Peter Wonka
KAUST
Geometry without Position? When Positional Embeddings Help and Hurt Spatial Reasoning
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:This paper revisits the role of positional embeddings (PEs) within vision transformers (ViTs) from a geometric perspective. We show that PEs are not mere token indices but effectively function as geometric priors that shape the spatial structure of the representation. We introduce token-level diagnostics that measure how multi-view geometric consistency in ViT representation depends on consitent PEs. Through extensive experiments on 14 foundation ViT models, we reveal how PEs influence multi-view geometry and spatial reasoning. Our findings clarify the role of PEs as a causal mechanism that governs spatial structure in ViT representations. Our code is provided in https://github.com/shijianjian/vit-geometry-probes
ATATA: One Algorithm to Align Them All
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:We suggest a new multi-modal algorithm for joint inference of paired structurally aligned samples with Rectified Flow models. While some existing methods propose a codependent generation process, they do not view the problem of joint generation from a structural alignment perspective. Recent work uses Score Distillation Sampling to generate aligned 3D models, but SDS is known to be time-consuming, prone to mode collapse, and often provides cartoonish results. By contrast, our suggested approach relies on the joint transport of a segment in the sample space, yielding faster computation at inference time. Our approach can be built on top of an arbitrary Rectified Flow model operating on the structured latent space. We show the applicability of our method to the domains of image, video, and 3D shape generation using state-of-the-art baselines and evaluate it against both editing-based and joint inference-based competing approaches. We demonstrate a high degree of structural alignment for the sample pairs obtained with our method and a high visual quality of the samples. Our method improves the state-of-the-art for image and video generation pipelines. For 3D generation, it is able to show comparable quality while working orders of magnitude faster.
PatchAlign3D: Local Feature Alignment for Dense 3D Shape understanding
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Current foundation models for 3D shapes excel at global tasks (retrieval, classification) but transfer poorly to local part-level reasoning. Recent approaches leverage vision and language foundation models to directly solve dense tasks through multi-view renderings and text queries. While promising, these pipelines require expensive inference over multiple renderings, depend heavily on large language-model (LLM) prompt engineering for captions, and fail to exploit the inherent 3D geometry of shapes. We address this gap by introducing an encoder-only 3D model that produces language-aligned patch-level features directly from point clouds. Our pre-training approach builds on existing data engines that generate part-annotated 3D shapes by pairing multi-view SAM regions with VLM captioning. Using this data, we train a point cloud transformer encoder in two stages: (1) distillation of dense 2D features from visual encoders such as DINOv2 into 3D patches, and (2) alignment of these patch embeddings with part-level text embeddings through a multi-positive contrastive objective. Our 3D encoder achieves zero-shot 3D part segmentation with fast single-pass inference without any test-time multi-view rendering, while significantly outperforming previous rendering-based and feed-forward approaches across several 3D part segmentation benchmarks. Project website: https://souhail-hadgi.github.io/patchalign3dsite/
EasyV2V: A High-quality Instruction-based Video Editing Framework
Dec 18, 2025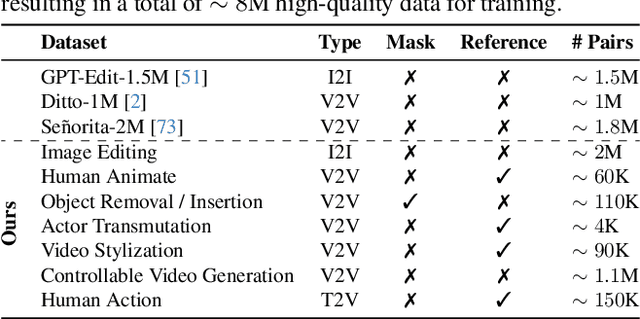

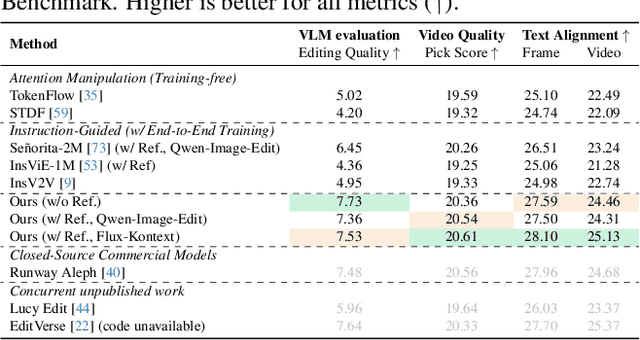
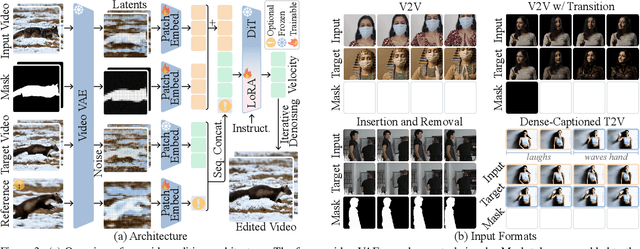
Abstract:While image editing has advanced rapidly, video editing remains less explored, facing challenges in consistency, control, and generalization. We study the design space of data, architecture, and control, and introduce \emph{EasyV2V}, a simple and effective framework for instruction-based video editing. On the data side, we compose existing experts with fast inverses to build diverse video pairs, lift image edit pairs into videos via single-frame supervision and pseudo pairs with shared affine motion, mine dense-captioned clips for video pairs, and add transition supervision to teach how edits unfold. On the model side, we observe that pretrained text-to-video models possess editing capability, motivating a simplified design. Simple sequence concatenation for conditioning with light LoRA fine-tuning suffices to train a strong model. For control, we unify spatiotemporal control via a single mask mechanism and support optional reference images. Overall, EasyV2V works with flexible inputs, e.g., video+text, video+mask+text, video+mask+reference+text, and achieves state-of-the-art video editing results, surpassing concurrent and commercial systems. Project page: https://snap-research.github.io/easyv2v/
PoseGAM: Robust Unseen Object Pose Estimation via Geometry-Aware Multi-View Reasoning
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:6D object pose estimation, which predicts the transformation of an object relative to the camera, remains challenging for unseen objects. Existing approaches typically rely on explicitly constructing feature correspondences between the query image and either the object model or template images. In this work, we propose PoseGAM, a geometry-aware multi-view framework that directly predicts object pose from a query image and multiple template images, eliminating the need for explicit matching. Built upon recent multi-view-based foundation model architectures, the method integrates object geometry information through two complementary mechanisms: explicit point-based geometry and learned features from geometry representation networks. In addition, we construct a large-scale synthetic dataset containing more than 190k objects under diverse environmental conditions to enhance robustness and generalization. Extensive evaluations across multiple benchmarks demonstrate our state-of-the-art performance, yielding an average AR improvement of 5.1% over prior methods and achieving up to 17.6% gains on individual datasets, indicating strong generalization to unseen objects. Project page: https://windvchen.github.io/PoseGAM/ .
Human Geometry Distribution for 3D Animation Generation
Dec 08, 2025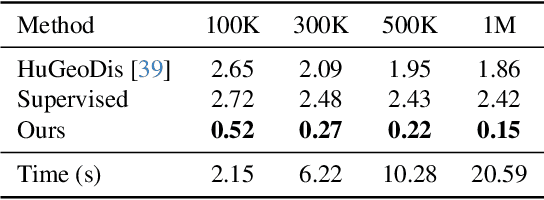
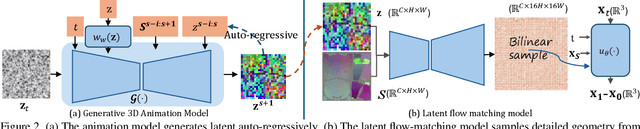
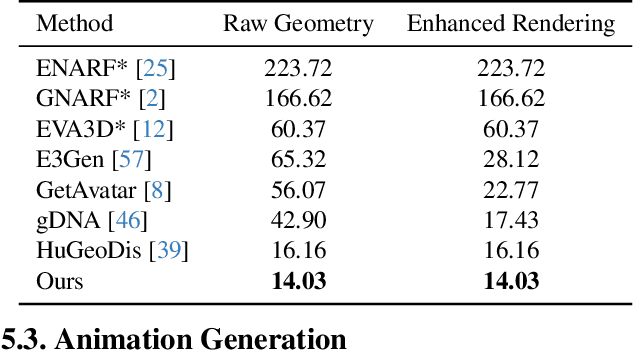
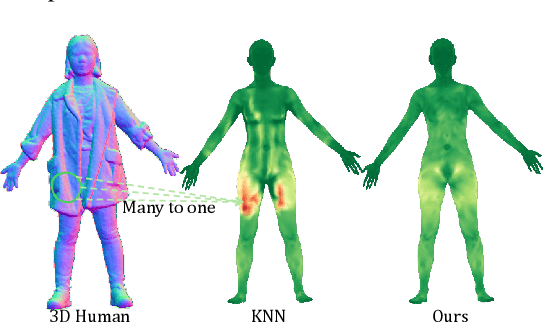
Abstract:Generating realistic human geometry animations remains a challenging task, as it requires modeling natural clothing dynamics with fine-grained geometric details under limited data. To address these challenges, we propose two novel designs. First, we propose a compact distribution-based latent representation that enables efficient and high-quality geometry generation. We improve upon previous work by establishing a more uniform mapping between SMPL and avatar geometries. Second, we introduce a generative animation model that fully exploits the diversity of limited motion data. We focus on short-term transitions while maintaining long-term consistency through an identity-conditioned design. These two designs formulate our method as a two-stage framework: the first stage learns a latent space, while the second learns to generate animations within this latent space. We conducted experiments on both our latent space and animation model. We demonstrate that our latent space produces high-fidelity human geometry surpassing previous methods ($90\%$ lower Chamfer Dist.). The animation model synthesizes diverse animations with detailed and natural dynamics ($2.2 \times$ higher user study score), achieving the best results across all evaluation metrics.
Mind-the-Glitch: Visual Correspondence for Detecting Inconsistencies in Subject-Driven Generation
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:We propose a novel approach for disentangling visual and semantic features from the backbones of pre-trained diffusion models, enabling visual correspondence in a manner analogous to the well-established semantic correspondence. While diffusion model backbones are known to encode semantically rich features, they must also contain visual features to support their image synthesis capabilities. However, isolating these visual features is challenging due to the absence of annotated datasets. To address this, we introduce an automated pipeline that constructs image pairs with annotated semantic and visual correspondences based on existing subject-driven image generation datasets, and design a contrastive architecture to separate the two feature types. Leveraging the disentangled representations, we propose a new metric, Visual Semantic Matching (VSM), that quantifies visual inconsistencies in subject-driven image generation. Empirical results show that our approach outperforms global feature-based metrics such as CLIP, DINO, and vision--language models in quantifying visual inconsistencies while also enabling spatial localization of inconsistent regions. To our knowledge, this is the first method that supports both quantification and localization of inconsistencies in subject-driven generation, offering a valuable tool for advancing this task. Project Page:https://abdo-eldesokey.github.io/mind-the-glitch/
PlanQA: A Benchmark for Spatial Reasoning in LLMs using Structured Representations
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:We introduce PlanQA, a diagnostic benchmark for evaluating geometric and spatial reasoning in large-language models (LLMs). PlanQA is grounded in structured representations of indoor scenes, such as kitchens, living rooms, and bedrooms, encoded in a symbolic format (e.g., JSON, XML layouts). The benchmark includes diverse question types that test not only metric and topological reasoning (e.g., distance, visibility, shortest paths) but also interior design constraints such as affordance, clearance, balance, and usability. Our results across a variety of frontier open-source and commercial LLMs show that while models may succeed in shallow queries, they often fail to simulate physical constraints, preserve spatial coherence, or generalize under layout perturbation. PlanQA uncovers a clear blind spot in today's LLMs: they do not consistently reason about real-world layouts. We hope that this benchmark inspires new work on language models that can accurately infer and manipulate spatial and geometric properties in practical settings.
efunc: An Efficient Function Representation without Neural Networks
May 27, 2025Abstract:Function fitting/approximation plays a fundamental role in computer graphics and other engineering applications. While recent advances have explored neural networks to address this task, these methods often rely on architectures with many parameters, limiting their practical applicability. In contrast, we pursue high-quality function approximation using parameter-efficient representations that eliminate the dependency on neural networks entirely. We first propose a novel framework for continuous function modeling. Most existing works can be formulated using this framework. We then introduce a compact function representation, which is based on polynomials interpolated using radial basis functions, bypassing both neural networks and complex/hierarchical data structures. We also develop memory-efficient CUDA-optimized algorithms that reduce computational time and memory consumption to less than 10% compared to conventional automatic differentiation frameworks. Finally, we validate our representation and optimization pipeline through extensive experiments on 3D signed distance functions (SDFs). The proposed representation achieves comparable or superior performance to state-of-the-art techniques (e.g., octree/hash-grid techniques) with significantly fewer parameters.
PlaceIt3D: Language-Guided Object Placement in Real 3D Scenes
May 08, 2025
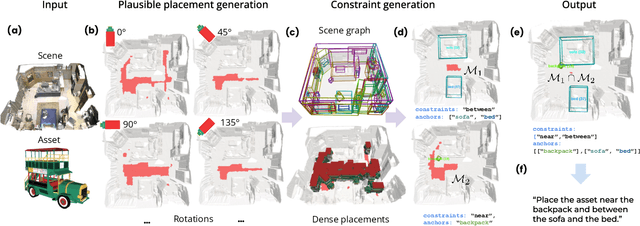
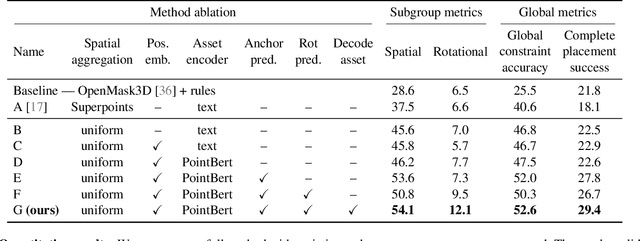
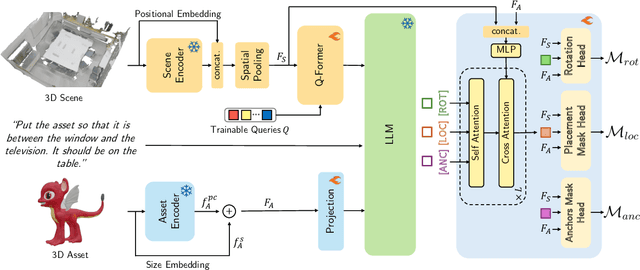
Abstract:We introduce the novel task of Language-Guided Object Placement in Real 3D Scenes. Our model is given a 3D scene's point cloud, a 3D asset, and a textual prompt broadly describing where the 3D asset should be placed. The task here is to find a valid placement for the 3D asset that respects the prompt. Compared with other language-guided localization tasks in 3D scenes such as grounding, this task has specific challenges: it is ambiguous because it has multiple valid solutions, and it requires reasoning about 3D geometric relationships and free space. We inaugurate this task by proposing a new benchmark and evaluation protocol. We also introduce a new dataset for training 3D LLMs on this task, as well as the first method to serve as a non-trivial baseline. We believe that this challenging task and our new benchmark could become part of the suite of benchmarks used to evaluate and compare generalist 3D LLM models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge