Anil Surisetty
DNN-GDITD: Out-of-distribution detection via Deep Neural Network based Gaussian Descriptor for Imbalanced Tabular Data
Sep 04, 2024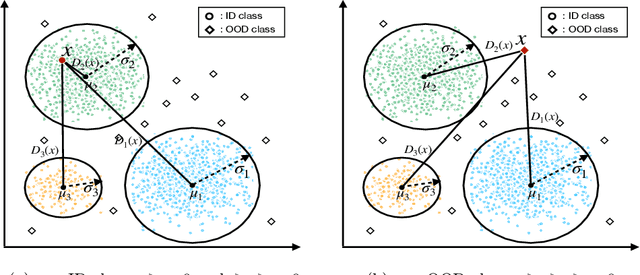
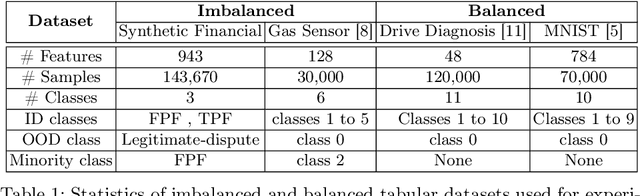

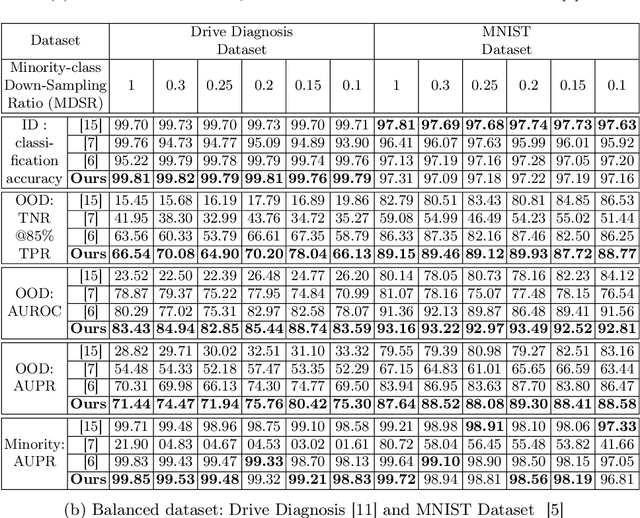
Abstract:Classification tasks present challenges due to class imbalances and evolving data distributions. Addressing these issues requires a robust method to handle imbalances while effectively detecting out-of-distribution (OOD) samples not encountered during training. This study introduces a novel OOD detection algorithm designed for tabular datasets, titled Deep Neural Network-based Gaussian Descriptor for Imbalanced Tabular Data (DNN-GDITD). The DNN-GDITD algorithm can be placed on top of any DNN to facilitate better classification of imbalanced data and OOD detection using spherical decision boundaries. Using a combination of Push, Score-based, and focal losses, DNN-GDITD assigns confidence scores to test data points, categorizing them as known classes or as an OOD sample. Extensive experimentation on tabular datasets demonstrates the effectiveness of DNN-GDITD compared to three OOD algorithms. Evaluation encompasses imbalanced and balanced scenarios on diverse tabular datasets, including a synthetic financial dispute dataset and publicly available tabular datasets like Gas Sensor, Drive Diagnosis, and MNIST, showcasing DNN-GDITD's versatility.
Entity Alignment For Knowledge Graphs: Progress, Challenges, and Empirical Studies
May 18, 2022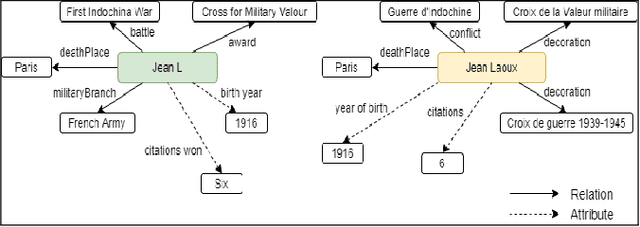
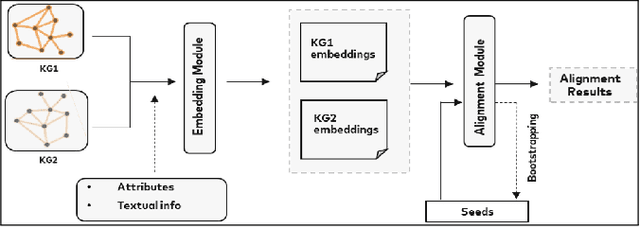
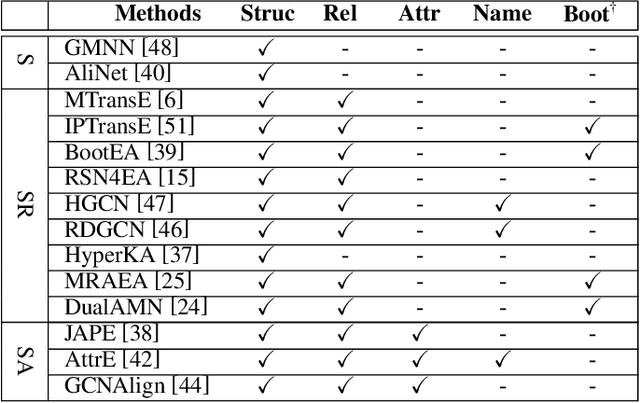
Abstract:Entity Alignment (EA) identifies entities across databases that refer to the same entity. Knowledge graph-based embedding methods have recently dominated EA techniques. Such methods map entities to a low-dimension space and align them based on their similarities. With the corpus of EA methodologies growing rapidly, this paper presents a comprehensive analysis of various existing EA methods, elaborating their applications and limitations. Further, we distinguish the methods based on their underlying algorithms and the information they incorporate to learn entity representations. Based on challenges in industrial datasets, we bring forward $4$ research questions (RQs). These RQs empirically analyse the algorithms from the perspective of \textit{Hubness, Degree distribution, Non-isomorphic neighbourhood,} and \textit{Name bias}. For Hubness, where one entity turns up as the nearest neighbour of many other entities, we define an $h$-score to quantify its effect on the performance of various algorithms. Additionally, we try to level the playing field for algorithms that rely primarily on name-bias existing in the benchmarking open-source datasets by creating a low name bias dataset. We further create an open-source repository for $14$ embedding-based EA methods and present the analysis for invoking further research motivations in the field of EA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge