Kristian Morin
The Hilti SLAM Challenge Dataset
Sep 23, 2021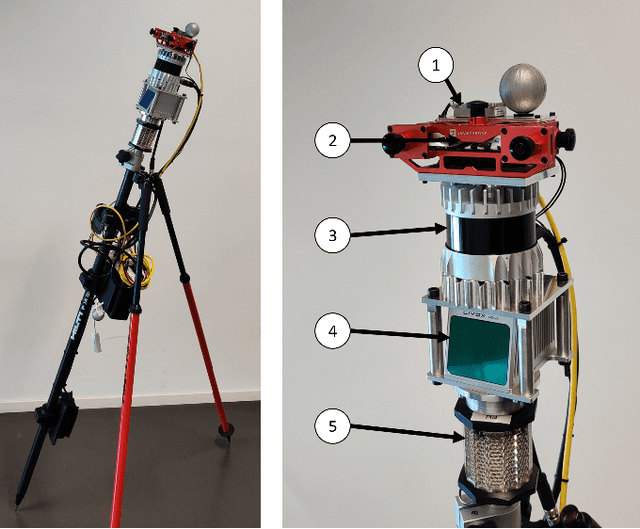


Abstract:Accurate and robust pose estimation is a fundamental capability for autonomous systems to navigate, map and perform tasks. Particularly, construction environments pose challenging problem to Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) algorithms due to sparsity, varying illumination conditions, and dynamic objects. Current academic research in SLAM is focused on developing more accurate and robust algorithms for example by fusing different sensor modalities. To help this research, we propose a new dataset, the Hilti SLAM Challenge Dataset. The sensor platform used to collect this dataset contains a number of visual, lidar and inertial sensors which have all been rigorously calibrated. All data is temporally aligned to support precise multi-sensor fusion. Each dataset includes accurate ground truth to allow direct testing of SLAM results. Raw data as well as intrinsic and extrinsic sensor calibration data from twelve datasets in various environments is provided. Each environment represents common scenarios found in building construction sites in various stages of completion.
Robot Vision: Calibration of Wide-Angle Lens Cameras Using Collinearity Condition and K-Nearest Neighbour Regression
Sep 29, 2018
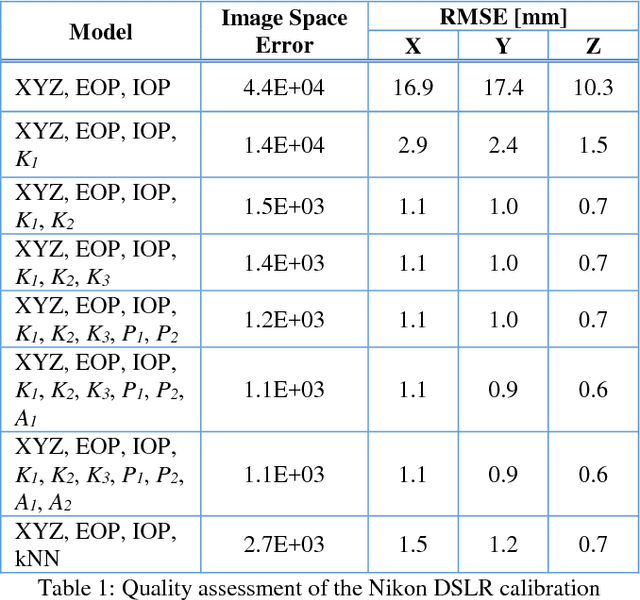
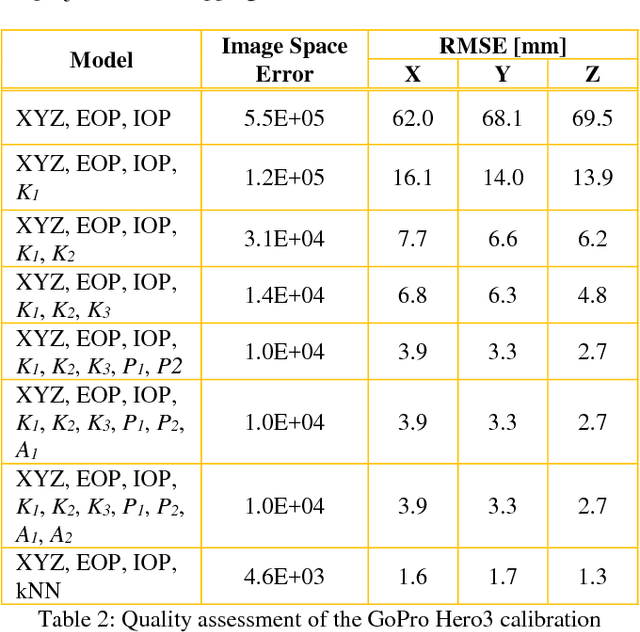
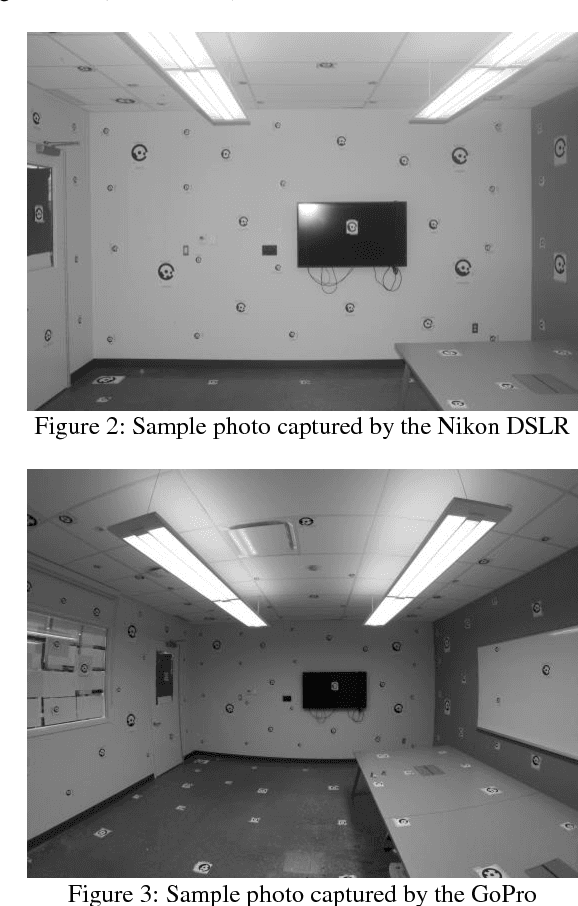
Abstract:Visual perception is regularly used by humans and robots for navigation. By either implicitly or explicitly mapping the environment, ego-motion can be determined and a path of actions can be planned. The process of mapping and navigation are delicately intertwined; therefore, improving one can often lead to an improvement of the other. Both processes are sensitive to the interior orientation parameters of the camera system and mathematically modelling these systematic errors can often improve the precision and accuracy of the overall solution. This paper presents an automatic camera calibration method suitable for any lens, without having prior knowledge about the sensor. Statistical inference is performed to map the environment and localize the camera simultaneously. K-nearest neighbour regression is used to model the geometric distortions of the images. A normal-angle lens Nikon camera and wide-angle lens GoPro camera were calibrated using the proposed method, as well as the conventional bundle adjustment with self-calibration method (for comparison). Results showed that the mapping error was reduced from an average of 14.9 mm to 1.2 mm (i.e. a 92% improvement) and 66.6 mm to 1.5 mm (i.e. a 98% improvement) using the proposed method for the Nikon and GoPro cameras, respectively. In contrast, the conventional approach achieved an average 3D error of 0.9 mm (i.e. 94% improvement) and 3.3 mm (i.e. 95% improvement) for the Nikon and GoPro cameras, respectively. Thus, the proposed method performs well irrespective of the lens/sensor used: it yields results that are comparable to the conventional approach for normal-angle lens cameras, and it has the additional benefit of improving calibration results for wide-angle lens cameras.
* ISPRS TC I Mid-term Symposium "Innovative Sensing - From Sensors to Methods and Applications", 10-12 October 2018. Karlsruhe, Germany
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge