Brian Ichter
$π^{*}_{0.6}$: a VLA That Learns From Experience
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:We study how vision-language-action (VLA) models can improve through real-world deployments via reinforcement learning (RL). We present a general-purpose method, RL with Experience and Corrections via Advantage-conditioned Policies (RECAP), that provides for RL training of VLAs via advantage conditioning. Our method incorporates heterogeneous data into the self-improvement process, including demonstrations, data from on-policy collection, and expert teleoperated interventions provided during autonomous execution. RECAP starts by pre-training a generalist VLA with offline RL, which we call $π^{*}_{0.6}$, that can then be specialized to attain high performance on downstream tasks through on-robot data collection. We show that the $π^{*}_{0.6}$ model trained with the full RECAP method can fold laundry in real homes, reliably assemble boxes, and make espresso drinks using a professional espresso machine. On some of the hardest tasks, RECAP more than doubles task throughput and roughly halves the task failure rate.
Knowledge Insulating Vision-Language-Action Models: Train Fast, Run Fast, Generalize Better
May 29, 2025Abstract:Vision-language-action (VLA) models provide a powerful approach to training control policies for physical systems, such as robots, by combining end-to-end learning with transfer of semantic knowledge from web-scale vision-language model (VLM) training. However, the constraints of real-time control are often at odds with the design of VLMs: the most powerful VLMs have tens or hundreds of billions of parameters, presenting an obstacle to real-time inference, and operate on discrete tokens rather than the continuous-valued outputs that are required for controlling robots. To address this challenge, recent VLA models have used specialized modules for efficient continuous control, such as action experts or continuous output heads, which typically require adding new untrained parameters to the pretrained VLM backbone. While these modules improve real-time and control capabilities, it remains an open question whether they preserve or degrade the semantic knowledge contained in the pretrained VLM, and what effect they have on the VLA training dynamics. In this paper, we study this question in the context of VLAs that include a continuous diffusion or flow matching action expert, showing that naively including such experts significantly harms both training speed and knowledge transfer. We provide an extensive analysis of various design choices, their impact on performance and knowledge transfer, and propose a technique for insulating the VLM backbone during VLA training that mitigates this issue. Videos are available at https://pi.website/research/knowledge_insulation.
$π_{0.5}$: a Vision-Language-Action Model with Open-World Generalization
Apr 22, 2025



Abstract:In order for robots to be useful, they must perform practically relevant tasks in the real world, outside of the lab. While vision-language-action (VLA) models have demonstrated impressive results for end-to-end robot control, it remains an open question how far such models can generalize in the wild. We describe $\pi_{0.5}$, a new model based on $\pi_{0}$ that uses co-training on heterogeneous tasks to enable broad generalization. $\pi_{0.5}$\ uses data from multiple robots, high-level semantic prediction, web data, and other sources to enable broadly generalizable real-world robotic manipulation. Our system uses a combination of co-training and hybrid multi-modal examples that combine image observations, language commands, object detections, semantic subtask prediction, and low-level actions. Our experiments show that this kind of knowledge transfer is essential for effective generalization, and we demonstrate for the first time that an end-to-end learning-enabled robotic system can perform long-horizon and dexterous manipulation skills, such as cleaning a kitchen or bedroom, in entirely new homes.
Hi Robot: Open-Ended Instruction Following with Hierarchical Vision-Language-Action Models
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Generalist robots that can perform a range of different tasks in open-world settings must be able to not only reason about the steps needed to accomplish their goals, but also process complex instructions, prompts, and even feedback during task execution. Intricate instructions (e.g., "Could you make me a vegetarian sandwich?" or "I don't like that one") require not just the ability to physically perform the individual steps, but the ability to situate complex commands and feedback in the physical world. In this work, we describe a system that uses vision-language models in a hierarchical structure, first reasoning over complex prompts and user feedback to deduce the most appropriate next step to fulfill the task, and then performing that step with low-level actions. In contrast to direct instruction following methods that can fulfill simple commands ("pick up the cup"), our system can reason through complex prompts and incorporate situated feedback during task execution ("that's not trash"). We evaluate our system across three robotic platforms, including single-arm, dual-arm, and dual-arm mobile robots, demonstrating its ability to handle tasks such as cleaning messy tables, making sandwiches, and grocery shopping.
FAST: Efficient Action Tokenization for Vision-Language-Action Models
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:Autoregressive sequence models, such as Transformer-based vision-language action (VLA) policies, can be tremendously effective for capturing complex and generalizable robotic behaviors. However, such models require us to choose a tokenization of our continuous action signals, which determines how the discrete symbols predicted by the model map to continuous robot actions. We find that current approaches for robot action tokenization, based on simple per-dimension, per-timestep binning schemes, typically perform poorly when learning dexterous skills from high-frequency robot data. To address this challenge, we propose a new compression-based tokenization scheme for robot actions, based on the discrete cosine transform. Our tokenization approach, Frequency-space Action Sequence Tokenization (FAST), enables us to train autoregressive VLAs for highly dexterous and high-frequency tasks where standard discretization methods fail completely. Based on FAST, we release FAST+, a universal robot action tokenizer, trained on 1M real robot action trajectories. It can be used as a black-box tokenizer for a wide range of robot action sequences, with diverse action spaces and control frequencies. Finally, we show that, when combined with the pi0 VLA, our method can scale to training on 10k hours of robot data and match the performance of diffusion VLAs, while reducing training time by up to 5x.
Thinking Forward and Backward: Effective Backward Planning with Large Language Models
Nov 04, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have exhibited remarkable reasoning and planning capabilities. Most prior work in this area has used LLMs to reason through steps from an initial to a goal state or criterion, thereby effectively reasoning in a forward direction. Nonetheless, many planning problems exhibit an inherent asymmetry such that planning backward from the goal is significantly easier -- for example, if there are bottlenecks close to the goal. We take inspiration from this observation and demonstrate that this bias holds for LLM planning as well: planning performance in one direction correlates with the planning complexity of the problem in that direction. However, our experiments also reveal systematic biases which lead to poor planning in the backward direction. With this knowledge, we propose a backward planning algorithm for LLMs that first flips the problem and then plans forward in the flipped problem. This helps avoid the backward bias, generate more diverse candidate plans, and exploit asymmetries between the forward and backward directions in planning problems -- we find that combining planning in both directions with self-verification improves the overall planning success rates by 4-24% in three planning domains.
$π_0$: A Vision-Language-Action Flow Model for General Robot Control
Oct 31, 2024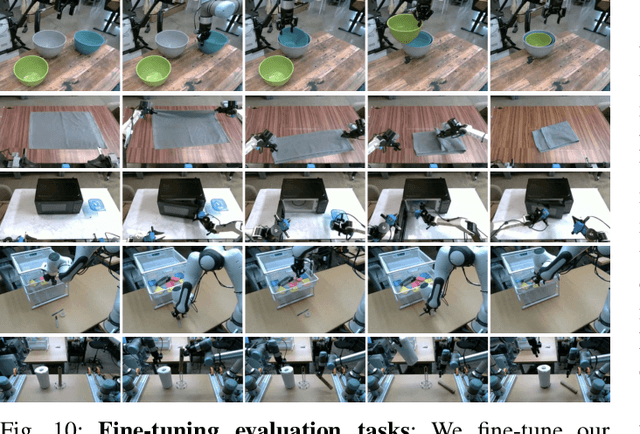
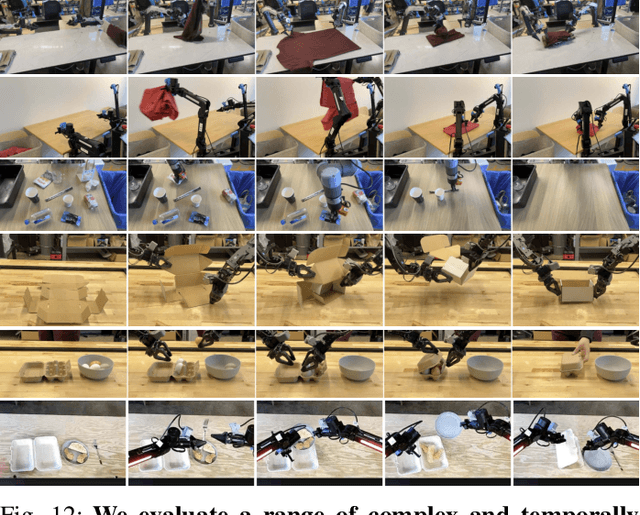
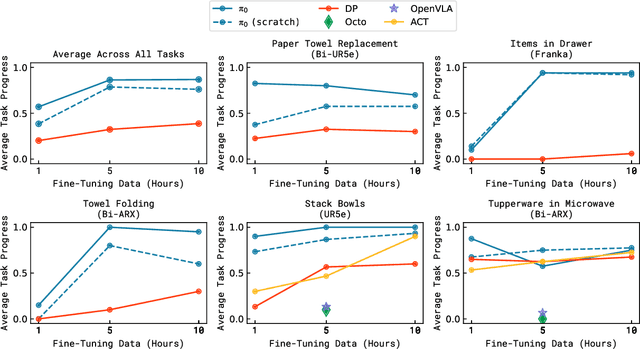

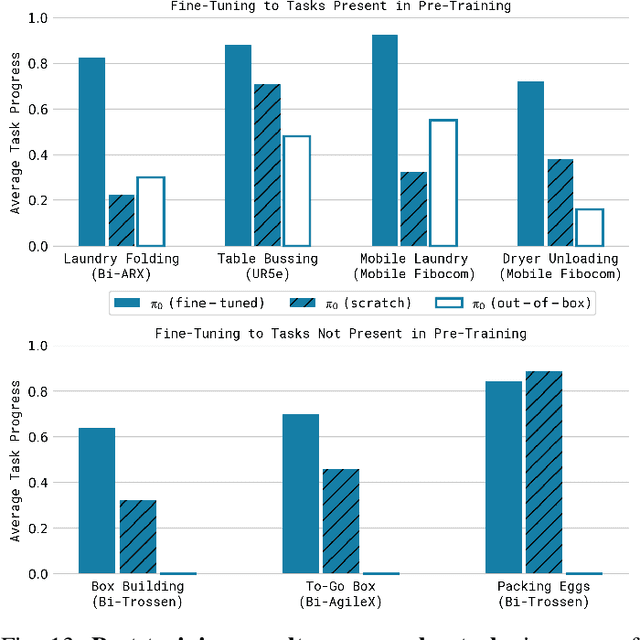
Abstract:Robot learning holds tremendous promise to unlock the full potential of flexible, general, and dexterous robot systems, as well as to address some of the deepest questions in artificial intelligence. However, bringing robot learning to the level of generality required for effective real-world systems faces major obstacles in terms of data, generalization, and robustness. In this paper, we discuss how generalist robot policies (i.e., robot foundation models) can address these challenges, and how we can design effective generalist robot policies for complex and highly dexterous tasks. We propose a novel flow matching architecture built on top of a pre-trained vision-language model (VLM) to inherit Internet-scale semantic knowledge. We then discuss how this model can be trained on a large and diverse dataset from multiple dexterous robot platforms, including single-arm robots, dual-arm robots, and mobile manipulators. We evaluate our model in terms of its ability to perform tasks in zero shot after pre-training, follow language instructions from people and from a high-level VLM policy, and its ability to acquire new skills via fine-tuning. Our results cover a wide variety of tasks, such as laundry folding, table cleaning, and assembling boxes.
Long-Horizon Planning for Multi-Agent Robots in Partially Observable Environments
Jul 14, 2024



Abstract:The ability of Language Models (LMs) to understand natural language makes them a powerful tool for parsing human instructions into task plans for autonomous robots. Unlike traditional planning methods that rely on domain-specific knowledge and handcrafted rules, LMs generalize from diverse data and adapt to various tasks with minimal tuning, acting as a compressed knowledge base. However, LMs in their standard form face challenges with long-horizon tasks, particularly in partially observable multi-agent settings. We propose an LM-based Long-Horizon Planner for Multi-Agent Robotics (LLaMAR), a cognitive architecture for planning that achieves state-of-the-art results in long-horizon tasks within partially observable environments. LLaMAR employs a plan-act-correct-verify framework, allowing self-correction from action execution feedback without relying on oracles or simulators. Additionally, we present MAP-THOR, a comprehensive test suite encompassing household tasks of varying complexity within the AI2-THOR environment. Experiments show that LLaMAR achieves a 30% higher success rate compared to other state-of-the-art LM-based multi-agent planners.
CoNVOI: Context-aware Navigation using Vision Language Models in Outdoor and Indoor Environments
Mar 22, 2024



Abstract:We present ConVOI, a novel method for autonomous robot navigation in real-world indoor and outdoor environments using Vision Language Models (VLMs). We employ VLMs in two ways: first, we leverage their zero-shot image classification capability to identify the context or scenario (e.g., indoor corridor, outdoor terrain, crosswalk, etc) of the robot's surroundings, and formulate context-based navigation behaviors as simple text prompts (e.g. ``stay on the pavement"). Second, we utilize their state-of-the-art semantic understanding and logical reasoning capabilities to compute a suitable trajectory given the identified context. To this end, we propose a novel multi-modal visual marking approach to annotate the obstacle-free regions in the RGB image used as input to the VLM with numbers, by correlating it with a local occupancy map of the environment. The marked numbers ground image locations in the real-world, direct the VLM's attention solely to navigable locations, and elucidate the spatial relationships between them and terrains depicted in the image to the VLM. Next, we query the VLM to select numbers on the marked image that satisfy the context-based behavior text prompt, and construct a reference path using the selected numbers. Finally, we propose a method to extrapolate the reference trajectory when the robot's environmental context has not changed to prevent unnecessary VLM queries. We use the reference trajectory to guide a motion planner, and demonstrate that it leads to human-like behaviors (e.g. not cutting through a group of people, using crosswalks, etc.) in various real-world indoor and outdoor scenarios.
Learning to Learn Faster from Human Feedback with Language Model Predictive Control
Feb 18, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been shown to exhibit a wide range of capabilities, such as writing robot code from language commands -- enabling non-experts to direct robot behaviors, modify them based on feedback, or compose them to perform new tasks. However, these capabilities (driven by in-context learning) are limited to short-term interactions, where users' feedback remains relevant for only as long as it fits within the context size of the LLM, and can be forgotten over longer interactions. In this work, we investigate fine-tuning the robot code-writing LLMs, to remember their in-context interactions and improve their teachability i.e., how efficiently they adapt to human inputs (measured by average number of corrections before the user considers the task successful). Our key observation is that when human-robot interactions are formulated as a partially observable Markov decision process (in which human language inputs are observations, and robot code outputs are actions), then training an LLM to complete previous interactions can be viewed as training a transition dynamics model -- that can be combined with classic robotics techniques such as model predictive control (MPC) to discover shorter paths to success. This gives rise to Language Model Predictive Control (LMPC), a framework that fine-tunes PaLM 2 to improve its teachability on 78 tasks across 5 robot embodiments -- improving non-expert teaching success rates of unseen tasks by 26.9% while reducing the average number of human corrections from 2.4 to 1.9. Experiments show that LMPC also produces strong meta-learners, improving the success rate of in-context learning new tasks on unseen robot embodiments and APIs by 31.5%. See videos, code, and demos at: https://robot-teaching.github.io/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge