Karthik Mahadevan
AeroHaptix: A Wearable Vibrotactile Feedback System for Enhancing Collision Avoidance in UAV Teleoperation
Jul 16, 2024Abstract:Haptic feedback enhances collision avoidance by providing directional obstacle information to operators in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) teleoperation. However, such feedback is often rendered via haptic joysticks, which are unfamiliar to UAV operators and limited to single-directional force feedback. Additionally, the direct coupling of the input device and the feedback method diminishes the operators' control authority and causes oscillatory movements. To overcome these limitations, we propose AeroHaptix, a wearable haptic feedback system that uses high-resolution vibrations to communicate multiple obstacle directions simultaneously. The vibrotactile actuators' layout was optimized based on a perceptual study to eliminate perceptual biases and achieve uniform spatial coverage. A novel rendering algorithm, MultiCBF, was adapted from control barrier functions to support multi-directional feedback. System evaluation showed that AeroHaptix effectively reduced collisions in complex environment, and operators reported significantly lower physical workload, improved situational awareness, and increased control authority.
Generative Expressive Robot Behaviors using Large Language Models
Jan 30, 2024Abstract:People employ expressive behaviors to effectively communicate and coordinate their actions with others, such as nodding to acknowledge a person glancing at them or saying "excuse me" to pass people in a busy corridor. We would like robots to also demonstrate expressive behaviors in human-robot interaction. Prior work proposes rule-based methods that struggle to scale to new communication modalities or social situations, while data-driven methods require specialized datasets for each social situation the robot is used in. We propose to leverage the rich social context available from large language models (LLMs) and their ability to generate motion based on instructions or user preferences, to generate expressive robot motion that is adaptable and composable, building upon each other. Our approach utilizes few-shot chain-of-thought prompting to translate human language instructions into parametrized control code using the robot's available and learned skills. Through user studies and simulation experiments, we demonstrate that our approach produces behaviors that users found to be competent and easy to understand. Supplementary material can be found at https://generative-expressive-motion.github.io/.
"Grip-that-there": An Investigation of Explicit and Implicit Task Allocation Techniques for Human-Robot Collaboration
Feb 03, 2021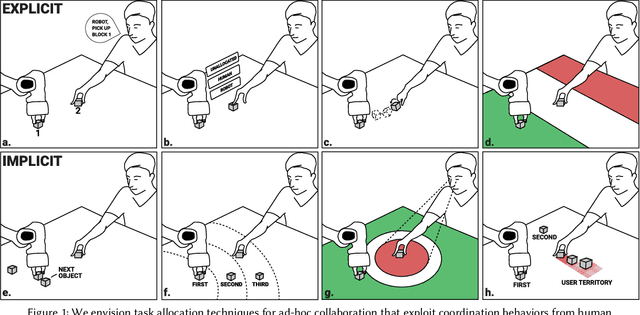
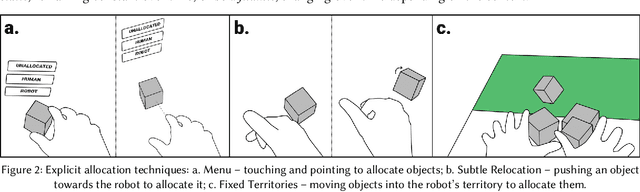
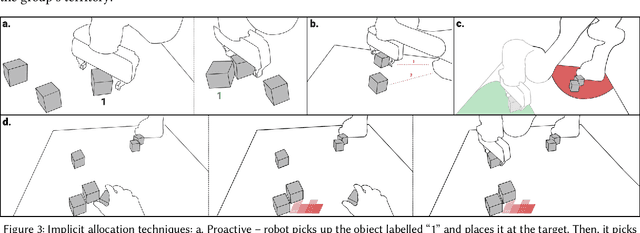
Abstract:In ad-hoc human-robot collaboration (HRC), humans and robots work on a task without pre-planning the robot's actions prior to execution; instead, task allocation occurs in real-time. However, prior research has largely focused on task allocations that are pre-planned - there has not been a comprehensive exploration or evaluation of techniques where task allocation is adjusted in real-time. Inspired by HCI research on territoriality and proxemics, we propose a design space of novel task allocation techniques including both explicit techniques, where the user maintains agency, and implicit techniques, where the efficiency of automation can be leveraged. The techniques were implemented and evaluated using a tabletop HRC simulation in VR. A 16-participant study, which presented variations of a collaborative block stacking task, showed that implicit techniques enable efficient task completion and task parallelization, and should be augmented with explicit mechanisms to provide users with fine-grained control.
Robot Vision: Calibration of Wide-Angle Lens Cameras Using Collinearity Condition and K-Nearest Neighbour Regression
Sep 29, 2018
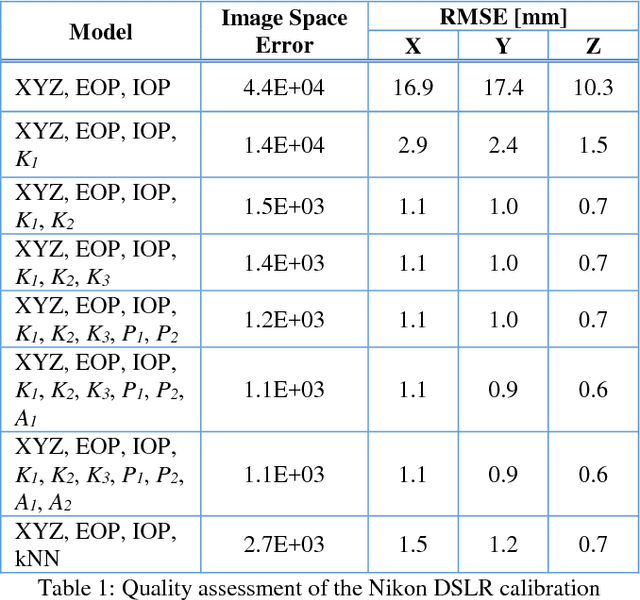
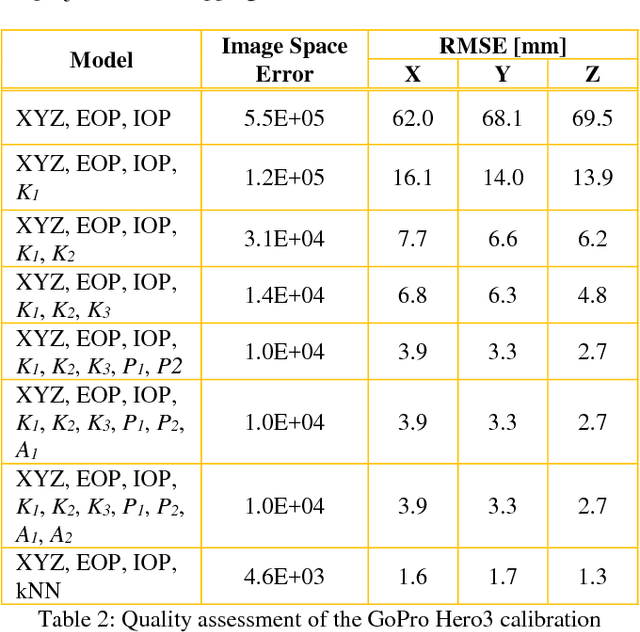
Abstract:Visual perception is regularly used by humans and robots for navigation. By either implicitly or explicitly mapping the environment, ego-motion can be determined and a path of actions can be planned. The process of mapping and navigation are delicately intertwined; therefore, improving one can often lead to an improvement of the other. Both processes are sensitive to the interior orientation parameters of the camera system and mathematically modelling these systematic errors can often improve the precision and accuracy of the overall solution. This paper presents an automatic camera calibration method suitable for any lens, without having prior knowledge about the sensor. Statistical inference is performed to map the environment and localize the camera simultaneously. K-nearest neighbour regression is used to model the geometric distortions of the images. A normal-angle lens Nikon camera and wide-angle lens GoPro camera were calibrated using the proposed method, as well as the conventional bundle adjustment with self-calibration method (for comparison). Results showed that the mapping error was reduced from an average of 14.9 mm to 1.2 mm (i.e. a 92% improvement) and 66.6 mm to 1.5 mm (i.e. a 98% improvement) using the proposed method for the Nikon and GoPro cameras, respectively. In contrast, the conventional approach achieved an average 3D error of 0.9 mm (i.e. 94% improvement) and 3.3 mm (i.e. 95% improvement) for the Nikon and GoPro cameras, respectively. Thus, the proposed method performs well irrespective of the lens/sensor used: it yields results that are comparable to the conventional approach for normal-angle lens cameras, and it has the additional benefit of improving calibration results for wide-angle lens cameras.
* ISPRS TC I Mid-term Symposium "Innovative Sensing - From Sensors to Methods and Applications", 10-12 October 2018. Karlsruhe, Germany
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge