Florian Shkurti
University of Toronto
MATTERIX: toward a digital twin for robotics-assisted chemistry laboratory automation
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Accelerated materials discovery is critical for addressing global challenges. However, developing new laboratory workflows relies heavily on real-world experimental trials, and this can hinder scalability because of the need for numerous physical make-and-test iterations. Here we present MATTERIX, a multiscale, graphics processing unit-accelerated robotic simulation framework designed to create high-fidelity digital twins of chemistry laboratories, thus accelerating workflow development. This multiscale digital twin simulates robotic physical manipulation, powder and liquid dynamics, device functionalities, heat transfer and basic chemical reaction kinetics. This is enabled by integrating realistic physics simulation and photorealistic rendering with a modular graphics processing unit-accelerated semantics engine, which models logical states and continuous behaviors to simulate chemistry workflows across different levels of abstraction. MATTERIX streamlines the creation of digital twin environments through open-source asset libraries and interfaces, while enabling flexible workflow design via hierarchical plan definition and a modular skill library that incorporates learning-based methods. Our approach demonstrates sim-to-real transfer in robotic chemistry setups, reducing reliance on costly real-world experiments and enabling the testing of hypothetical automated workflows in silico. The project website is available at https://accelerationconsortium.github.io/Matterix/ .
Informing Acquisition Functions via Foundation Models for Molecular Discovery
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Bayesian Optimization (BO) is a key methodology for accelerating molecular discovery by estimating the mapping from molecules to their properties while seeking the optimal candidate. Typically, BO iteratively updates a probabilistic surrogate model of this mapping and optimizes acquisition functions derived from the model to guide molecule selection. However, its performance is limited in low-data regimes with insufficient prior knowledge and vast candidate spaces. Large language models (LLMs) and chemistry foundation models offer rich priors to enhance BO, but high-dimensional features, costly in-context learning, and the computational burden of deep Bayesian surrogates hinder their full utilization. To address these challenges, we propose a likelihood-free BO method that bypasses explicit surrogate modeling and directly leverages priors from general LLMs and chemistry-specific foundation models to inform acquisition functions. Our method also learns a tree-structured partition of the molecular search space with local acquisition functions, enabling efficient candidate selection via Monte Carlo Tree Search. By further incorporating coarse-grained LLM-based clustering, it substantially improves scalability to large candidate sets by restricting acquisition function evaluations to clusters with statistically higher property values. We show through extensive experiments and ablations that the proposed method substantially improves scalability, robustness, and sample efficiency in LLM-guided BO for molecular discovery.
Scalable Policy Evaluation with Video World Models
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Training generalist policies for robotic manipulation has shown great promise, as they enable language-conditioned, multi-task behaviors across diverse scenarios. However, evaluating these policies remains difficult because real-world testing is expensive, time-consuming, and labor-intensive. It also requires frequent environment resets and carries safety risks when deploying unproven policies on physical robots. Manually creating and populating simulation environments with assets for robotic manipulation has not addressed these issues, primarily due to the significant engineering effort required and the often substantial sim-to-real gap, both in terms of physics and rendering. In this paper, we explore the use of action-conditional video generation models as a scalable way to learn world models for policy evaluation. We demonstrate how to incorporate action conditioning into existing pre-trained video generation models. This allows leveraging internet-scale in-the-wild online videos during the pre-training stage, and alleviates the need for a large dataset of paired video-action data, which is expensive to collect for robotic manipulation. Our paper examines the effect of dataset diversity, pre-trained weight and common failure cases for the proposed evaluation pipeline. Our experiments demonstrate that, across various metrics, including policy ranking and the correlation between actual policy values and predicted policy values, these models offer a promising approach for evaluating policies without requiring real-world interactions.
SAFE: Multitask Failure Detection for Vision-Language-Action Models
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:While vision-language-action models (VLAs) have shown promising robotic behaviors across a diverse set of manipulation tasks, they achieve limited success rates when deployed on novel tasks out-of-the-box. To allow these policies to safely interact with their environments, we need a failure detector that gives a timely alert such that the robot can stop, backtrack, or ask for help. However, existing failure detectors are trained and tested only on one or a few specific tasks, while VLAs require the detector to generalize and detect failures also in unseen tasks and novel environments. In this paper, we introduce the multitask failure detection problem and propose SAFE, a failure detector for generalist robot policies such as VLAs. We analyze the VLA feature space and find that VLAs have sufficient high-level knowledge about task success and failure, which is generic across different tasks. Based on this insight, we design SAFE to learn from VLA internal features and predict a single scalar indicating the likelihood of task failure. SAFE is trained on both successful and failed rollouts, and is evaluated on unseen tasks. SAFE is compatible with different policy architectures. We test it on OpenVLA, $\pi_0$, and $\pi_0$-FAST in both simulated and real-world environments extensively. We compare SAFE with diverse baselines and show that SAFE achieves state-of-the-art failure detection performance and the best trade-off between accuracy and detection time using conformal prediction. More qualitative results can be found at https://vla-safe.github.io/.
Deploying SICNav in the Field: Safe and Interactive Crowd Navigation using MPC and Bilevel Optimization
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Safe and efficient navigation in crowded environments remains a critical challenge for robots that provide a variety of service tasks such as food delivery or autonomous wheelchair mobility. Classical robot crowd navigation methods decouple human motion prediction from robot motion planning, which neglects the closed-loop interactions between humans and robots. This lack of a model for human reactions to the robot plan (e.g. moving out of the way) can cause the robot to get stuck. Our proposed Safe and Interactive Crowd Navigation (SICNav) method is a bilevel Model Predictive Control (MPC) framework that combines prediction and planning into one optimization problem, explicitly modeling interactions among agents. In this paper, we present a systems overview of the crowd navigation platform we use to deploy SICNav in previously unseen indoor and outdoor environments. We provide a preliminary analysis of the system's operation over the course of nearly 7 km of autonomous navigation over two hours in both indoor and outdoor environments.
STITCH-OPE: Trajectory Stitching with Guided Diffusion for Off-Policy Evaluation
May 27, 2025Abstract:Off-policy evaluation (OPE) estimates the performance of a target policy using offline data collected from a behavior policy, and is crucial in domains such as robotics or healthcare where direct interaction with the environment is costly or unsafe. Existing OPE methods are ineffective for high-dimensional, long-horizon problems, due to exponential blow-ups in variance from importance weighting or compounding errors from learned dynamics models. To address these challenges, we propose STITCH-OPE, a model-based generative framework that leverages denoising diffusion for long-horizon OPE in high-dimensional state and action spaces. Starting with a diffusion model pre-trained on the behavior data, STITCH-OPE generates synthetic trajectories from the target policy by guiding the denoising process using the score function of the target policy. STITCH-OPE proposes two technical innovations that make it advantageous for OPE: (1) prevents over-regularization by subtracting the score of the behavior policy during guidance, and (2) generates long-horizon trajectories by stitching partial trajectories together end-to-end. We provide a theoretical guarantee that under mild assumptions, these modifications result in an exponential reduction in variance versus long-horizon trajectory diffusion. Experiments on the D4RL and OpenAI Gym benchmarks show substantial improvement in mean squared error, correlation, and regret metrics compared to state-of-the-art OPE methods.
What Do You Need for Diverse Trajectory Stitching in Diffusion Planning?
May 23, 2025Abstract:In planning, stitching is an ability of algorithms to piece together sub-trajectories of data they are trained on to generate new and diverse behaviours. While stitching is historically a strength of offline reinforcement learning, recent generative behavioural cloning (BC) methods have also shown proficiency at stitching. However, the main factors behind this are poorly understood, hindering the development of new algorithms that can reliably stitch. Focusing on diffusion planners trained via BC, we find two properties are needed to compose: \emph{positional equivariance} and \emph{local receptiveness}. We use these two properties to explain architecture, data, and inference choices in existing generative BC methods based on diffusion planning, including replanning frequency, data augmentation, and data scaling. Experimental comparisions show that (1) while locality is more important than positional equivariance in creating a diffusion planner capable of composition, both are crucial (2) enabling these properties through relatively simple architecture choices can be competitive with more computationally expensive methods such as replanning or scaling data, and (3) simple inpainting-based guidance can guide architecturally compositional models to enable generalization in goal-conditioned settings.
RoboCulture: A Robotics Platform for Automated Biological Experimentation
May 20, 2025Abstract:Automating biological experimentation remains challenging due to the need for millimeter-scale precision, long and multi-step experiments, and the dynamic nature of living systems. Current liquid handlers only partially automate workflows, requiring human intervention for plate loading, tip replacement, and calibration. Industrial solutions offer more automation but are costly and lack the flexibility needed in research settings. Meanwhile, research in autonomous robotics has yet to bridge the gap for long-duration, failure-sensitive biological experiments. We introduce RoboCulture, a cost-effective and flexible platform that uses a general-purpose robotic manipulator to automate key biological tasks. RoboCulture performs liquid handling, interacts with lab equipment, and leverages computer vision for real-time decisions using optical density-based growth monitoring. We demonstrate a fully autonomous 15-hour yeast culture experiment where RoboCulture uses vision and force feedback and a modular behavior tree framework to robustly execute, monitor, and manage experiments.
Search-TTA: A Multimodal Test-Time Adaptation Framework for Visual Search in the Wild
May 16, 2025
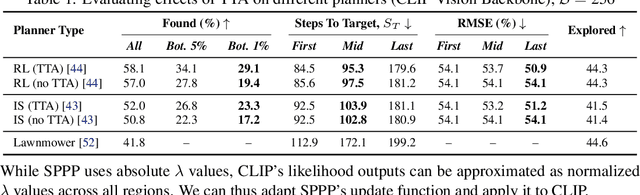
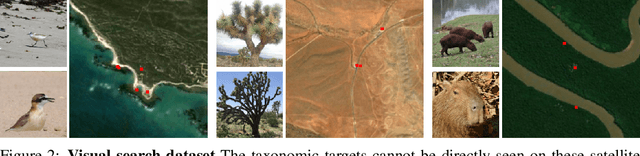
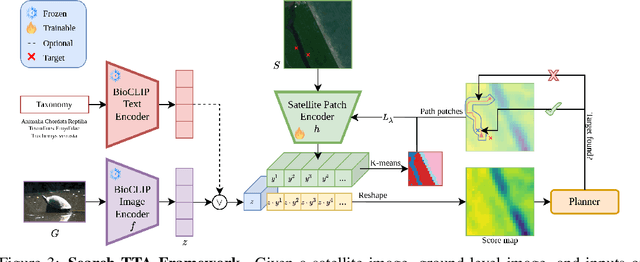
Abstract:To perform autonomous visual search for environmental monitoring, a robot may leverage satellite imagery as a prior map. This can help inform coarse, high-level search and exploration strategies, even when such images lack sufficient resolution to allow fine-grained, explicit visual recognition of targets. However, there are some challenges to overcome with using satellite images to direct visual search. For one, targets that are unseen in satellite images are underrepresented (compared to ground images) in most existing datasets, and thus vision models trained on these datasets fail to reason effectively based on indirect visual cues. Furthermore, approaches which leverage large Vision Language Models (VLMs) for generalization may yield inaccurate outputs due to hallucination, leading to inefficient search. To address these challenges, we introduce Search-TTA, a multimodal test-time adaptation framework that can accept text and/or image input. First, we pretrain a remote sensing image encoder to align with CLIP's visual encoder to output probability distributions of target presence used for visual search. Second, our framework dynamically refines CLIP's predictions during search using a test-time adaptation mechanism. Through a feedback loop inspired by Spatial Poisson Point Processes, gradient updates (weighted by uncertainty) are used to correct (potentially inaccurate) predictions and improve search performance. To validate Search-TTA's performance, we curate a visual search dataset based on internet-scale ecological data. We find that Search-TTA improves planner performance by up to 9.7%, particularly in cases with poor initial CLIP predictions. It also achieves comparable performance to state-of-the-art VLMs. Finally, we deploy Search-TTA on a real UAV via hardware-in-the-loop testing, by simulating its operation within a large-scale simulation that provides onboard sensing.
RaSCL: Radar to Satellite Crossview Localization
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:GNSS is unreliable, inaccurate, and insufficient in many real-time autonomous field applications. In this work, we present a GNSS-free global localization solution that contains a method of registering imaging radar on the ground with overhead RGB imagery, with joint optimization of relative poses from odometry and global poses from our overhead registration. Previous works have used various combinations of ground sensors and overhead imagery, and different feature extraction and matching methods. These include various handcrafted and deep-learning-based methods for extracting features from overhead imagery. Our work presents insights on extracting essential features from RGB overhead images for effective global localization against overhead imagery using only ground radar and a single georeferenced initial guess. We motivate our method by evaluating it on datasets in diverse geographic conditions and robotic platforms, including on an Unmanned Surface Vessel (USV) as well as urban and suburban driving datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge