Leila Takayama
Hoku Labs
Achieving Human Level Competitive Robot Table Tennis
Aug 07, 2024



Abstract:Achieving human-level speed and performance on real world tasks is a north star for the robotics research community. This work takes a step towards that goal and presents the first learned robot agent that reaches amateur human-level performance in competitive table tennis. Table tennis is a physically demanding sport which requires human players to undergo years of training to achieve an advanced level of proficiency. In this paper, we contribute (1) a hierarchical and modular policy architecture consisting of (i) low level controllers with their detailed skill descriptors which model the agent's capabilities and help to bridge the sim-to-real gap and (ii) a high level controller that chooses the low level skills, (2) techniques for enabling zero-shot sim-to-real including an iterative approach to defining the task distribution that is grounded in the real-world and defines an automatic curriculum, and (3) real time adaptation to unseen opponents. Policy performance was assessed through 29 robot vs. human matches of which the robot won 45% (13/29). All humans were unseen players and their skill level varied from beginner to tournament level. Whilst the robot lost all matches vs. the most advanced players it won 100% matches vs. beginners and 55% matches vs. intermediate players, demonstrating solidly amateur human-level performance. Videos of the matches can be viewed at https://sites.google.com/view/competitive-robot-table-tennis
VADER: Visual Affordance Detection and Error Recovery for Multi Robot Human Collaboration
May 25, 2024



Abstract:Robots today can exploit the rich world knowledge of large language models to chain simple behavioral skills into long-horizon tasks. However, robots often get interrupted during long-horizon tasks due to primitive skill failures and dynamic environments. We propose VADER, a plan, execute, detect framework with seeking help as a new skill that enables robots to recover and complete long-horizon tasks with the help of humans or other robots. VADER leverages visual question answering (VQA) modules to detect visual affordances and recognize execution errors. It then generates prompts for a language model planner (LMP) which decides when to seek help from another robot or human to recover from errors in long-horizon task execution. We show the effectiveness of VADER with two long-horizon robotic tasks. Our pilot study showed that VADER is capable of performing complex long-horizon tasks by asking for help from another robot to clear a table. Our user study showed that VADER is capable of performing complex long-horizon tasks by asking for help from a human to clear a path. We gathered feedback from people (N=19) about the performance of the VADER performance vs. a robot that did not ask for help. https://google-vader.github.io/
Prosody for Intuitive Robotic Interface Design: It's Not What You Said, It's How You Said It
Mar 13, 2024

Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the use of 'prosody' (the musical elements of speech) as a communicative signal for intuitive human-robot interaction interfaces. Our approach, rooted in Research through Design (RtD), examines the application of prosody in directing a quadruped robot navigation. We involved ten team members in an experiment to command a robot through an obstacle course using natural interaction. A human operator, serving as the robot's sensory and processing proxy, translated human communication into a basic set of navigation commands, effectively simulating an intuitive interface. During our analysis of interaction videos, when lexical and visual cues proved insufficient for accurate command interpretation, we turned to non-verbal auditory cues. Qualitative evidence suggests that participants intuitively relied on prosody to control robot navigation. We highlight specific distinct prosodic constructs that emerged from this preliminary exploration and discuss their pragmatic functions. This work contributes a discussion on the broader potential of prosody as a multifunctional communicative signal for designing future intuitive robotic interfaces, enabling lifelong learning and personalization in human-robot interaction.
Learning to Learn Faster from Human Feedback with Language Model Predictive Control
Feb 18, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been shown to exhibit a wide range of capabilities, such as writing robot code from language commands -- enabling non-experts to direct robot behaviors, modify them based on feedback, or compose them to perform new tasks. However, these capabilities (driven by in-context learning) are limited to short-term interactions, where users' feedback remains relevant for only as long as it fits within the context size of the LLM, and can be forgotten over longer interactions. In this work, we investigate fine-tuning the robot code-writing LLMs, to remember their in-context interactions and improve their teachability i.e., how efficiently they adapt to human inputs (measured by average number of corrections before the user considers the task successful). Our key observation is that when human-robot interactions are formulated as a partially observable Markov decision process (in which human language inputs are observations, and robot code outputs are actions), then training an LLM to complete previous interactions can be viewed as training a transition dynamics model -- that can be combined with classic robotics techniques such as model predictive control (MPC) to discover shorter paths to success. This gives rise to Language Model Predictive Control (LMPC), a framework that fine-tunes PaLM 2 to improve its teachability on 78 tasks across 5 robot embodiments -- improving non-expert teaching success rates of unseen tasks by 26.9% while reducing the average number of human corrections from 2.4 to 1.9. Experiments show that LMPC also produces strong meta-learners, improving the success rate of in-context learning new tasks on unseen robot embodiments and APIs by 31.5%. See videos, code, and demos at: https://robot-teaching.github.io/.
Generative Expressive Robot Behaviors using Large Language Models
Jan 30, 2024Abstract:People employ expressive behaviors to effectively communicate and coordinate their actions with others, such as nodding to acknowledge a person glancing at them or saying "excuse me" to pass people in a busy corridor. We would like robots to also demonstrate expressive behaviors in human-robot interaction. Prior work proposes rule-based methods that struggle to scale to new communication modalities or social situations, while data-driven methods require specialized datasets for each social situation the robot is used in. We propose to leverage the rich social context available from large language models (LLMs) and their ability to generate motion based on instructions or user preferences, to generate expressive robot motion that is adaptable and composable, building upon each other. Our approach utilizes few-shot chain-of-thought prompting to translate human language instructions into parametrized control code using the robot's available and learned skills. Through user studies and simulation experiments, we demonstrate that our approach produces behaviors that users found to be competent and easy to understand. Supplementary material can be found at https://generative-expressive-motion.github.io/.
Robots That Ask For Help: Uncertainty Alignment for Large Language Model Planners
Jul 04, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) exhibit a wide range of promising capabilities -- from step-by-step planning to commonsense reasoning -- that may provide utility for robots, but remain prone to confidently hallucinated predictions. In this work, we present KnowNo, which is a framework for measuring and aligning the uncertainty of LLM-based planners such that they know when they don't know and ask for help when needed. KnowNo builds on the theory of conformal prediction to provide statistical guarantees on task completion while minimizing human help in complex multi-step planning settings. Experiments across a variety of simulated and real robot setups that involve tasks with different modes of ambiguity (e.g., from spatial to numeric uncertainties, from human preferences to Winograd schemas) show that KnowNo performs favorably over modern baselines (which may involve ensembles or extensive prompt tuning) in terms of improving efficiency and autonomy, while providing formal assurances. KnowNo can be used with LLMs out of the box without model-finetuning, and suggests a promising lightweight approach to modeling uncertainty that can complement and scale with the growing capabilities of foundation models. Website: https://robot-help.github.io
Learning Model Predictive Controllers with Real-Time Attention for Real-World Navigation
Sep 24, 2022
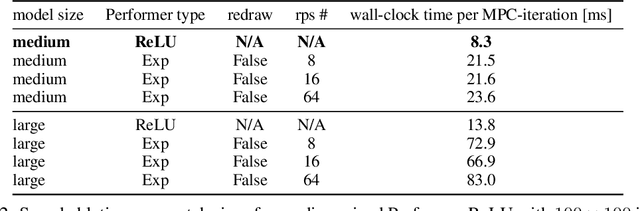
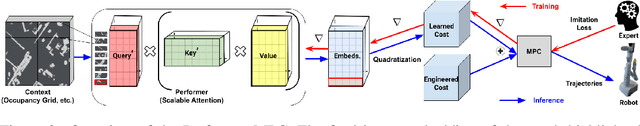
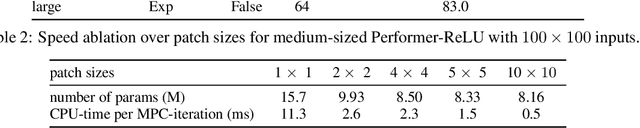
Abstract:Despite decades of research, existing navigation systems still face real-world challenges when deployed in the wild, e.g., in cluttered home environments or in human-occupied public spaces. To address this, we present a new class of implicit control policies combining the benefits of imitation learning with the robust handling of system constraints from Model Predictive Control (MPC). Our approach, called Performer-MPC, uses a learned cost function parameterized by vision context embeddings provided by Performers -- a low-rank implicit-attention Transformer. We jointly train the cost function and construct the controller relying on it, effectively solving end-to-end the corresponding bi-level optimization problem. We show that the resulting policy improves standard MPC performance by leveraging a few expert demonstrations of the desired navigation behavior in different challenging real-world scenarios. Compared with a standard MPC policy, Performer-MPC achieves >40% better goal reached in cluttered environments and >65% better on social metrics when navigating around humans.
Gesture2Path: Imitation Learning for Gesture-aware Navigation
Sep 19, 2022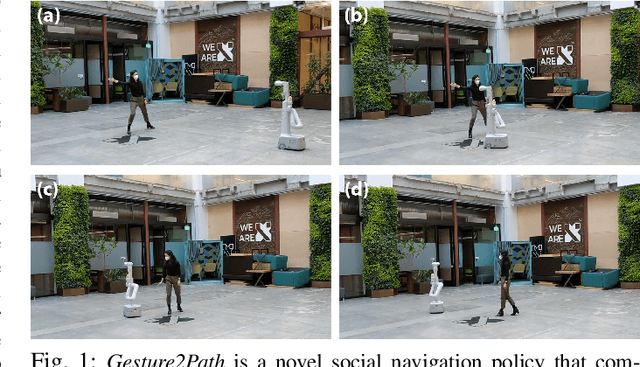

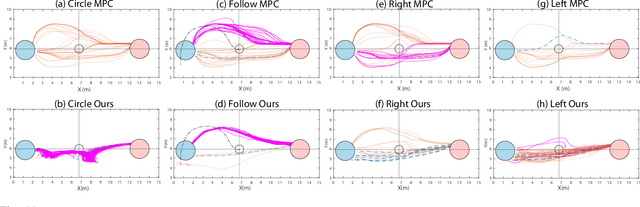

Abstract:As robots increasingly enter human-centered environments, they must not only be able to navigate safely around humans, but also adhere to complex social norms. Humans often rely on non-verbal communication through gestures and facial expressions when navigating around other people, especially in densely occupied spaces. Consequently, robots also need to be able to interpret gestures as part of solving social navigation tasks. To this end, we present Gesture2Path, a novel social navigation approach that combines image-based imitation learning with model-predictive control. Gestures are interpreted based on a neural network that operates on streams of images, while we use a state-of-the-art model predictive control algorithm to solve point-to-point navigation tasks. We deploy our method on real robots and showcase the effectiveness of our approach for the four gestures-navigation scenarios: left/right, follow me, and make a circle. Our experiments indicate that our method is able to successfully interpret complex human gestures and to use them as a signal to generate socially compliant trajectories for navigation tasks. We validated our method based on in-situ ratings of participants interacting with the robots.
A Protocol for Validating Social Navigation Policies
Apr 11, 2022
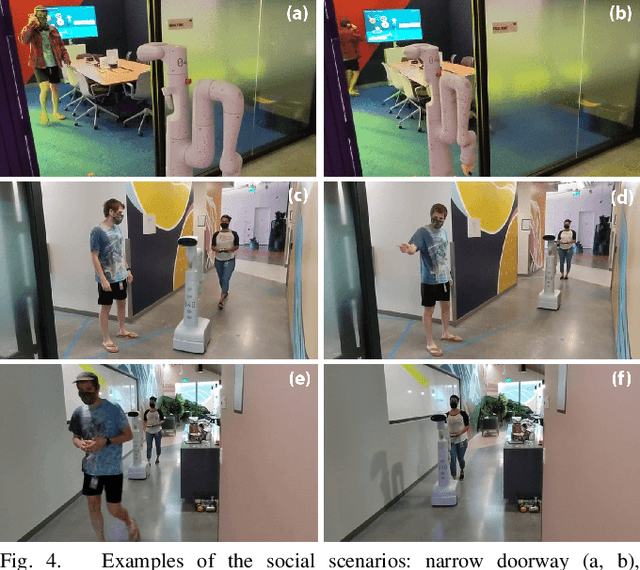
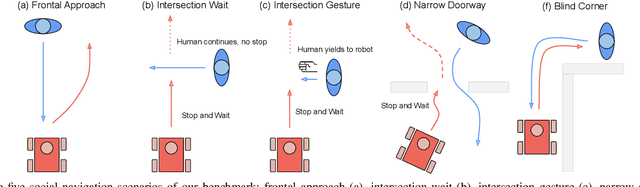
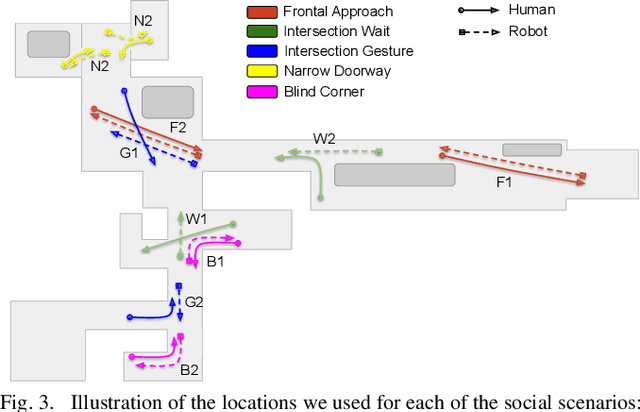

Abstract:Enabling socially acceptable behavior for situated agents is a major goal of recent robotics research. Robots should not only operate safely around humans, but also abide by complex social norms. A key challenge for developing socially-compliant policies is measuring the quality of their behavior. Social behavior is enormously complex, making it difficult to create reliable metrics to gauge the performance of algorithms. In this paper, we propose a protocol for social navigation benchmarking that defines a set of canonical social navigation scenarios and an in-situ metric for evaluating performance on these scenarios using questionnaires. Our experiments show this protocol is realistic, scalable, and repeatable across runs and physical spaces. Our protocol can be replicated verbatim or it can be used to define a social navigation benchmark for novel scenarios. Our goal is to introduce a protocol for benchmarking social scenarios that is homogeneous and comparable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge