Stephen Tu
Maestro: Learning to Collaborate via Conditional Listwise Policy Optimization for Multi-Agent LLMs
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:Multi-agent systems (MAS) built on Large Language Models (LLMs) are being used to approach complex problems and can surpass single model inference. However, their success hinges on navigating a fundamental cognitive tension: the need to balance broad, divergent exploration of the solution space with a principled, convergent synthesis to the optimal solution. Existing paradigms often struggle to manage this duality, leading to premature consensus, error propagation, and a critical credit assignment problem that fails to distinguish between genuine reasoning and superficially plausible arguments. To resolve this core challenge, we propose the Multi-Agent Exploration-Synthesis framework Through Role Orchestration (Maestro), a principled paradigm for collaboration that structurally decouples these cognitive modes. Maestro uses a collective of parallel Execution Agents for diverse exploration and a specialized Central Agent for convergent, evaluative synthesis. To operationalize this critical synthesis phase, we introduce Conditional Listwise Policy Optimization (CLPO), a reinforcement learning objective that disentangles signals for strategic decisions and tactical rationales. By combining decision-focused policy gradients with a list-wise ranking loss over justifications, CLPO achieves clean credit assignment and stronger comparative supervision. Experiments on mathematical reasoning and general problem-solving benchmarks demonstrate that Maestro, coupled with CLPO, consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art multi-agent approaches, delivering absolute accuracy gains of 6% on average and up to 10% at best.
CLAM: Continuous Latent Action Models for Robot Learning from Unlabeled Demonstrations
May 08, 2025Abstract:Learning robot policies using imitation learning requires collecting large amounts of costly action-labeled expert demonstrations, which fundamentally limits the scale of training data. A promising approach to address this bottleneck is to harness the abundance of unlabeled observations-e.g., from video demonstrations-to learn latent action labels in an unsupervised way. However, we find that existing methods struggle when applied to complex robot tasks requiring fine-grained motions. We design continuous latent action models (CLAM) which incorporate two key ingredients we find necessary for learning to solve complex continuous control tasks from unlabeled observation data: (a) using continuous latent action labels instead of discrete representations, and (b) jointly training an action decoder to ensure that the latent action space can be easily grounded to real actions with relatively few labeled examples. Importantly, the labeled examples can be collected from non-optimal play data, enabling CLAM to learn performant policies without access to any action-labeled expert data. We demonstrate on continuous control benchmarks in DMControl (locomotion) and MetaWorld (manipulation), as well as on a real WidowX robot arm that CLAM significantly outperforms prior state-of-the-art methods, remarkably with a 2-3x improvement in task success rate compared to the best baseline. Videos and code can be found at clamrobot.github.io.
Integration Matters for Learning PDEs with Backwards SDEs
May 02, 2025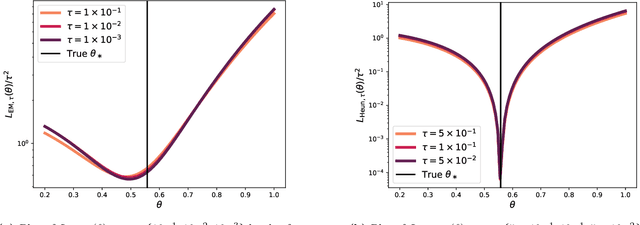
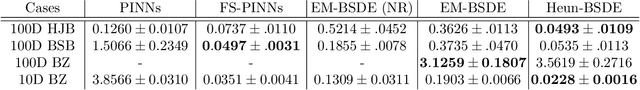
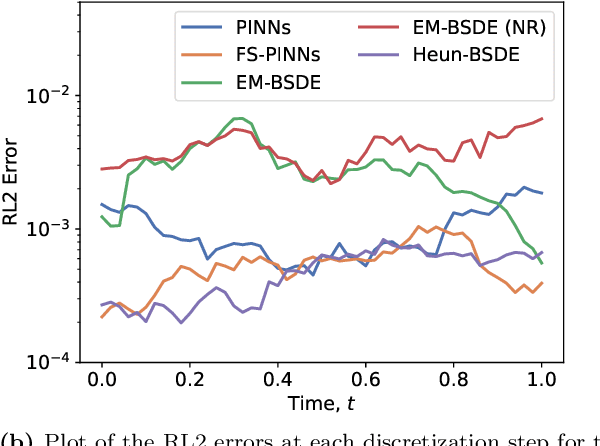
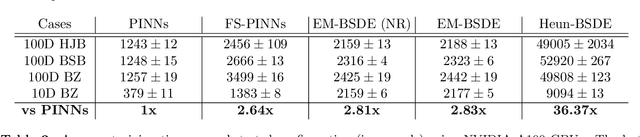
Abstract:Backward stochastic differential equation (BSDE)-based deep learning methods provide an alternative to Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) for solving high-dimensional partial differential equations (PDEs), offering algorithmic advantages in settings such as stochastic optimal control, where the PDEs of interest are tied to an underlying dynamical system. However, existing BSDE-based solvers have empirically been shown to underperform relative to PINNs in the literature. In this paper, we identify the root cause of this performance gap as a discretization bias introduced by the standard Euler-Maruyama (EM) integration scheme applied to short-horizon self-consistency BSDE losses, which shifts the optimization landscape off target. We find that this bias cannot be satisfactorily addressed through finer step sizes or longer self-consistency horizons. To properly handle this issue, we propose a Stratonovich-based BSDE formulation, which we implement with stochastic Heun integration. We show that our proposed approach completely eliminates the bias issues faced by EM integration. Furthermore, our empirical results show that our Heun-based BSDE method consistently outperforms EM-based variants and achieves competitive results with PINNs across multiple high-dimensional benchmarks. Our findings highlight the critical role of integration schemes in BSDE-based PDE solvers, an algorithmic detail that has received little attention thus far in the literature.
Stability properties of gradient flow dynamics for the symmetric low-rank matrix factorization problem
Nov 24, 2024Abstract:The symmetric low-rank matrix factorization serves as a building block in many learning tasks, including matrix recovery and training of neural networks. However, despite a flurry of recent research, the dynamics of its training via non-convex factorized gradient-descent-type methods is not fully understood especially in the over-parameterized regime where the fitted rank is higher than the true rank of the target matrix. To overcome this challenge, we characterize equilibrium points of the gradient flow dynamics and examine their local and global stability properties. To facilitate a precise global analysis, we introduce a nonlinear change of variables that brings the dynamics into a cascade connection of three subsystems whose structure is simpler than the structure of the original system. We demonstrate that the Schur complement to a principal eigenspace of the target matrix is governed by an autonomous system that is decoupled from the rest of the dynamics. In the over-parameterized regime, we show that this Schur complement vanishes at an $O(1/t)$ rate, thereby capturing the slow dynamics that arises from excess parameters. We utilize a Lyapunov-based approach to establish exponential convergence of the other two subsystems. By decoupling the fast and slow parts of the dynamics, we offer new insight into the shape of the trajectories associated with local search algorithms and provide a complete characterization of the equilibrium points and their global stability properties. Such an analysis via nonlinear control techniques may prove useful in several related over-parameterized problems.
Shallow diffusion networks provably learn hidden low-dimensional structure
Oct 15, 2024Abstract:Diffusion-based generative models provide a powerful framework for learning to sample from a complex target distribution. The remarkable empirical success of these models applied to high-dimensional signals, including images and video, stands in stark contrast to classical results highlighting the curse of dimensionality for distribution recovery. In this work, we take a step towards understanding this gap through a careful analysis of learning diffusion models over the Barron space of single layer neural networks. In particular, we show that these shallow models provably adapt to simple forms of low dimensional structure, thereby avoiding the curse of dimensionality. We combine our results with recent analyses of sampling with diffusion models to provide an end-to-end sample complexity bound for learning to sample from structured distributions. Importantly, our results do not require specialized architectures tailored to particular latent structures, and instead rely on the low-index structure of the Barron space to adapt to the underlying distribution.
Sharp Rates in Dependent Learning Theory: Avoiding Sample Size Deflation for the Square Loss
Feb 08, 2024Abstract:In this work, we study statistical learning with dependent ($\beta$-mixing) data and square loss in a hypothesis class $\mathscr{F}\subset L_{\Psi_p}$ where $\Psi_p$ is the norm $\|f\|_{\Psi_p} \triangleq \sup_{m\geq 1} m^{-1/p} \|f\|_{L^m} $ for some $p\in [2,\infty]$. Our inquiry is motivated by the search for a sharp noise interaction term, or variance proxy, in learning with dependent data. Absent any realizability assumption, typical non-asymptotic results exhibit variance proxies that are deflated \emph{multiplicatively} by the mixing time of the underlying covariates process. We show that whenever the topologies of $L^2$ and $\Psi_p$ are comparable on our hypothesis class $\mathscr{F}$ -- that is, $\mathscr{F}$ is a weakly sub-Gaussian class: $\|f\|_{\Psi_p} \lesssim \|f\|_{L^2}^\eta$ for some $\eta\in (0,1]$ -- the empirical risk minimizer achieves a rate that only depends on the complexity of the class and second order statistics in its leading term. Our result holds whether the problem is realizable or not and we refer to this as a \emph{near mixing-free rate}, since direct dependence on mixing is relegated to an additive higher order term. We arrive at our result by combining the above notion of a weakly sub-Gaussian class with mixed tail generic chaining. This combination allows us to compute sharp, instance-optimal rates for a wide range of problems. %Our approach, reliant on mixed tail generic chaining, allows us to obtain sharp, instance-optimal rates. Examples that satisfy our framework include sub-Gaussian linear regression, more general smoothly parameterized function classes, finite hypothesis classes, and bounded smoothness classes.
Revisiting Energy Based Models as Policies: Ranking Noise Contrastive Estimation and Interpolating Energy Models
Sep 11, 2023Abstract:A crucial design decision for any robot learning pipeline is the choice of policy representation: what type of model should be used to generate the next set of robot actions? Owing to the inherent multi-modal nature of many robotic tasks, combined with the recent successes in generative modeling, researchers have turned to state-of-the-art probabilistic models such as diffusion models for policy representation. In this work, we revisit the choice of energy-based models (EBM) as a policy class. We show that the prevailing folklore -- that energy models in high dimensional continuous spaces are impractical to train -- is false. We develop a practical training objective and algorithm for energy models which combines several key ingredients: (i) ranking noise contrastive estimation (R-NCE), (ii) learnable negative samplers, and (iii) non-adversarial joint training. We prove that our proposed objective function is asymptotically consistent and quantify its limiting variance. On the other hand, we show that the Implicit Behavior Cloning (IBC) objective is actually biased even at the population level, providing a mathematical explanation for the poor performance of IBC trained energy policies in several independent follow-up works. We further extend our algorithm to learn a continuous stochastic process that bridges noise and data, modeling this process with a family of EBMs indexed by scale variable. In doing so, we demonstrate that the core idea behind recent progress in generative modeling is actually compatible with EBMs. Altogether, our proposed training algorithms enable us to train energy-based models as policies which compete with -- and even outperform -- diffusion models and other state-of-the-art approaches in several challenging multi-modal benchmarks: obstacle avoidance path planning and contact-rich block pushing.
Robots That Ask For Help: Uncertainty Alignment for Large Language Model Planners
Jul 04, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) exhibit a wide range of promising capabilities -- from step-by-step planning to commonsense reasoning -- that may provide utility for robots, but remain prone to confidently hallucinated predictions. In this work, we present KnowNo, which is a framework for measuring and aligning the uncertainty of LLM-based planners such that they know when they don't know and ask for help when needed. KnowNo builds on the theory of conformal prediction to provide statistical guarantees on task completion while minimizing human help in complex multi-step planning settings. Experiments across a variety of simulated and real robot setups that involve tasks with different modes of ambiguity (e.g., from spatial to numeric uncertainties, from human preferences to Winograd schemas) show that KnowNo performs favorably over modern baselines (which may involve ensembles or extensive prompt tuning) in terms of improving efficiency and autonomy, while providing formal assurances. KnowNo can be used with LLMs out of the box without model-finetuning, and suggests a promising lightweight approach to modeling uncertainty that can complement and scale with the growing capabilities of foundation models. Website: https://robot-help.github.io
Bootstrapped Representations in Reinforcement Learning
Jun 16, 2023Abstract:In reinforcement learning (RL), state representations are key to dealing with large or continuous state spaces. While one of the promises of deep learning algorithms is to automatically construct features well-tuned for the task they try to solve, such a representation might not emerge from end-to-end training of deep RL agents. To mitigate this issue, auxiliary objectives are often incorporated into the learning process and help shape the learnt state representation. Bootstrapping methods are today's method of choice to make these additional predictions. Yet, it is unclear which features these algorithms capture and how they relate to those from other auxiliary-task-based approaches. In this paper, we address this gap and provide a theoretical characterization of the state representation learnt by temporal difference learning (Sutton, 1988). Surprisingly, we find that this representation differs from the features learned by Monte Carlo and residual gradient algorithms for most transition structures of the environment in the policy evaluation setting. We describe the efficacy of these representations for policy evaluation, and use our theoretical analysis to design new auxiliary learning rules. We complement our theoretical results with an empirical comparison of these learning rules for different cumulant functions on classic domains such as the four-room domain (Sutton et al, 1999) and Mountain Car (Moore, 1990).
Agile Catching with Whole-Body MPC and Blackbox Policy Learning
Jun 14, 2023


Abstract:We address a benchmark task in agile robotics: catching objects thrown at high-speed. This is a challenging task that involves tracking, intercepting, and cradling a thrown object with access only to visual observations of the object and the proprioceptive state of the robot, all within a fraction of a second. We present the relative merits of two fundamentally different solution strategies: (i) Model Predictive Control using accelerated constrained trajectory optimization, and (ii) Reinforcement Learning using zeroth-order optimization. We provide insights into various performance trade-offs including sample efficiency, sim-to-real transfer, robustness to distribution shifts, and whole-body multimodality via extensive on-hardware experiments. We conclude with proposals on fusing "classical" and "learning-based" techniques for agile robot control. Videos of our experiments may be found at https://sites.google.com/view/agile-catching
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge