Keypoint Detection
Keypoint detection is essential for analyzing and interpreting images in computer vision. It involves simultaneously detecting and localizing interesting points in an image. Keypoints, also known as interest points, are spatial locations or points in the image that define what is interesting or what stands out. They are invariant to image rotation, shrinkage, translation, distortion, etc. Keypoint examples include body joints, facial landmarks, or any other salient points in objects. Keypoints have uses in problems such as pose estimation, object detection and tracking, facial analysis, and augmented reality.
Papers and Code
RoboKeyGen: Robot Pose and Joint Angles Estimation via Diffusion-based 3D Keypoint Generation
Mar 27, 2024



Estimating robot pose and joint angles is significant in advanced robotics, enabling applications like robot collaboration and online hand-eye calibration.However, the introduction of unknown joint angles makes prediction more complex than simple robot pose estimation, due to its higher dimensionality.Previous methods either regress 3D keypoints directly or utilise a render&compare strategy. These approaches often falter in terms of performance or efficiency and grapple with the cross-camera gap problem.This paper presents a novel framework that bifurcates the high-dimensional prediction task into two manageable subtasks: 2D keypoints detection and lifting 2D keypoints to 3D. This separation promises enhanced performance without sacrificing the efficiency innate to keypoint-based techniques.A vital component of our method is the lifting of 2D keypoints to 3D keypoints. Common deterministic regression methods may falter when faced with uncertainties from 2D detection errors or self-occlusions.Leveraging the robust modeling potential of diffusion models, we reframe this issue as a conditional 3D keypoints generation task. To bolster cross-camera adaptability, we introduce theNormalised Camera Coordinate Space (NCCS), ensuring alignment of estimated 2D keypoints across varying camera intrinsics.Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art render\&compare method and achieves higher inference speed.Furthermore, the tests accentuate our method's robust cross-camera generalisation capabilities.We intend to release both the dataset and code in https://nimolty.github.io/Robokeygen/
Using joint angles based on the international biomechanical standards for human action recognition and related tasks
Jun 25, 2024



Keypoint data has received a considerable amount of attention in machine learning for tasks like action detection and recognition. However, human experts in movement such as doctors, physiotherapists, sports scientists and coaches use a notion of joint angles standardised by the International Society of Biomechanics to precisely and efficiently communicate static body poses and movements. In this paper, we introduce the basic biomechanical notions and show how they can be used to convert common keypoint data into joint angles that uniquely describe the given pose and have various desirable mathematical properties, such as independence of both the camera viewpoint and the person performing the action. We experimentally demonstrate that the joint angle representation of keypoint data is suitable for machine learning applications and can in some cases bring an immediate performance gain. The use of joint angles as a human meaningful representation of kinematic data is in particular promising for applications where interpretability and dialog with human experts is important, such as many sports and medical applications. To facilitate further research in this direction, we will release a python package to convert keypoint data into joint angles as outlined in this paper.
To deform or not: treatment-aware longitudinal registration for breast DCE-MRI during neoadjuvant chemotherapy via unsupervised keypoints detection
Jan 17, 2024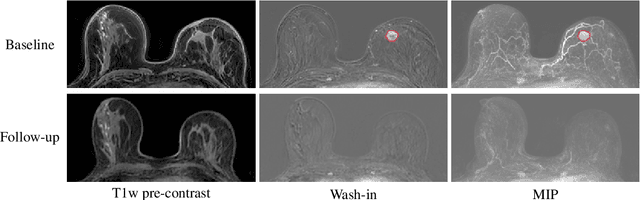
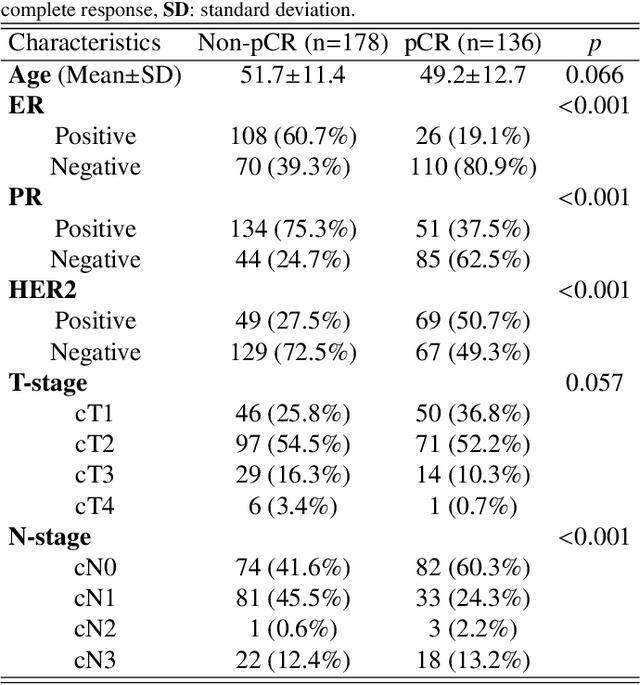
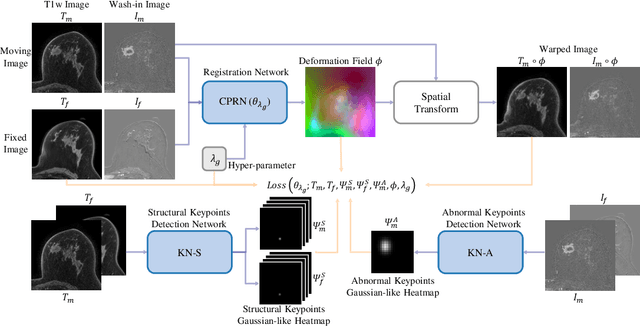
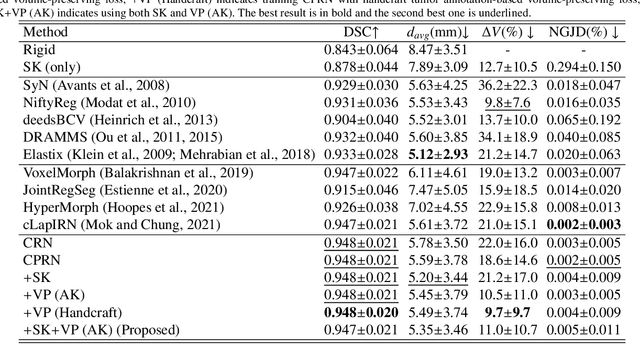
Clinicians compare breast DCE-MRI after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) with pre-treatment scans to evaluate the response to NAC. Clinical evidence supports that accurate longitudinal deformable registration without deforming treated tumor regions is key to quantifying tumor changes. We propose a conditional pyramid registration network based on unsupervised keypoint detection and selective volume-preserving to quantify changes over time. In this approach, we extract the structural and the abnormal keypoints from DCE-MRI, apply the structural keypoints for the registration algorithm to restrict large deformation, and employ volume-preserving loss based on abnormal keypoints to keep the volume of the tumor unchanged after registration. We use a clinical dataset with 1630 MRI scans from 314 patients treated with NAC. The results demonstrate that our method registers with better performance and better volume preservation of the tumors. Furthermore, a local-global-combining biomarker based on the proposed method achieves high accuracy in pathological complete response (pCR) prediction, indicating that predictive information exists outside tumor regions. The biomarkers could potentially be used to avoid unnecessary surgeries for certain patients. It may be valuable for clinicians and/or computer systems to conduct follow-up tumor segmentation and response prediction on images registered by our method. Our code is available on \url{https://github.com/fiy2W/Treatment-aware-Longitudinal-Registration}.
Temporally-consistent 3D Reconstruction of Birds
Aug 24, 2024This paper deals with 3D reconstruction of seabirds which recently came into focus of environmental scientists as valuable bio-indicators for environmental change. Such 3D information is beneficial for analyzing the bird's behavior and physiological shape, for example by tracking motion, shape, and appearance changes. From a computer vision perspective birds are especially challenging due to their rapid and oftentimes non-rigid motions. We propose an approach to reconstruct the 3D pose and shape from monocular videos of a specific breed of seabird - the common murre. Our approach comprises a full pipeline of detection, tracking, segmentation, and temporally consistent 3D reconstruction. Additionally, we propose a temporal loss that extends current single-image 3D bird pose estimators to the temporal domain. Moreover, we provide a real-world dataset of 10000 frames of video observations on average capture nine birds simultaneously, comprising a large variety of motions and interactions, including a smaller test set with bird-specific keypoint labels. Using our temporal optimization, we achieve state-of-the-art performance for the challenging sequences in our dataset.
Personalized Topology-Informed 12-Lead ECG Electrode Localization from Incomplete Cardiac MRIs for Efficient Cardiac Digital Twins
Aug 25, 2024Cardiac digital twins (CDTs) offer personalized \textit{in-silico} cardiac representations for the inference of multi-scale properties tied to cardiac mechanisms. The creation of CDTs requires precise information about the electrode position on the torso, especially for the personalized electrocardiogram (ECG) calibration. However, current studies commonly rely on additional acquisition of torso imaging and manual/semi-automatic methods for ECG electrode localization. In this study, we propose a novel and efficient topology-informed model to fully automatically extract personalized ECG electrode locations from 2D clinically standard cardiac MRIs. Specifically, we obtain the sparse torso contours from the cardiac MRIs and then localize the electrodes from the contours. Cardiac MRIs aim at imaging of the heart instead of the torso, leading to incomplete torso geometry within the imaging. To tackle the missing topology, we incorporate the electrodes as a subset of the keypoints, which can be explicitly aligned with the 3D torso topology. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms the time-consuming conventional method in terms of accuracy (Euclidean distance: $1.24 \pm 0.293$ cm vs. $1.48 \pm 0.362$ cm) and efficiency ($2$~s vs. $30$-$35$~min). We further demonstrate the effectiveness of using the detected electrodes for \textit{in-silico} ECG simulation, highlighting their potential for creating accurate and efficient CDT models. The code will be released publicly after the manuscript is accepted for publication.
SD-Net: Symmetric-Aware Keypoint Prediction and Domain Adaptation for 6D Pose Estimation In Bin-picking Scenarios
Mar 14, 2024



Despite the success in 6D pose estimation in bin-picking scenarios, existing methods still struggle to produce accurate prediction results for symmetry objects and real world scenarios. The primary bottlenecks include 1) the ambiguity keypoints caused by object symmetries; 2) the domain gap between real and synthetic data. To circumvent these problem, we propose a new 6D pose estimation network with symmetric-aware keypoint prediction and self-training domain adaptation (SD-Net). SD-Net builds on pointwise keypoint regression and deep hough voting to perform reliable detection keypoint under clutter and occlusion. Specifically, at the keypoint prediction stage, we designe a robust 3D keypoints selection strategy considering the symmetry class of objects and equivalent keypoints, which facilitate locating 3D keypoints even in highly occluded scenes. Additionally, we build an effective filtering algorithm on predicted keypoint to dynamically eliminate multiple ambiguity and outlier keypoint candidates. At the domain adaptation stage, we propose the self-training framework using a student-teacher training scheme. To carefully distinguish reliable predictions, we harnesses a tailored heuristics for 3D geometry pseudo labelling based on semi-chamfer distance. On public Sil'eane dataset, SD-Net achieves state-of-the-art results, obtaining an average precision of 96%. Testing learning and generalization abilities on public Parametric datasets, SD-Net is 8% higher than the state-of-the-art method. The code is available at https://github.com/dingthuang/SD-Net.
MMVR: Millimeter-wave Multi-View Radar Dataset and Benchmark for Indoor Perception
Jun 15, 2024



Compared with an extensive list of automotive radar datasets that support autonomous driving, indoor radar datasets are scarce at a smaller scale in the format of low-resolution radar point clouds and usually under an open-space single-room setting. In this paper, we scale up indoor radar data collection using multi-view high-resolution radar heatmap in a multi-day, multi-room, and multi-subject setting, with an emphasis on the diversity of environment and subjects. Referred to as the millimeter-wave multi-view radar (MMVR) dataset, it consists of $345$K multi-view radar frames collected from $25$ human subjects over $6$ different rooms, $446$K annotated bounding boxes/segmentation instances, and $7.59$ million annotated keypoints to support three major perception tasks of object detection, pose estimation, and instance segmentation, respectively. For each task, we report performance benchmarks under two protocols: a single subject in an open space and multiple subjects in several cluttered rooms with two data splits: random split and cross-environment split over $395$ 1-min data segments. We anticipate that MMVR facilitates indoor radar perception development for indoor vehicle (robot/humanoid) navigation, building energy management, and elderly care for better efficiency, user experience, and safety.
Self-supervised 3D Patient Modeling with Multi-modal Attentive Fusion
Mar 05, 20243D patient body modeling is critical to the success of automated patient positioning for smart medical scanning and operating rooms. Existing CNN-based end-to-end patient modeling solutions typically require a) customized network designs demanding large amount of relevant training data, covering extensive realistic clinical scenarios (e.g., patient covered by sheets), which leads to suboptimal generalizability in practical deployment, b) expensive 3D human model annotations, i.e., requiring huge amount of manual effort, resulting in systems that scale poorly. To address these issues, we propose a generic modularized 3D patient modeling method consists of (a) a multi-modal keypoint detection module with attentive fusion for 2D patient joint localization, to learn complementary cross-modality patient body information, leading to improved keypoint localization robustness and generalizability in a wide variety of imaging (e.g., CT, MRI etc.) and clinical scenarios (e.g., heavy occlusions); and (b) a self-supervised 3D mesh regression module which does not require expensive 3D mesh parameter annotations to train, bringing immediate cost benefits for clinical deployment. We demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed method by extensive patient positioning experiments on both public and clinical data. Our evaluation results achieve superior patient positioning performance across various imaging modalities in real clinical scenarios.
3D Extended Object Tracking by Fusing Roadside Sparse Radar Point Clouds and Pixel Keypoints
Apr 27, 2024



Roadside perception is a key component in intelligent transportation systems. In this paper, we present a novel three-dimensional (3D) extended object tracking (EOT) method, which simultaneously estimates the object kinematics and extent state, in roadside perception using both the radar and camera data. Because of the influence of sensor viewing angle and limited angle resolution, radar measurements from objects are sparse and non-uniformly distributed, leading to inaccuracies in object extent and position estimation. To address this problem, we present a novel spherical Gaussian function weighted Gaussian mixture model. This model assumes that radar measurements originate from a series of probabilistic weighted radar reflectors on the vehicle's extent. Additionally, we utilize visual detection of vehicle keypoints to provide additional information on the positions of radar reflectors. Since keypoints may not always correspond to radar reflectors, we propose an elastic skeleton fusion mechanism, which constructs a virtual force to establish the relationship between the radar reflectors on the vehicle and its extent. Furthermore, to better describe the kinematic state of the vehicle and constrain its extent state, we develop a new 3D constant turn rate and velocity motion model, considering the complex 3D motion of the vehicle relative to the roadside sensor. Finally, we apply variational Bayesian approximation to the intractable measurement update step to enable recursive Bayesian estimation of the object's state. Simulation results using the Carla simulator and experimental results on the nuScenes dataset demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method in comparison to several state-of-the-art 3D EOT methods.
3D Kinematics Estimation from Video with a Biomechanical Model and Synthetic Training Data
Feb 26, 2024Accurate 3D kinematics estimation of human body is crucial in various applications for human health and mobility, such as rehabilitation, injury prevention, and diagnosis, as it helps to understand the biomechanical loading experienced during movement. Conventional marker-based motion capture is expensive in terms of financial investment, time, and the expertise required. Moreover, due to the scarcity of datasets with accurate annotations, existing markerless motion capture methods suffer from challenges including unreliable 2D keypoint detection, limited anatomic accuracy, and low generalization capability. In this work, we propose a novel biomechanics-aware network that directly outputs 3D kinematics from two input views with consideration of biomechanical prior and spatio-temporal information. To train the model, we create synthetic dataset ODAH with accurate kinematics annotations generated by aligning the body mesh from the SMPL-X model and a full-body OpenSim skeletal model. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed approach, only trained on synthetic data, outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods when evaluated across multiple datasets, revealing a promising direction for enhancing video-based human motion capture.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge