Yulu Gan
FoundationMotion: Auto-Labeling and Reasoning about Spatial Movement in Videos
Dec 11, 2025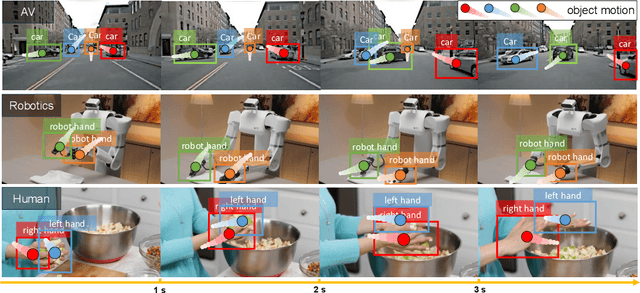
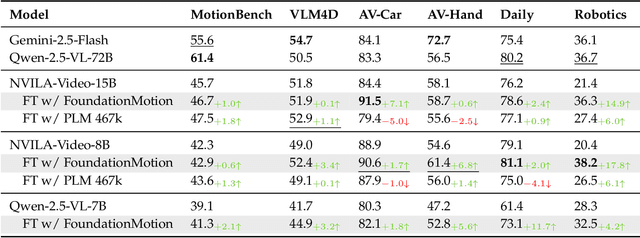
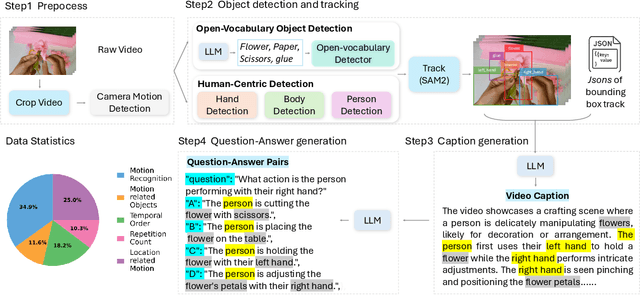
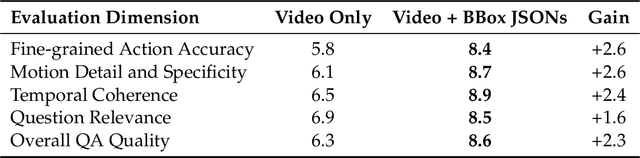
Abstract:Motion understanding is fundamental to physical reasoning, enabling models to infer dynamics and predict future states. However, state-of-the-art models still struggle on recent motion benchmarks, primarily due to the scarcity of large-scale, fine-grained motion datasets. Existing motion datasets are often constructed from costly manual annotation, severely limiting scalability. To address this challenge, we introduce FoundationMotion, a fully automated data curation pipeline that constructs large-scale motion datasets. Our approach first detects and tracks objects in videos to extract their trajectories, then leverages these trajectories and video frames with Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate fine-grained captions and diverse question-answer pairs about motion and spatial reasoning. Using datasets produced by this pipeline, we fine-tune open-source models including NVILA-Video-15B and Qwen2.5-7B, achieving substantial improvements in motion understanding without compromising performance on other tasks. Notably, our models outperform strong closed-source baselines like Gemini-2.5 Flash and large open-source models such as Qwen2.5-VL-72B across diverse motion understanding datasets and benchmarks. FoundationMotion thus provides a scalable solution for curating fine-grained motion datasets that enable effective fine-tuning of diverse models to enhance motion understanding and spatial reasoning capabilities.
Position: Simulating Society Requires Simulating Thought
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Simulating society with large language models (LLMs), we argue, requires more than generating plausible behavior -- it demands cognitively grounded reasoning that is structured, revisable, and traceable. LLM-based agents are increasingly used to emulate individual and group behavior -- primarily through prompting and supervised fine-tuning. Yet they often lack internal coherence, causal reasoning, and belief traceability -- making them unreliable for analyzing how people reason, deliberate, or respond to interventions. To address this, we present a conceptual modeling paradigm, Generative Minds (GenMinds), which draws from cognitive science to support structured belief representations in generative agents. To evaluate such agents, we introduce the RECAP (REconstructing CAusal Paths) framework, a benchmark designed to assess reasoning fidelity via causal traceability, demographic grounding, and intervention consistency. These contributions advance a broader shift: from surface-level mimicry to generative agents that simulate thought -- not just language -- for social simulations.
Self-Assembly of a Biologically Plausible Learning Circuit
Dec 28, 2024



Abstract:Over the last four decades, the amazing success of deep learning has been driven by the use of Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) as the main optimization technique. The default implementation for the computation of the gradient for SGD is backpropagation, which, with its variations, is used to this day in almost all computer implementations. From the perspective of neuroscientists, however, the consensus is that backpropagation is unlikely to be used by the brain. Though several alternatives have been discussed, none is so far supported by experimental evidence. Here we propose a circuit for updating the weights in a network that is biologically plausible, works as well as backpropagation, and leads to verifiable predictions about the anatomy and the physiology of a characteristic motif of four plastic synapses between ascending and descending cortical streams. A key prediction of our proposal is a surprising property of self-assembly of the basic circuit, emerging from initial random connectivity and heterosynaptic plasticity rules.
On the Power of Decision Trees in Auto-Regressive Language Modeling
Sep 27, 2024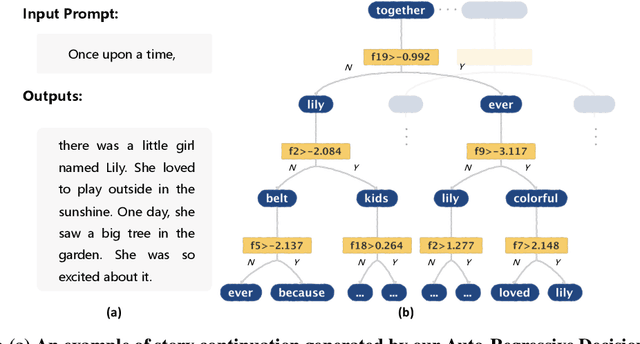
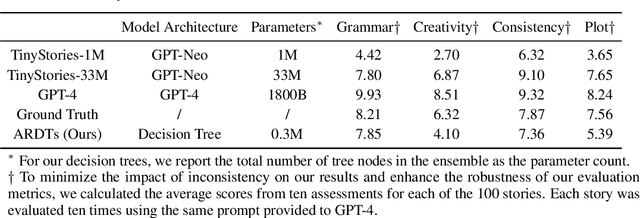
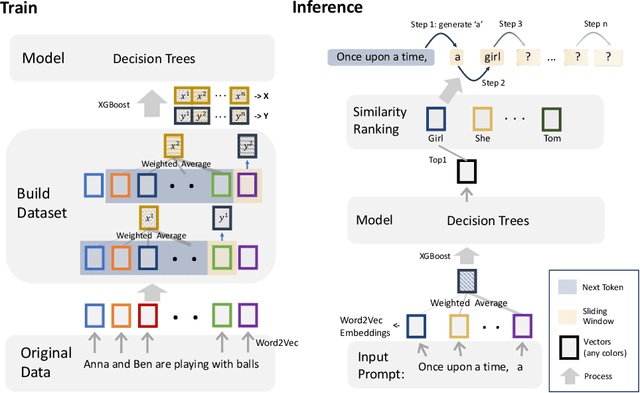
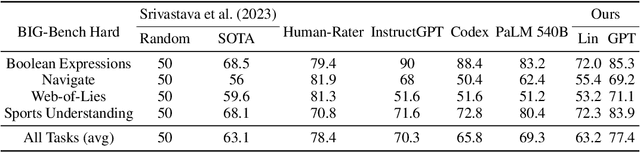
Abstract:Originally proposed for handling time series data, Auto-regressive Decision Trees (ARDTs) have not yet been explored for language modeling. This paper delves into both the theoretical and practical applications of ARDTs in this new context. We theoretically demonstrate that ARDTs can compute complex functions, such as simulating automata, Turing machines, and sparse circuits, by leveraging "chain-of-thought" computations. Our analysis provides bounds on the size, depth, and computational efficiency of ARDTs, highlighting their surprising computational power. Empirically, we train ARDTs on simple language generation tasks, showing that they can learn to generate coherent and grammatically correct text on par with a smaller Transformer model. Additionally, we show that ARDTs can be used on top of transformer representations to solve complex reasoning tasks. This research reveals the unique computational abilities of ARDTs, aiming to broaden the architectural diversity in language model development.
Split-Ensemble: Efficient OOD-aware Ensemble via Task and Model Splitting
Dec 14, 2023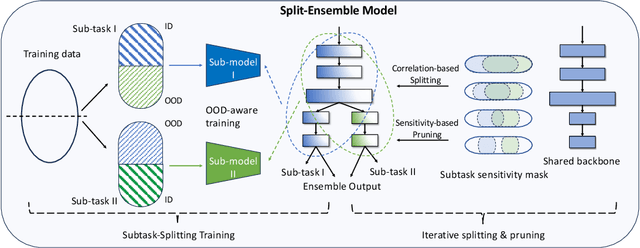
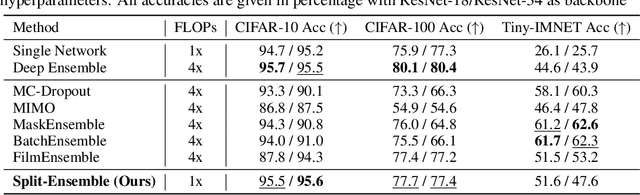
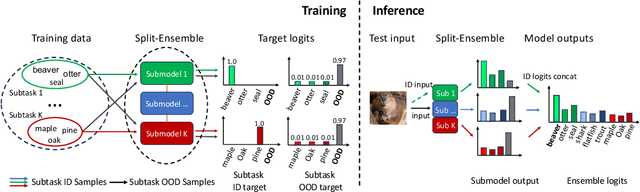
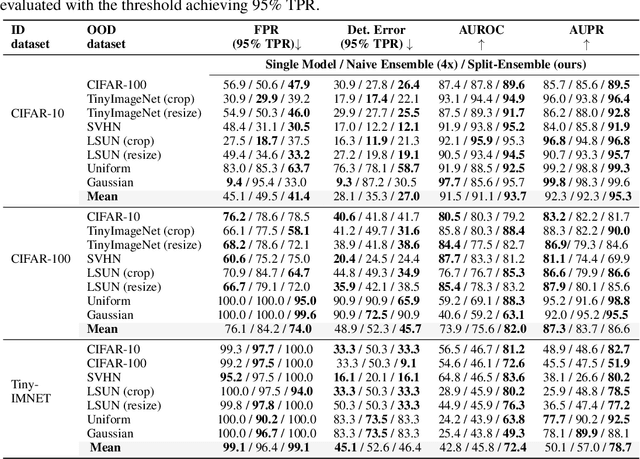
Abstract:Uncertainty estimation is crucial for machine learning models to detect out-of-distribution (OOD) inputs. However, the conventional discriminative deep learning classifiers produce uncalibrated closed-set predictions for OOD data. A more robust classifiers with the uncertainty estimation typically require a potentially unavailable OOD dataset for outlier exposure training, or a considerable amount of additional memory and compute to build ensemble models. In this work, we improve on uncertainty estimation without extra OOD data or additional inference costs using an alternative Split-Ensemble method. Specifically, we propose a novel subtask-splitting ensemble training objective, where a common multiclass classification task is split into several complementary subtasks. Then, each subtask's training data can be considered as OOD to the other subtasks. Diverse submodels can therefore be trained on each subtask with OOD-aware objectives. The subtask-splitting objective enables us to share low-level features across submodels to avoid parameter and computational overheads. In particular, we build a tree-like Split-Ensemble architecture by performing iterative splitting and pruning from a shared backbone model, where each branch serves as a submodel corresponding to a subtask. This leads to improved accuracy and uncertainty estimation across submodels under a fixed ensemble computation budget. Empirical study with ResNet-18 backbone shows Split-Ensemble, without additional computation cost, improves accuracy over a single model by 0.8%, 1.8%, and 25.5% on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and Tiny-ImageNet, respectively. OOD detection for the same backbone and in-distribution datasets surpasses a single model baseline by, correspondingly, 2.2%, 8.1%, and 29.6% mean AUROC. Codes will be publicly available at https://antonioo-c.github.io/projects/split-ensemble
Decouple Content and Motion for Conditional Image-to-Video Generation
Nov 24, 2023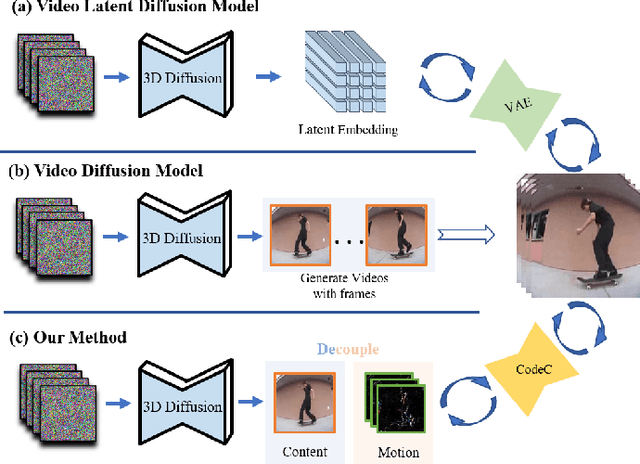

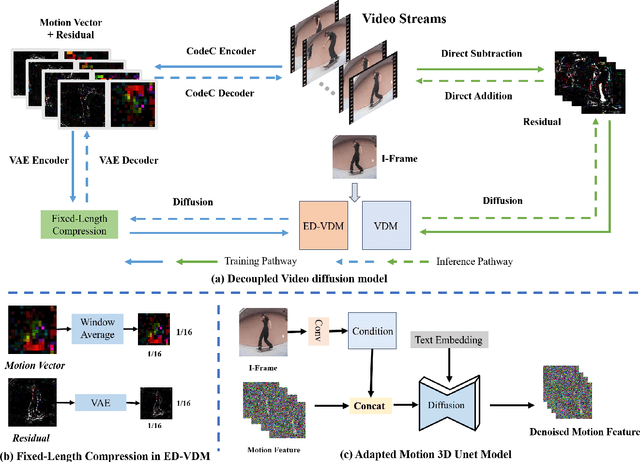

Abstract:The goal of conditional image-to-video (cI2V) generation is to create a believable new video by beginning with the condition, i.e., one image and text.The previous cI2V generation methods conventionally perform in RGB pixel space, with limitations in modeling motion consistency and visual continuity. Additionally, the efficiency of generating videos in pixel space is quite low.In this paper, we propose a novel approach to address these challenges by disentangling the target RGB pixels into two distinct components: spatial content and temporal motions. Specifically, we predict temporal motions which include motion vector and residual based on a 3D-UNet diffusion model. By explicitly modeling temporal motions and warping them to the starting image, we improve the temporal consistency of generated videos. This results in a reduction of spatial redundancy, emphasizing temporal details. Our proposed method achieves performance improvements by disentangling content and motion, all without introducing new structural complexities to the model. Extensive experiments on various datasets confirm our approach's superior performance over the majority of state-of-the-art methods in both effectiveness and efficiency.
Assessing and Enhancing Robustness of Deep Learning Models with Corruption Emulation in Digital Pathology
Oct 31, 2023



Abstract:Deep learning in digital pathology brings intelligence and automation as substantial enhancements to pathological analysis, the gold standard of clinical diagnosis. However, multiple steps from tissue preparation to slide imaging introduce various image corruptions, making it difficult for deep neural network (DNN) models to achieve stable diagnostic results for clinical use. In order to assess and further enhance the robustness of the models, we analyze the physical causes of the full-stack corruptions throughout the pathological life-cycle and propose an Omni-Corruption Emulation (OmniCE) method to reproduce 21 types of corruptions quantified with 5-level severity. We then construct three OmniCE-corrupted benchmark datasets at both patch level and slide level and assess the robustness of popular DNNs in classification and segmentation tasks. Further, we explore to use the OmniCE-corrupted datasets as augmentation data for training and experiments to verify that the generalization ability of the models has been significantly enhanced.
InstructCV: Instruction-Tuned Text-to-Image Diffusion Models as Vision Generalists
Sep 30, 2023



Abstract:Recent advances in generative diffusion models have enabled text-controlled synthesis of realistic and diverse images with impressive quality. Despite these remarkable advances, the application of text-to-image generative models in computer vision for standard visual recognition tasks remains limited. The current de facto approach for these tasks is to design model architectures and loss functions that are tailored to the task at hand. In this paper, we develop a unified language interface for computer vision tasks that abstracts away task-specific design choices and enables task execution by following natural language instructions. Our approach involves casting multiple computer vision tasks as text-to-image generation problems. Here, the text represents an instruction describing the task, and the resulting image is a visually-encoded task output. To train our model, we pool commonly-used computer vision datasets covering a range of tasks, including segmentation, object detection, depth estimation, and classification. We then use a large language model to paraphrase prompt templates that convey the specific tasks to be conducted on each image, and through this process, we create a multi-modal and multi-task training dataset comprising input and output images along with annotated instructions. Following the InstructPix2Pix architecture, we apply instruction-tuning to a text-to-image diffusion model using our constructed dataset, steering its functionality from a generative model to an instruction-guided multi-task vision learner. Experiments demonstrate that our model, dubbed InstructCV, performs competitively compared to other generalist and task-specific vision models. Moreover, it exhibits compelling generalization capabilities to unseen data, categories, and user instructions.
DiffuseIR:Diffusion Models For Isotropic Reconstruction of 3D Microscopic Images
Jun 21, 2023



Abstract:Three-dimensional microscopy is often limited by anisotropic spatial resolution, resulting in lower axial resolution than lateral resolution. Current State-of-The-Art (SoTA) isotropic reconstruction methods utilizing deep neural networks can achieve impressive super-resolution performance in fixed imaging settings. However, their generality in practical use is limited by degraded performance caused by artifacts and blurring when facing unseen anisotropic factors. To address these issues, we propose DiffuseIR, an unsupervised method for isotropic reconstruction based on diffusion models. First, we pre-train a diffusion model to learn the structural distribution of biological tissue from lateral microscopic images, resulting in generating naturally high-resolution images. Then we use low-axial-resolution microscopy images to condition the generation process of the diffusion model and generate high-axial-resolution reconstruction results. Since the diffusion model learns the universal structural distribution of biological tissues, which is independent of the axial resolution, DiffuseIR can reconstruct authentic images with unseen low-axial resolutions into a high-axial resolution without requiring re-training. The proposed DiffuseIR achieves SoTA performance in experiments on EM data and can even compete with supervised methods.
Chain of Thought Prompt Tuning in Vision Language Models
Apr 16, 2023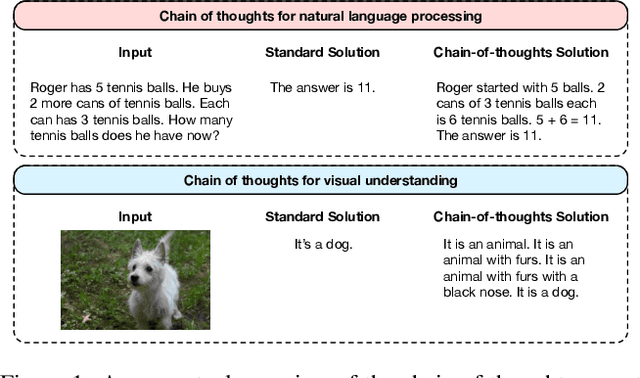
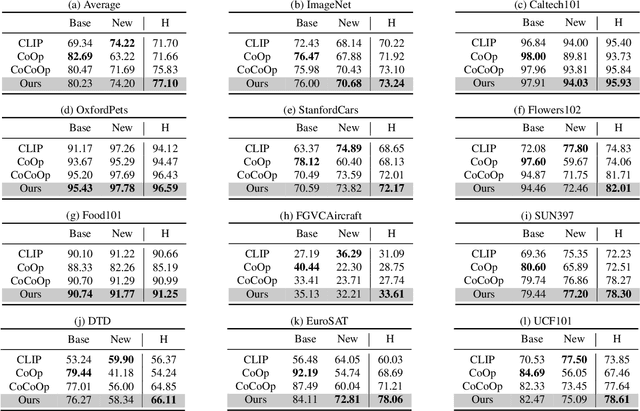
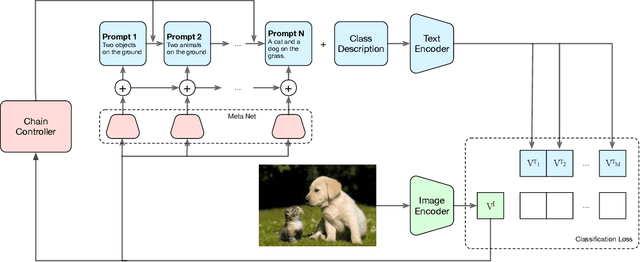
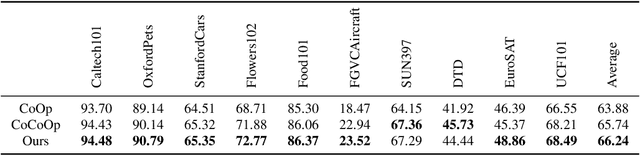
Abstract:Language-Image Pre-training has demonstrated promising results on zero-shot and few-shot downstream tasks by prompting visual models with natural language prompts. However, most recent studies only use a single prompt for tuning, neglecting the inherent step-to-step cognitive reasoning process that humans conduct in complex task settings, for example, when processing images from unfamiliar domains. Chain of Thought is a simple and effective approximation to human reasoning process and has been proven useful for natural language processing (NLP) tasks. Based on this cognitive intuition, we believe that conducting effective reasoning is also an important problem in visual tasks, and a chain of thought could be a solution to this problem. In this work, we propose a novel chain of thought prompt tuning for vision-language modeling. Extensive experiments show that our method not only generalizes better in image classification tasks, has greater transferability beyond a single dataset, and has stronger domain generalization performance, but also performs much better in imagetext retrieval and visual question answering, which require more reasoning capabilities. We are the first to successfully adapt chain-of-thought prompting that combines visual and textual embeddings. We will release our codes
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge