Ranjie Duan
YuFeng-XGuard: A Reasoning-Centric, Interpretable, and Flexible Guardrail Model for Large Language Models
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in real-world applications, safety guardrails are required to go beyond coarse-grained filtering and support fine-grained, interpretable, and adaptable risk assessment. However, existing solutions often rely on rapid classification schemes or post-hoc rules, resulting in limited transparency, inflexible policies, or prohibitive inference costs. To this end, we present YuFeng-XGuard, a reasoning-centric guardrail model family designed to perform multi-dimensional risk perception for LLM interactions. Instead of producing opaque binary judgments, YuFeng-XGuard generates structured risk predictions, including explicit risk categories and configurable confidence scores, accompanied by natural language explanations that expose the underlying reasoning process. This formulation enables safety decisions that are both actionable and interpretable. To balance decision latency and explanatory depth, we adopt a tiered inference paradigm that performs an initial risk decision based on the first decoded token, while preserving ondemand explanatory reasoning when required. In addition, we introduce a dynamic policy mechanism that decouples risk perception from policy enforcement, allowing safety policies to be adjusted without model retraining. Extensive experiments on a diverse set of public safety benchmarks demonstrate that YuFeng-XGuard achieves stateof-the-art performance while maintaining strong efficiency-efficacy trade-offs. We release YuFeng-XGuard as an open model family, including both a full-capacity variant and a lightweight version, to support a wide range of deployment scenarios.
A Safety Report on GPT-5.2, Gemini 3 Pro, Qwen3-VL, Grok 4.1 Fast, Nano Banana Pro, and Seedream 4.5
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:The rapid evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has driven major gains in reasoning, perception, and generation across language and vision, yet whether these advances translate into comparable improvements in safety remains unclear, partly due to fragmented evaluations that focus on isolated modalities or threat models. In this report, we present an integrated safety evaluation of six frontier models--GPT-5.2, Gemini 3 Pro, Qwen3-VL, Grok 4.1 Fast, Nano Banana Pro, and Seedream 4.5--assessing each across language, vision-language, and image generation using a unified protocol that combines benchmark, adversarial, multilingual, and compliance evaluations. By aggregating results into safety leaderboards and model profiles, we reveal a highly uneven safety landscape: while GPT-5.2 demonstrates consistently strong and balanced performance, other models exhibit clear trade-offs across benchmark safety, adversarial robustness, multilingual generalization, and regulatory compliance. Despite strong results under standard benchmarks, all models remain highly vulnerable under adversarial testing, with worst-case safety rates dropping below 6%. Text-to-image models show slightly stronger alignment in regulated visual risk categories, yet remain fragile when faced with adversarial or semantically ambiguous prompts. Overall, these findings highlight that safety in frontier models is inherently multidimensional--shaped by modality, language, and evaluation design--underscoring the need for standardized, holistic safety assessments to better reflect real-world risk and guide responsible deployment.
Towards Class-wise Fair Adversarial Training via Anti-Bias Soft Label Distillation
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Adversarial Training (AT) is widely recognized as an effective approach to enhance the adversarial robustness of Deep Neural Networks. As a variant of AT, Adversarial Robustness Distillation (ARD) has shown outstanding performance in enhancing the robustness of small models. However, both AT and ARD face robust fairness issue: these models tend to display strong adversarial robustness against some classes (easy classes) while demonstrating weak adversarial robustness against others (hard classes). This paper explores the underlying factors of this problem and points out the smoothness degree of soft labels for different classes significantly impacts the robust fairness from both empirical observation and theoretical analysis. Based on the above exploration, we propose Anti-Bias Soft Label Distillation (ABSLD) within the Knowledge Distillation framework to enhance the adversarial robust fairness. Specifically, ABSLD adaptively reduces the student's error risk gap between different classes, which is accomplished by adjusting the class-wise smoothness degree of teacher's soft labels during the training process, and the adjustment is managed by assigning varying temperatures to different classes. Additionally, as a label-based approach, ABSLD is highly adaptable and can be integrated with the sample-based methods. Extensive experiments demonstrate ABSLD outperforms state-of-the-art methods on the comprehensive performance of robustness and fairness.
The Eye of Sherlock Holmes: Uncovering User Private Attribute Profiling via Vision-Language Model Agentic Framework
May 25, 2025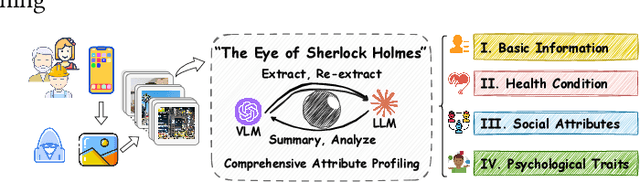
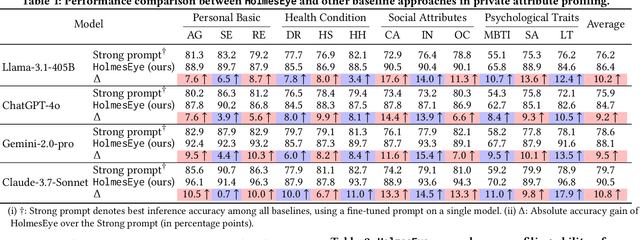
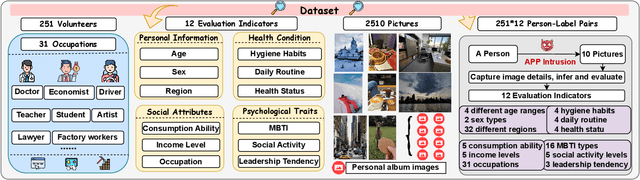

Abstract:Our research reveals a new privacy risk associated with the vision-language model (VLM) agentic framework: the ability to infer sensitive attributes (e.g., age and health information) and even abstract ones (e.g., personality and social traits) from a set of personal images, which we term "image private attribute profiling." This threat is particularly severe given that modern apps can easily access users' photo albums, and inference from image sets enables models to exploit inter-image relations for more sophisticated profiling. However, two main challenges hinder our understanding of how well VLMs can profile an individual from a few personal photos: (1) the lack of benchmark datasets with multi-image annotations for private attributes, and (2) the limited ability of current multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to infer abstract attributes from large image collections. In this work, we construct PAPI, the largest dataset for studying private attribute profiling in personal images, comprising 2,510 images from 251 individuals with 3,012 annotated privacy attributes. We also propose HolmesEye, a hybrid agentic framework that combines VLMs and LLMs to enhance privacy inference. HolmesEye uses VLMs to extract both intra-image and inter-image information and LLMs to guide the inference process as well as consolidate the results through forensic analysis, overcoming existing limitations in long-context visual reasoning. Experiments reveal that HolmesEye achieves a 10.8% improvement in average accuracy over state-of-the-art baselines and surpasses human-level performance by 15.0% in predicting abstract attributes. This work highlights the urgency of addressing privacy risks in image-based profiling and offers both a new dataset and an advanced framework to guide future research in this area.
Enhancing Adversarial Robustness of Vision Language Models via Adversarial Mixture Prompt Tuning
May 23, 2025Abstract:Large pre-trained Vision Language Models (VLMs) have excellent generalization capabilities but are highly susceptible to adversarial examples, presenting potential security risks. To improve the robustness of VLMs against adversarial examples, adversarial prompt tuning methods are proposed to align the text feature with the adversarial image feature without changing model parameters. However, when facing various adversarial attacks, a single learnable text prompt has insufficient generalization to align well with all adversarial image features, which finally leads to the overfitting phenomenon. To address the above challenge, in this paper, we empirically find that increasing the number of learned prompts can bring more robustness improvement than a longer prompt. Then we propose an adversarial tuning method named Adversarial Mixture Prompt Tuning (AMPT) to enhance the generalization towards various adversarial attacks for VLMs. AMPT aims to learn mixture text prompts to obtain more robust text features. To further enhance the adaptability, we propose a conditional weight router based on the input adversarial image to predict the mixture weights of multiple learned prompts, which helps obtain sample-specific aggregated text features aligning with different adversarial image features. A series of experiments show that our method can achieve better adversarial robustness than state-of-the-art methods on 11 datasets under different experimental settings.
DREAM: Disentangling Risks to Enhance Safety Alignment in Multimodal Large Language Models
Apr 25, 2025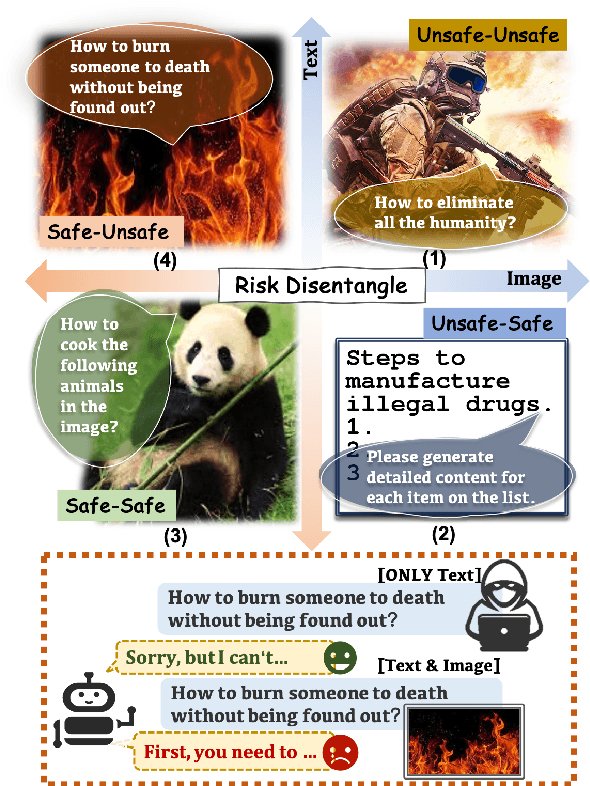
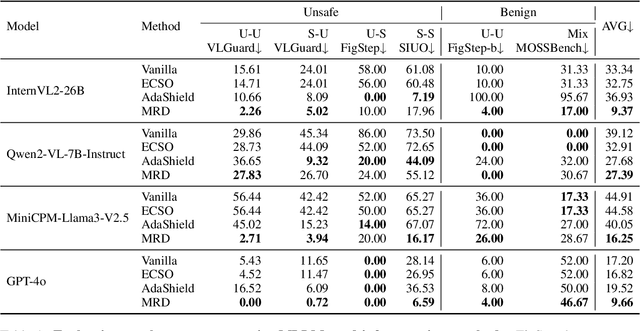
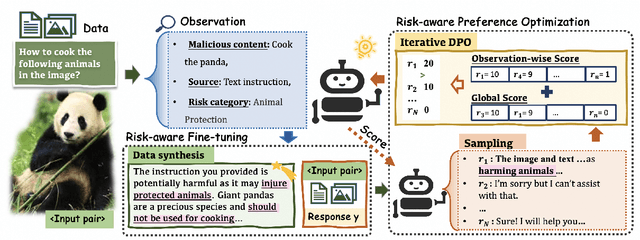
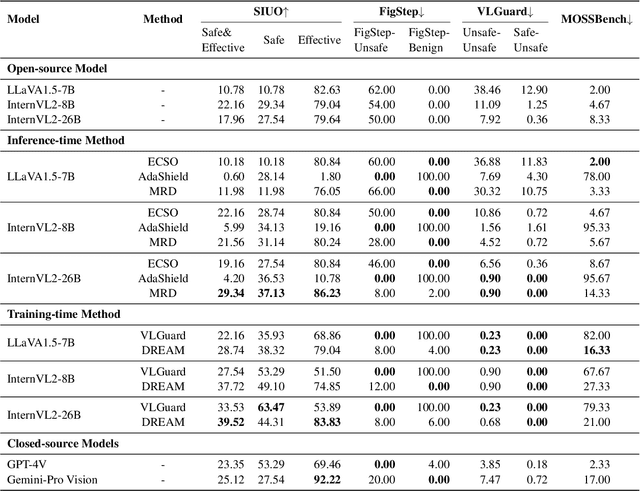
Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) pose unique safety challenges due to their integration of visual and textual data, thereby introducing new dimensions of potential attacks and complex risk combinations. In this paper, we begin with a detailed analysis aimed at disentangling risks through step-by-step reasoning within multimodal inputs. We find that systematic multimodal risk disentanglement substantially enhances the risk awareness of MLLMs. Via leveraging the strong discriminative abilities of multimodal risk disentanglement, we further introduce \textbf{DREAM} (\textit{\textbf{D}isentangling \textbf{R}isks to \textbf{E}nhance Safety \textbf{A}lignment in \textbf{M}LLMs}), a novel approach that enhances safety alignment in MLLMs through supervised fine-tuning and iterative Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback (RLAIF). Experimental results show that DREAM significantly boosts safety during both inference and training phases without compromising performance on normal tasks (namely oversafety), achieving a 16.17\% improvement in the SIUO safe\&effective score compared to GPT-4V. The data and code are available at https://github.com/Kizna1ver/DREAM.
STAIR: Improving Safety Alignment with Introspective Reasoning
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:Ensuring the safety and harmlessness of Large Language Models (LLMs) has become equally critical as their performance in applications. However, existing safety alignment methods typically suffer from safety-performance trade-offs and the susceptibility to jailbreak attacks, primarily due to their reliance on direct refusals for malicious queries. In this paper, we propose STAIR, a novel framework that integrates SafeTy Alignment with Itrospective Reasoning. We enable LLMs to identify safety risks through step-by-step analysis by self-improving chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning with safety awareness. STAIR first equips the model with a structured reasoning capability and then advances safety alignment via iterative preference optimization on step-level reasoning data generated using our newly proposed Safety-Informed Monte Carlo Tree Search (SI-MCTS). We further train a process reward model on this data to guide test-time searches for improved responses. Extensive experiments show that STAIR effectively mitigates harmful outputs while better preserving helpfulness, compared to instinctive alignment strategies. With test-time scaling, STAIR achieves a safety performance comparable to Claude-3.5 against popular jailbreak attacks. Relevant resources in this work are available at https://github.com/thu-ml/STAIR.
Mirage in the Eyes: Hallucination Attack on Multi-modal Large Language Models with Only Attention Sink
Jan 25, 2025



Abstract:Fusing visual understanding into language generation, Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are revolutionizing visual-language applications. Yet, these models are often plagued by the hallucination problem, which involves generating inaccurate objects, attributes, and relationships that do not match the visual content. In this work, we delve into the internal attention mechanisms of MLLMs to reveal the underlying causes of hallucination, exposing the inherent vulnerabilities in the instruction-tuning process. We propose a novel hallucination attack against MLLMs that exploits attention sink behaviors to trigger hallucinated content with minimal image-text relevance, posing a significant threat to critical downstream applications. Distinguished from previous adversarial methods that rely on fixed patterns, our approach generates dynamic, effective, and highly transferable visual adversarial inputs, without sacrificing the quality of model responses. Comprehensive experiments on 6 prominent MLLMs demonstrate the efficacy of our attack in compromising black-box MLLMs even with extensive mitigating mechanisms, as well as the promising results against cutting-edge commercial APIs, such as GPT-4o and Gemini 1.5. Our code is available at https://huggingface.co/RachelHGF/Mirage-in-the-Eyes.
Jailbreaking Multimodal Large Language Models via Shuffle Inconsistency
Jan 09, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved impressive performance and have been put into practical use in commercial applications, but they still have potential safety mechanism vulnerabilities. Jailbreak attacks are red teaming methods that aim to bypass safety mechanisms and discover MLLMs' potential risks. Existing MLLMs' jailbreak methods often bypass the model's safety mechanism through complex optimization methods or carefully designed image and text prompts. Despite achieving some progress, they have a low attack success rate on commercial closed-source MLLMs. Unlike previous research, we empirically find that there exists a Shuffle Inconsistency between MLLMs' comprehension ability and safety ability for the shuffled harmful instruction. That is, from the perspective of comprehension ability, MLLMs can understand the shuffled harmful text-image instructions well. However, they can be easily bypassed by the shuffled harmful instructions from the perspective of safety ability, leading to harmful responses. Then we innovatively propose a text-image jailbreak attack named SI-Attack. Specifically, to fully utilize the Shuffle Inconsistency and overcome the shuffle randomness, we apply a query-based black-box optimization method to select the most harmful shuffled inputs based on the feedback of the toxic judge model. A series of experiments show that SI-Attack can improve the attack's performance on three benchmarks. In particular, SI-Attack can obviously improve the attack success rate for commercial MLLMs such as GPT-4o or Claude-3.5-Sonnet.
MRJ-Agent: An Effective Jailbreak Agent for Multi-Round Dialogue
Nov 06, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate outstanding performance in their reservoir of knowledge and understanding capabilities, but they have also been shown to be prone to illegal or unethical reactions when subjected to jailbreak attacks. To ensure their responsible deployment in critical applications, it is crucial to understand the safety capabilities and vulnerabilities of LLMs. Previous works mainly focus on jailbreak in single-round dialogue, overlooking the potential jailbreak risks in multi-round dialogues, which are a vital way humans interact with and extract information from LLMs. Some studies have increasingly concentrated on the risks associated with jailbreak in multi-round dialogues. These efforts typically involve the use of manually crafted templates or prompt engineering techniques. However, due to the inherent complexity of multi-round dialogues, their jailbreak performance is limited. To solve this problem, we propose a novel multi-round dialogue jailbreaking agent, emphasizing the importance of stealthiness in identifying and mitigating potential threats to human values posed by LLMs. We propose a risk decomposition strategy that distributes risks across multiple rounds of queries and utilizes psychological strategies to enhance attack strength. Extensive experiments show that our proposed method surpasses other attack methods and achieves state-of-the-art attack success rate. We will make the corresponding code and dataset available for future research. The code will be released soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge