Yihang Lou
Decorate the Newcomers: Visual Domain Prompt for Continual Test Time Adaptation
Dec 08, 2022



Abstract:Continual Test-Time Adaptation (CTTA) aims to adapt the source model to continually changing unlabeled target domains without access to the source data. Existing methods mainly focus on model-based adaptation in a self-training manner, such as predicting pseudo labels for new domain datasets. Since pseudo labels are noisy and unreliable, these methods suffer from catastrophic forgetting and error accumulation when dealing with dynamic data distributions. Motivated by the prompt learning in NLP, in this paper, we propose to learn an image-level visual domain prompt for target domains while having the source model parameters frozen. During testing, the changing target datasets can be adapted to the source model by reformulating the input data with the learned visual prompts. Specifically, we devise two types of prompts, i.e., domains-specific prompts and domains-agnostic prompts, to extract current domain knowledge and maintain the domain-shared knowledge in the continual adaptation. Furthermore, we design a homeostasis-based prompt adaptation strategy to suppress domain-sensitive parameters in domain-invariant prompts to learn domain-shared knowledge more effectively. This transition from the model-dependent paradigm to the model-free one enables us to bypass the catastrophic forgetting and error accumulation problems. Experiments show that our proposed method achieves significant performance gains over state-of-the-art methods on four widely-used benchmarks, including CIFAR-10C, CIFAR-100C, ImageNet-C, and VLCS datasets.
Memory-Based Label-Text Tuning for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Jul 03, 2022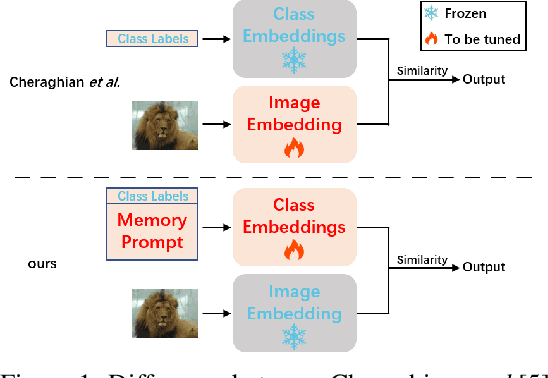
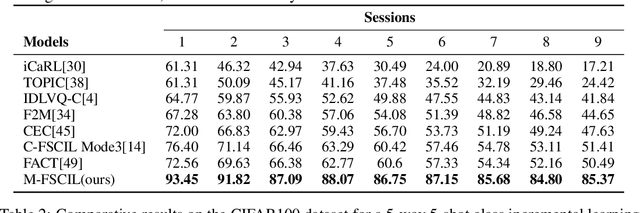
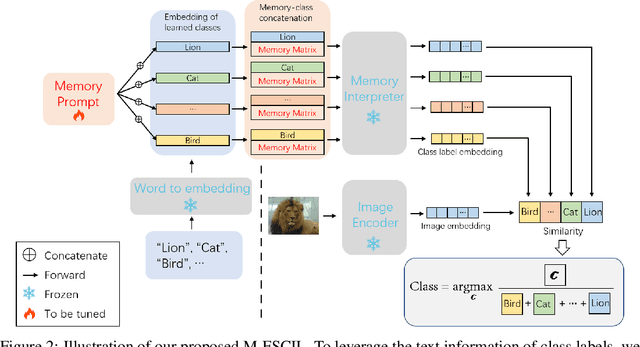
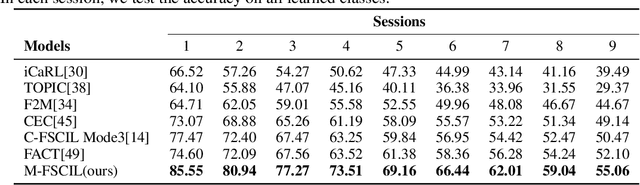
Abstract:Few-shot class-incremental learning(FSCIL) focuses on designing learning algorithms that can continually learn a sequence of new tasks from a few samples without forgetting old ones. The difficulties are that training on a sequence of limited data from new tasks leads to severe overfitting issues and causes the well-known catastrophic forgetting problem. Existing researches mainly utilize the image information, such as storing the image knowledge of previous tasks or limiting classifiers updating. However, they ignore analyzing the informative and less noisy text information of class labels. In this work, we propose leveraging the label-text information by adopting the memory prompt. The memory prompt can learn new data sequentially, and meanwhile store the previous knowledge. Furthermore, to optimize the memory prompt without undermining the stored knowledge, we propose a stimulation-based training strategy. It optimizes the memory prompt depending on the image embedding stimulation, which is the distribution of the image embedding elements. Experiments show that our proposed method outperforms all prior state-of-the-art approaches, significantly mitigating the catastrophic forgetting and overfitting problems.
Switchable Representation Learning Framework with Self-compatibility
Jun 16, 2022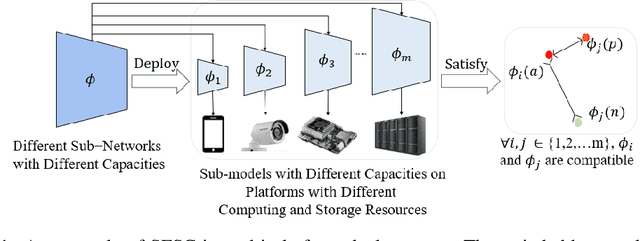
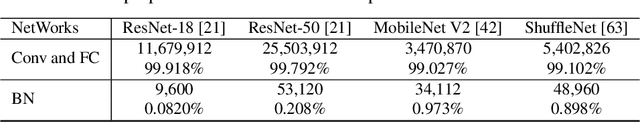
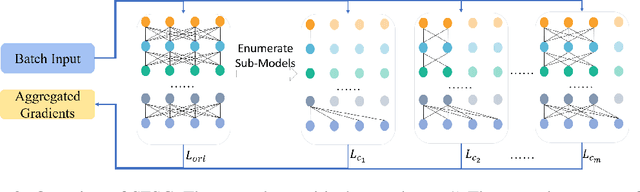
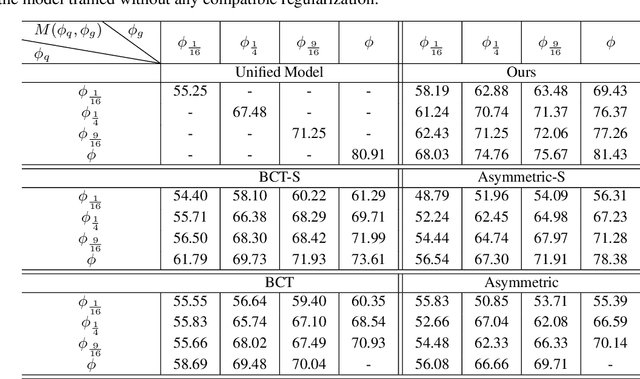
Abstract:Real-world visual search systems involve deployments on multiple platforms with different computing and storage resources. Deploying a unified model that suits the minimal-constrain platforms leads to limited accuracy. It is expected to deploy models with different capacities adapting to the resource constraints, which requires features extracted by these models to be aligned in the metric space. The method to achieve feature alignments is called "compatible learning". Existing research mainly focuses on the one-to-one compatible paradigm, which is limited in learning compatibility among multiple models. We propose a Switchable representation learning Framework with Self-Compatibility (SFSC). SFSC generates a series of compatible sub-models with different capacities through one training process. The optimization of sub-models faces gradients conflict, and we mitigate it from the perspective of the magnitude and direction. We adjust the priorities of sub-models dynamically through uncertainty estimation to co-optimize sub-models properly. Besides, the gradients with conflicting directions are projected to avoid mutual interference. SFSC achieves state-of-art performance on the evaluated dataset.
Neighborhood Consensus Contrastive Learning for Backward-Compatible Representation
Sep 09, 2021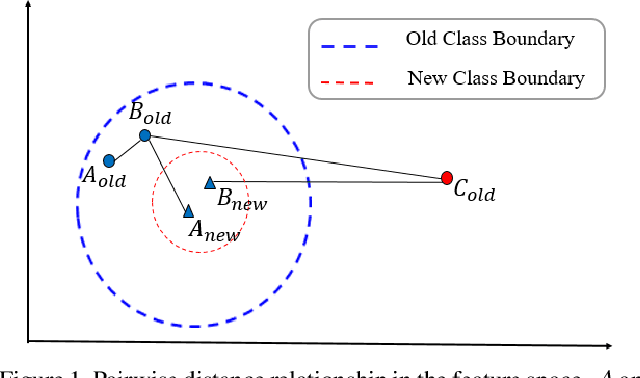
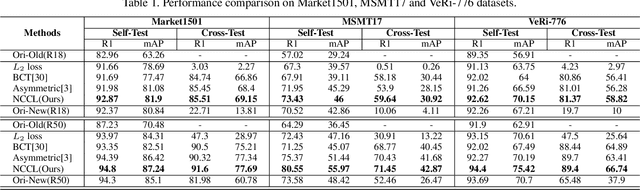
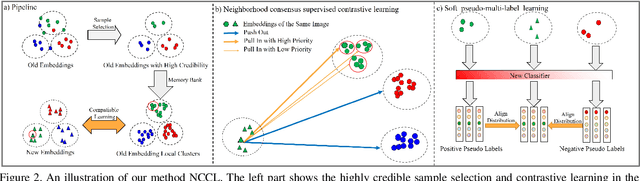
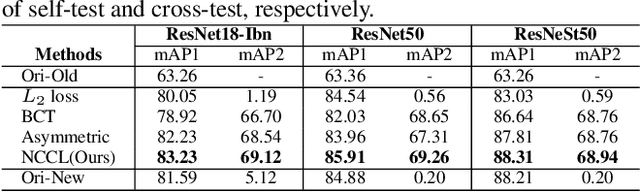
Abstract:In object re-identification (ReID), the development of deep learning techniques often involves model updates and deployment. It is unbearable to re-embedding and re-index with the system suspended when deploying new models. Therefore, backward-compatible representation is proposed to enable "new" features to be compared with "old" features directly, which means that the database is active when there are both "new" and "old" features in it. Thus we can scroll-refresh the database or even do nothing on the database to update. The existing backward-compatible methods either require a strong overlap between old and new training data or simply conduct constraints at the instance level. Thus they are difficult in handling complicated cluster structures and are limited in eliminating the impact of outliers in old embeddings, resulting in a risk of damaging the discriminative capability of new features. In this work, we propose a Neighborhood Consensus Contrastive Learning (NCCL) method. With no assumptions about the new training data, we estimate the sub-cluster structures of old embeddings. A new embedding is constrained with multiple old embeddings in both embedding space and discrimination space at the sub-class level. The effect of outliers diminished, as the multiple samples serve as "mean teachers". Besides, we also propose a scheme to filter the old embeddings with low credibility, further improving the compatibility robustness. Our method ensures backward compatibility without impairing the accuracy of the new model. And it can even improve the new model's accuracy in most scenarios.
Dual-Tuning: Joint Prototype Transfer and Structure Regularization for Compatible Feature Learning
Aug 06, 2021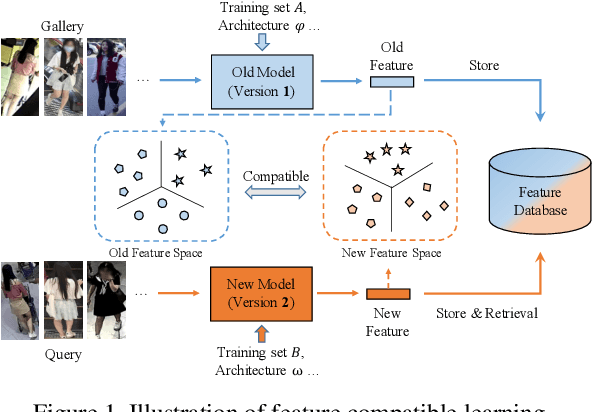
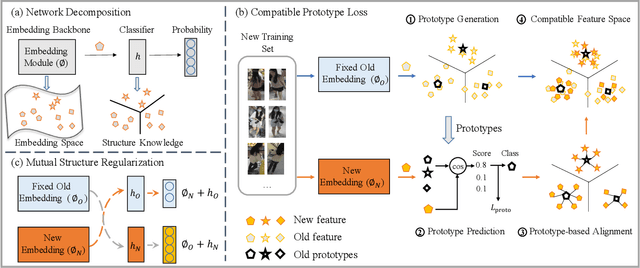
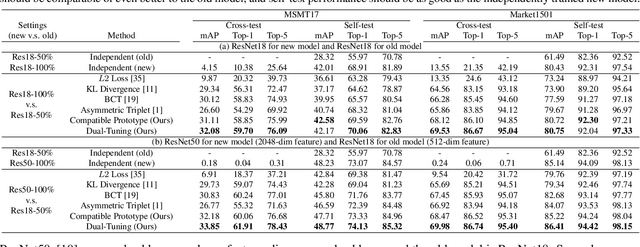
Abstract:Visual retrieval system faces frequent model update and deployment. It is a heavy workload to re-extract features of the whole database every time.Feature compatibility enables the learned new visual features to be directly compared with the old features stored in the database. In this way, when updating the deployed model, we can bypass the inflexible and time-consuming feature re-extraction process. However, the old feature space that needs to be compatible is not ideal and faces the distribution discrepancy problem with the new space caused by different supervision losses. In this work, we propose a global optimization Dual-Tuning method to obtain feature compatibility against different networks and losses. A feature-level prototype loss is proposed to explicitly align two types of embedding features, by transferring global prototype information. Furthermore, we design a component-level mutual structural regularization to implicitly optimize the feature intrinsic structure. Experimental results on million-scale datasets demonstrate that our Dual-Tuning is able to obtain feature compatibility without sacrificing performance. (Our code will be avaliable at https://github.com/yanbai1993/Dual-Tuning)
Towards Digital Retina in Smart Cities: A Model Generation, Utilization and Communication Paradigm
Jul 31, 2019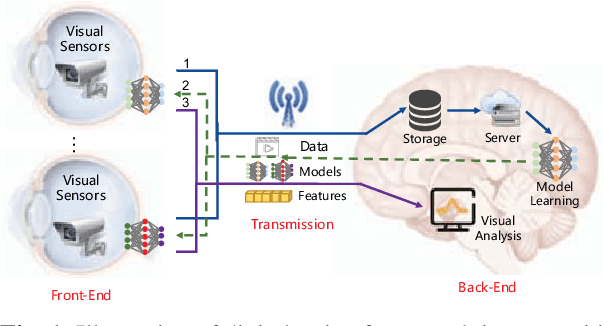
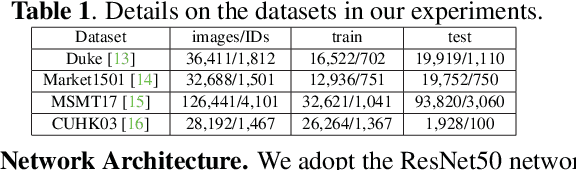
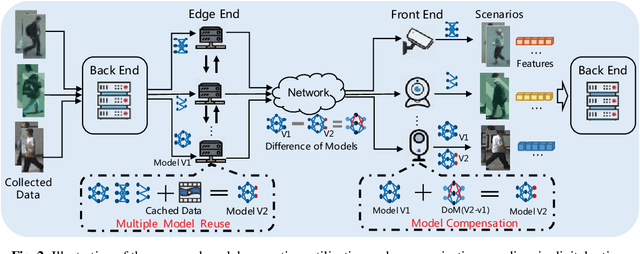
Abstract:The digital retina in smart cities is to select what the City Eye tells the City Brain, and convert the acquired visual data from front-end visual sensors to features in an intelligent sensing manner. By deploying deep learning and/or handcrafted models in front-end devices, the compact features can be extracted and subsequently delivered to back-end cloud for search and advanced analytics. In this context, we propose a model generation, utilization, and communication paradigm, aiming to address a set of unique challenges for better artificial intelligence services in smart cities. In particular, we present an integrated multiple deep learning models reuse and prediction strategy, which greatly increases the feasibility of the digital retina in processing and analyzing the large-scale visual data in smart cities. The promise of the proposed paradigm is demonstrated through a set of experiments.
AI Oriented Large-Scale Video Management for Smart City: Technologies, Standards and Beyond
Dec 05, 2017



Abstract:Deep learning has achieved substantial success in a series of tasks in computer vision. Intelligent video analysis, which can be broadly applied to video surveillance in various smart city applications, can also be driven by such powerful deep learning engines. To practically facilitate deep neural network models in the large-scale video analysis, there are still unprecedented challenges for the large-scale video data management. Deep feature coding, instead of video coding, provides a practical solution for handling the large-scale video surveillance data. To enable interoperability in the context of deep feature coding, standardization is urgent and important. However, due to the explosion of deep learning algorithms and the particularity of feature coding, there are numerous remaining problems in the standardization process. This paper envisions the future deep feature coding standard for the AI oriented large-scale video management, and discusses existing techniques, standards and possible solutions for these open problems.
Compact Descriptors for Video Analysis: the Emerging MPEG Standard
Apr 26, 2017



Abstract:This paper provides an overview of the on-going compact descriptors for video analysis standard (CDVA) from the ISO/IEC moving pictures experts group (MPEG). MPEG-CDVA targets at defining a standardized bitstream syntax to enable interoperability in the context of video analysis applications. During the developments of MPEGCDVA, a series of techniques aiming to reduce the descriptor size and improve the video representation ability have been proposed. This article describes the new standard that is being developed and reports the performance of these key technical contributions.
Improving Object Detection with Region Similarity Learning
Mar 01, 2017



Abstract:Object detection aims to identify instances of semantic objects of a certain class in images or videos. The success of state-of-the-art approaches is attributed to the significant progress of object proposal and convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Most promising detectors involve multi-task learning with an optimization objective of softmax loss and regression loss. The first is for multi-class categorization, while the latter is for improving localization accuracy. However, few of them attempt to further investigate the hardness of distinguishing different sorts of distracting background regions (i.e., negatives) from true object regions (i.e., positives). To improve the performance of classifying positive object regions vs. a variety of negative background regions, we propose to incorporate triplet embedding into learning objective. The triplet units are formed by assigning each negative region to a meaningful object class and establishing class- specific negatives, followed by triplets construction. Over the benchmark PASCAL VOC 2007, the proposed triplet em- bedding has improved the performance of well-known FastRCNN model with a mAP gain of 2.1%. In particular, the state-of-the-art approach OHEM can benefit from the triplet embedding and has achieved a mAP improvement of 1.2%.
Incorporating Intra-Class Variance to Fine-Grained Visual Recognition
Mar 01, 2017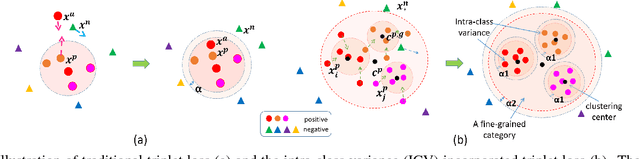
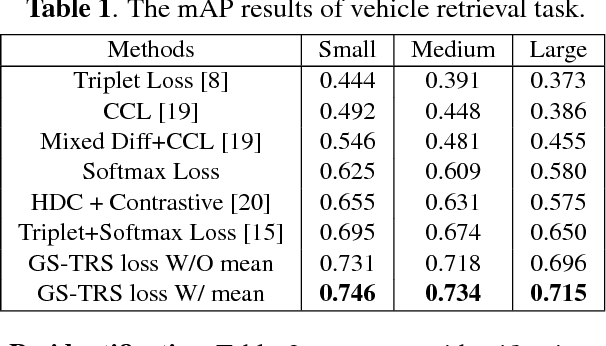

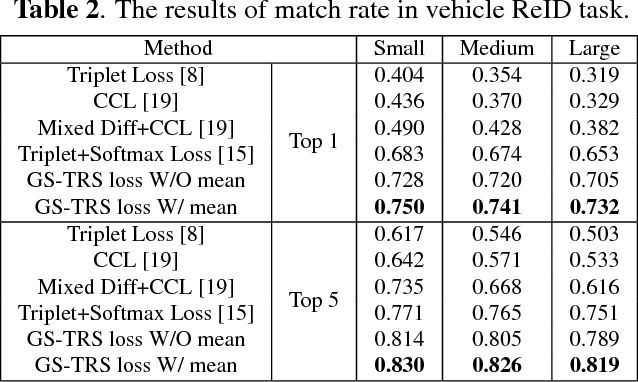
Abstract:Fine-grained visual recognition aims to capture discriminative characteristics amongst visually similar categories. The state-of-the-art research work has significantly improved the fine-grained recognition performance by deep metric learning using triplet network. However, the impact of intra-category variance on the performance of recognition and robust feature representation has not been well studied. In this paper, we propose to leverage intra-class variance in metric learning of triplet network to improve the performance of fine-grained recognition. Through partitioning training images within each category into a few groups, we form the triplet samples across different categories as well as different groups, which is called Group Sensitive TRiplet Sampling (GS-TRS). Accordingly, the triplet loss function is strengthened by incorporating intra-class variance with GS-TRS, which may contribute to the optimization objective of triplet network. Extensive experiments over benchmark datasets CompCar and VehicleID show that the proposed GS-TRS has significantly outperformed state-of-the-art approaches in both classification and retrieval tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge