3D Wireframe Reconstruction
Papers and Code
Flatten The Complex: Joint B-Rep Generation via Compositional $k$-Cell Particles
Jan 25, 2026Boundary Representation (B-Rep) is the widely adopted standard in Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and manufacturing. However, generative modeling of B-Reps remains a formidable challenge due to their inherent heterogeneity as geometric cell complexes, which entangles topology with geometry across cells of varying orders (i.e., $k$-cells such as vertices, edges, faces). Previous methods typically rely on cascaded sequences to handle this hierarchy, which fails to fully exploit the geometric relationships between cells, such as adjacency and sharing, limiting context awareness and error recovery. To fill this gap, we introduce a novel paradigm that reformulates B-Reps into sets of compositional $k$-cell particles. Our approach encodes each topological entity as a composition of particles, where adjacent cells share identical latents at their interfaces, thereby promoting geometric coupling along shared boundaries. By decoupling the rigid hierarchy, our representation unifies vertices, edges, and faces, enabling the joint generation of topology and geometry with global context awareness. We synthesize these particle sets using a multi-modal flow matching framework to handle unconditional generation as well as precise conditional tasks, such as 3D reconstruction from single-view or point cloud. Furthermore, the explicit and localized nature of our representation naturally extends to downstream tasks like local in-painting and enables the direct synthesis of non-manifold structures (e.g., wireframes). Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method produces high-fidelity CAD models with superior validity and editability compared to state-of-the-art methods.
CLR-Wire: Towards Continuous Latent Representations for 3D Curve Wireframe Generation
May 01, 2025We introduce CLR-Wire, a novel framework for 3D curve-based wireframe generation that integrates geometry and topology into a unified Continuous Latent Representation. Unlike conventional methods that decouple vertices, edges, and faces, CLR-Wire encodes curves as Neural Parametric Curves along with their topological connectivity into a continuous and fixed-length latent space using an attention-driven variational autoencoder (VAE). This unified approach facilitates joint learning and generation of both geometry and topology. To generate wireframes, we employ a flow matching model to progressively map Gaussian noise to these latents, which are subsequently decoded into complete 3D wireframes. Our method provides fine-grained modeling of complex shapes and irregular topologies, and supports both unconditional generation and generation conditioned on point cloud or image inputs. Experimental results demonstrate that, compared with state-of-the-art generative approaches, our method achieves substantial improvements in accuracy, novelty, and diversity, offering an efficient and comprehensive solution for CAD design, geometric reconstruction, and 3D content creation.
Img2CAD: Conditioned 3D CAD Model Generation from Single Image with Structured Visual Geometry
Oct 04, 2024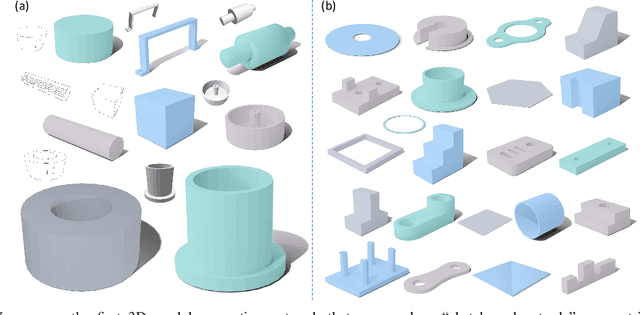
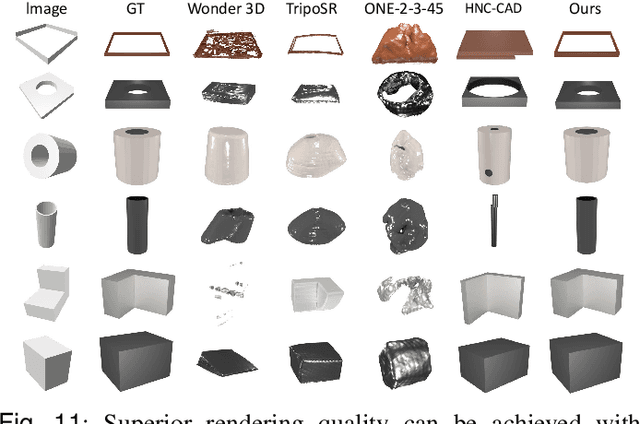
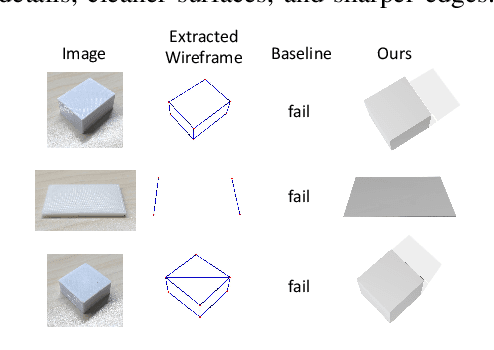

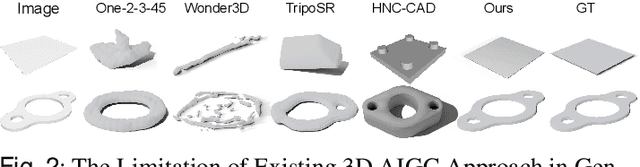
In this paper, we propose Img2CAD, the first approach to our knowledge that uses 2D image inputs to generate CAD models with editable parameters. Unlike existing AI methods for 3D model generation using text or image inputs often rely on mesh-based representations, which are incompatible with CAD tools and lack editability and fine control, Img2CAD enables seamless integration between AI-based 3D reconstruction and CAD software. We have identified an innovative intermediate representation called Structured Visual Geometry (SVG), characterized by vectorized wireframes extracted from objects. This representation significantly enhances the performance of generating conditioned CAD models. Additionally, we introduce two new datasets to further support research in this area: ABC-mono, the largest known dataset comprising over 200,000 3D CAD models with rendered images, and KOCAD, the first dataset featuring real-world captured objects alongside their ground truth CAD models, supporting further research in conditioned CAD model generation.
LRM-Zero: Training Large Reconstruction Models with Synthesized Data
Jun 13, 2024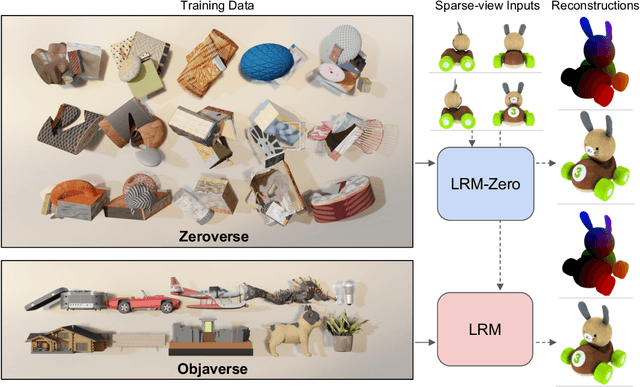
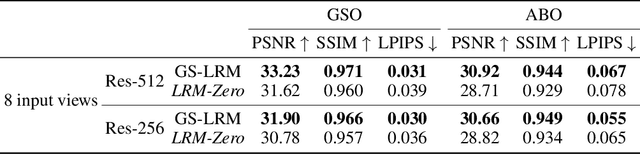
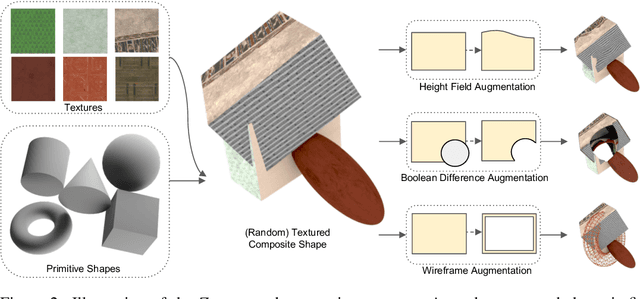
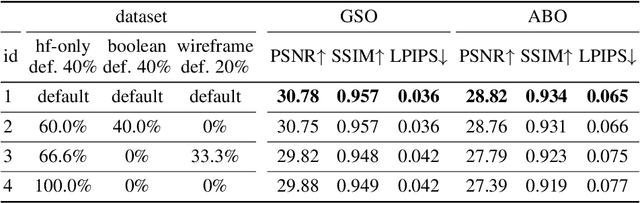
We present LRM-Zero, a Large Reconstruction Model (LRM) trained entirely on synthesized 3D data, achieving high-quality sparse-view 3D reconstruction. The core of LRM-Zero is our procedural 3D dataset, Zeroverse, which is automatically synthesized from simple primitive shapes with random texturing and augmentations (e.g., height fields, boolean differences, and wireframes). Unlike previous 3D datasets (e.g., Objaverse) which are often captured or crafted by humans to approximate real 3D data, Zeroverse completely ignores realistic global semantics but is rich in complex geometric and texture details that are locally similar to or even more intricate than real objects. We demonstrate that our LRM-Zero, trained with our fully synthesized Zeroverse, can achieve high visual quality in the reconstruction of real-world objects, competitive with models trained on Objaverse. We also analyze several critical design choices of Zeroverse that contribute to LRM-Zero's capability and training stability. Our work demonstrates that 3D reconstruction, one of the core tasks in 3D vision, can potentially be addressed without the semantics of real-world objects. The Zeroverse's procedural synthesis code and interactive visualization are available at: https://desaixie.github.io/lrm-zero/.
PBWR: Parametric Building Wireframe Reconstruction from Aerial LiDAR Point Clouds
Nov 18, 2023


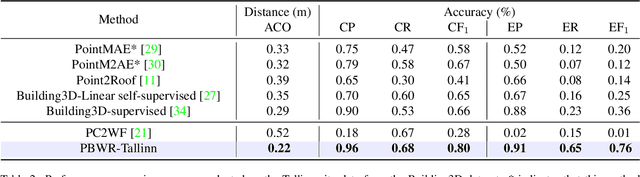
In this paper, we present an end-to-end 3D building wireframe reconstruction method to regress edges directly from aerial LiDAR point clouds.Our method, named Parametric Building Wireframe Reconstruction (PBWR), takes aerial LiDAR point clouds and initial edge entities as input, and fully uses self-attention mechanism of transformers to regress edge parameters without any intermediate steps such as corner prediction. We propose an edge non-maximum suppression (E-NMS) module based on edge similarityto remove redundant edges. Additionally, a dedicated edge loss function is utilized to guide the PBWR in regressing edges parameters, where simple use of edge distance loss isn't suitable. In our experiments, we demonstrate state-of-the-art results on the Building3D dataset, achieving an improvement of approximately 36% in entry-level dataset edge accuracy and around 42% improvement in the Tallinn dataset.
Learning to Construct 3D Building Wireframes from 3D Line Clouds
Aug 25, 2022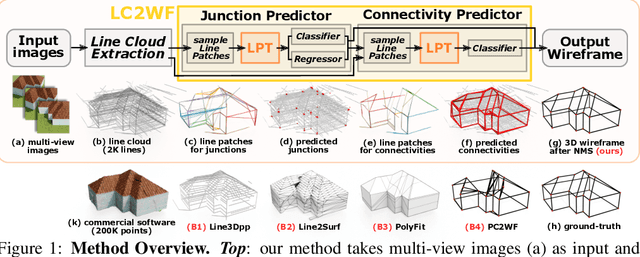
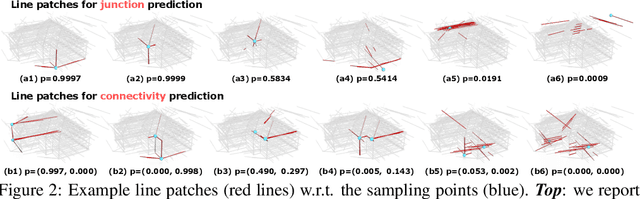
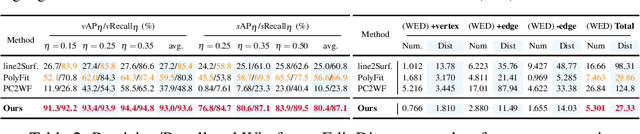
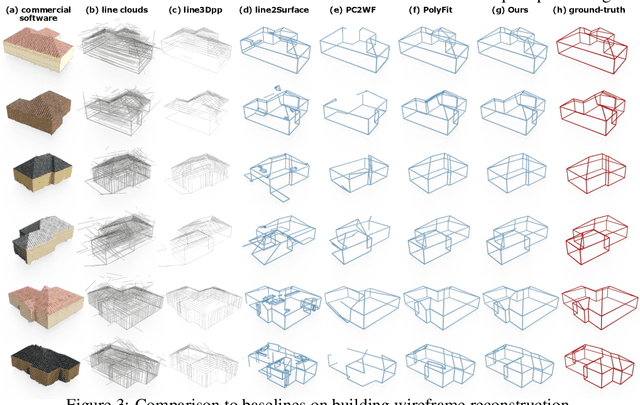
Line clouds, though under-investigated in the previous work, potentially encode more compact structural information of buildings than point clouds extracted from multi-view images. In this work, we propose the first network to process line clouds for building wireframe abstraction. The network takes a line cloud as input , i.e., a nonstructural and unordered set of 3D line segments extracted from multi-view images, and outputs a 3D wireframe of the underlying building, which consists of a sparse set of 3D junctions connected by line segments. We observe that a line patch, i.e., a group of neighboring line segments, encodes sufficient contour information to predict the existence and even the 3D position of a potential junction, as well as the likelihood of connectivity between two query junctions. We therefore introduce a two-layer Line-Patch Transformer to extract junctions and connectivities from sampled line patches to form a 3D building wireframe model. We also introduce a synthetic dataset of multi-view images with ground-truth 3D wireframe. We extensively justify that our reconstructed 3D wireframe models significantly improve upon multiple baseline building reconstruction methods.
HoW-3D: Holistic 3D Wireframe Perception from a Single Image
Aug 19, 2022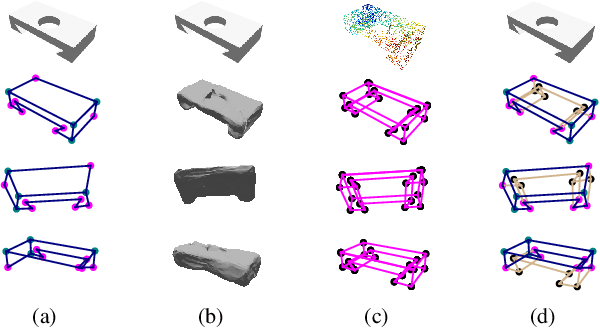
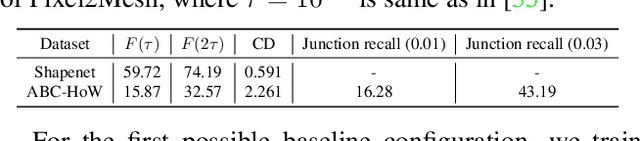
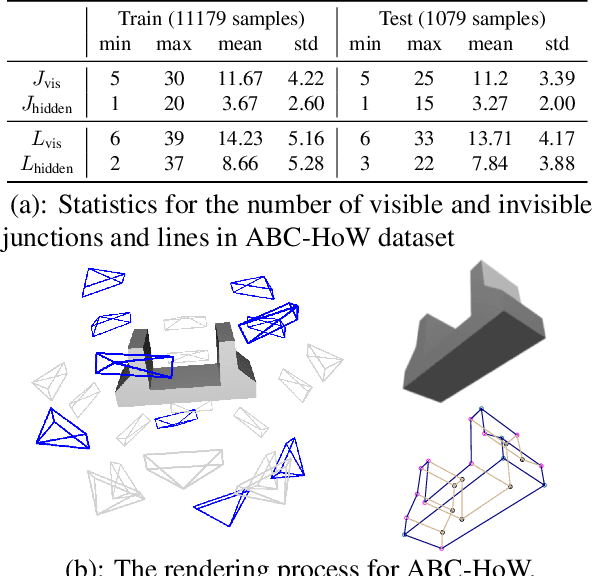
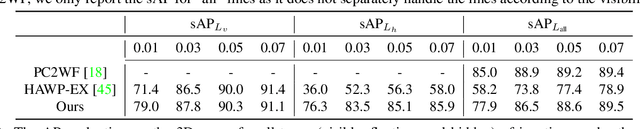
This paper studies the problem of holistic 3D wireframe perception (HoW-3D), a new task of perceiving both the visible 3D wireframes and the invisible ones from single-view 2D images. As the non-front surfaces of an object cannot be directly observed in a single view, estimating the non-line-of-sight (NLOS) geometries in HoW-3D is a fundamentally challenging problem and remains open in computer vision. We study the problem of HoW-3D by proposing an ABC-HoW benchmark, which is created on top of CAD models sourced from the ABC-dataset with 12k single-view images and the corresponding holistic 3D wireframe models. With our large-scale ABC-HoW benchmark available, we present a novel Deep Spatial Gestalt (DSG) model to learn the visible junctions and line segments as the basis and then infer the NLOS 3D structures from the visible cues by following the Gestalt principles of human vision systems. In our experiments, we demonstrate that our DSG model performs very well in inferring the holistic 3D wireframes from single-view images. Compared with the strong baseline methods, our DSG model outperforms the previous wireframe detectors in detecting the invisible line geometry in single-view images and is even very competitive with prior arts that take high-fidelity PointCloud as inputs on reconstructing 3D wireframes.
Detecting Line Segments in Motion-blurred Images with Events
Nov 20, 2022



Making line segment detectors more reliable under motion blurs is one of the most important challenges for practical applications, such as visual SLAM and 3D reconstruction. Existing line segment detection methods face severe performance degradation for accurately detecting and locating line segments when motion blur occurs. While event data shows strong complementary characteristics to images for minimal blur and edge awareness at high-temporal resolution, potentially beneficial for reliable line segment recognition. To robustly detect line segments over motion blurs, we propose to leverage the complementary information of images and events. To achieve this, we first design a general frame-event feature fusion network to extract and fuse the detailed image textures and low-latency event edges, which consists of a channel-attention-based shallow fusion module and a self-attention-based dual hourglass module. We then utilize two state-of-the-art wireframe parsing networks to detect line segments on the fused feature map. Besides, we contribute a synthetic and a realistic dataset for line segment detection, i.e., FE-Wireframe and FE-Blurframe, with pairwise motion-blurred images and events. Extensive experiments on both datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. When tested on the real dataset, our method achieves 63.3% mean structural average precision (msAP) with the model pre-trained on the FE-Wireframe and fine-tuned on the FE-Blurframe, improved by 32.6 and 11.3 points compared with models trained on synthetic only and real only, respectively. The codes, datasets, and trained models are released at: https://levenberg.github.io/FE-LSD
PC2WF: 3D Wireframe Reconstruction from Raw Point Clouds
Mar 04, 2021



We introduce PC2WF, the first end-to-end trainable deep network architecture to convert a 3D point cloud into a wireframe model. The network takes as input an unordered set of 3D points sampled from the surface of some object, and outputs a wireframe of that object, i.e., a sparse set of corner points linked by line segments. Recovering the wireframe is a challenging task, where the numbers of both vertices and edges are different for every instance, and a-priori unknown. Our architecture gradually builds up the model: It starts by encoding the points into feature vectors. Based on those features, it identifies a pool of candidate vertices, then prunes those candidates to a final set of corner vertices and refines their locations. Next, the corners are linked with an exhaustive set of candidate edges, which is again pruned to obtain the final wireframe. All steps are trainable, and errors can be backpropagated through the entire sequence. We validate the proposed model on a publicly available synthetic dataset, for which the ground truth wireframes are accessible, as well as on a new real-world dataset. Our model produces wireframe abstractions of good quality and outperforms several baselines.
Neural Face Identification in a 2D Wireframe Projection of a Manifold Object
Mar 08, 2022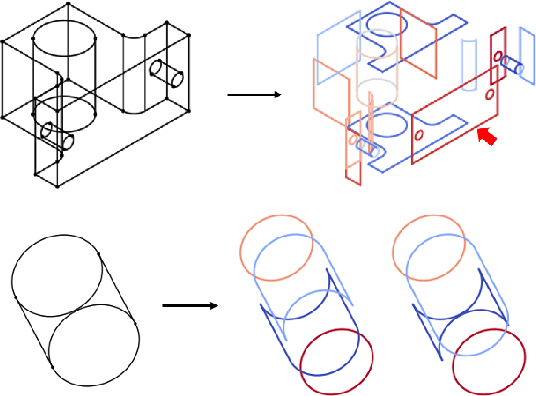

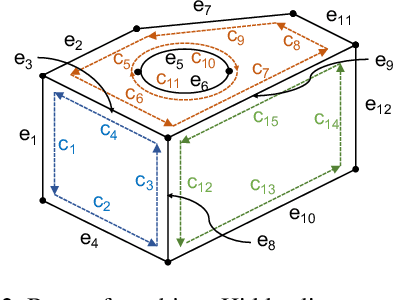
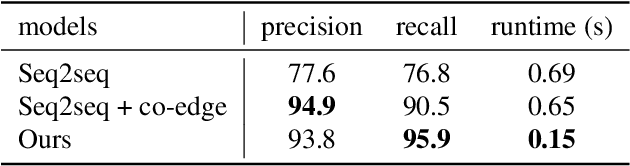
In computer-aided design (CAD) systems, 2D line drawings are commonly used to illustrate 3D object designs. To reconstruct the 3D models depicted by a single 2D line drawing, an important key is finding the edge loops in the line drawing which correspond to the actual faces of the 3D object. In this paper, we approach the classical problem of face identification from a novel data-driven point of view. We cast it as a sequence generation problem: starting from an arbitrary edge, we adopt a variant of the popular Transformer model to predict the edges associated with the same face in a natural order. This allows us to avoid searching the space of all possible edge loops with various hand-crafted rules and heuristics as most existing methods do, deal with challenging cases such as curved surfaces and nested edge loops, and leverage additional cues such as face types. We further discuss how possibly imperfect predictions can be used for 3D object reconstruction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge