Xing Wang
China Mobile Research Institute, Beijing, China
FlowAct-R1: Towards Interactive Humanoid Video Generation
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Interactive humanoid video generation aims to synthesize lifelike visual agents that can engage with humans through continuous and responsive video. Despite recent advances in video synthesis, existing methods often grapple with the trade-off between high-fidelity synthesis and real-time interaction requirements. In this paper, we propose FlowAct-R1, a framework specifically designed for real-time interactive humanoid video generation. Built upon a MMDiT architecture, FlowAct-R1 enables the streaming synthesis of video with arbitrary durations while maintaining low-latency responsiveness. We introduce a chunkwise diffusion forcing strategy, complemented by a novel self-forcing variant, to alleviate error accumulation and ensure long-term temporal consistency during continuous interaction. By leveraging efficient distillation and system-level optimizations, our framework achieves a stable 25fps at 480p resolution with a time-to-first-frame (TTFF) of only around 1.5 seconds. The proposed method provides holistic and fine-grained full-body control, enabling the agent to transition naturally between diverse behavioral states in interactive scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate that FlowAct-R1 achieves exceptional behavioral vividness and perceptual realism, while maintaining robust generalization across diverse character styles.
High Dimensional Data Decomposition for Anomaly Detection of Textured Images
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:In the realm of diverse high-dimensional data, images play a significant role across various processes of manufacturing systems where efficient image anomaly detection has emerged as a core technology of utmost importance. However, when applied to textured defect images, conventional anomaly detection methods have limitations including non-negligible misidentification, low robustness, and excessive reliance on large-scale and structured datasets. This paper proposes a texture basis integrated smooth decomposition (TBSD) approach, which is targeted at efficient anomaly detection in textured images with smooth backgrounds and sparse anomalies. Mathematical formulation of quasi-periodicity and its theoretical properties are investigated for image texture estimation. TBSD method consists of two principal processes: the first process learns the texture basis functions to effectively extract quasi-periodic texture patterns; the subsequent anomaly detection process utilizes that texture basis as prior knowledge to prevent texture misidentification and capture potential anomalies with high accuracy.The proposed method surpasses benchmarks with less misidentification, smaller training dataset requirement, and superior anomaly detection performance on both simulation and real-world datasets.
InfinityStar: Unified Spacetime AutoRegressive Modeling for Visual Generation
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:We introduce InfinityStar, a unified spacetime autoregressive framework for high-resolution image and dynamic video synthesis. Building on the recent success of autoregressive modeling in both vision and language, our purely discrete approach jointly captures spatial and temporal dependencies within a single architecture. This unified design naturally supports a variety of generation tasks such as text-to-image, text-to-video, image-to-video, and long interactive video synthesis via straightforward temporal autoregression. Extensive experiments demonstrate that InfinityStar scores 83.74 on VBench, outperforming all autoregressive models by large margins, even surpassing some diffusion competitors like HunyuanVideo. Without extra optimizations, our model generates a 5s, 720p video approximately 10x faster than leading diffusion-based methods. To our knowledge, InfinityStar is the first discrete autoregressive video generator capable of producing industrial level 720p videos. We release all code and models to foster further research in efficient, high-quality video generation.
Adversarial Distribution Matching for Diffusion Distillation Towards Efficient Image and Video Synthesis
Jul 24, 2025
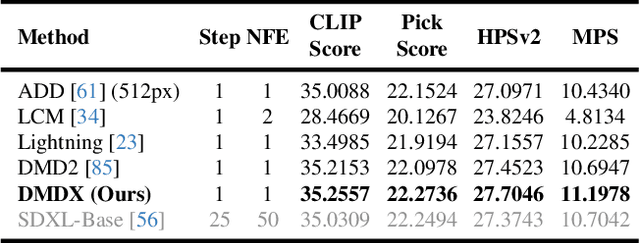
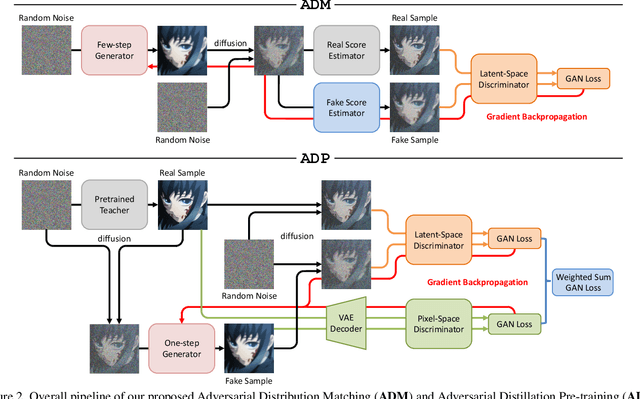
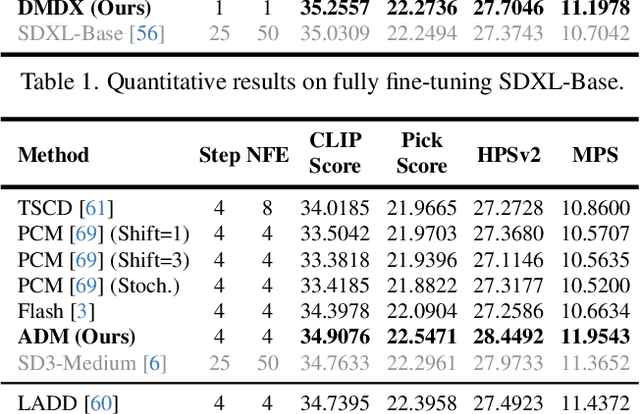
Abstract:Distribution Matching Distillation (DMD) is a promising score distillation technique that compresses pre-trained teacher diffusion models into efficient one-step or multi-step student generators. Nevertheless, its reliance on the reverse Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence minimization potentially induces mode collapse (or mode-seeking) in certain applications. To circumvent this inherent drawback, we propose Adversarial Distribution Matching (ADM), a novel framework that leverages diffusion-based discriminators to align the latent predictions between real and fake score estimators for score distillation in an adversarial manner. In the context of extremely challenging one-step distillation, we further improve the pre-trained generator by adversarial distillation with hybrid discriminators in both latent and pixel spaces. Different from the mean squared error used in DMD2 pre-training, our method incorporates the distributional loss on ODE pairs collected from the teacher model, and thus providing a better initialization for score distillation fine-tuning in the next stage. By combining the adversarial distillation pre-training with ADM fine-tuning into a unified pipeline termed DMDX, our proposed method achieves superior one-step performance on SDXL compared to DMD2 while consuming less GPU time. Additional experiments that apply multi-step ADM distillation on SD3-Medium, SD3.5-Large, and CogVideoX set a new benchmark towards efficient image and video synthesis.
Improving U-Net Confidence on TEM Image Data with L2-Regularization, Transfer Learning, and Deep Fine-Tuning
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:With ever-increasing data volumes, it is essential to develop automated approaches for identifying nanoscale defects in transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images. However, compared to features in conventional photographs, nanoscale defects in TEM images exhibit far greater variation due to the complex contrast mechanisms and intricate defect structures. These challenges often result in much less labeled data and higher rates of annotation errors, posing significant obstacles to improving machine learning model performance for TEM image analysis. To address these limitations, we examined transfer learning by leveraging large, pre-trained models used for natural images. We demonstrated that by using the pre-trained encoder and L2-regularization, semantically complex features are ignored in favor of simpler, more reliable cues, substantially improving the model performance. However, this improvement cannot be captured by conventional evaluation metrics such as F1-score, which can be skewed by human annotation errors treated as ground truth. Instead, we introduced novel evaluation metrics that are independent of the annotation accuracy. Using grain boundary detection in UO2 TEM images as a case study, we found that our approach led to a 57% improvement in defect detection rate, which is a robust and holistic measure of model performance on the TEM dataset used in this work. Finally, we showed that model self-confidence is only achieved through transfer learning and fine-tuning of very deep layers.
Training-free Diffusion Acceleration with Bottleneck Sampling
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in visual content generation but remain challenging to deploy due to their high computational cost during inference. This computational burden primarily arises from the quadratic complexity of self-attention with respect to image or video resolution. While existing acceleration methods often compromise output quality or necessitate costly retraining, we observe that most diffusion models are pre-trained at lower resolutions, presenting an opportunity to exploit these low-resolution priors for more efficient inference without degrading performance. In this work, we introduce Bottleneck Sampling, a training-free framework that leverages low-resolution priors to reduce computational overhead while preserving output fidelity. Bottleneck Sampling follows a high-low-high denoising workflow: it performs high-resolution denoising in the initial and final stages while operating at lower resolutions in intermediate steps. To mitigate aliasing and blurring artifacts, we further refine the resolution transition points and adaptively shift the denoising timesteps at each stage. We evaluate Bottleneck Sampling on both image and video generation tasks, where extensive experiments demonstrate that it accelerates inference by up to 3$\times$ for image generation and 2.5$\times$ for video generation, all while maintaining output quality comparable to the standard full-resolution sampling process across multiple evaluation metrics.
The Morphology-Control Trade-Off: Insights into Soft Robotic Efficiency
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Soft robotics holds transformative potential for enabling adaptive and adaptable systems in dynamic environments. However, the interplay between morphological and control complexities and their collective impact on task performance remains poorly understood. Therefore, in this study, we investigate these trade-offs across tasks of differing difficulty levels using four well-used morphological complexity metrics and control complexity measured by FLOPs. We investigate how these factors jointly influence task performance by utilizing the evolutionary robot experiments. Results show that optimal performance depends on the alignment between morphology and control: simpler morphologies and lightweight controllers suffice for easier tasks, while harder tasks demand higher complexities in both dimensions. In addition, a clear trade-off between morphological and control complexities that achieve the same task performance can be observed. Moreover, we also propose a sensitivity analysis to expose the task-specific contributions of individual morphological metrics. Our study establishes a framework for investigating the relationships between morphology, control, and task performance, advancing the development of task-specific robotic designs that balance computational efficiency with adaptability. This study contributes to the practical application of soft robotics in real-world scenarios by providing actionable insights.
RaSA: Rank-Sharing Low-Rank Adaptation
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) has been prominently employed for parameter-efficient fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs). However, the limited expressive capacity of LoRA, stemming from the low-rank constraint, has been recognized as a bottleneck, particularly in rigorous tasks like code generation and mathematical reasoning. To address this limitation, we introduce Rank-Sharing Low-Rank Adaptation (RaSA), an innovative extension that enhances the expressive capacity of LoRA by leveraging partial rank sharing across layers. By forming a shared rank pool and applying layer-specific weighting, RaSA effectively increases the number of ranks without augmenting parameter overhead. Our theoretically grounded and empirically validated approach demonstrates that RaSA not only maintains the core advantages of LoRA but also significantly boosts performance in challenging code and math tasks. Code, data and scripts are available at: https://github.com/zwhe99/RaSA.
RayFlow: Instance-Aware Diffusion Acceleration via Adaptive Flow Trajectories
Mar 10, 2025



Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success across various domains. However, their slow generation speed remains a critical challenge. Existing acceleration methods, while aiming to reduce steps, often compromise sample quality, controllability, or introduce training complexities. Therefore, we propose RayFlow, a novel diffusion framework that addresses these limitations. Unlike previous methods, RayFlow guides each sample along a unique path towards an instance-specific target distribution. This method minimizes sampling steps while preserving generation diversity and stability. Furthermore, we introduce Time Sampler, an importance sampling technique to enhance training efficiency by focusing on crucial timesteps. Extensive experiments demonstrate RayFlow's superiority in generating high-quality images with improved speed, control, and training efficiency compared to existing acceleration techniques.
Goku: Flow Based Video Generative Foundation Models
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:This paper introduces Goku, a state-of-the-art family of joint image-and-video generation models leveraging rectified flow Transformers to achieve industry-leading performance. We detail the foundational elements enabling high-quality visual generation, including the data curation pipeline, model architecture design, flow formulation, and advanced infrastructure for efficient and robust large-scale training. The Goku models demonstrate superior performance in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations, setting new benchmarks across major tasks. Specifically, Goku achieves 0.76 on GenEval and 83.65 on DPG-Bench for text-to-image generation, and 84.85 on VBench for text-to-video tasks. We believe that this work provides valuable insights and practical advancements for the research community in developing joint image-and-video generation models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge