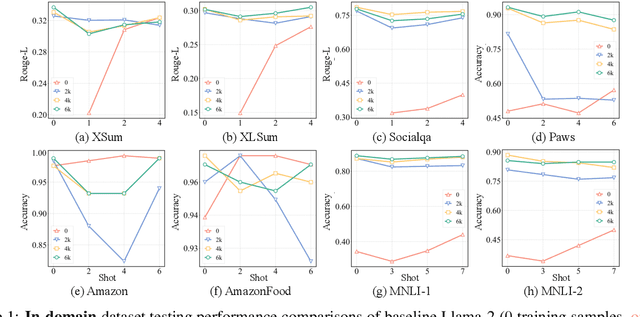
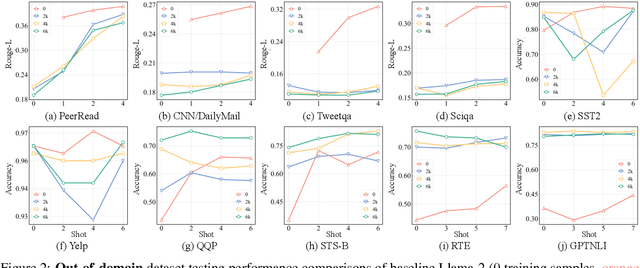
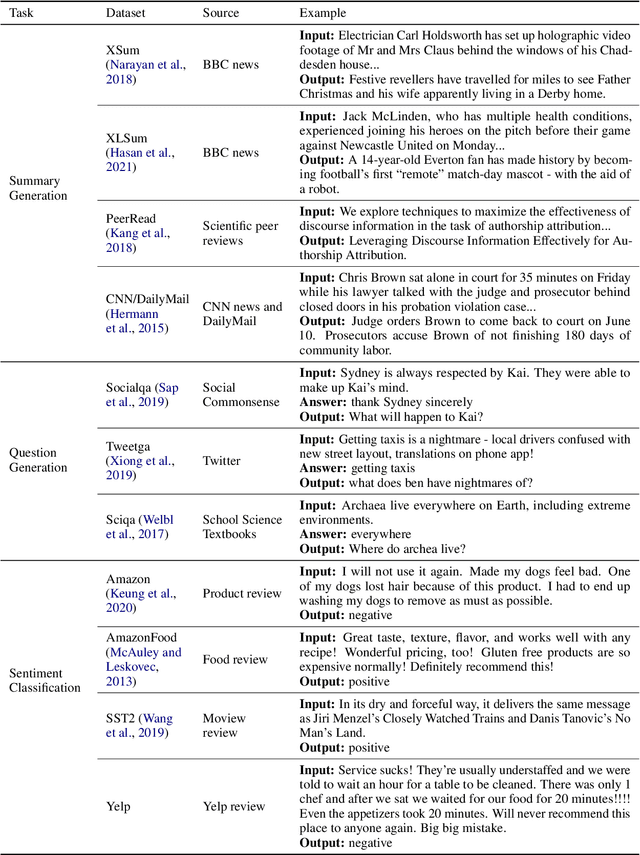
Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated exceptional multitasking abilities, fine-tuning these models on downstream, domain-specific datasets is often necessary to yield superior performance on test sets compared to their counterparts without fine-tuning. However, the comprehensive effects of fine-tuning on the LLMs' generalization ability are not fully understood. This paper delves into the differences between original, unmodified LLMs and their fine-tuned variants. Our primary investigation centers on whether fine-tuning affects the generalization ability intrinsic to LLMs. To elaborate on this, we conduct extensive experiments across five distinct language tasks on various datasets. Our main findings reveal that models fine-tuned on generation and classification tasks exhibit dissimilar behaviors in generalizing to different domains and tasks. Intriguingly, we observe that integrating the in-context learning strategy during fine-tuning on generation tasks can enhance the model's generalization ability. Through this systematic investigation, we aim to contribute valuable insights into the evolving landscape of fine-tuning practices for LLMs.
An Autonomous Large Language Model Agent for Chemical Literature Data Mining
Feb 20, 2024



Abstract:Chemical synthesis, which is crucial for advancing material synthesis and drug discovery, impacts various sectors including environmental science and healthcare. The rise of technology in chemistry has generated extensive chemical data, challenging researchers to discern patterns and refine synthesis processes. Artificial intelligence (AI) helps by analyzing data to optimize synthesis and increase yields. However, AI faces challenges in processing literature data due to the unstructured format and diverse writing style of chemical literature. To overcome these difficulties, we introduce an end-to-end AI agent framework capable of high-fidelity extraction from extensive chemical literature. This AI agent employs large language models (LLMs) for prompt generation and iterative optimization. It functions as a chemistry assistant, automating data collection and analysis, thereby saving manpower and enhancing performance. Our framework's efficacy is evaluated using accuracy, recall, and F1 score of reaction condition data, and we compared our method with human experts in terms of content correctness and time efficiency. The proposed approach marks a significant advancement in automating chemical literature extraction and demonstrates the potential for AI to revolutionize data management and utilization in chemistry.
A Survey of Reasoning with Foundation Models
Dec 26, 2023

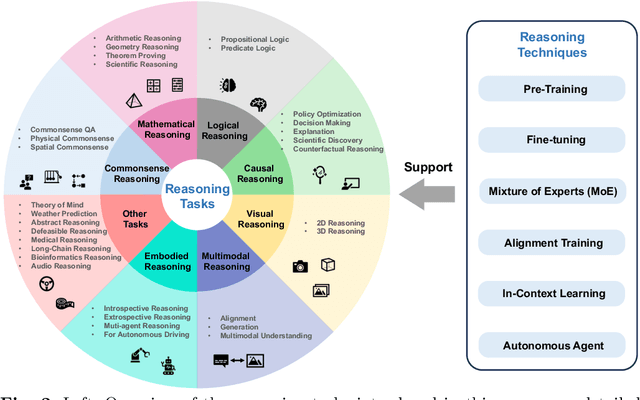

Abstract:Reasoning, a crucial ability for complex problem-solving, plays a pivotal role in various real-world settings such as negotiation, medical diagnosis, and criminal investigation. It serves as a fundamental methodology in the field of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). With the ongoing development of foundation models, there is a growing interest in exploring their abilities in reasoning tasks. In this paper, we introduce seminal foundation models proposed or adaptable for reasoning, highlighting the latest advancements in various reasoning tasks, methods, and benchmarks. We then delve into the potential future directions behind the emergence of reasoning abilities within foundation models. We also discuss the relevance of multimodal learning, autonomous agents, and super alignment in the context of reasoning. By discussing these future research directions, we hope to inspire researchers in their exploration of this field, stimulate further advancements in reasoning with foundation models, and contribute to the development of AGI.
Towards an Automatic AI Agent for Reaction Condition Recommendation in Chemical Synthesis
Nov 28, 2023



Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) for reaction condition optimization has become an important topic in the pharmaceutical industry, given that a data-driven AI model can assist drug discovery and accelerate reaction design. However, existing AI models lack the chemical insights and real-time knowledge acquisition abilities of experienced human chemists. This paper proposes a Large Language Model (LLM) empowered AI agent to bridge this gap. We put forth a novel three-phase paradigm and applied advanced intelligence-enhancement methods like in-context learning and multi-LLM debate so that the AI agent can borrow human insight and update its knowledge by searching the latest chemical literature. Additionally, we introduce a novel Coarse-label Contrastive Learning (CCL) based chemical fingerprint that greatly enhances the agent's performance in optimizing the reaction condition. With the above efforts, the proposed AI agent can autonomously generate the optimal reaction condition recommendation without any human interaction. Further, the agent is highly professional in terms of chemical reactions. It demonstrates close-to-human performance and strong generalization capability in both dry-lab and wet-lab experiments. As the first attempt in the chemical AI agent, this work goes a step further in the field of "AI for chemistry" and opens up new possibilities for computer-aided synthesis planning.
Joint-MAE: 2D-3D Joint Masked Autoencoders for 3D Point Cloud Pre-training
Feb 27, 2023



Abstract:Masked Autoencoders (MAE) have shown promising performance in self-supervised learning for both 2D and 3D computer vision. However, existing MAE-style methods can only learn from the data of a single modality, i.e., either images or point clouds, which neglect the implicit semantic and geometric correlation between 2D and 3D. In this paper, we explore how the 2D modality can benefit 3D masked autoencoding, and propose Joint-MAE, a 2D-3D joint MAE framework for self-supervised 3D point cloud pre-training. Joint-MAE randomly masks an input 3D point cloud and its projected 2D images, and then reconstructs the masked information of the two modalities. For better cross-modal interaction, we construct our JointMAE by two hierarchical 2D-3D embedding modules, a joint encoder, and a joint decoder with modal-shared and model-specific decoders. On top of this, we further introduce two cross-modal strategies to boost the 3D representation learning, which are local-aligned attention mechanisms for 2D-3D semantic cues, and a cross-reconstruction loss for 2D-3D geometric constraints. By our pre-training paradigm, Joint-MAE achieves superior performance on multiple downstream tasks, e.g., 92.4% accuracy for linear SVM on ModelNet40 and 86.07% accuracy on the hardest split of ScanObjectNN.
DLTTA: Dynamic Learning Rate for Test-time Adaptation on Cross-domain Medical Images
May 27, 2022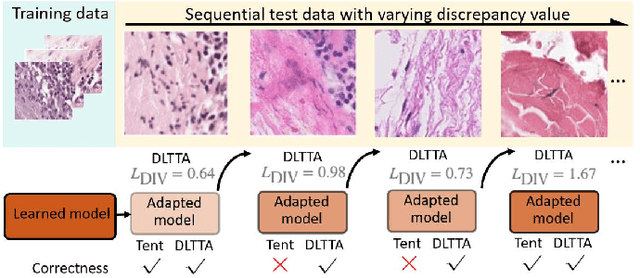
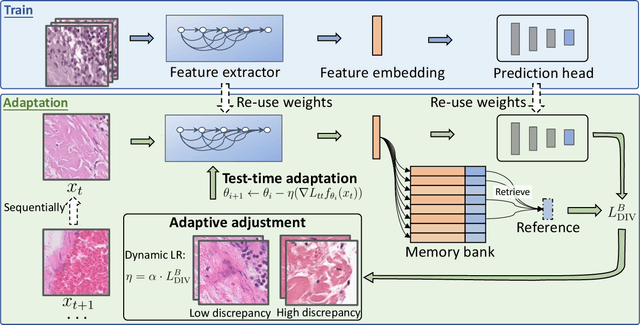
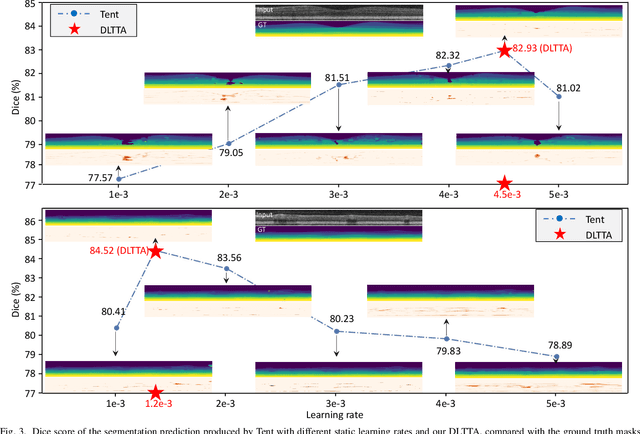
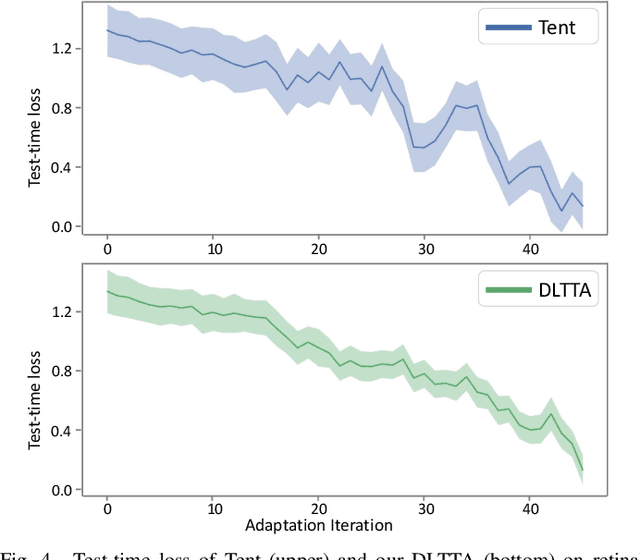
Abstract:Test-time adaptation (TTA) has increasingly been an important topic to efficiently tackle the cross-domain distribution shift at test time for medical images from different institutions. Previous TTA methods have a common limitation of using a fixed learning rate for all the test samples. Such a practice would be sub-optimal for TTA, because test data may arrive sequentially therefore the scale of distribution shift would change frequently. To address this problem, we propose a novel dynamic learning rate adjustment method for test-time adaptation, called DLTTA, which dynamically modulates the amount of weights update for each test image to account for the differences in their distribution shift. Specifically, our DLTTA is equipped with a memory bank based estimation scheme to effectively measure the discrepancy of a given test sample. Based on this estimated discrepancy, a dynamic learning rate adjustment strategy is then developed to achieve a suitable degree of adaptation for each test sample. The effectiveness and general applicability of our DLTTA is extensively demonstrated on three tasks including retinal optical coherence tomography (OCT) segmentation, histopathological image classification, and prostate 3D MRI segmentation. Our method achieves effective and fast test-time adaptation with consistent performance improvement over current state-of-the-art test-time adaptation methods. Code is available at: https://github.com/med-air/DLTTA.
Federated Learning Enables Big Data for Rare Cancer Boundary Detection
Apr 25, 2022Abstract:Although machine learning (ML) has shown promise in numerous domains, there are concerns about generalizability to out-of-sample data. This is currently addressed by centrally sharing ample, and importantly diverse, data from multiple sites. However, such centralization is challenging to scale (or even not feasible) due to various limitations. Federated ML (FL) provides an alternative to train accurate and generalizable ML models, by only sharing numerical model updates. Here we present findings from the largest FL study to-date, involving data from 71 healthcare institutions across 6 continents, to generate an automatic tumor boundary detector for the rare disease of glioblastoma, utilizing the largest dataset of such patients ever used in the literature (25,256 MRI scans from 6,314 patients). We demonstrate a 33% improvement over a publicly trained model to delineate the surgically targetable tumor, and 23% improvement over the tumor's entire extent. We anticipate our study to: 1) enable more studies in healthcare informed by large and diverse data, ensuring meaningful results for rare diseases and underrepresented populations, 2) facilitate further quantitative analyses for glioblastoma via performance optimization of our consensus model for eventual public release, and 3) demonstrate the effectiveness of FL at such scale and task complexity as a paradigm shift for multi-site collaborations, alleviating the need for data sharing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge