Tyler Han
Demonstrating Wheeled Lab: Modern Sim2Real for Low-cost, Open-source Wheeled Robotics
Feb 11, 2025
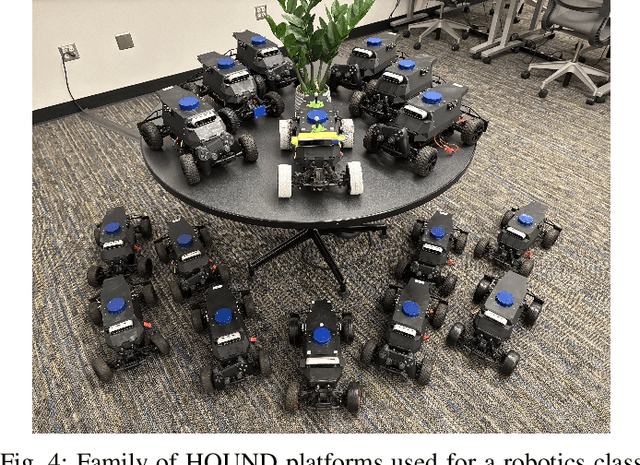
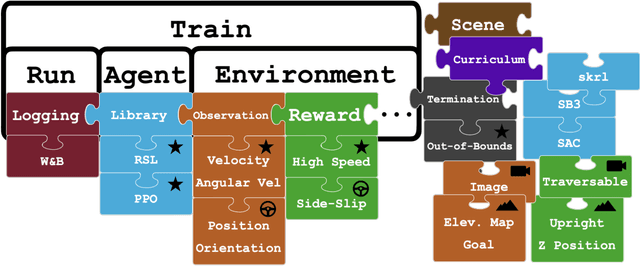

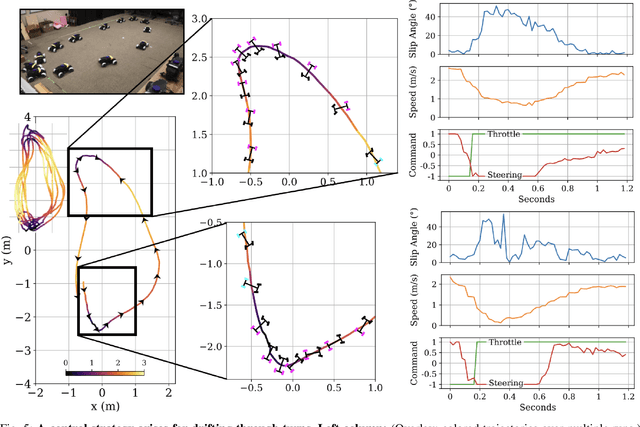
Abstract:Simulation has been pivotal in recent robotics milestones and is poised to play a prominent role in the field's future. However, recent robotic advances often rely on expensive and high-maintenance platforms, limiting access to broader robotics audiences. This work introduces Wheeled Lab, a framework for the low-cost, open-source wheeled platforms that are already widely established in education and research. Through integration with Isaac Lab, Wheeled Lab introduces modern techniques in Sim2Real, such as domain randomization, sensor simulation, and end-to-end learning, to new user communities. To kickstart education and demonstrate the framework's capabilities, we develop three state-of-the-art policies for small-scale RC cars: controlled drifting, elevation traversal, and visual navigation, each trained in simulation and deployed in the real world. By bridging the gap between advanced Sim2Real methods and affordable, available robotics, Wheeled Lab aims to democratize access to cutting-edge tools, fostering innovation and education in a broader robotics context. The full stack, from hardware to software, is low cost and open-source.
Dynamics Models in the Aggressive Off-Road Driving Regime
May 26, 2024



Abstract:Current developments in autonomous off-road driving are steadily increasing performance through higher speeds and more challenging, unstructured environments. However, this operating regime subjects the vehicle to larger inertial effects, where consideration of higher-order states is necessary to avoid failures such as rollovers or excessive impact forces. Aggressive driving through Model Predictive Control (MPC) in these conditions requires dynamics models that accurately predict safety-critical information. This work aims to empirically quantify this aggressive operating regime and its effects on the performance of current models. We evaluate three dynamics models of varying complexity on two distinct off-road driving datasets: one simulated and the other real-world. By conditioning trajectory data on higher-order states, we show that model accuracy degrades with aggressiveness and simpler models degrade faster. These models are also validated across datasets, where accuracies over safety-critical states are reported and provide benchmarks for future work.
Transferable Reinforcement Learning via Generalized Occupancy Models
Mar 10, 2024Abstract:Intelligent agents must be generalists - showing the ability to quickly adapt and generalize to varying tasks. Within the framework of reinforcement learning (RL), model-based RL algorithms learn a task-agnostic dynamics model of the world, in principle allowing them to generalize to arbitrary rewards. However, one-step models naturally suffer from compounding errors, making them ineffective for problems with long horizons and large state spaces. In this work, we propose a novel class of models - generalized occupancy models (GOMs) - that retain the generality of model-based RL while avoiding compounding error. The key idea behind GOMs is to model the distribution of all possible long-term outcomes from a given state under the coverage of a stationary dataset, along with a policy that realizes a particular outcome from the given state. These models can then quickly be used to select the optimal action for arbitrary new tasks, without having to redo policy optimization. By directly modeling long-term outcomes, GOMs avoid compounding error while retaining generality across arbitrary reward functions. We provide a practical instantiation of GOMs using diffusion models and show its efficacy as a new class of transferable models, both theoretically and empirically across a variety of simulated robotics problems. Videos and code at https://weirdlabuw.github.io/gom/.
Deep Learning for Koopman-based Dynamic Movement Primitives
Dec 06, 2023Abstract:The challenge of teaching robots to perform dexterous manipulation, dynamic locomotion, or whole--body manipulation from a small number of demonstrations is an important research field that has attracted interest from across the robotics community. In this work, we propose a novel approach by joining the theories of Koopman Operators and Dynamic Movement Primitives to Learning from Demonstration. Our approach, named \gls{admd}, projects nonlinear dynamical systems into linear latent spaces such that a solution reproduces the desired complex motion. Use of an autoencoder in our approach enables generalizability and scalability, while the constraint to a linear system attains interpretability. Our results are comparable to the Extended Dynamic Mode Decomposition on the LASA Handwriting dataset but with training on only a small fractions of the letters.
Model Predictive Control for Aggressive Driving Over Uneven Terrain
Nov 21, 2023



Abstract:Terrain traversability in off-road autonomy has traditionally relied on semantic classification or resource-intensive dynamics models to capture vehicle-terrain interactions. However, our experiences in the development of a high-speed off-road platform have revealed several critical challenges that are not adequately addressed by current methods at our operating speeds of 7--10 m/s. This study focuses particularly on uneven terrain geometries such as hills, banks, and ditches. These common high-risk geometries are capable of disabling the vehicle and causing severe passenger injuries if poorly traversed. We introduce a physics-based framework for identifying traversability constraints on terrain dynamics. Using this framework, we then derive two fundamental constraints, with a primary focus on mitigating rollover and ditch-crossing failures. In addition, we present the design of our planning and control system, which uses Model Predictive Control (MPC) and a low-level controller to enable the fast and efficient computation of these constraints to meet the demands of our aggressive driving. Through real-world experimentation and traversal of hills and ditches, our approach is tested and benchmarked against a human expert. These results demonstrate that our approach captures fundamental elements of safe and aggressive control on these terrain features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge