Tiankai Hang
Incorporating Pre-trained Diffusion Models in Solving the Schrödinger Bridge Problem
Aug 25, 2025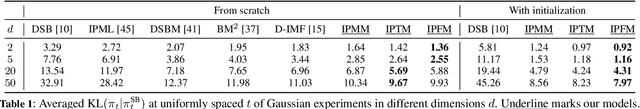
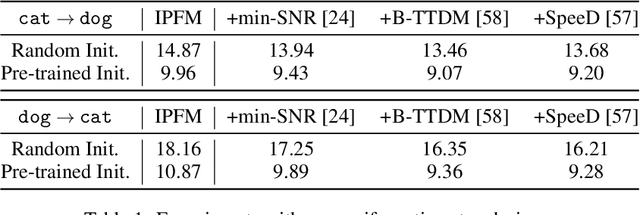

Abstract:This paper aims to unify Score-based Generative Models (SGMs), also known as Diffusion models, and the Schr\"odinger Bridge (SB) problem through three reparameterization techniques: Iterative Proportional Mean-Matching (IPMM), Iterative Proportional Terminus-Matching (IPTM), and Iterative Proportional Flow-Matching (IPFM). These techniques significantly accelerate and stabilize the training of SB-based models. Furthermore, the paper introduces novel initialization strategies that use pre-trained SGMs to effectively train SB-based models. By using SGMs as initialization, we leverage the advantages of both SB-based models and SGMs, ensuring efficient training of SB-based models and further improving the performance of SGMs. Extensive experiments demonstrate the significant effectiveness and improvements of the proposed methods. We believe this work contributes to and paves the way for future research on generative models.
Fast Autoregressive Models for Continuous Latent Generation
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Autoregressive models have demonstrated remarkable success in sequential data generation, particularly in NLP, but their extension to continuous-domain image generation presents significant challenges. Recent work, the masked autoregressive model (MAR), bypasses quantization by modeling per-token distributions in continuous spaces using a diffusion head but suffers from slow inference due to the high computational cost of the iterative denoising process. To address this, we propose the Fast AutoRegressive model (FAR), a novel framework that replaces MAR's diffusion head with a lightweight shortcut head, enabling efficient few-step sampling while preserving autoregressive principles. Additionally, FAR seamlessly integrates with causal Transformers, extending them from discrete to continuous token generation without requiring architectural modifications. Experiments demonstrate that FAR achieves $2.3\times$ faster inference than MAR while maintaining competitive FID and IS scores. This work establishes the first efficient autoregressive paradigm for high-fidelity continuous-space image generation, bridging the critical gap between quality and scalability in visual autoregressive modeling.
Improved Noise Schedule for Diffusion Training
Jul 03, 2024Abstract:Diffusion models have emerged as the de facto choice for generating visual signals. However, training a single model to predict noise across various levels poses significant challenges, necessitating numerous iterations and incurring significant computational costs. Various approaches, such as loss weighting strategy design and architectural refinements, have been introduced to expedite convergence. In this study, we propose a novel approach to design the noise schedule for enhancing the training of diffusion models. Our key insight is that the importance sampling of the logarithm of the Signal-to-Noise ratio (logSNR), theoretically equivalent to a modified noise schedule, is particularly beneficial for training efficiency when increasing the sample frequency around $\log \text{SNR}=0$. We empirically demonstrate the superiority of our noise schedule over the standard cosine schedule. Furthermore, we highlight the advantages of our noise schedule design on the ImageNet benchmark, showing that the designed schedule consistently benefits different prediction targets.
Step-aware Preference Optimization: Aligning Preference with Denoising Performance at Each Step
Jun 06, 2024



Abstract:Recently, Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) has extended its success from aligning large language models (LLMs) to aligning text-to-image diffusion models with human preferences. Unlike most existing DPO methods that assume all diffusion steps share a consistent preference order with the final generated images, we argue that this assumption neglects step-specific denoising performance and that preference labels should be tailored to each step's contribution. To address this limitation, we propose Step-aware Preference Optimization (SPO), a novel post-training approach that independently evaluates and adjusts the denoising performance at each step, using a step-aware preference model and a step-wise resampler to ensure accurate step-aware supervision. Specifically, at each denoising step, we sample a pool of images, find a suitable win-lose pair, and, most importantly, randomly select a single image from the pool to initialize the next denoising step. This step-wise resampler process ensures the next win-lose image pair comes from the same image, making the win-lose comparison independent of the previous step. To assess the preferences at each step, we train a separate step-aware preference model that can be applied to both noisy and clean images. Our experiments with Stable Diffusion v1.5 and SDXL demonstrate that SPO significantly outperforms the latest Diffusion-DPO in aligning generated images with complex, detailed prompts and enhancing aesthetics, while also achieving more than 20x times faster in training efficiency. Code and model: https://rockeycoss.github.io/spo.github.io/
Simplified Diffusion Schrödinger Bridge
Mar 27, 2024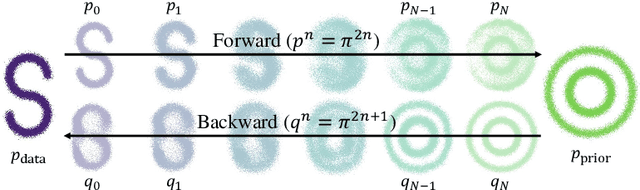


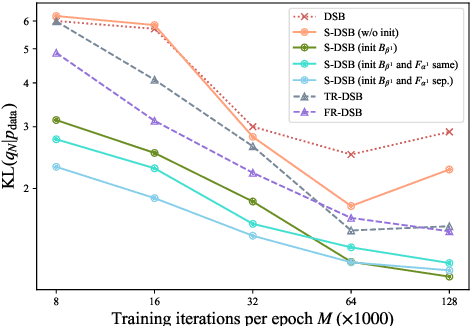
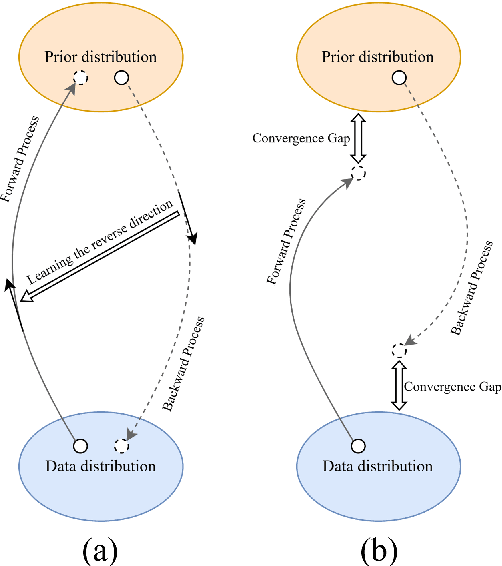
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel theoretical simplification of the Diffusion Schr\"odinger Bridge (DSB) that facilitates its unification with Score-based Generative Models (SGMs), addressing the limitations of DSB in complex data generation and enabling faster convergence and enhanced performance. By employing SGMs as an initial solution for DSB, our approach capitalizes on the strengths of both frameworks, ensuring a more efficient training process and improving the performance of SGM. We also propose a reparameterization technique that, despite theoretical approximations, practically improves the network's fitting capabilities. Our extensive experimental evaluations confirm the effectiveness of the simplified DSB, demonstrating its significant improvements. We believe the contributions of this work pave the way for advanced generative modeling. The code is available at https://github.com/checkcrab/SDSB.
CCA: Collaborative Competitive Agents for Image Editing
Jan 23, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a novel generative model, Collaborative Competitive Agents (CCA), which leverages the capabilities of multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) based agents to execute complex tasks. Drawing inspiration from Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), the CCA system employs two equal-status generator agents and a discriminator agent. The generators independently process user instructions and generate results, while the discriminator evaluates the outputs, and provides feedback for the generator agents to further reflect and improve the generation results. Unlike the previous generative model, our system can obtain the intermediate steps of generation. This allows each generator agent to learn from other successful executions due to its transparency, enabling a collaborative competition that enhances the quality and robustness of the system's results. The primary focus of this study is image editing, demonstrating the CCA's ability to handle intricate instructions robustly. The paper's main contributions include the introduction of a multi-agent-based generative model with controllable intermediate steps and iterative optimization, a detailed examination of agent relationships, and comprehensive experiments on image editing. Code is available at \href{https://github.com/TiankaiHang/CCA}{https://github.com/TiankaiHang/CCA}.
InstructDiffusion: A Generalist Modeling Interface for Vision Tasks
Sep 07, 2023Abstract:We present InstructDiffusion, a unifying and generic framework for aligning computer vision tasks with human instructions. Unlike existing approaches that integrate prior knowledge and pre-define the output space (e.g., categories and coordinates) for each vision task, we cast diverse vision tasks into a human-intuitive image-manipulating process whose output space is a flexible and interactive pixel space. Concretely, the model is built upon the diffusion process and is trained to predict pixels according to user instructions, such as encircling the man's left shoulder in red or applying a blue mask to the left car. InstructDiffusion could handle a variety of vision tasks, including understanding tasks (such as segmentation and keypoint detection) and generative tasks (such as editing and enhancement). It even exhibits the ability to handle unseen tasks and outperforms prior methods on novel datasets. This represents a significant step towards a generalist modeling interface for vision tasks, advancing artificial general intelligence in the field of computer vision.
Efficient Diffusion Training via Min-SNR Weighting Strategy
Mar 22, 2023Abstract:Denoising diffusion models have been a mainstream approach for image generation, however, training these models often suffers from slow convergence. In this paper, we discovered that the slow convergence is partly due to conflicting optimization directions between timesteps. To address this issue, we treat the diffusion training as a multi-task learning problem, and introduce a simple yet effective approach referred to as Min-SNR-$\gamma$. This method adapts loss weights of timesteps based on clamped signal-to-noise ratios, which effectively balances the conflicts among timesteps. Our results demonstrate a significant improvement in converging speed, 3.4$\times$ faster than previous weighting strategies. It is also more effective, achieving a new record FID score of 2.06 on the ImageNet $256\times256$ benchmark using smaller architectures than that employed in previous state-of-the-art. The code is available at https://github.com/TiankaiHang/Min-SNR-Diffusion-Training.
Language-Guided Face Animation by Recurrent StyleGAN-based Generator
Aug 11, 2022


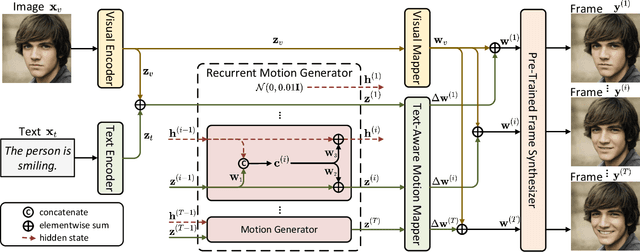
Abstract:Recent works on language-guided image manipulation have shown great power of language in providing rich semantics, especially for face images. However, the other natural information, motions, in language is less explored. In this paper, we leverage the motion information and study a novel task, language-guided face animation, that aims to animate a static face image with the help of languages. To better utilize both semantics and motions from languages, we propose a simple yet effective framework. Specifically, we propose a recurrent motion generator to extract a series of semantic and motion information from the language and feed it along with visual information to a pre-trained StyleGAN to generate high-quality frames. To optimize the proposed framework, three carefully designed loss functions are proposed including a regularization loss to keep the face identity, a path length regularization loss to ensure motion smoothness, and a contrastive loss to enable video synthesis with various language guidance in one single model. Extensive experiments with both qualitative and quantitative evaluations on diverse domains (\textit{e.g.,} human face, anime face, and dog face) demonstrate the superiority of our model in generating high-quality and realistic videos from one still image with the guidance of language. Code will be available at https://github.com/TiankaiHang/language-guided-animation.git.
Advancing High-Resolution Video-Language Representation with Large-Scale Video Transcriptions
Nov 19, 2021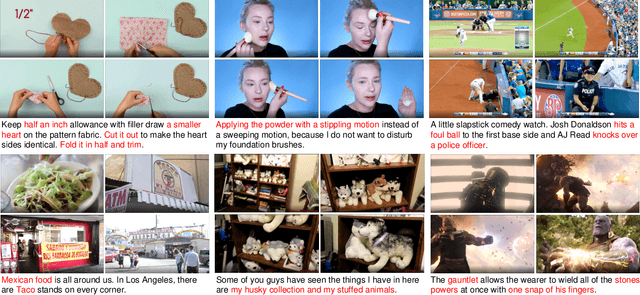
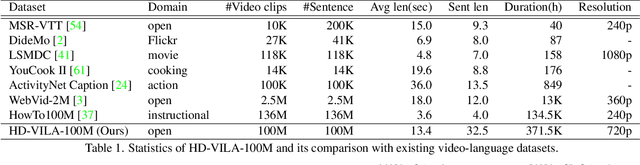
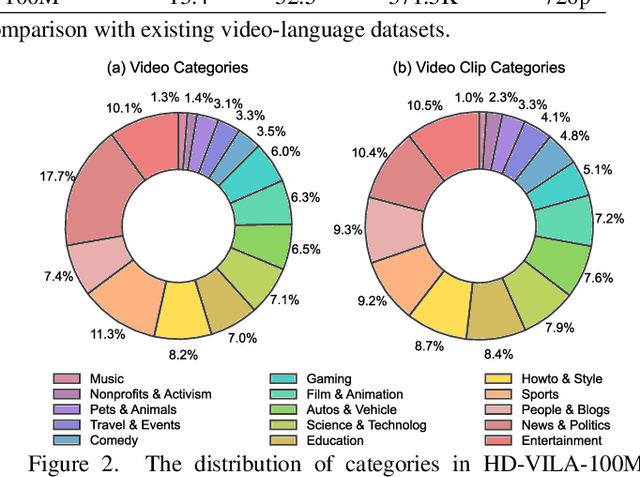
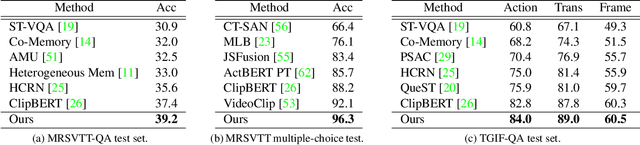
Abstract:We study joint video and language (VL) pre-training to enable cross-modality learning and benefit plentiful downstream VL tasks. Existing works either extract low-quality video features or learn limited text embedding, while neglecting that high-resolution videos and diversified semantics can significantly improve cross-modality learning. In this paper, we propose a novel High-resolution and Diversified VIdeo-LAnguage pre-training model (HD-VILA) for many visual tasks. In particular, we collect a large dataset with two distinct properties: 1) the first high-resolution dataset including 371.5k hours of 720p videos, and 2) the most diversified dataset covering 15 popular YouTube categories. To enable VL pre-training, we jointly optimize the HD-VILA model by a hybrid Transformer that learns rich spatiotemporal features, and a multimodal Transformer that enforces interactions of the learned video features with diversified texts. Our pre-training model achieves new state-of-the-art results in 10 VL understanding tasks and 2 more novel text-to-visual generation tasks. For example, we outperform SOTA models with relative increases of 38.5% R@1 in zero-shot MSR-VTT text-to-video retrieval task, and 53.6% in high-resolution dataset LSMDC. The learned VL embedding is also effective in generating visually pleasing and semantically relevant results in text-to-visual manipulation and super-resolution tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge