G Anthony Reina
Federated Learning Enables Big Data for Rare Cancer Boundary Detection
Apr 25, 2022Abstract:Although machine learning (ML) has shown promise in numerous domains, there are concerns about generalizability to out-of-sample data. This is currently addressed by centrally sharing ample, and importantly diverse, data from multiple sites. However, such centralization is challenging to scale (or even not feasible) due to various limitations. Federated ML (FL) provides an alternative to train accurate and generalizable ML models, by only sharing numerical model updates. Here we present findings from the largest FL study to-date, involving data from 71 healthcare institutions across 6 continents, to generate an automatic tumor boundary detector for the rare disease of glioblastoma, utilizing the largest dataset of such patients ever used in the literature (25,256 MRI scans from 6,314 patients). We demonstrate a 33% improvement over a publicly trained model to delineate the surgically targetable tumor, and 23% improvement over the tumor's entire extent. We anticipate our study to: 1) enable more studies in healthcare informed by large and diverse data, ensuring meaningful results for rare diseases and underrepresented populations, 2) facilitate further quantitative analyses for glioblastoma via performance optimization of our consensus model for eventual public release, and 3) demonstrate the effectiveness of FL at such scale and task complexity as a paradigm shift for multi-site collaborations, alleviating the need for data sharing.
MedPerf: Open Benchmarking Platform for Medical Artificial Intelligence using Federated Evaluation
Oct 08, 2021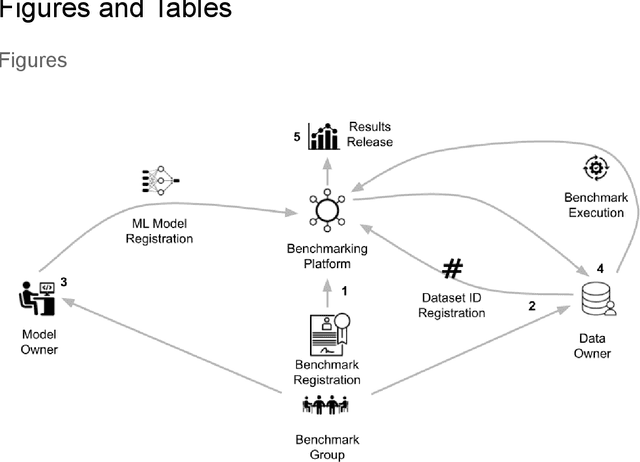
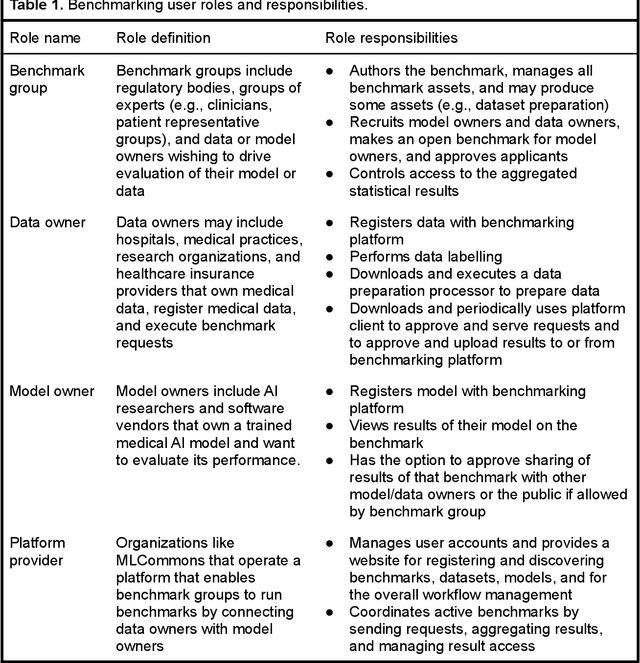
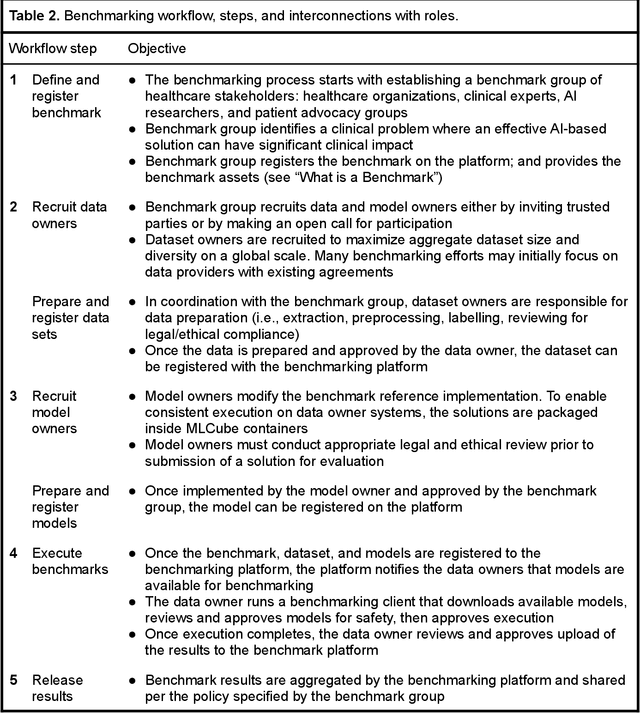
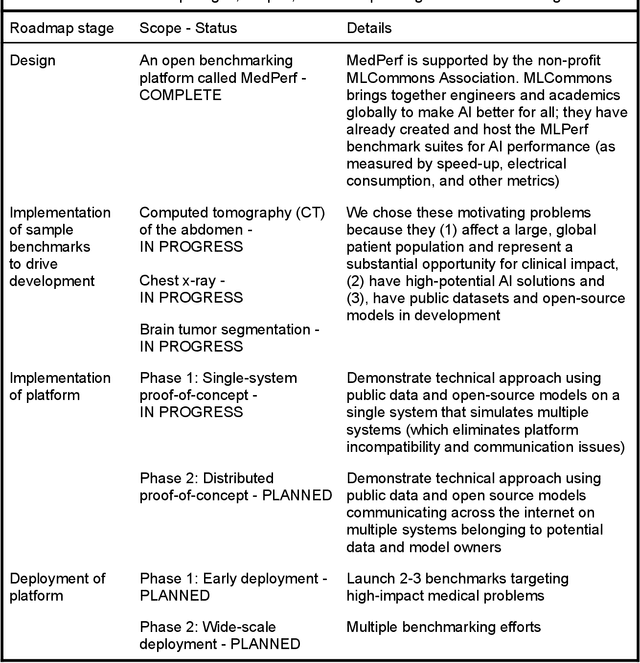
Abstract:Medical AI has tremendous potential to advance healthcare by supporting the evidence-based practice of medicine, personalizing patient treatment, reducing costs, and improving provider and patient experience. We argue that unlocking this potential requires a systematic way to measure the performance of medical AI models on large-scale heterogeneous data. To meet this need, we are building MedPerf, an open framework for benchmarking machine learning in the medical domain. MedPerf will enable federated evaluation in which models are securely distributed to different facilities for evaluation, thereby empowering healthcare organizations to assess and verify the performance of AI models in an efficient and human-supervised process, while prioritizing privacy. We describe the current challenges healthcare and AI communities face, the need for an open platform, the design philosophy of MedPerf, its current implementation status, and our roadmap. We call for researchers and organizations to join us in creating the MedPerf open benchmarking platform.
OpenFL: An open-source framework for Federated Learning
May 13, 2021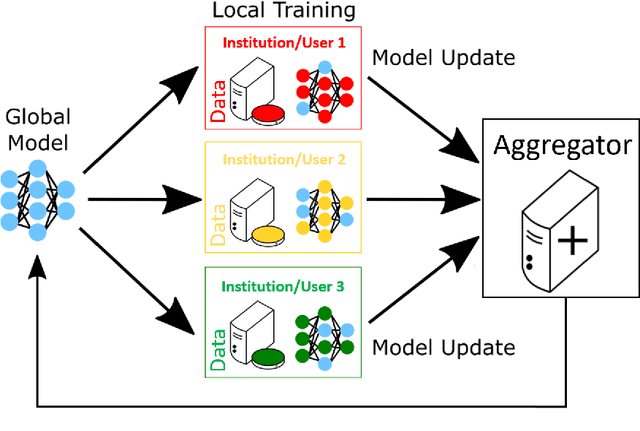
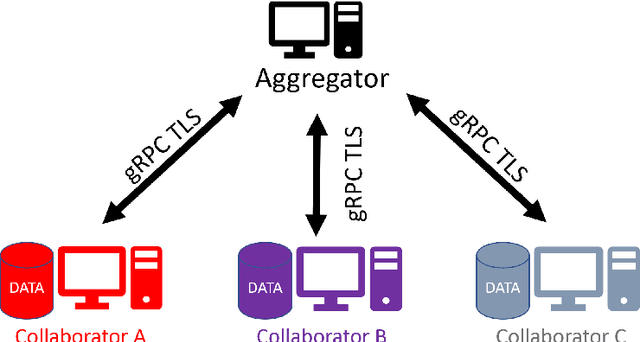
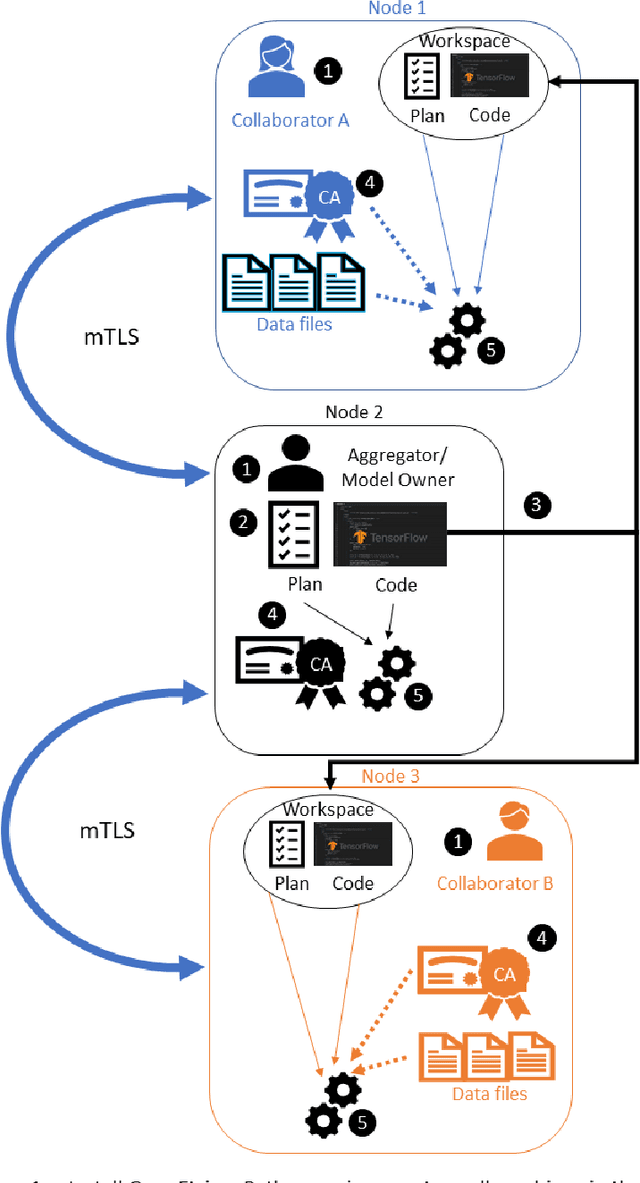
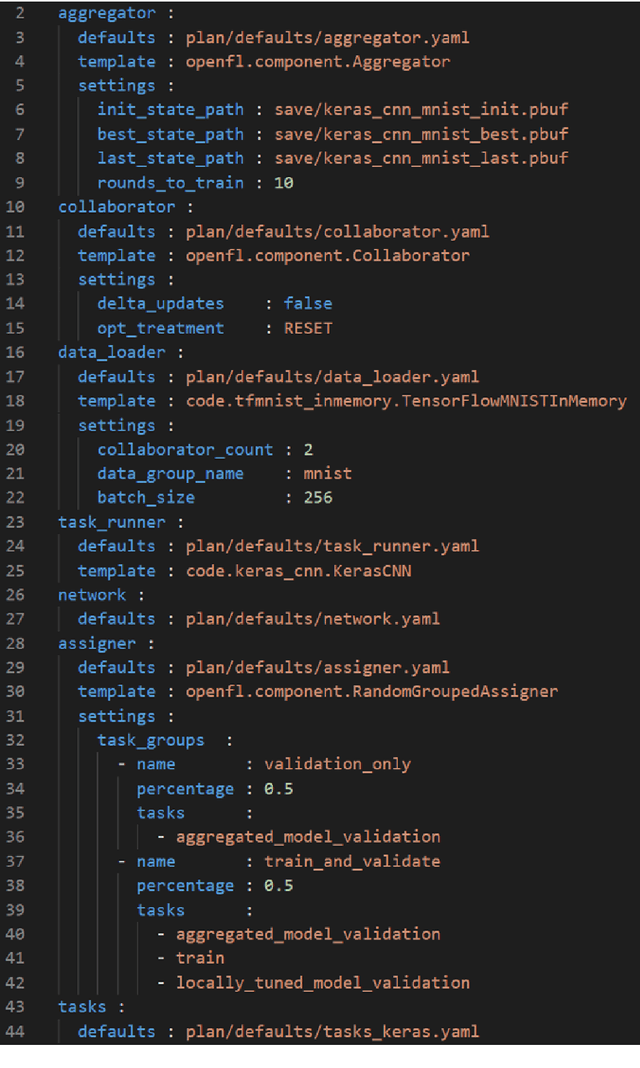
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is a computational paradigm that enables organizations to collaborate on machine learning (ML) projects without sharing sensitive data, such as, patient records, financial data, or classified secrets. Open Federated Learning (OpenFL https://github.com/intel/openfl) is an open-source framework for training ML algorithms using the data-private collaborative learning paradigm of FL. OpenFL works with training pipelines built with both TensorFlow and PyTorch, and can be easily extended to other ML and deep learning frameworks. Here, we summarize the motivation and development characteristics of OpenFL, with the intention of facilitating its application to existing ML model training in a production environment. Finally, we describe the first use of the OpenFL framework to train consensus ML models in a consortium of international healthcare organizations, as well as how it facilitates the first computational competition on FL.
Multi-Institutional Deep Learning Modeling Without Sharing Patient Data: A Feasibility Study on Brain Tumor Segmentation
Oct 22, 2018



Abstract:Deep learning models for semantic segmentation of images require large amounts of data. In the medical imaging domain, acquiring sufficient data is a significant challenge. Labeling medical image data requires expert knowledge. Collaboration between institutions could address this challenge, but sharing medical data to a centralized location faces various legal, privacy, technical, and data-ownership challenges, especially among international institutions. In this study, we introduce the first use of federated learning for multi-institutional collaboration, enabling deep learning modeling without sharing patient data. Our quantitative results demonstrate that the performance of federated semantic segmentation models (Dice=0.852) on multimodal brain scans is similar to that of models trained by sharing data (Dice=0.862). We compare federated learning with two alternative collaborative learning methods and find that they fail to match the performance of federated learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge