Rohan Panicker
Dynamics Models in the Aggressive Off-Road Driving Regime
May 26, 2024



Abstract:Current developments in autonomous off-road driving are steadily increasing performance through higher speeds and more challenging, unstructured environments. However, this operating regime subjects the vehicle to larger inertial effects, where consideration of higher-order states is necessary to avoid failures such as rollovers or excessive impact forces. Aggressive driving through Model Predictive Control (MPC) in these conditions requires dynamics models that accurately predict safety-critical information. This work aims to empirically quantify this aggressive operating regime and its effects on the performance of current models. We evaluate three dynamics models of varying complexity on two distinct off-road driving datasets: one simulated and the other real-world. By conditioning trajectory data on higher-order states, we show that model accuracy degrades with aggressiveness and simpler models degrade faster. These models are also validated across datasets, where accuracies over safety-critical states are reported and provide benchmarks for future work.
Voice Controlled Upper Body Exoskeleton: A Development For Industrial Application
Sep 17, 2020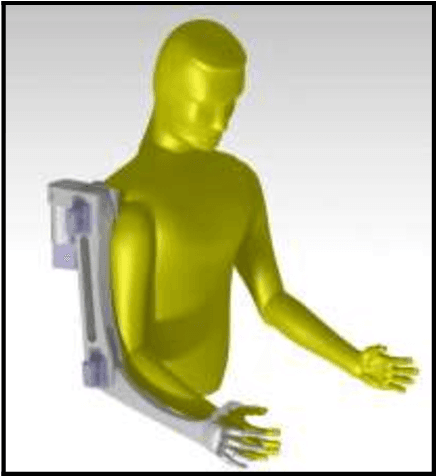
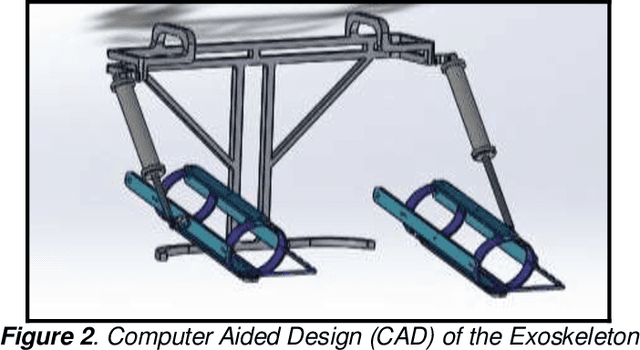
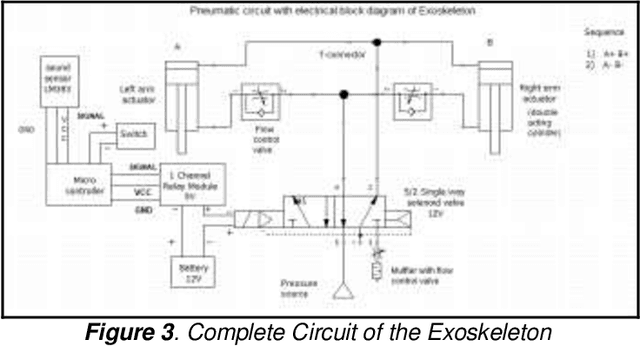

Abstract:An exoskeleton is a wearable electromechanical structure that is intended to resemble and allow movements in a manner similar to the human skeletal system. They can be used by both disabled and able people alike to increase physical strength in carrying out tasks that would be otherwise difficult, or as a rehabilitation device to aid in physiotherapeutic activities of a weakened body part. This paper intends to introduce a voicecontrolled upper body exoskeleton for industrial applications which can aid workers wearing it by reducing stresses on their arms and shoulders over longer periods and add up to 20kg more strength in lifting applications. The 3D design, calculations and considerations, and load analysis are presented along with brief results of a basic prototype model of the exoskeleton.
* 6 pages, 15 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge