Jingzhou Liu
From Solving to Verifying: A Unified Objective for Robust Reasoning in LLMs
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:The reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) have been significantly improved through reinforcement learning (RL). Nevertheless, LLMs still struggle to consistently verify their own reasoning traces. This raises the research question of how to enhance the self-verification ability of LLMs and whether such an ability can further improve reasoning performance. In this work, we propose GRPO-Verif, an algorithm that jointly optimizes solution generation and self-verification within a unified loss function, with an adjustable hyperparameter controlling the weight of the verification signal. Experimental results demonstrate that our method enhances self-verification capability while maintaining comparable performance in reasoning.
Unveiling User Satisfaction and Creator Productivity Trade-Offs in Recommendation Platforms
Oct 31, 2024



Abstract:On User-Generated Content (UGC) platforms, recommendation algorithms significantly impact creators' motivation to produce content as they compete for algorithmically allocated user traffic. This phenomenon subtly shapes the volume and diversity of the content pool, which is crucial for the platform's sustainability. In this work, we demonstrate, both theoretically and empirically, that a purely relevance-driven policy with low exploration strength boosts short-term user satisfaction but undermines the long-term richness of the content pool. In contrast, a more aggressive exploration policy may slightly compromise user satisfaction but promote higher content creation volume. Our findings reveal a fundamental trade-off between immediate user satisfaction and overall content production on UGC platforms. Building on this finding, we propose an efficient optimization method to identify the optimal exploration strength, balancing user and creator engagement. Our model can serve as a pre-deployment audit tool for recommendation algorithms on UGC platforms, helping to align their immediate objectives with sustainable, long-term goals.
Synthetica: Large Scale Synthetic Data for Robot Perception
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:Vision-based object detectors are a crucial basis for robotics applications as they provide valuable information about object localisation in the environment. These need to ensure high reliability in different lighting conditions, occlusions, and visual artifacts, all while running in real-time. Collecting and annotating real-world data for these networks is prohibitively time consuming and costly, especially for custom assets, such as industrial objects, making it untenable for generalization to in-the-wild scenarios. To this end, we present Synthetica, a method for large-scale synthetic data generation for training robust state estimators. This paper focuses on the task of object detection, an important problem which can serve as the front-end for most state estimation problems, such as pose estimation. Leveraging data from a photorealistic ray-tracing renderer, we scale up data generation, generating 2.7 million images, to train highly accurate real-time detection transformers. We present a collection of rendering randomization and training-time data augmentation techniques conducive to robust sim-to-real performance for vision tasks. We demonstrate state-of-the-art performance on the task of object detection while having detectors that run at 50-100Hz which is 9 times faster than the prior SOTA. We further demonstrate the usefulness of our training methodology for robotics applications by showcasing a pipeline for use in the real world with custom objects for which there do not exist prior datasets. Our work highlights the importance of scaling synthetic data generation for robust sim-to-real transfer while achieving the fastest real-time inference speeds. Videos and supplementary information can be found at this URL: https://sites.google.com/view/synthetica-vision.
ORBIT-Surgical: An Open-Simulation Framework for Learning Surgical Augmented Dexterity
Apr 24, 2024



Abstract:Physics-based simulations have accelerated progress in robot learning for driving, manipulation, and locomotion. Yet, a fast, accurate, and robust surgical simulation environment remains a challenge. In this paper, we present ORBIT-Surgical, a physics-based surgical robot simulation framework with photorealistic rendering in NVIDIA Omniverse. We provide 14 benchmark surgical tasks for the da Vinci Research Kit (dVRK) and Smart Tissue Autonomous Robot (STAR) which represent common subtasks in surgical training. ORBIT-Surgical leverages GPU parallelization to train reinforcement learning and imitation learning algorithms to facilitate study of robot learning to augment human surgical skills. ORBIT-Surgical also facilitates realistic synthetic data generation for active perception tasks. We demonstrate ORBIT-Surgical sim-to-real transfer of learned policies onto a physical dVRK robot. Project website: orbit-surgical.github.io
Geometry Matching for Multi-Embodiment Grasping
Dec 06, 2023



Abstract:Many existing learning-based grasping approaches concentrate on a single embodiment, provide limited generalization to higher DoF end-effectors and cannot capture a diverse set of grasp modes. We tackle the problem of grasping using multiple embodiments by learning rich geometric representations for both objects and end-effectors using Graph Neural Networks. Our novel method - GeoMatch - applies supervised learning on grasping data from multiple embodiments, learning end-to-end contact point likelihood maps as well as conditional autoregressive predictions of grasps keypoint-by-keypoint. We compare our method against baselines that support multiple embodiments. Our approach performs better across three end-effectors, while also producing diverse grasps. Examples, including real robot demos, can be found at geo-match.github.io.
HandyPriors: Physically Consistent Perception of Hand-Object Interactions with Differentiable Priors
Dec 03, 2023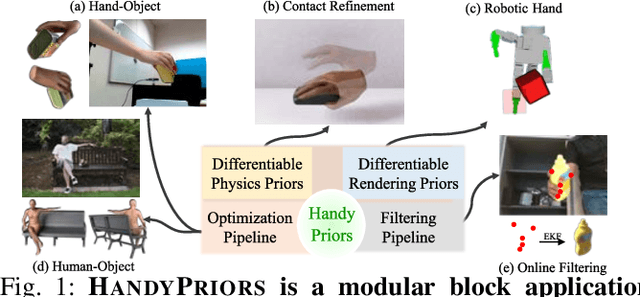
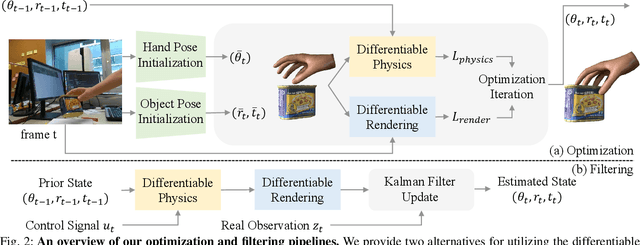
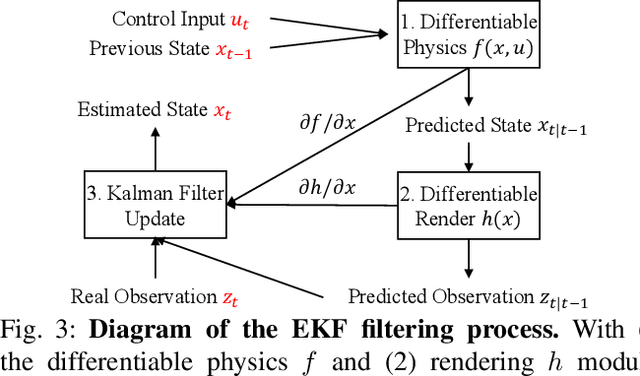
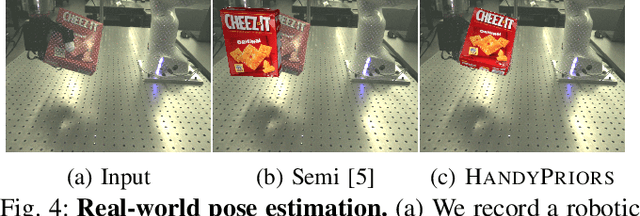
Abstract:Various heuristic objectives for modeling hand-object interaction have been proposed in past work. However, due to the lack of a cohesive framework, these objectives often possess a narrow scope of applicability and are limited by their efficiency or accuracy. In this paper, we propose HandyPriors, a unified and general pipeline for pose estimation in human-object interaction scenes by leveraging recent advances in differentiable physics and rendering. Our approach employs rendering priors to align with input images and segmentation masks along with physics priors to mitigate penetration and relative-sliding across frames. Furthermore, we present two alternatives for hand and object pose estimation. The optimization-based pose estimation achieves higher accuracy, while the filtering-based tracking, which utilizes the differentiable priors as dynamics and observation models, executes faster. We demonstrate that HandyPriors attains comparable or superior results in the pose estimation task, and that the differentiable physics module can predict contact information for pose refinement. We also show that our approach generalizes to perception tasks, including robotic hand manipulation and human-object pose estimation in the wild.
On the Equivalence of Graph Convolution and Mixup
Sep 29, 2023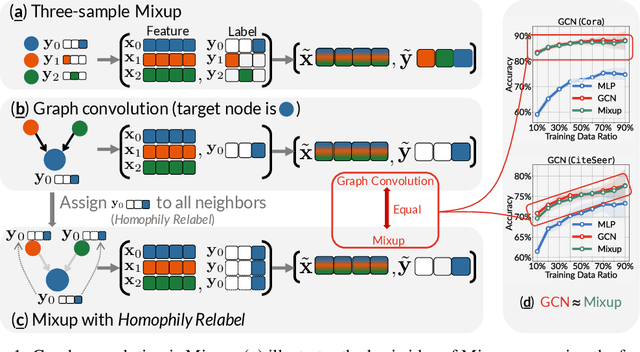
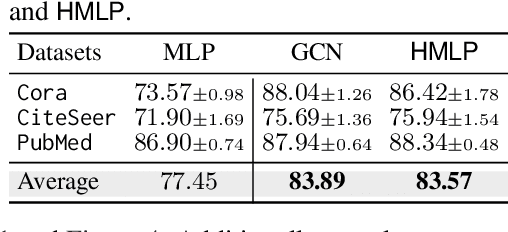
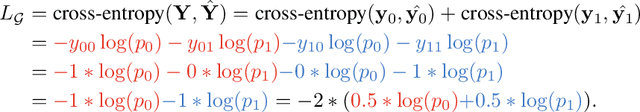
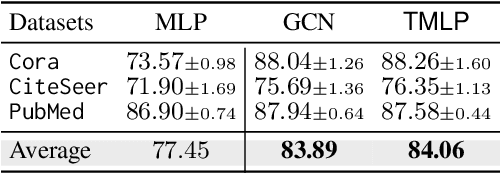
Abstract:This paper investigates the relationship between graph convolution and Mixup techniques. Graph convolution in a graph neural network involves aggregating features from neighboring samples to learn representative features for a specific node or sample. On the other hand, Mixup is a data augmentation technique that generates new examples by averaging features and one-hot labels from multiple samples. One commonality between these techniques is their utilization of information from multiple samples to derive feature representation. This study aims to explore whether a connection exists between these two approaches. Our investigation reveals that, under two mild conditions, graph convolution can be viewed as a specialized form of Mixup that is applied during both the training and testing phases. The two conditions are: 1) \textit{Homophily Relabel} - assigning the target node's label to all its neighbors, and 2) \textit{Test-Time Mixup} - Mixup the feature during the test time. We establish this equivalence mathematically by demonstrating that graph convolution networks (GCN) and simplified graph convolution (SGC) can be expressed as a form of Mixup. We also empirically verify the equivalence by training an MLP using the two conditions to achieve comparable performance.
Fast-Grasp'D: Dexterous Multi-finger Grasp Generation Through Differentiable Simulation
Jun 13, 2023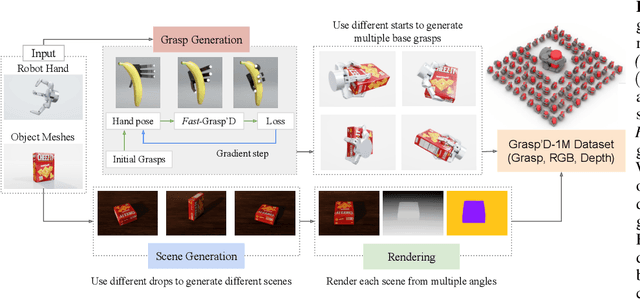
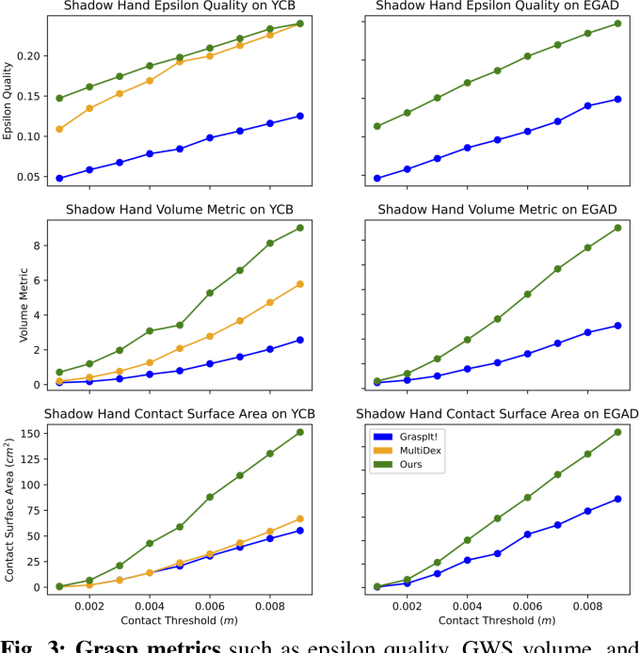
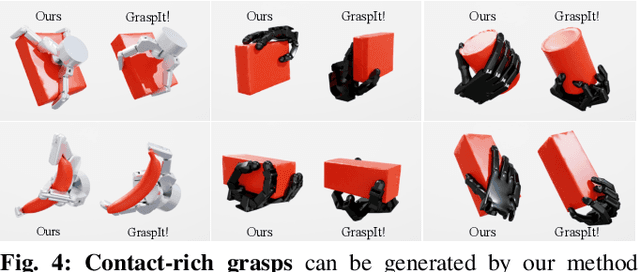

Abstract:Multi-finger grasping relies on high quality training data, which is hard to obtain: human data is hard to transfer and synthetic data relies on simplifying assumptions that reduce grasp quality. By making grasp simulation differentiable, and contact dynamics amenable to gradient-based optimization, we accelerate the search for high-quality grasps with fewer limiting assumptions. We present Grasp'D-1M: a large-scale dataset for multi-finger robotic grasping, synthesized with Fast- Grasp'D, a novel differentiable grasping simulator. Grasp'D- 1M contains one million training examples for three robotic hands (three, four and five-fingered), each with multimodal visual inputs (RGB+depth+segmentation, available in mono and stereo). Grasp synthesis with Fast-Grasp'D is 10x faster than GraspIt! and 20x faster than the prior Grasp'D differentiable simulator. Generated grasps are more stable and contact-rich than GraspIt! grasps, regardless of the distance threshold used for contact generation. We validate the usefulness of our dataset by retraining an existing vision-based grasping pipeline on Grasp'D-1M, and showing a dramatic increase in model performance, predicting grasps with 30% more contact, a 33% higher epsilon metric, and 35% lower simulated displacement. Additional details at https://dexgrasp.github.io.
ORBIT: A Unified Simulation Framework for Interactive Robot Learning Environments
Jan 10, 2023



Abstract:We present ORBIT, a unified and modular framework for robot learning powered by NVIDIA Isaac Sim. It offers a modular design to easily and efficiently create robotic environments with photo-realistic scenes and fast and accurate rigid and deformable body simulation. With ORBIT, we provide a suite of benchmark tasks of varying difficulty -- from single-stage cabinet opening and cloth folding to multi-stage tasks such as room reorganization. To support working with diverse observations and action spaces, we include fixed-arm and mobile manipulators with different physically-based sensors and motion generators. ORBIT allows training reinforcement learning policies and collecting large demonstration datasets from hand-crafted or expert solutions in a matter of minutes by leveraging GPU-based parallelization. In summary, we offer an open-sourced framework that readily comes with 16 robotic platforms, 4 sensor modalities, 10 motion generators, more than 20 benchmark tasks, and wrappers to 4 learning libraries. With this framework, we aim to support various research areas, including representation learning, reinforcement learning, imitation learning, and task and motion planning. We hope it helps establish interdisciplinary collaborations in these communities, and its modularity makes it easily extensible for more tasks and applications in the future. For videos, documentation, and code: https://isaac-orbit.github.io/.
DeXtreme: Transfer of Agile In-hand Manipulation from Simulation to Reality
Oct 25, 2022Abstract:Recent work has demonstrated the ability of deep reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms to learn complex robotic behaviours in simulation, including in the domain of multi-fingered manipulation. However, such models can be challenging to transfer to the real world due to the gap between simulation and reality. In this paper, we present our techniques to train a) a policy that can perform robust dexterous manipulation on an anthropomorphic robot hand and b) a robust pose estimator suitable for providing reliable real-time information on the state of the object being manipulated. Our policies are trained to adapt to a wide range of conditions in simulation. Consequently, our vision-based policies significantly outperform the best vision policies in the literature on the same reorientation task and are competitive with policies that are given privileged state information via motion capture systems. Our work reaffirms the possibilities of sim-to-real transfer for dexterous manipulation in diverse kinds of hardware and simulator setups, and in our case, with the Allegro Hand and Isaac Gym GPU-based simulation. Furthermore, it opens up possibilities for researchers to achieve such results with commonly-available, affordable robot hands and cameras. Videos of the resulting policy and supplementary information, including experiments and demos, can be found at \url{https://dextreme.org/}
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge