Byron Boots
University of Washington
Visuo-Tactile World Models
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:We introduce multi-task Visuo-Tactile World Models (VT-WM), which capture the physics of contact through touch reasoning. By complementing vision with tactile sensing, VT-WM better understands robot-object interactions in contact-rich tasks, avoiding common failure modes of vision-only models under occlusion or ambiguous contact states, such as objects disappearing, teleporting, or moving in ways that violate basic physics. Trained across a set of contact-rich manipulation tasks, VT-WM improves physical fidelity in imagination, achieving 33% better performance at maintaining object permanence and 29% better compliance with the laws of motion in autoregressive rollouts. Moreover, experiments show that grounding in contact dynamics also translates to planning. In zero-shot real-robot experiments, VT-WM achieves up to 35% higher success rates, with the largest gains in multi-step, contact-rich tasks. Finally, VT-WM demonstrates significant downstream versatility, effectively adapting its learned contact dynamics to a novel task and achieving reliable planning success with only a limited set of demonstrations.
VAMOS: A Hierarchical Vision-Language-Action Model for Capability-Modulated and Steerable Navigation
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:A fundamental challenge in robot navigation lies in learning policies that generalize across diverse environments while conforming to the unique physical constraints and capabilities of a specific embodiment (e.g., quadrupeds can walk up stairs, but rovers cannot). We propose VAMOS, a hierarchical VLA that decouples semantic planning from embodiment grounding: a generalist planner learns from diverse, open-world data, while a specialist affordance model learns the robot's physical constraints and capabilities in safe, low-cost simulation. We enabled this separation by carefully designing an interface that lets a high-level planner propose candidate paths directly in image space that the affordance model then evaluates and re-ranks. Our real-world experiments show that VAMOS achieves higher success rates in both indoor and complex outdoor navigation than state-of-the-art model-based and end-to-end learning methods. We also show that our hierarchical design enables cross-embodied navigation across legged and wheeled robots and is easily steerable using natural language. Real-world ablations confirm that the specialist model is key to embodiment grounding, enabling a single high-level planner to be deployed across physically distinct wheeled and legged robots. Finally, this model significantly enhances single-robot reliability, achieving 3X higher success rates by rejecting physically infeasible plans. Website: https://vamos-vla.github.io/
Uncertainty-aware Accurate Elevation Modeling for Off-road Navigation via Neural Processes
Aug 05, 2025Abstract:Terrain elevation modeling for off-road navigation aims to accurately estimate changes in terrain geometry in real-time and quantify the corresponding uncertainties. Having precise estimations and uncertainties plays a crucial role in planning and control algorithms to explore safe and reliable maneuver strategies. However, existing approaches, such as Gaussian Processes (GPs) and neural network-based methods, often fail to meet these needs. They are either unable to perform in real-time due to high computational demands, underestimating sharp geometry changes, or harming elevation accuracy when learned with uncertainties. Recently, Neural Processes (NPs) have emerged as a promising approach that integrates the Bayesian uncertainty estimation of GPs with the efficiency and flexibility of neural networks. Inspired by NPs, we propose an effective NP-based method that precisely estimates sharp elevation changes and quantifies the corresponding predictive uncertainty without losing elevation accuracy. Our method leverages semantic features from LiDAR and camera sensors to improve interpolation and extrapolation accuracy in unobserved regions. Also, we introduce a local ball-query attention mechanism to effectively reduce the computational complexity of global attention by 17\% while preserving crucial local and spatial information. We evaluate our method on off-road datasets having interesting geometric features, collected from trails, deserts, and hills. Our results demonstrate superior performance over baselines and showcase the potential of neural processes for effective and expressive terrain modeling in complex off-road environments.
Tactile Beyond Pixels: Multisensory Touch Representations for Robot Manipulation
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:We present Sparsh-X, the first multisensory touch representations across four tactile modalities: image, audio, motion, and pressure. Trained on ~1M contact-rich interactions collected with the Digit 360 sensor, Sparsh-X captures complementary touch signals at diverse temporal and spatial scales. By leveraging self-supervised learning, Sparsh-X fuses these modalities into a unified representation that captures physical properties useful for robot manipulation tasks. We study how to effectively integrate real-world touch representations for both imitation learning and tactile adaptation of sim-trained policies, showing that Sparsh-X boosts policy success rates by 63% over an end-to-end model using tactile images and improves robustness by 90% in recovering object states from touch. Finally, we benchmark Sparsh-X ability to make inferences about physical properties, such as object-action identification, material-quantity estimation, and force estimation. Sparsh-X improves accuracy in characterizing physical properties by 48% compared to end-to-end approaches, demonstrating the advantages of multisensory pretraining for capturing features essential for dexterous manipulation.
Self-supervised perception for tactile skin covered dexterous hands
May 16, 2025Abstract:We present Sparsh-skin, a pre-trained encoder for magnetic skin sensors distributed across the fingertips, phalanges, and palm of a dexterous robot hand. Magnetic tactile skins offer a flexible form factor for hand-wide coverage with fast response times, in contrast to vision-based tactile sensors that are restricted to the fingertips and limited by bandwidth. Full hand tactile perception is crucial for robot dexterity. However, a lack of general-purpose models, challenges with interpreting magnetic flux and calibration have limited the adoption of these sensors. Sparsh-skin, given a history of kinematic and tactile sensing across a hand, outputs a latent tactile embedding that can be used in any downstream task. The encoder is self-supervised via self-distillation on a variety of unlabeled hand-object interactions using an Allegro hand sensorized with Xela uSkin. In experiments across several benchmark tasks, from state estimation to policy learning, we find that pretrained Sparsh-skin representations are both sample efficient in learning downstream tasks and improve task performance by over 41% compared to prior work and over 56% compared to end-to-end learning.
Long Range Navigator (LRN): Extending robot planning horizons beyond metric maps
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:A robot navigating an outdoor environment with no prior knowledge of the space must rely on its local sensing to perceive its surroundings and plan. This can come in the form of a local metric map or local policy with some fixed horizon. Beyond that, there is a fog of unknown space marked with some fixed cost. A limited planning horizon can often result in myopic decisions leading the robot off course or worse, into very difficult terrain. Ideally, we would like the robot to have full knowledge that can be orders of magnitude larger than a local cost map. In practice, this is intractable due to sparse sensing information and often computationally expensive. In this work, we make a key observation that long-range navigation only necessitates identifying good frontier directions for planning instead of full map knowledge. To this end, we propose Long Range Navigator (LRN), that learns an intermediate affordance representation mapping high-dimensional camera images to `affordable' frontiers for planning, and then optimizing for maximum alignment with the desired goal. LRN notably is trained entirely on unlabeled ego-centric videos making it easy to scale and adapt to new platforms. Through extensive off-road experiments on Spot and a Big Vehicle, we find that augmenting existing navigation stacks with LRN reduces human interventions at test-time and leads to faster decision making indicating the relevance of LRN. https://personalrobotics.github.io/lrn
Demonstrating Wheeled Lab: Modern Sim2Real for Low-cost, Open-source Wheeled Robotics
Feb 11, 2025
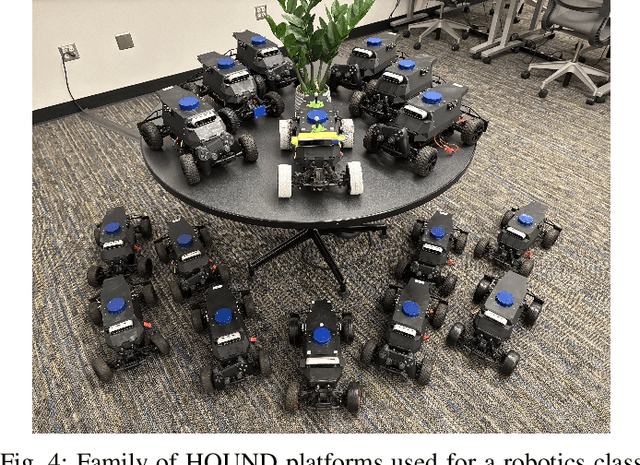
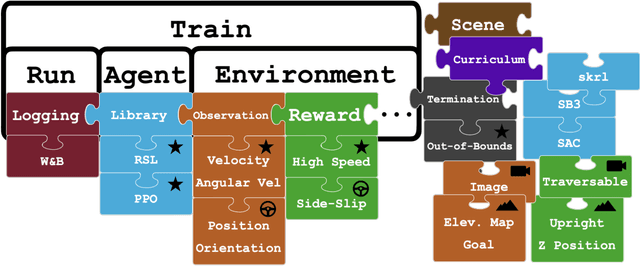

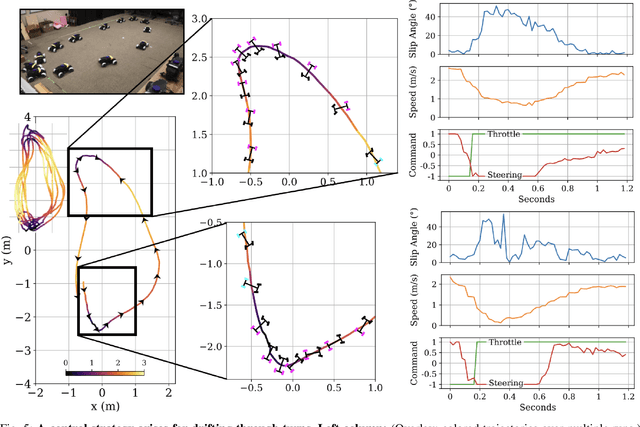
Abstract:Simulation has been pivotal in recent robotics milestones and is poised to play a prominent role in the field's future. However, recent robotic advances often rely on expensive and high-maintenance platforms, limiting access to broader robotics audiences. This work introduces Wheeled Lab, a framework for the low-cost, open-source wheeled platforms that are already widely established in education and research. Through integration with Isaac Lab, Wheeled Lab introduces modern techniques in Sim2Real, such as domain randomization, sensor simulation, and end-to-end learning, to new user communities. To kickstart education and demonstrate the framework's capabilities, we develop three state-of-the-art policies for small-scale RC cars: controlled drifting, elevation traversal, and visual navigation, each trained in simulation and deployed in the real world. By bridging the gap between advanced Sim2Real methods and affordable, available robotics, Wheeled Lab aims to democratize access to cutting-edge tools, fostering innovation and education in a broader robotics context. The full stack, from hardware to software, is low cost and open-source.
Dynamic Non-Prehensile Object Transport via Model-Predictive Reinforcement Learning
Nov 27, 2024



Abstract:We investigate the problem of teaching a robot manipulator to perform dynamic non-prehensile object transport, also known as the `robot waiter' task, from a limited set of real-world demonstrations. We propose an approach that combines batch reinforcement learning (RL) with model-predictive control (MPC) by pretraining an ensemble of value functions from demonstration data, and utilizing them online within an uncertainty-aware MPC scheme to ensure robustness to limited data coverage. Our approach is straightforward to integrate with off-the-shelf MPC frameworks and enables learning solely from task space demonstrations with sparsely labeled transitions, while leveraging MPC to ensure smooth joint space motions and constraint satisfaction. We validate the proposed approach through extensive simulated and real-world experiments on a Franka Panda robot performing the robot waiter task and demonstrate robust deployment of value functions learned from 50-100 demonstrations. Furthermore, our approach enables generalization to novel objects not seen during training and can improve upon suboptimal demonstrations. We believe that such a framework can reduce the burden of providing extensive demonstrations and facilitate rapid training of robot manipulators to perform non-prehensile manipulation tasks. Project videos and supplementary material can be found at: https://sites.google.com/view/cvmpc.
Sparsh: Self-supervised touch representations for vision-based tactile sensing
Oct 31, 2024Abstract:In this work, we introduce general purpose touch representations for the increasingly accessible class of vision-based tactile sensors. Such sensors have led to many recent advances in robot manipulation as they markedly complement vision, yet solutions today often rely on task and sensor specific handcrafted perception models. Collecting real data at scale with task centric ground truth labels, like contact forces and slip, is a challenge further compounded by sensors of various form factor differing in aspects like lighting and gel markings. To tackle this we turn to self-supervised learning (SSL) that has demonstrated remarkable performance in computer vision. We present Sparsh, a family of SSL models that can support various vision-based tactile sensors, alleviating the need for custom labels through pre-training on 460k+ tactile images with masking and self-distillation in pixel and latent spaces. We also build TacBench, to facilitate standardized benchmarking across sensors and models, comprising of six tasks ranging from comprehending tactile properties to enabling physical perception and manipulation planning. In evaluations, we find that SSL pre-training for touch representation outperforms task and sensor-specific end-to-end training by 95.1% on average over TacBench, and Sparsh (DINO) and Sparsh (IJEPA) are the most competitive, indicating the merits of learning in latent space for tactile images. Project page: https://sparsh-ssl.github.io/
Overcoming the Sim-to-Real Gap: Leveraging Simulation to Learn to Explore for Real-World RL
Oct 26, 2024



Abstract:In order to mitigate the sample complexity of real-world reinforcement learning, common practice is to first train a policy in a simulator where samples are cheap, and then deploy this policy in the real world, with the hope that it generalizes effectively. Such \emph{direct sim2real} transfer is not guaranteed to succeed, however, and in cases where it fails, it is unclear how to best utilize the simulator. In this work, we show that in many regimes, while direct sim2real transfer may fail, we can utilize the simulator to learn a set of \emph{exploratory} policies which enable efficient exploration in the real world. In particular, in the setting of low-rank MDPs, we show that coupling these exploratory policies with simple, practical approaches -- least-squares regression oracles and naive randomized exploration -- yields a polynomial sample complexity in the real world, an exponential improvement over direct sim2real transfer, or learning without access to a simulator. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first evidence that simulation transfer yields a provable gain in reinforcement learning in settings where direct sim2real transfer fails. We validate our theoretical results on several realistic robotic simulators and a real-world robotic sim2real task, demonstrating that transferring exploratory policies can yield substantial gains in practice as well.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge