Micah Sheller
Analysis of the MICCAI Brain Tumor Segmentation -- Metastases (BraTS-METS) 2025 Lighthouse Challenge: Brain Metastasis Segmentation on Pre- and Post-treatment MRI
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Despite continuous advancements in cancer treatment, brain metastatic disease remains a significant complication of primary cancer and is associated with an unfavorable prognosis. One approach for improving diagnosis, management, and outcomes is to implement algorithms based on artificial intelligence for the automated segmentation of both pre- and post-treatment MRI brain images. Such algorithms rely on volumetric criteria for lesion identification and treatment response assessment, which are still not available in clinical practice. Therefore, it is critical to establish tools for rapid volumetric segmentations methods that can be translated to clinical practice and that are trained on high quality annotated data. The BraTS-METS 2025 Lighthouse Challenge aims to address this critical need by establishing inter-rater and intra-rater variability in dataset annotation by generating high quality annotated datasets from four individual instances of segmentation by neuroradiologists while being recorded on video (two instances doing "from scratch" and two instances after AI pre-segmentation). This high-quality annotated dataset will be used for testing phase in 2025 Lighthouse challenge and will be publicly released at the completion of the challenge. The 2025 Lighthouse challenge will also release the 2023 and 2024 segmented datasets that were annotated using an established pipeline of pre-segmentation, student annotation, two neuroradiologists checking, and one neuroradiologist finalizing the process. It builds upon its previous edition by including post-treatment cases in the dataset. Using these high-quality annotated datasets, the 2025 Lighthouse challenge plans to test benchmark algorithms for automated segmentation of pre-and post-treatment brain metastases (BM), trained on diverse and multi-institutional datasets of MRI images obtained from patients with brain metastases.
Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) Challenge 2024: Meningioma Radiotherapy Planning Automated Segmentation
May 28, 2024Abstract:The 2024 Brain Tumor Segmentation Meningioma Radiotherapy (BraTS-MEN-RT) challenge aims to advance automated segmentation algorithms using the largest known multi-institutional dataset of radiotherapy planning brain MRIs with expert-annotated target labels for patients with intact or post-operative meningioma that underwent either conventional external beam radiotherapy or stereotactic radiosurgery. Each case includes a defaced 3D post-contrast T1-weighted radiotherapy planning MRI in its native acquisition space, accompanied by a single-label "target volume" representing the gross tumor volume (GTV) and any at-risk post-operative site. Target volume annotations adhere to established radiotherapy planning protocols, ensuring consistency across cases and institutions. For pre-operative meningiomas, the target volume encompasses the entire GTV and associated nodular dural tail, while for post-operative cases, it includes at-risk resection cavity margins as determined by the treating institution. Case annotations were reviewed and approved by expert neuroradiologists and radiation oncologists. Participating teams will develop, containerize, and evaluate automated segmentation models using this comprehensive dataset. Model performance will be assessed using the lesion-wise Dice Similarity Coefficient and the 95% Hausdorff distance. The top-performing teams will be recognized at the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention Conference in October 2024. BraTS-MEN-RT is expected to significantly advance automated radiotherapy planning by enabling precise tumor segmentation and facilitating tailored treatment, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Analysis of the BraTS 2023 Intracranial Meningioma Segmentation Challenge
May 16, 2024



Abstract:We describe the design and results from the BraTS 2023 Intracranial Meningioma Segmentation Challenge. The BraTS Meningioma Challenge differed from prior BraTS Glioma challenges in that it focused on meningiomas, which are typically benign extra-axial tumors with diverse radiologic and anatomical presentation and a propensity for multiplicity. Nine participating teams each developed deep-learning automated segmentation models using image data from the largest multi-institutional systematically expert annotated multilabel multi-sequence meningioma MRI dataset to date, which included 1000 training set cases, 141 validation set cases, and 283 hidden test set cases. Each case included T2, T2/FLAIR, T1, and T1Gd brain MRI sequences with associated tumor compartment labels delineating enhancing tumor, non-enhancing tumor, and surrounding non-enhancing T2/FLAIR hyperintensity. Participant automated segmentation models were evaluated and ranked based on a scoring system evaluating lesion-wise metrics including dice similarity coefficient (DSC) and 95% Hausdorff Distance. The top ranked team had a lesion-wise median dice similarity coefficient (DSC) of 0.976, 0.976, and 0.964 for enhancing tumor, tumor core, and whole tumor, respectively and a corresponding average DSC of 0.899, 0.904, and 0.871, respectively. These results serve as state-of-the-art benchmarks for future pre-operative meningioma automated segmentation algorithms. Additionally, we found that 1286 of 1424 cases (90.3%) had at least 1 compartment voxel abutting the edge of the skull-stripped image edge, which requires further investigation into optimal pre-processing face anonymization steps.
Federated Learning Enables Big Data for Rare Cancer Boundary Detection
Apr 25, 2022Abstract:Although machine learning (ML) has shown promise in numerous domains, there are concerns about generalizability to out-of-sample data. This is currently addressed by centrally sharing ample, and importantly diverse, data from multiple sites. However, such centralization is challenging to scale (or even not feasible) due to various limitations. Federated ML (FL) provides an alternative to train accurate and generalizable ML models, by only sharing numerical model updates. Here we present findings from the largest FL study to-date, involving data from 71 healthcare institutions across 6 continents, to generate an automatic tumor boundary detector for the rare disease of glioblastoma, utilizing the largest dataset of such patients ever used in the literature (25,256 MRI scans from 6,314 patients). We demonstrate a 33% improvement over a publicly trained model to delineate the surgically targetable tumor, and 23% improvement over the tumor's entire extent. We anticipate our study to: 1) enable more studies in healthcare informed by large and diverse data, ensuring meaningful results for rare diseases and underrepresented populations, 2) facilitate further quantitative analyses for glioblastoma via performance optimization of our consensus model for eventual public release, and 3) demonstrate the effectiveness of FL at such scale and task complexity as a paradigm shift for multi-site collaborations, alleviating the need for data sharing.
The Federated Tumor Segmentation (FeTS) Challenge
May 14, 2021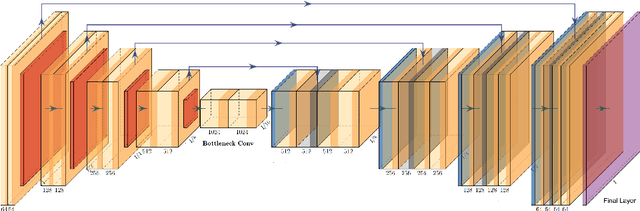
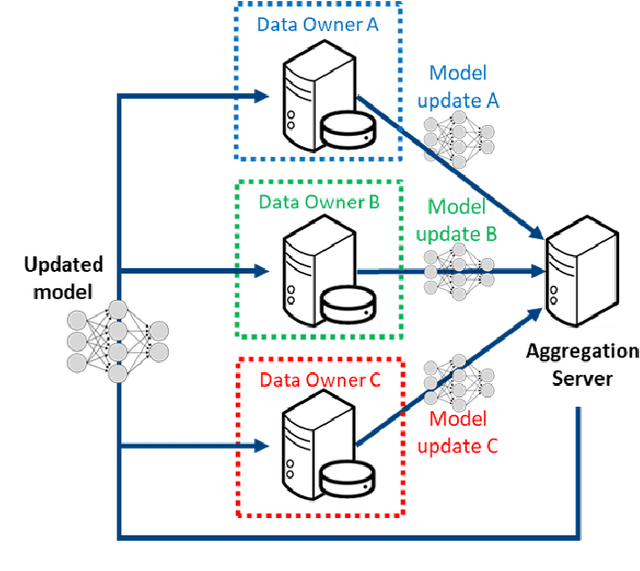
Abstract:This manuscript describes the first challenge on Federated Learning, namely the Federated Tumor Segmentation (FeTS) challenge 2021. International challenges have become the standard for validation of biomedical image analysis methods. However, the actual performance of participating (even the winning) algorithms on "real-world" clinical data often remains unclear, as the data included in challenges are usually acquired in very controlled settings at few institutions. The seemingly obvious solution of just collecting increasingly more data from more institutions in such challenges does not scale well due to privacy and ownership hurdles. Towards alleviating these concerns, we are proposing the FeTS challenge 2021 to cater towards both the development and the evaluation of models for the segmentation of intrinsically heterogeneous (in appearance, shape, and histology) brain tumors, namely gliomas. Specifically, the FeTS 2021 challenge uses clinically acquired, multi-institutional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans from the BraTS 2020 challenge, as well as from various remote independent institutions included in the collaborative network of a real-world federation (https://www.fets.ai/). The goals of the FeTS challenge are directly represented by the two included tasks: 1) the identification of the optimal weight aggregation approach towards the training of a consensus model that has gained knowledge via federated learning from multiple geographically distinct institutions, while their data are always retained within each institution, and 2) the federated evaluation of the generalizability of brain tumor segmentation models "in the wild", i.e. on data from institutional distributions that were not part of the training datasets.
GaNDLF: A Generally Nuanced Deep Learning Framework for Scalable End-to-End Clinical Workflows in Medical Imaging
Feb 26, 2021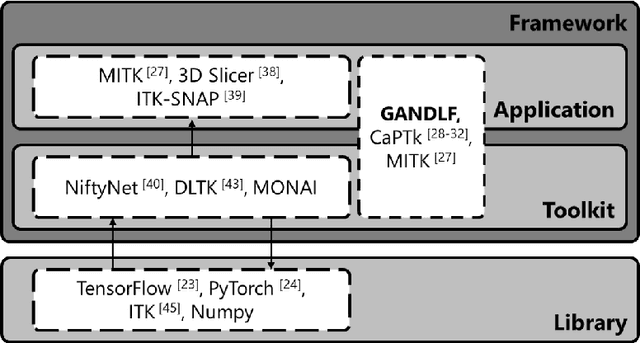
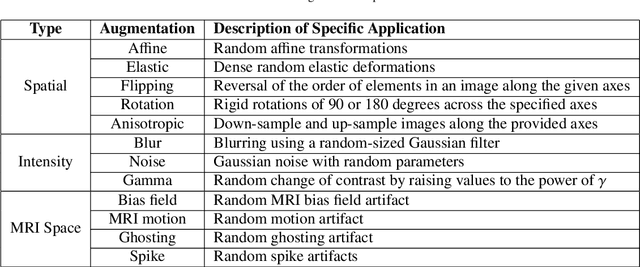
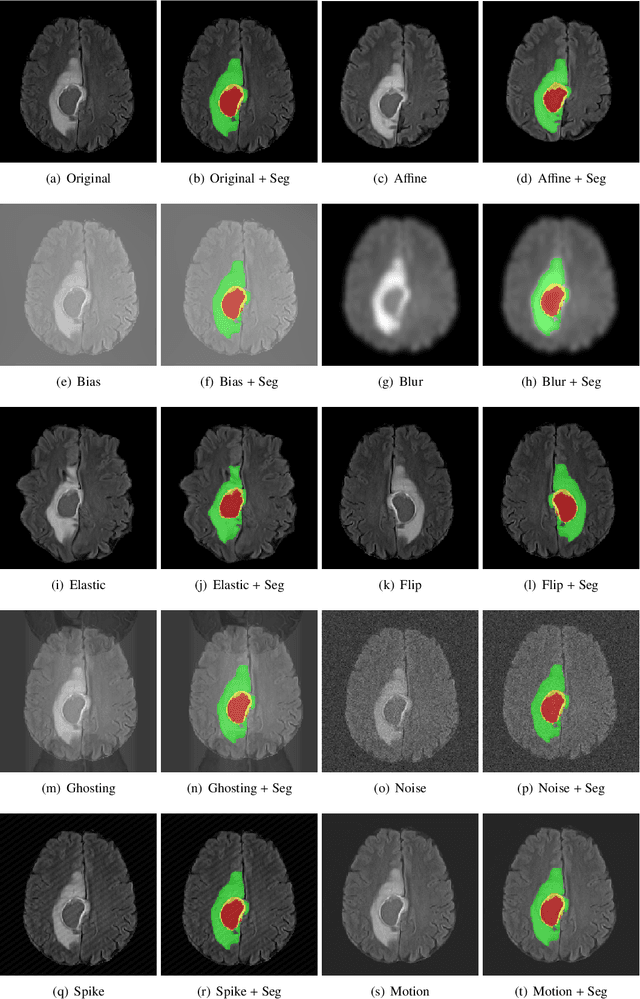
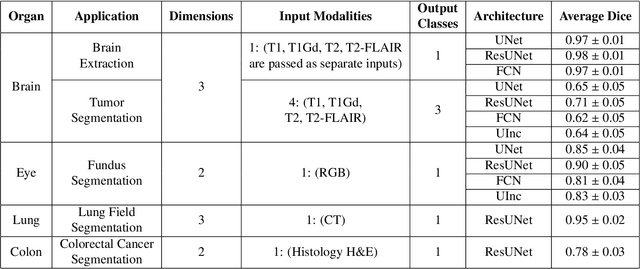
Abstract:Deep Learning (DL) has greatly highlighted the potential impact of optimized machine learning in both the scientific and clinical communities. The advent of open-source DL libraries from major industrial entities, such as TensorFlow (Google), PyTorch (Facebook), and MXNet (Apache), further contributes to DL promises on the democratization of computational analytics. However, increased technical and specialized background is required to develop DL algorithms, and the variability of implementation details hinders their reproducibility. Towards lowering the barrier and making the mechanism of DL development, training, and inference more stable, reproducible, and scalable, without requiring an extensive technical background, this manuscript proposes the \textbf{G}ener\textbf{a}lly \textbf{N}uanced \textbf{D}eep \textbf{L}earning \textbf{F}ramework (GaNDLF). With built-in support for $k$-fold cross-validation, data augmentation, multiple modalities and output classes, and multi-GPU training, as well as the ability to work with both radiographic and histologic imaging, GaNDLF aims to provide an end-to-end solution for all DL-related tasks, to tackle problems in medical imaging and provide a robust application framework for deployment in clinical workflows.
The Future of Digital Health with Federated Learning
Mar 18, 2020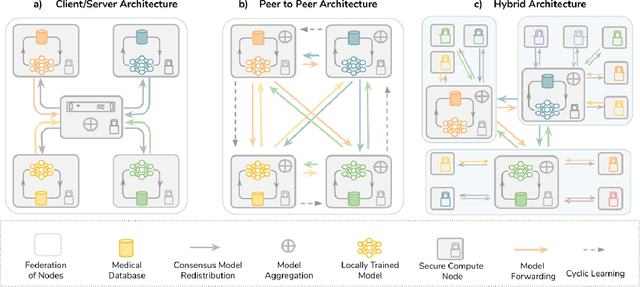
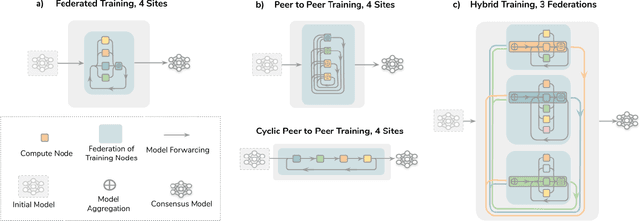
Abstract:Data-driven Machine Learning has emerged as a promising approach for building accurate and robust statistical models from medical data, which is collected in huge volumes by modern healthcare systems. Existing medical data is not fully exploited by ML primarily because it sits in data silos and privacy concerns restrict access to this data. However, without access to sufficient data, ML will be prevented from reaching its full potential and, ultimately, from making the transition from research to clinical practice. This paper considers key factors contributing to this issue, explores how Federated Learning (FL) may provide a solution for the future of digital health and highlights the challenges and considerations that need to be addressed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge