Erwin Coumans
MaskedManipulator: Versatile Whole-Body Control for Loco-Manipulation
May 25, 2025Abstract:Humans interact with their world while leveraging precise full-body control to achieve versatile goals. This versatility allows them to solve long-horizon, underspecified problems, such as placing a cup in a sink, by seamlessly sequencing actions like approaching the cup, grasping, transporting it, and finally placing it in the sink. Such goal-driven control can enable new procedural tools for animation systems, enabling users to define partial objectives while the system naturally ``fills in'' the intermediate motions. However, while current methods for whole-body dexterous manipulation in physics-based animation achieve success in specific interaction tasks, they typically employ control paradigms (e.g., detailed kinematic motion tracking, continuous object trajectory following, or direct VR teleoperation) that offer limited versatility for high-level goal specification across the entire coupled human-object system. To bridge this gap, we present MaskedManipulator, a unified and generative policy developed through a two-stage learning approach. First, our system trains a tracking controller to physically reconstruct complex human-object interactions from large-scale human mocap datasets. This tracking controller is then distilled into MaskedManipulator, which provides users with intuitive control over both the character's body and the manipulated object. As a result, MaskedManipulator enables users to specify complex loco-manipulation tasks through intuitive high-level objectives (e.g., target object poses, key character stances), and MaskedManipulator then synthesizes the necessary full-body actions for a physically simulated humanoid to achieve these goals, paving the way for more interactive and life-like virtual characters.
Achieving Human Level Competitive Robot Table Tennis
Aug 07, 2024



Abstract:Achieving human-level speed and performance on real world tasks is a north star for the robotics research community. This work takes a step towards that goal and presents the first learned robot agent that reaches amateur human-level performance in competitive table tennis. Table tennis is a physically demanding sport which requires human players to undergo years of training to achieve an advanced level of proficiency. In this paper, we contribute (1) a hierarchical and modular policy architecture consisting of (i) low level controllers with their detailed skill descriptors which model the agent's capabilities and help to bridge the sim-to-real gap and (ii) a high level controller that chooses the low level skills, (2) techniques for enabling zero-shot sim-to-real including an iterative approach to defining the task distribution that is grounded in the real-world and defines an automatic curriculum, and (3) real time adaptation to unseen opponents. Policy performance was assessed through 29 robot vs. human matches of which the robot won 45% (13/29). All humans were unseen players and their skill level varied from beginner to tournament level. Whilst the robot lost all matches vs. the most advanced players it won 100% matches vs. beginners and 55% matches vs. intermediate players, demonstrating solidly amateur human-level performance. Videos of the matches can be viewed at https://sites.google.com/view/competitive-robot-table-tennis
Robotic Table Tennis: A Case Study into a High Speed Learning System
Sep 06, 2023



Abstract:We present a deep-dive into a real-world robotic learning system that, in previous work, was shown to be capable of hundreds of table tennis rallies with a human and has the ability to precisely return the ball to desired targets. This system puts together a highly optimized perception subsystem, a high-speed low-latency robot controller, a simulation paradigm that can prevent damage in the real world and also train policies for zero-shot transfer, and automated real world environment resets that enable autonomous training and evaluation on physical robots. We complement a complete system description, including numerous design decisions that are typically not widely disseminated, with a collection of studies that clarify the importance of mitigating various sources of latency, accounting for training and deployment distribution shifts, robustness of the perception system, sensitivity to policy hyper-parameters, and choice of action space. A video demonstrating the components of the system and details of experimental results can be found at https://youtu.be/uFcnWjB42I0.
Barkour: Benchmarking Animal-level Agility with Quadruped Robots
May 24, 2023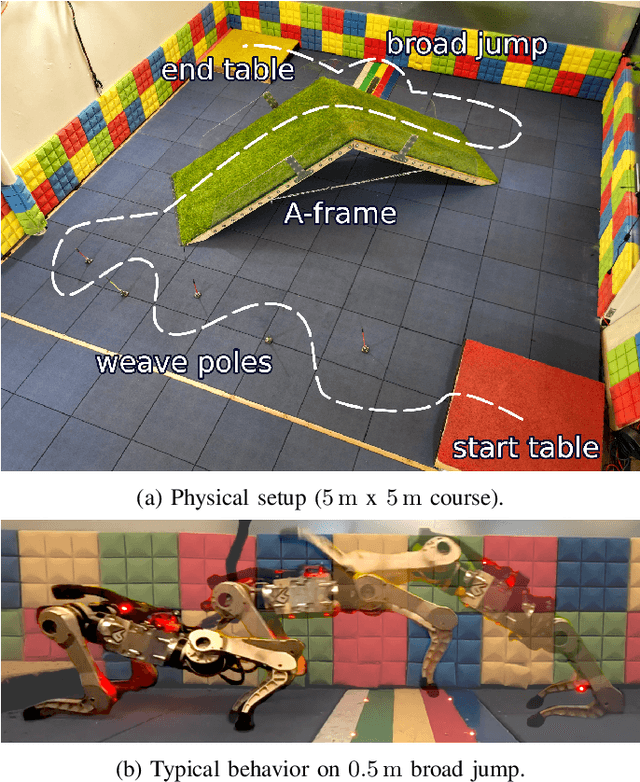
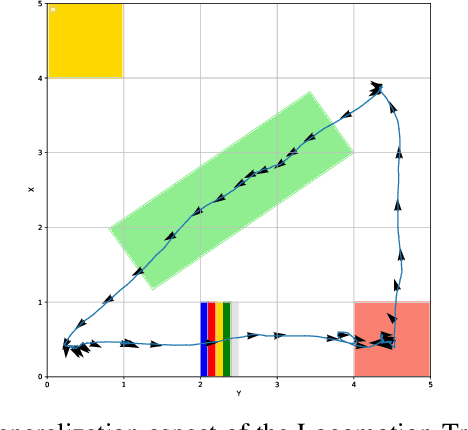
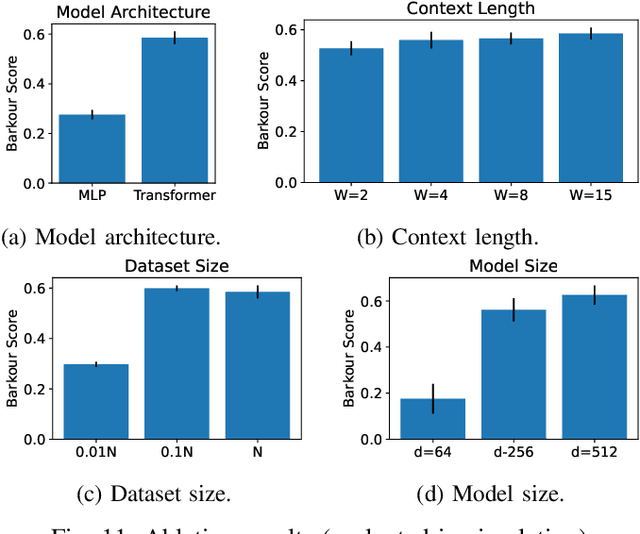

Abstract:Animals have evolved various agile locomotion strategies, such as sprinting, leaping, and jumping. There is a growing interest in developing legged robots that move like their biological counterparts and show various agile skills to navigate complex environments quickly. Despite the interest, the field lacks systematic benchmarks to measure the performance of control policies and hardware in agility. We introduce the Barkour benchmark, an obstacle course to quantify agility for legged robots. Inspired by dog agility competitions, it consists of diverse obstacles and a time based scoring mechanism. This encourages researchers to develop controllers that not only move fast, but do so in a controllable and versatile way. To set strong baselines, we present two methods for tackling the benchmark. In the first approach, we train specialist locomotion skills using on-policy reinforcement learning methods and combine them with a high-level navigation controller. In the second approach, we distill the specialist skills into a Transformer-based generalist locomotion policy, named Locomotion-Transformer, that can handle various terrains and adjust the robot's gait based on the perceived environment and robot states. Using a custom-built quadruped robot, we demonstrate that our method can complete the course at half the speed of a dog. We hope that our work represents a step towards creating controllers that enable robots to reach animal-level agility.
Differentiable Dynamics for Articulated 3d Human Motion Reconstruction
May 24, 2022
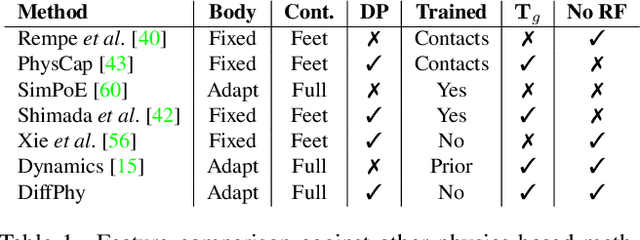
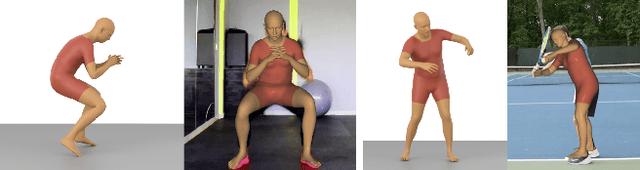
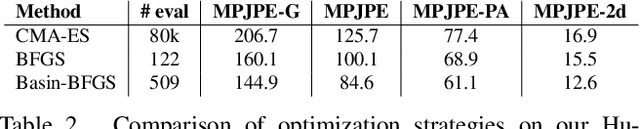
Abstract:We introduce DiffPhy, a differentiable physics-based model for articulated 3d human motion reconstruction from video. Applications of physics-based reasoning in human motion analysis have so far been limited, both by the complexity of constructing adequate physical models of articulated human motion, and by the formidable challenges of performing stable and efficient inference with physics in the loop. We jointly address such modeling and inference challenges by proposing an approach that combines a physically plausible body representation with anatomical joint limits, a differentiable physics simulator, and optimization techniques that ensure good performance and robustness to suboptimal local optima. In contrast to several recent methods, our approach readily supports full-body contact including interactions with objects in the scene. Most importantly, our model connects end-to-end with images, thus supporting direct gradient-based physics optimization by means of image-based loss functions. We validate the model by demonstrating that it can accurately reconstruct physically plausible 3d human motion from monocular video, both on public benchmarks with available 3d ground-truth, and on videos from the internet.
Inferring Articulated Rigid Body Dynamics from RGBD Video
Mar 20, 2022
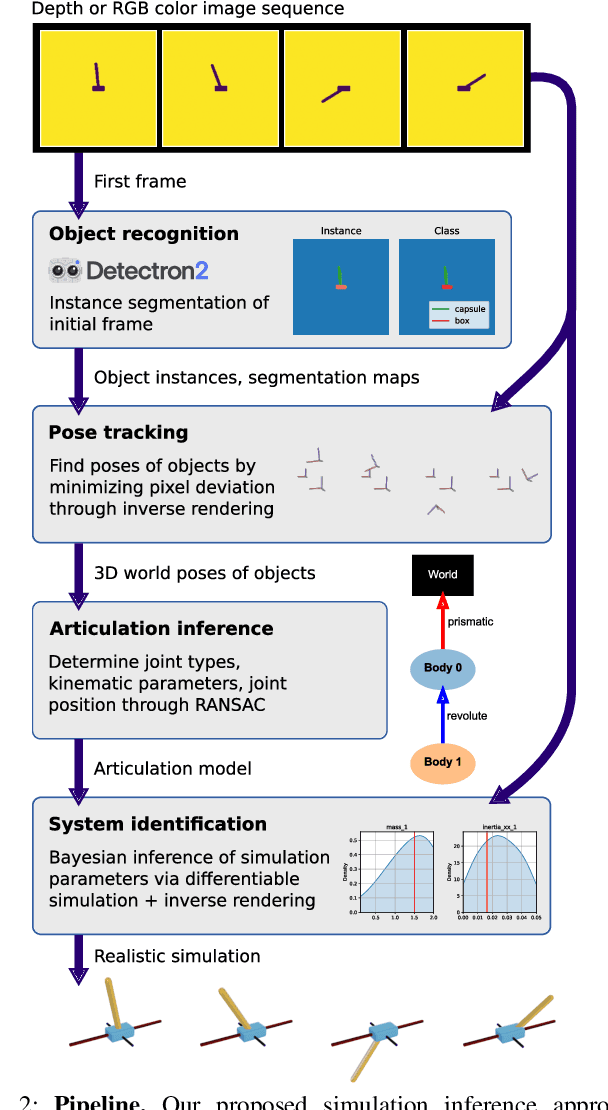
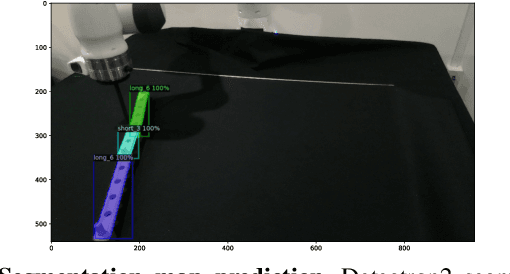
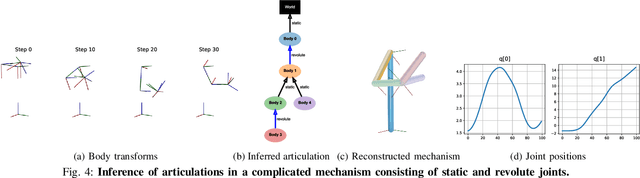
Abstract:Being able to reproduce physical phenomena ranging from light interaction to contact mechanics, simulators are becoming increasingly useful in more and more application domains where real-world interaction or labeled data are difficult to obtain. Despite recent progress, significant human effort is needed to configure simulators to accurately reproduce real-world behavior. We introduce a pipeline that combines inverse rendering with differentiable simulation to create digital twins of real-world articulated mechanisms from depth or RGB videos. Our approach automatically discovers joint types and estimates their kinematic parameters, while the dynamic properties of the overall mechanism are tuned to attain physically accurate simulations. Control policies optimized in our derived simulation transfer successfully back to the original system, as we demonstrate on a simulated system. Further, our approach accurately reconstructs the kinematic tree of an articulated mechanism being manipulated by a robot, and highly nonlinear dynamics of a real-world coupled pendulum mechanism. Website: https://eric-heiden.github.io/video2sim
Braxlines: Fast and Interactive Toolkit for RL-driven Behavior Engineering beyond Reward Maximization
Oct 10, 2021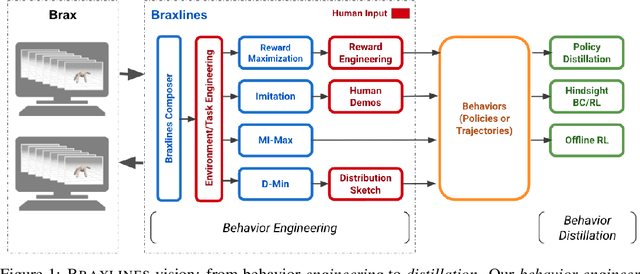
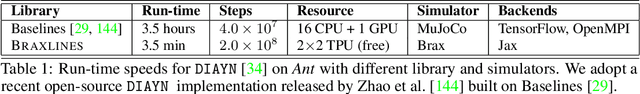

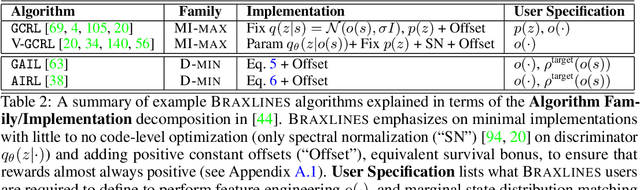
Abstract:The goal of continuous control is to synthesize desired behaviors. In reinforcement learning (RL)-driven approaches, this is often accomplished through careful task reward engineering for efficient exploration and running an off-the-shelf RL algorithm. While reward maximization is at the core of RL, reward engineering is not the only -- sometimes nor the easiest -- way for specifying complex behaviors. In this paper, we introduce \braxlines, a toolkit for fast and interactive RL-driven behavior generation beyond simple reward maximization that includes Composer, a programmatic API for generating continuous control environments, and set of stable and well-tested baselines for two families of algorithms -- mutual information maximization (MiMax) and divergence minimization (DMin) -- supporting unsupervised skill learning and distribution sketching as other modes of behavior specification. In addition, we discuss how to standardize metrics for evaluating these algorithms, which can no longer rely on simple reward maximization. Our implementations build on a hardware-accelerated Brax simulator in Jax with minimal modifications, enabling behavior synthesis within minutes of training. We hope Braxlines can serve as an interactive toolkit for rapid creation and testing of environments and behaviors, empowering explosions of future benchmark designs and new modes of RL-driven behavior generation and their algorithmic research.
Multi-Task Learning with Sequence-Conditioned Transporter Networks
Sep 15, 2021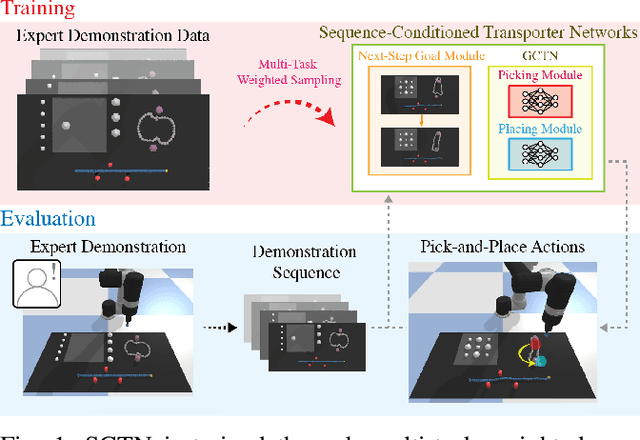
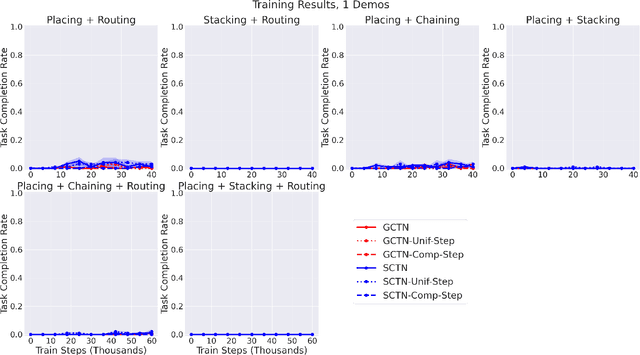
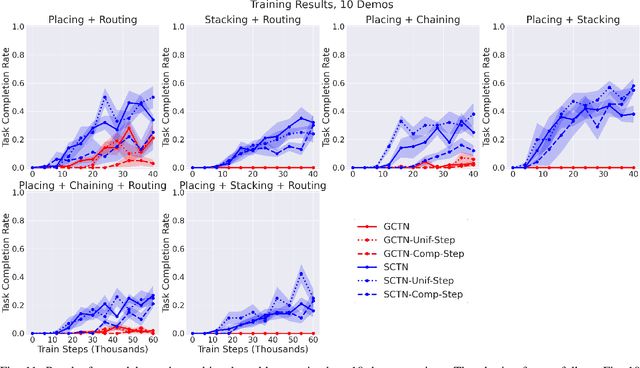
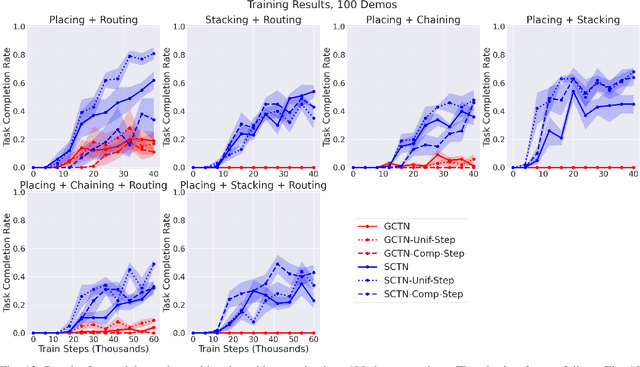
Abstract:Enabling robots to solve multiple manipulation tasks has a wide range of industrial applications. While learning-based approaches enjoy flexibility and generalizability, scaling these approaches to solve such compositional tasks remains a challenge. In this work, we aim to solve multi-task learning through the lens of sequence-conditioning and weighted sampling. First, we propose a new suite of benchmark specifically aimed at compositional tasks, MultiRavens, which allows defining custom task combinations through task modules that are inspired by industrial tasks and exemplify the difficulties in vision-based learning and planning methods. Second, we propose a vision-based end-to-end system architecture, Sequence-Conditioned Transporter Networks, which augments Goal-Conditioned Transporter Networks with sequence-conditioning and weighted sampling and can efficiently learn to solve multi-task long horizon problems. Our analysis suggests that not only the new framework significantly improves pick-and-place performance on novel 10 multi-task benchmark problems, but also the multi-task learning with weighted sampling can vastly improve learning and agent performances on individual tasks.
Fast and Efficient Locomotion via Learned Gait Transitions
Apr 09, 2021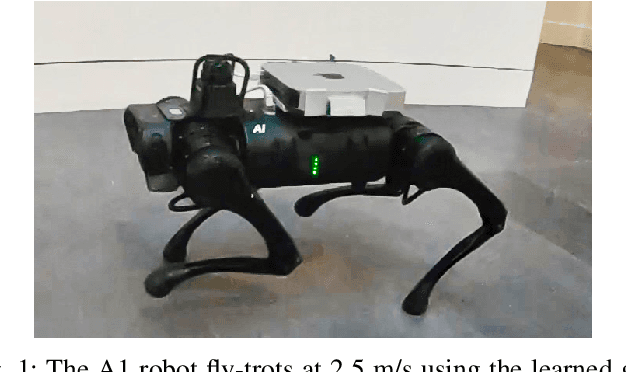
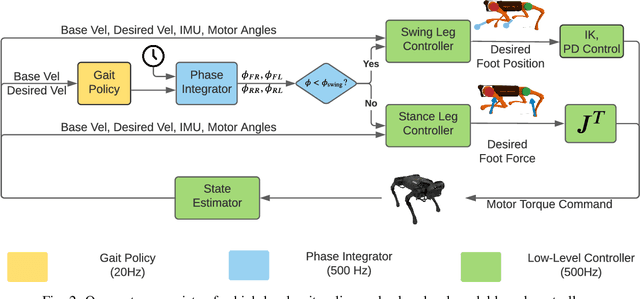
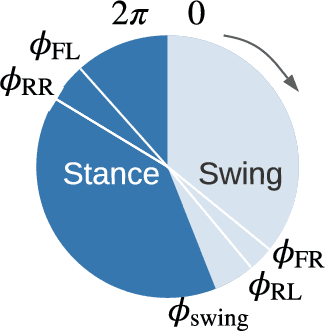
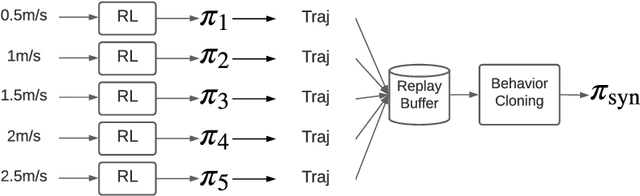
Abstract:We focus on the problem of developing efficient controllers for quadrupedal robots. Animals can actively switch gaits at different speeds to lower their energy consumption. In this paper, we devise a hierarchical learning framework, in which distinctive locomotion gaits and natural gait transitions emerge automatically with a simple reward of energy minimization. We use reinforcement learning to train a high-level gait policy that specifies the contact schedules of each foot, while the low-level Model Predictive Controller (MPC) optimizes the motor torques so that the robot can walk at a desired velocity using that gait pattern. We test our learning framework on a quadruped robot and demonstrate automatic gait transitions, from walking to trotting and to fly-trotting, as the robot increases its speed up to 2.5m/s (5 body lengths/s). We show that the learned hierarchical controller consumes much less energy across a wide range of locomotion speed than baseline controllers.
Learning to Rearrange Deformable Cables, Fabrics, and Bags with Goal-Conditioned Transporter Networks
Dec 18, 2020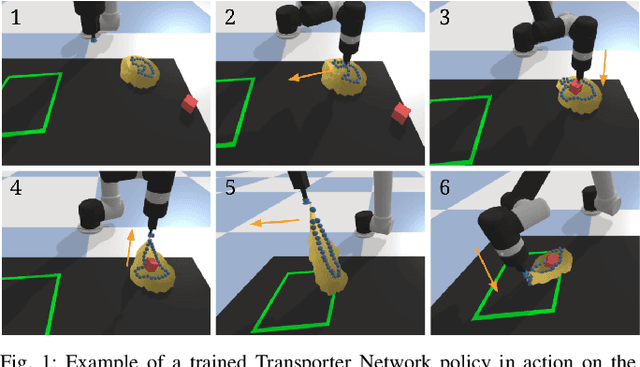

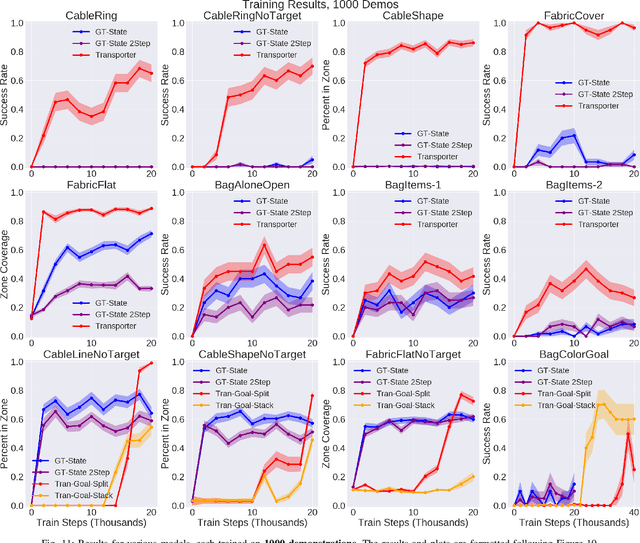
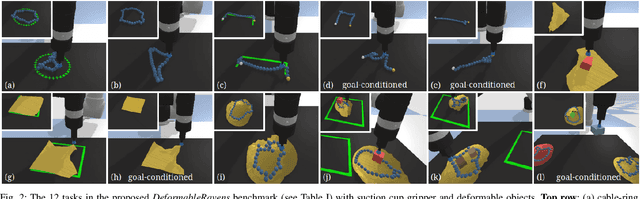
Abstract:Rearranging and manipulating deformable objects such as cables, fabrics, and bags is a long-standing challenge in robotic manipulation. The complex dynamics and high-dimensional configuration spaces of deformables, compared to rigid objects, make manipulation difficult not only for multi-step planning, but even for goal specification. Goals cannot be as easily specified as rigid object poses, and may involve complex relative spatial relations such as "place the item inside the bag". In this work, we develop a suite of simulated benchmarks with 1D, 2D, and 3D deformable structures, including tasks that involve image-based goal-conditioning and multi-step deformable manipulation. We propose embedding goal-conditioning into Transporter Networks, a recently proposed model architecture for learning robotic manipulation that rearranges deep features to infer displacements that can represent pick and place actions. We demonstrate that goal-conditioned Transporter Networks enable agents to manipulate deformable structures into flexibly specified configurations without test-time visual anchors for target locations. We also significantly extend prior results using Transporter Networks for manipulating deformable objects by testing on tasks with 2D and 3D deformables. Supplementary material is available at https://berkeleyautomation.github.io/bags/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge