Nitish Kumar
Performance of a Deep Learning-Based Segmentation Model for Pancreatic Tumors on Public Endoscopic Ultrasound Datasets
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Background: Pancreatic cancer is one of the most aggressive cancers, with poor survival rates. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a key diagnostic modality, but its effectiveness is constrained by operator subjectivity. This study evaluates a Vision Transformer-based deep learning segmentation model for pancreatic tumors. Methods: A segmentation model using the USFM framework with a Vision Transformer backbone was trained and validated with 17,367 EUS images (from two public datasets) in 5-fold cross-validation. The model was tested on an independent dataset of 350 EUS images from another public dataset, manually segmented by radiologists. Preprocessing included grayscale conversion, cropping, and resizing to 512x512 pixels. Metrics included Dice similarity coefficient (DSC), intersection over union (IoU), sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy. Results: In 5-fold cross-validation, the model achieved a mean DSC of 0.651 +/- 0.738, IoU of 0.579 +/- 0.658, sensitivity of 69.8%, specificity of 98.8%, and accuracy of 97.5%. For the external validation set, the model achieved a DSC of 0.657 (95% CI: 0.634-0.769), IoU of 0.614 (95% CI: 0.590-0.689), sensitivity of 71.8%, and specificity of 97.7%. Results were consistent, but 9.7% of cases exhibited erroneous multiple predictions. Conclusions: The Vision Transformer-based model demonstrated strong performance for pancreatic tumor segmentation in EUS images. However, dataset heterogeneity and limited external validation highlight the need for further refinement, standardization, and prospective studies.
Real-Time LPV-Based Non-Linear Model Predictive Control for Robust Trajectory Tracking in Autonomous Vehicles
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:This paper presents the development and implementation of a Model Predictive Control (MPC) framework for trajectory tracking in autonomous vehicles under diverse driving conditions. The proposed approach incorporates a modular architecture that integrates state estimation, vehicle dynamics modeling, and optimization to ensure real-time performance. The state-space equations are formulated in a Linear Parameter Varying (LPV) form, and a curvature-based tuning method is introduced to optimize weight matrices for varying trajectories. The MPC framework is implemented using the Robot Operating System (ROS) for parallel execution of state estimation and control optimization, ensuring scalability and minimal latency. Extensive simulations and real-time experiments were conducted on multiple predefined trajectories, demonstrating high accuracy with minimal cross-track and orientation errors, even under aggressive maneuvers and high-speed conditions. The results highlight the robustness and adaptability of the proposed system, achieving seamless alignment between simulated and real-world performance. This work lays the foundation for dynamic weight tuning and integration into cooperative autonomous navigation systems, paving the way for enhanced safety and efficiency in autonomous driving applications.
V2X Enabled Emergency Vehicle Alert System
Mar 28, 2024Abstract:Today's major concern in traffic management systems includes time-efficient emergency transports. The awareness of environment and vehicle information is necessary for the emergency vehicles as well as the surrounding commercial vehicles that might be driven by inexperienced drivers to act accordingly if they both interact. The information exchange should be quick and accurate along with how much interactive the alerting system is with the drivers. Therefore, technologies like V2X-based alert systems can deal with such emergency situations and hence prevent potential health or social hazards. An alerting system as a part of a smart-connected city is proposed in this paper. The Dedicated Short Range Communication (DSRC) based system has tried to cover the major domain of information about misbehaving vehicles, any pedestrians on the road, and information about the emergency vehicle itself. The commercial vehicle also will have a similar alert system as an application of V2V and V2I. Further in this paper, a realtime monitoring system was developed using grafana dashboard which will be installed in the area's base station to monitor the vehicles in that area.
Entity Alignment For Knowledge Graphs: Progress, Challenges, and Empirical Studies
May 18, 2022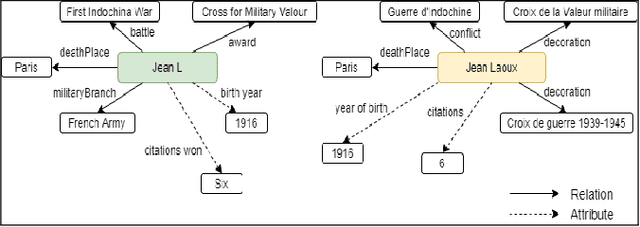
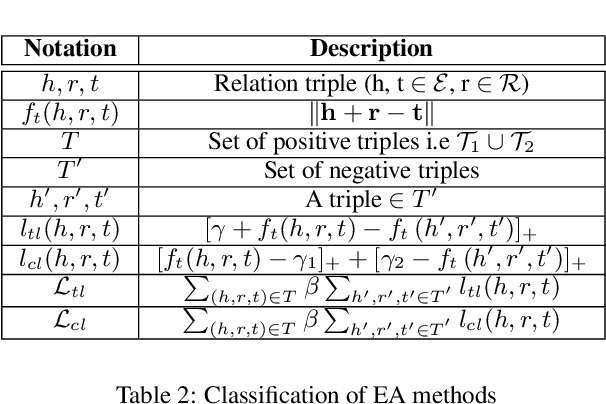
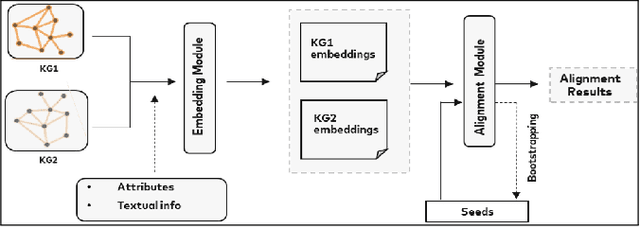
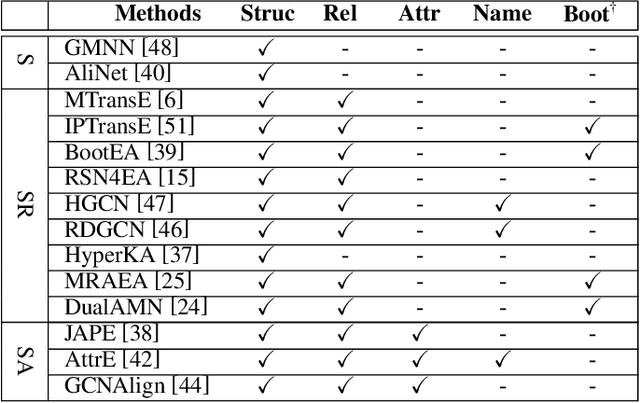
Abstract:Entity Alignment (EA) identifies entities across databases that refer to the same entity. Knowledge graph-based embedding methods have recently dominated EA techniques. Such methods map entities to a low-dimension space and align them based on their similarities. With the corpus of EA methodologies growing rapidly, this paper presents a comprehensive analysis of various existing EA methods, elaborating their applications and limitations. Further, we distinguish the methods based on their underlying algorithms and the information they incorporate to learn entity representations. Based on challenges in industrial datasets, we bring forward $4$ research questions (RQs). These RQs empirically analyse the algorithms from the perspective of \textit{Hubness, Degree distribution, Non-isomorphic neighbourhood,} and \textit{Name bias}. For Hubness, where one entity turns up as the nearest neighbour of many other entities, we define an $h$-score to quantify its effect on the performance of various algorithms. Additionally, we try to level the playing field for algorithms that rely primarily on name-bias existing in the benchmarking open-source datasets by creating a low name bias dataset. We further create an open-source repository for $14$ embedding-based EA methods and present the analysis for invoking further research motivations in the field of EA.
The Hilti SLAM Challenge Dataset
Sep 23, 2021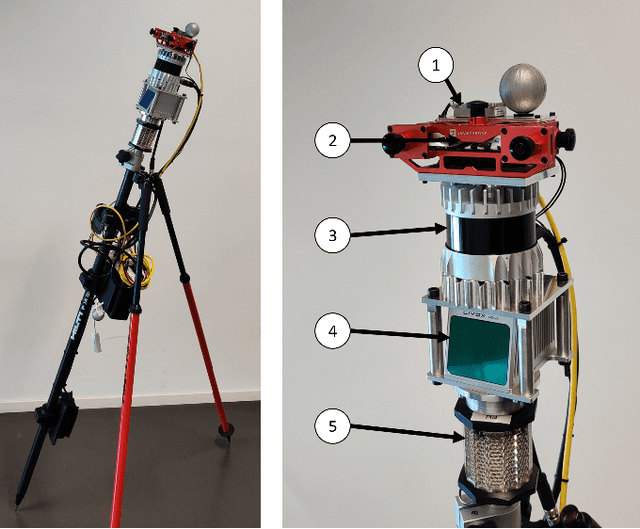

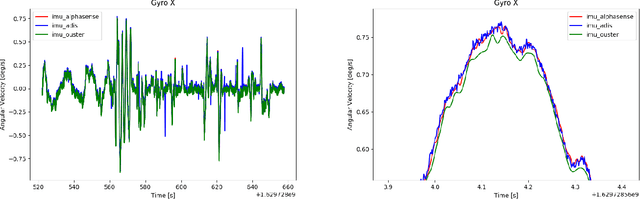

Abstract:Accurate and robust pose estimation is a fundamental capability for autonomous systems to navigate, map and perform tasks. Particularly, construction environments pose challenging problem to Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) algorithms due to sparsity, varying illumination conditions, and dynamic objects. Current academic research in SLAM is focused on developing more accurate and robust algorithms for example by fusing different sensor modalities. To help this research, we propose a new dataset, the Hilti SLAM Challenge Dataset. The sensor platform used to collect this dataset contains a number of visual, lidar and inertial sensors which have all been rigorously calibrated. All data is temporally aligned to support precise multi-sensor fusion. Each dataset includes accurate ground truth to allow direct testing of SLAM results. Raw data as well as intrinsic and extrinsic sensor calibration data from twelve datasets in various environments is provided. Each environment represents common scenarios found in building construction sites in various stages of completion.
Trajectory optimization for a class of robots belonging to Constrained Collaborative Mobile Agents family
Oct 12, 2019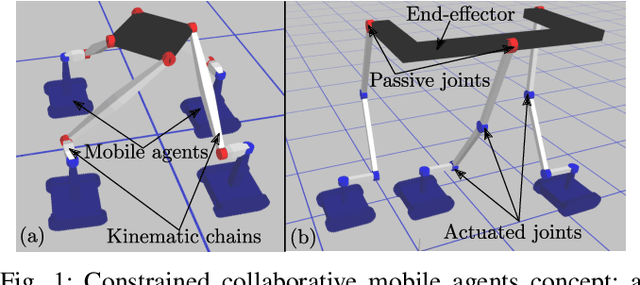
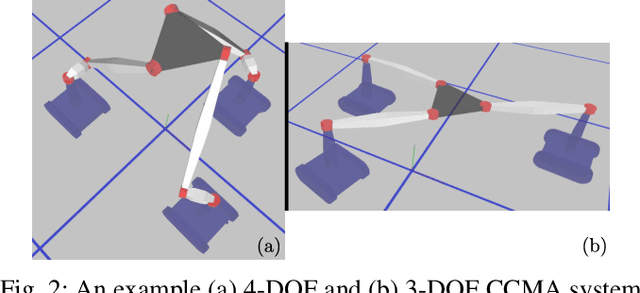
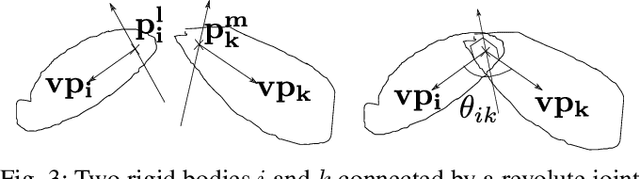
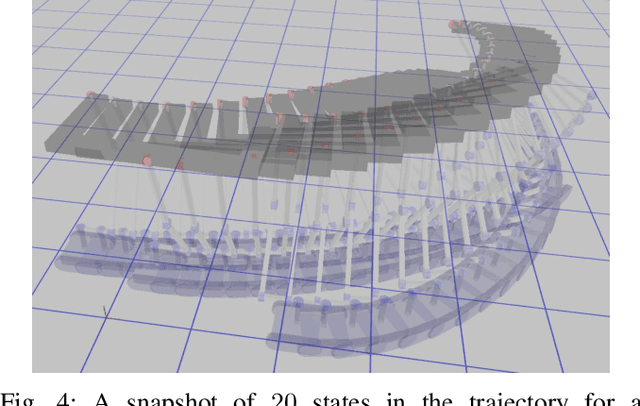
Abstract:We present a novel class of robots belonging to Constrained Collaborative Mobile Agents (CCMA) family which consists of ground mobile bases with non-holonomic constraints. Moreover, these mobile robots are constrained by closed-loop kinematic chains consisting of revolute joints which can be either passive or actuated. We also describe a novel trajectory optimization method which is general with respect to number of mobile robots, topology of the closed-loop kinematic chains and placement of the actuators at the revolute joints. We also extend the standalone trajectory optimization method to optimize concurrently the design parameters and the control policy. We describe various CCMA system examples, in simulation, differing in design, topology, number of mobile robots and actuation space. The simulation results for standalone trajectory optimization with fixed design parameters is presented for CCMA system examples. We also show how this method can be used for tasks other than end-effector positioning such as internal collision avoidance and external obstacle avoidance. The concurrent design and control policy optimization is demonstrated, in simulations, to increase the CCMA system workspace and manipulation capabilities. Finally, the trajectory optimization method is validated in experiments through two 4-DOF prototypes consisting of 3 tracked mobile bases.
An optimization framework for simulation and kinematic control of Constrained Collaborative Mobile Agents (CCMA) system
Mar 01, 2019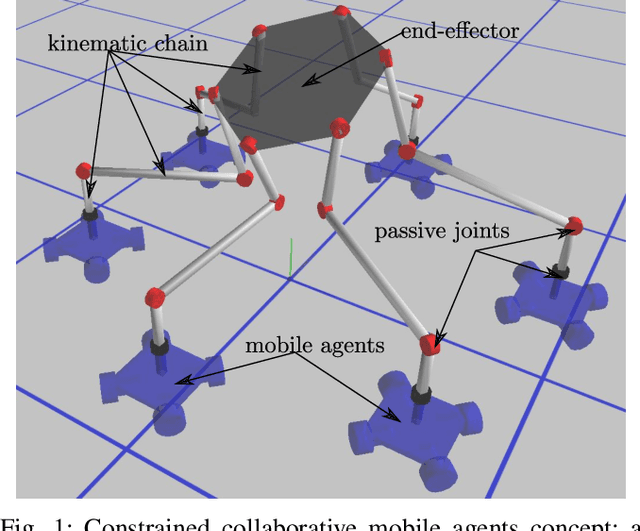
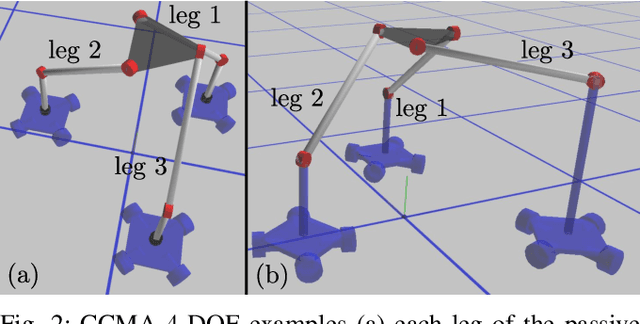
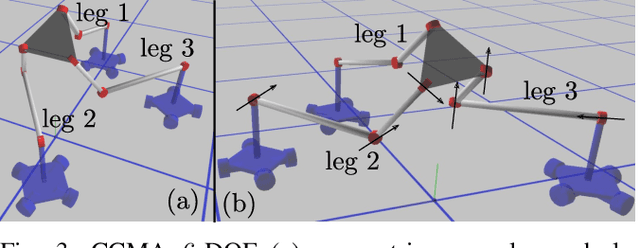
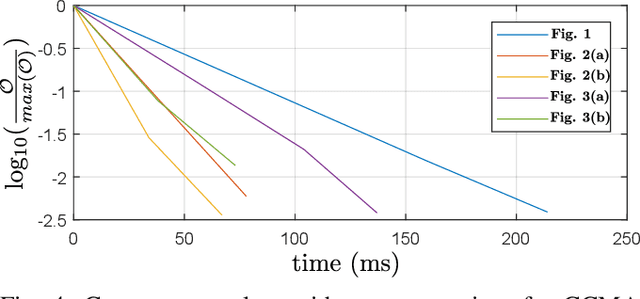
Abstract:We present a concept of constrained collaborative mobile agents (CCMA) system, which consists of multiple wheeled mobile agents constrained by a passive kinematic chain. This mobile robotic system is modular in nature, the passive kinematic chain can be easily replaced with different designs and morphologies for different functions and task adaptability. Depending solely on the actuation of the mobile agents, this mobile robotic system can manipulate or position an end-effector. However, the complexity of the system due to presence of several mobile agents, passivity of the kinematic chain and the nature of the constrained collaborative manipulation requires development of an optimization framework. We therefore present an optimization framework for forward simulation and kinematic control of this system. With this optimization framework, the number of deployed mobile agents, actuation schemes, the design and morphology of the passive kinematic chain can be easily changed, which reinforces the modularity and collaborative aspects of the mobile robotic system. We present results, in simulation, for spatial 4-DOF to 6-DOF CCMA system examples. Finally, we present experimental quantitative results for two different fabricated 4-DOF prototypes, which demonstrate different actuation schemes, control and collaborative manipulation of an end-effector.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge