Wenchao Ma
KALAHash: Knowledge-Anchored Low-Resource Adaptation for Deep Hashing
Dec 27, 2024



Abstract:Deep hashing has been widely used for large-scale approximate nearest neighbor search due to its storage and search efficiency. However, existing deep hashing methods predominantly rely on abundant training data, leaving the more challenging scenario of low-resource adaptation for deep hashing relatively underexplored. This setting involves adapting pre-trained models to downstream tasks with only an extremely small number of training samples available. Our preliminary benchmarks reveal that current methods suffer significant performance degradation due to the distribution shift caused by limited training samples. To address these challenges, we introduce Class-Calibration LoRA (CLoRA), a novel plug-and-play approach that dynamically constructs low-rank adaptation matrices by leveraging class-level textual knowledge embeddings. CLoRA effectively incorporates prior class knowledge as anchors, enabling parameter-efficient fine-tuning while maintaining the original data distribution. Furthermore, we propose Knowledge-Guided Discrete Optimization (KIDDO), a framework to utilize class knowledge to compensate for the scarcity of visual information and enhance the discriminability of hash codes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed method, Knowledge- Anchored Low-Resource Adaptation Hashing (KALAHash), significantly boosts retrieval performance and achieves a 4x data efficiency in low-resource scenarios.
AAAR-1.0: Assessing AI's Potential to Assist Research
Oct 29, 2024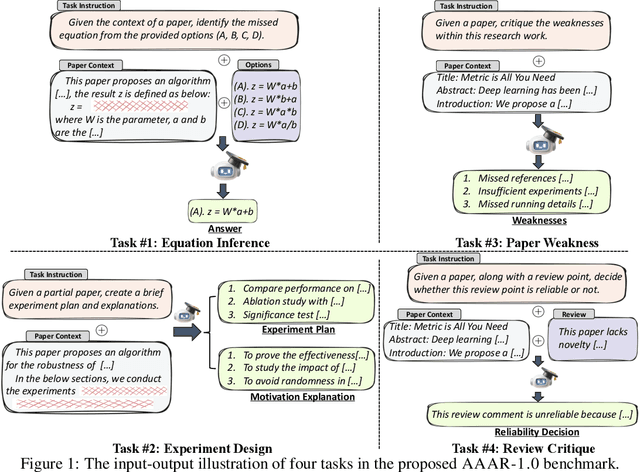
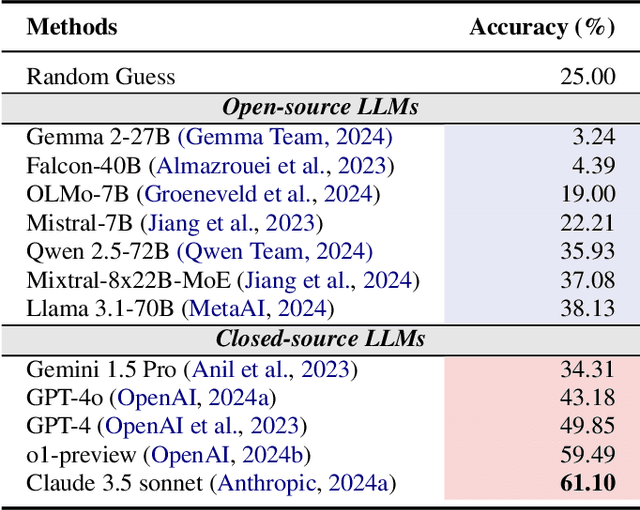
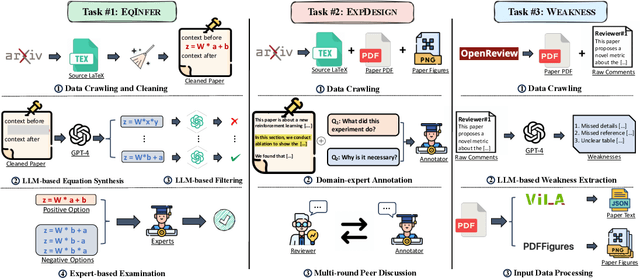
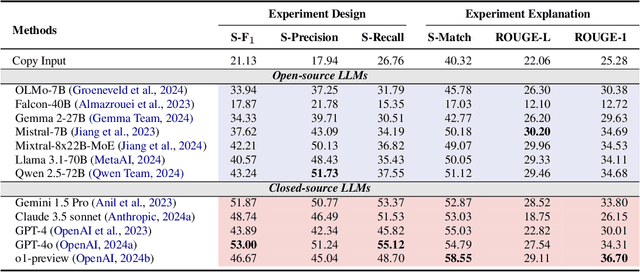
Abstract:Numerous studies have assessed the proficiency of AI systems, particularly large language models (LLMs), in facilitating everyday tasks such as email writing, question answering, and creative content generation. However, researchers face unique challenges and opportunities in leveraging LLMs for their own work, such as brainstorming research ideas, designing experiments, and writing or reviewing papers. In this study, we introduce AAAR-1.0, a benchmark dataset designed to evaluate LLM performance in three fundamental, expertise-intensive research tasks: (i) EquationInference, assessing the correctness of equations based on the contextual information in paper submissions; (ii) ExperimentDesign, designing experiments to validate research ideas and solutions; (iii) PaperWeakness, identifying weaknesses in paper submissions; and (iv) REVIEWCRITIQUE, identifying each segment in human reviews is deficient or not. AAAR-1.0 differs from prior benchmarks in two key ways: first, it is explicitly research-oriented, with tasks requiring deep domain expertise; second, it is researcher-oriented, mirroring the primary activities that researchers engage in on a daily basis. An evaluation of both open-source and proprietary LLMs reveals their potential as well as limitations in conducting sophisticated research tasks. We will keep iterating AAAR-1.0 to new versions.
Stratified Avatar Generation from Sparse Observations
Jun 03, 2024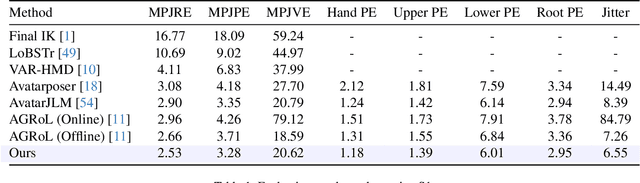
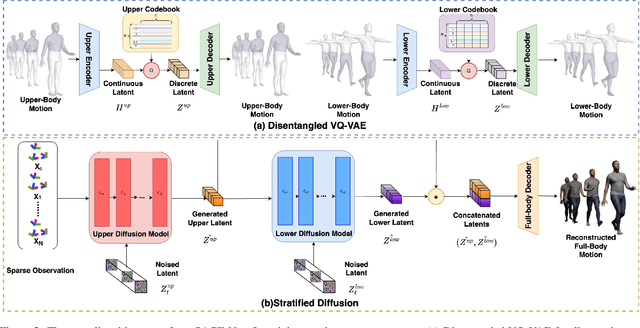
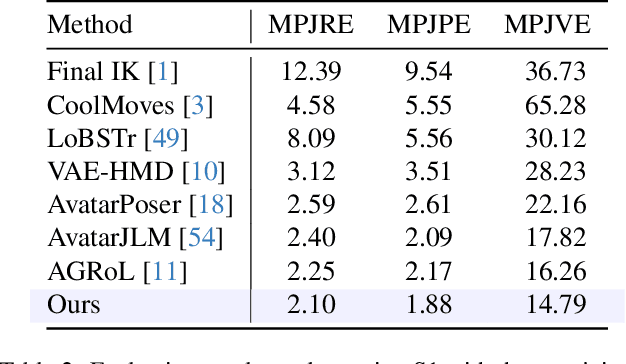
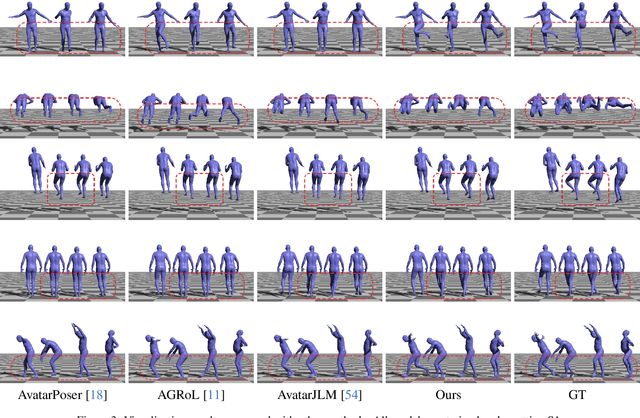
Abstract:Estimating 3D full-body avatars from AR/VR devices is essential for creating immersive experiences in AR/VR applications. This task is challenging due to the limited input from Head Mounted Devices, which capture only sparse observations from the head and hands. Predicting the full-body avatars, particularly the lower body, from these sparse observations presents significant difficulties. In this paper, we are inspired by the inherent property of the kinematic tree defined in the Skinned Multi-Person Linear (SMPL) model, where the upper body and lower body share only one common ancestor node, bringing the potential of decoupled reconstruction. We propose a stratified approach to decouple the conventional full-body avatar reconstruction pipeline into two stages, with the reconstruction of the upper body first and a subsequent reconstruction of the lower body conditioned on the previous stage. To implement this straightforward idea, we leverage the latent diffusion model as a powerful probabilistic generator, and train it to follow the latent distribution of decoupled motions explored by a VQ-VAE encoder-decoder model. Extensive experiments on AMASS mocap dataset demonstrate our state-of-the-art performance in the reconstruction of full-body motions.
GaussianFlow: Splatting Gaussian Dynamics for 4D Content Creation
Mar 19, 2024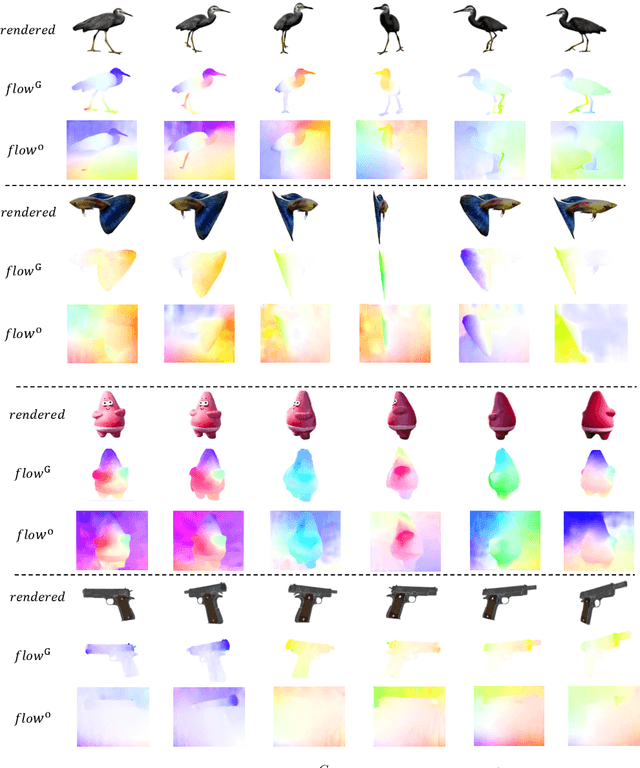
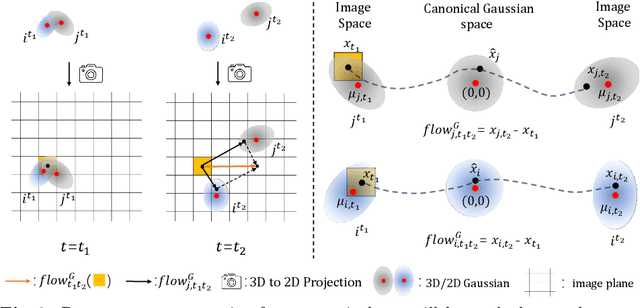
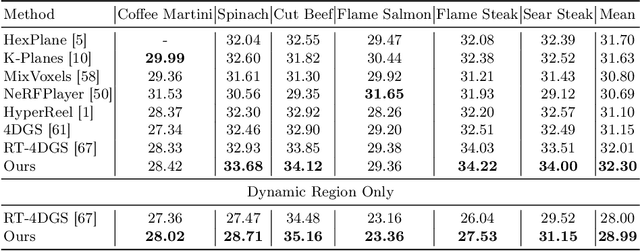
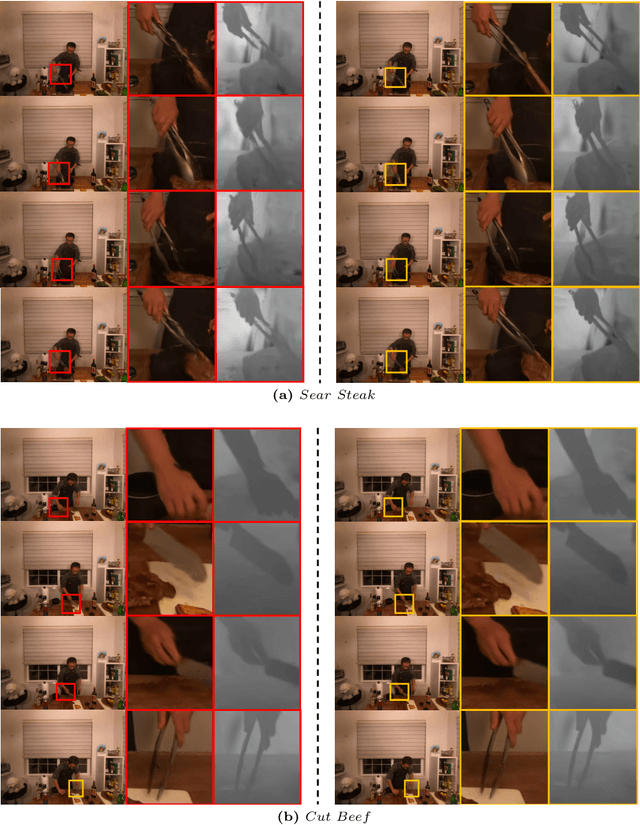
Abstract:Creating 4D fields of Gaussian Splatting from images or videos is a challenging task due to its under-constrained nature. While the optimization can draw photometric reference from the input videos or be regulated by generative models, directly supervising Gaussian motions remains underexplored. In this paper, we introduce a novel concept, Gaussian flow, which connects the dynamics of 3D Gaussians and pixel velocities between consecutive frames. The Gaussian flow can be efficiently obtained by splatting Gaussian dynamics into the image space. This differentiable process enables direct dynamic supervision from optical flow. Our method significantly benefits 4D dynamic content generation and 4D novel view synthesis with Gaussian Splatting, especially for contents with rich motions that are hard to be handled by existing methods. The common color drifting issue that happens in 4D generation is also resolved with improved Guassian dynamics. Superior visual quality on extensive experiments demonstrates our method's effectiveness. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations show that our method achieves state-of-the-art results on both tasks of 4D generation and 4D novel view synthesis. Project page: https://zerg-overmind.github.io/GaussianFlow.github.io/
HoW-3D: Holistic 3D Wireframe Perception from a Single Image
Aug 19, 2022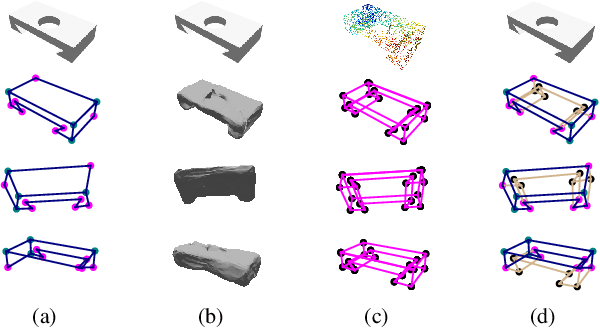
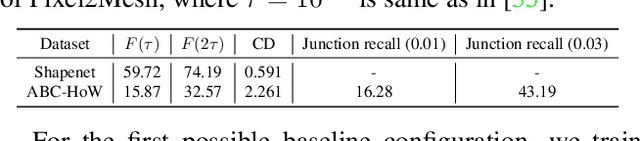
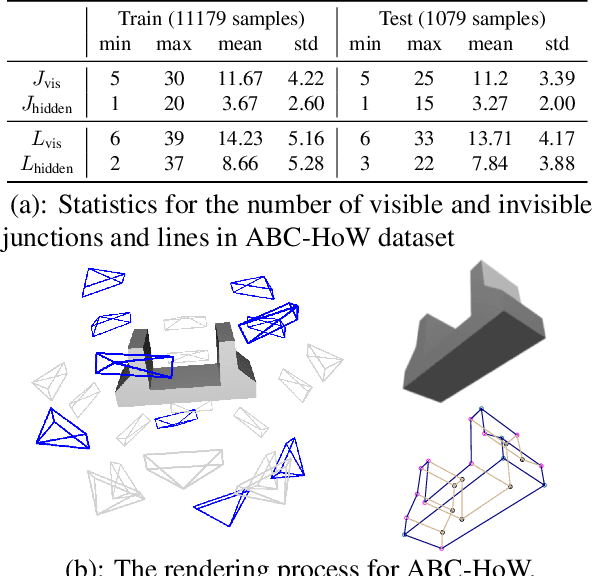
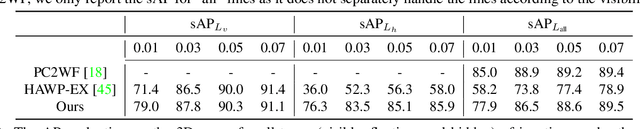
Abstract:This paper studies the problem of holistic 3D wireframe perception (HoW-3D), a new task of perceiving both the visible 3D wireframes and the invisible ones from single-view 2D images. As the non-front surfaces of an object cannot be directly observed in a single view, estimating the non-line-of-sight (NLOS) geometries in HoW-3D is a fundamentally challenging problem and remains open in computer vision. We study the problem of HoW-3D by proposing an ABC-HoW benchmark, which is created on top of CAD models sourced from the ABC-dataset with 12k single-view images and the corresponding holistic 3D wireframe models. With our large-scale ABC-HoW benchmark available, we present a novel Deep Spatial Gestalt (DSG) model to learn the visible junctions and line segments as the basis and then infer the NLOS 3D structures from the visible cues by following the Gestalt principles of human vision systems. In our experiments, we demonstrate that our DSG model performs very well in inferring the holistic 3D wireframes from single-view images. Compared with the strong baseline methods, our DSG model outperforms the previous wireframe detectors in detecting the invisible line geometry in single-view images and is even very competitive with prior arts that take high-fidelity PointCloud as inputs on reconstructing 3D wireframes.
Inverse-Designed Meta-Optics with Spectral-Spatial Engineered Response to Mimic Color Perception
Apr 28, 2022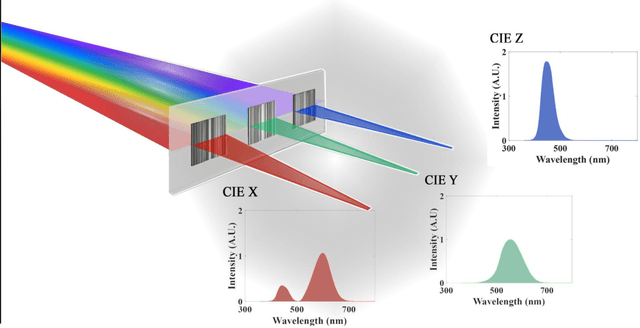
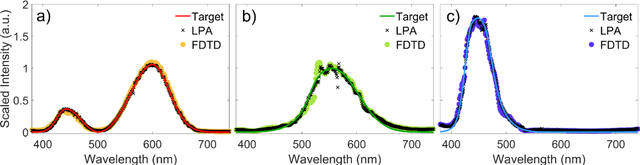
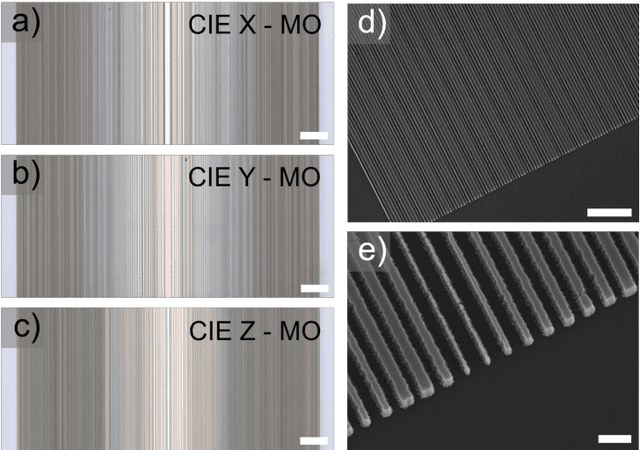
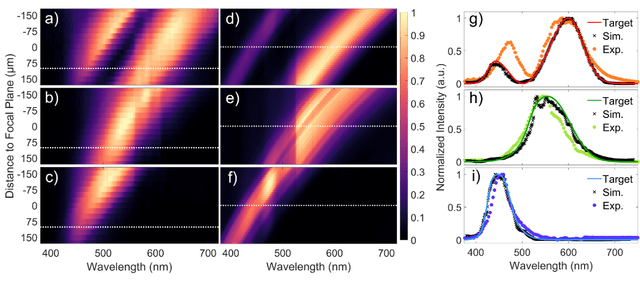
Abstract:Meta-optics have rapidly become a major research field within the optics and photonics community, strongly driven by the seemingly limitless opportunities made possible by controlling optical wavefronts through interaction with arrays of sub-wavelength scatterers. As more and more modalities are explored, the design strategies to achieve desired functionalities become increasingly demanding, necessitating more advanced design techniques. Herein, the inverse-design approach is utilized to create a set of single-layer meta-optics that simultaneously focus light and shape the spectra of focused light without using any filters. Thus, both spatial and spectral properties of the meta-optics are optimized, resulting in spectra that mimic the color matching functions of the CIE 1931 XYZ color space, which links the distributions of wavelengths in light and the color perception of a human eye. Experimental demonstrations of these meta-optics show qualitative agreement with the theoretical predictions and help elucidate the focusing mechanism of these devices.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge