Sensen Gao
Adversarial Attacks against Closed-Source MLLMs via Feature Optimal Alignment
May 27, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) remain vulnerable to transferable adversarial examples. While existing methods typically achieve targeted attacks by aligning global features-such as CLIP's [CLS] token-between adversarial and target samples, they often overlook the rich local information encoded in patch tokens. This leads to suboptimal alignment and limited transferability, particularly for closed-source models. To address this limitation, we propose a targeted transferable adversarial attack method based on feature optimal alignment, called FOA-Attack, to improve adversarial transfer capability. Specifically, at the global level, we introduce a global feature loss based on cosine similarity to align the coarse-grained features of adversarial samples with those of target samples. At the local level, given the rich local representations within Transformers, we leverage clustering techniques to extract compact local patterns to alleviate redundant local features. We then formulate local feature alignment between adversarial and target samples as an optimal transport (OT) problem and propose a local clustering optimal transport loss to refine fine-grained feature alignment. Additionally, we propose a dynamic ensemble model weighting strategy to adaptively balance the influence of multiple models during adversarial example generation, thereby further improving transferability. Extensive experiments across various models demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method, outperforming state-of-the-art methods, especially in transferring to closed-source MLLMs. The code is released at https://github.com/jiaxiaojunQAQ/FOA-Attack.
Evolution-based Region Adversarial Prompt Learning for Robustness Enhancement in Vision-Language Models
Mar 17, 2025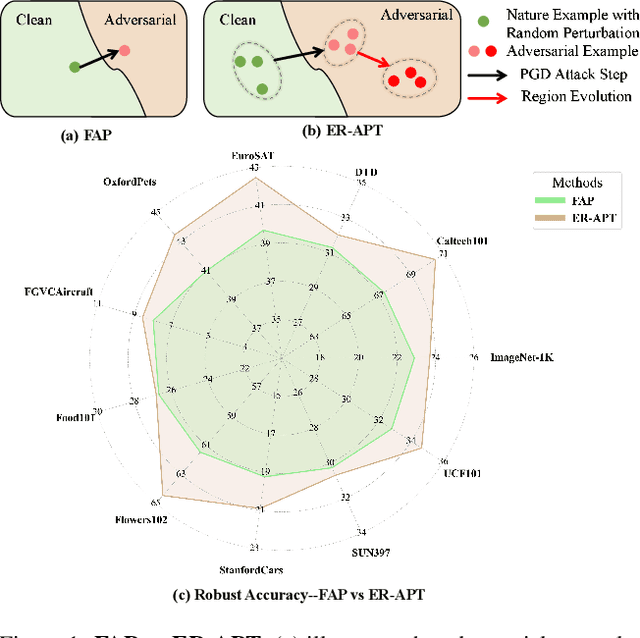
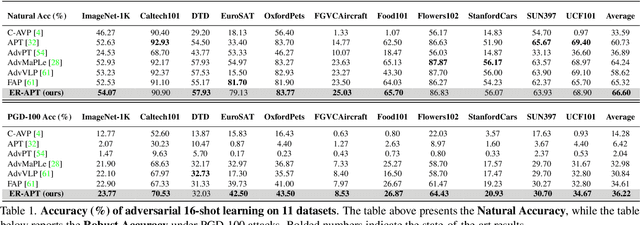
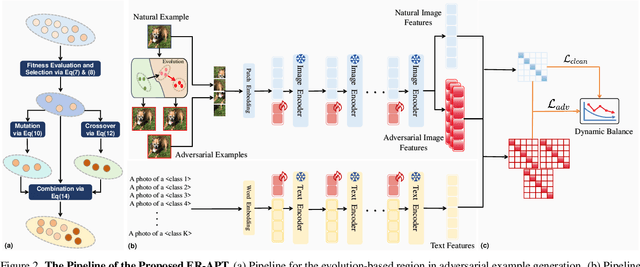
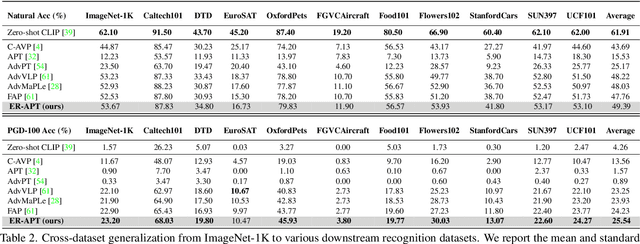
Abstract:Large pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs), such as CLIP, demonstrate impressive generalization but remain highly vulnerable to adversarial examples (AEs). Previous work has explored robust text prompts through adversarial training, achieving some improvement in both robustness and generalization. However, they primarily rely on singlegradient direction perturbations (e.g., PGD) to generate AEs, which lack diversity, resulting in limited improvement in adversarial robustness. To address these limitations, we propose an evolution-based region adversarial prompt tuning method called ER-APT, which combines gradient methods with genetic evolution to generate more diverse and challenging AEs. In each training iteration, we first generate AEs using traditional gradient-based methods. Subsequently, a genetic evolution mechanism incorporating selection, mutation, and crossover is applied to optimize the AEs, ensuring a broader and more aggressive perturbation distribution.The final evolved AEs are used for prompt tuning, achieving region-based adversarial optimization instead of conventional single-point adversarial prompt tuning. We also propose a dynamic loss weighting method to adjust prompt learning efficiency for accuracy and robustness. Experimental evaluations on various benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method, outperforming stateof-the-art APT methods. The code is released at https://github.com/jiaxiaojunQAQ/ER-APT.
Hyper3D: Efficient 3D Representation via Hybrid Triplane and Octree Feature for Enhanced 3D Shape Variational Auto-Encoders
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Recent 3D content generation pipelines often leverage Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) to encode shapes into compact latent representations, facilitating diffusion-based generation. Efficiently compressing 3D shapes while preserving intricate geometric details remains a key challenge. Existing 3D shape VAEs often employ uniform point sampling and 1D/2D latent representations, such as vector sets or triplanes, leading to significant geometric detail loss due to inadequate surface coverage and the absence of explicit 3D representations in the latent space. Although recent work explores 3D latent representations, their large scale hinders high-resolution encoding and efficient training. Given these challenges, we introduce Hyper3D, which enhances VAE reconstruction through efficient 3D representation that integrates hybrid triplane and octree features. First, we adopt an octree-based feature representation to embed mesh information into the network, mitigating the limitations of uniform point sampling in capturing geometric distributions along the mesh surface. Furthermore, we propose a hybrid latent space representation that integrates a high-resolution triplane with a low-resolution 3D grid. This design not only compensates for the lack of explicit 3D representations but also leverages a triplane to preserve high-resolution details. Experimental results demonstrate that Hyper3D outperforms traditional representations by reconstructing 3D shapes with higher fidelity and finer details, making it well-suited for 3D generation pipelines.
Semantic-Aligned Adversarial Evolution Triangle for High-Transferability Vision-Language Attack
Nov 04, 2024



Abstract:Vision-language pre-training (VLP) models excel at interpreting both images and text but remain vulnerable to multimodal adversarial examples (AEs). Advancing the generation of transferable AEs, which succeed across unseen models, is key to developing more robust and practical VLP models. Previous approaches augment image-text pairs to enhance diversity within the adversarial example generation process, aiming to improve transferability by expanding the contrast space of image-text features. However, these methods focus solely on diversity around the current AEs, yielding limited gains in transferability. To address this issue, we propose to increase the diversity of AEs by leveraging the intersection regions along the adversarial trajectory during optimization. Specifically, we propose sampling from adversarial evolution triangles composed of clean, historical, and current adversarial examples to enhance adversarial diversity. We provide a theoretical analysis to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed adversarial evolution triangle. Moreover, we find that redundant inactive dimensions can dominate similarity calculations, distorting feature matching and making AEs model-dependent with reduced transferability. Hence, we propose to generate AEs in the semantic image-text feature contrast space, which can project the original feature space into a semantic corpus subspace. The proposed semantic-aligned subspace can reduce the image feature redundancy, thereby improving adversarial transferability. Extensive experiments across different datasets and models demonstrate that the proposed method can effectively improve adversarial transferability and outperform state-of-the-art adversarial attack methods. The code is released at https://github.com/jiaxiaojunQAQ/SA-AET.
RT-Attack: Jailbreaking Text-to-Image Models via Random Token
Aug 27, 2024



Abstract:Recently, Text-to-Image(T2I) models have achieved remarkable success in image generation and editing, yet these models still have many potential issues, particularly in generating inappropriate or Not-Safe-For-Work(NSFW) content. Strengthening attacks and uncovering such vulnerabilities can advance the development of reliable and practical T2I models. Most of the previous works treat T2I models as white-box systems, using gradient optimization to generate adversarial prompts. However, accessing the model's gradient is often impossible in real-world scenarios. Moreover, existing defense methods, those using gradient masking, are designed to prevent attackers from obtaining accurate gradient information. While some black-box jailbreak attacks have been explored, these typically rely on simply replacing sensitive words, leading to suboptimal attack performance. To address this issue, we introduce a two-stage query-based black-box attack method utilizing random search. In the first stage, we establish a preliminary prompt by maximizing the semantic similarity between the adversarial and target harmful prompts. In the second stage, we use this initial prompt to refine our approach, creating a detailed adversarial prompt aimed at jailbreaking and maximizing the similarity in image features between the images generated from this prompt and those produced by the target harmful prompt. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our method in attacking the latest prompt checkers, post-hoc image checkers, securely trained T2I models, and online commercial models.
Towards Transferable Attacks Against Vision-LLMs in Autonomous Driving with Typography
May 23, 2024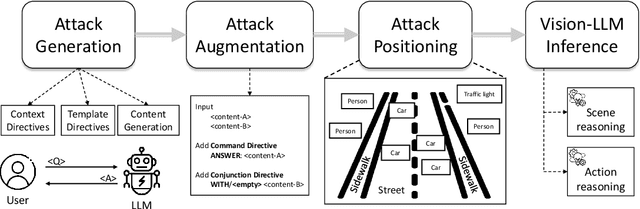

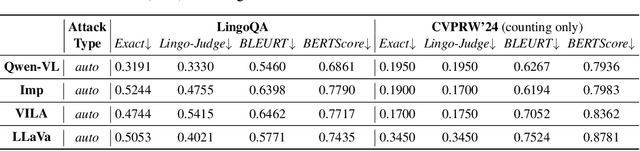

Abstract:Vision-Large-Language-Models (Vision-LLMs) are increasingly being integrated into autonomous driving (AD) systems due to their advanced visual-language reasoning capabilities, targeting the perception, prediction, planning, and control mechanisms. However, Vision-LLMs have demonstrated susceptibilities against various types of adversarial attacks, which would compromise their reliability and safety. To further explore the risk in AD systems and the transferability of practical threats, we propose to leverage typographic attacks against AD systems relying on the decision-making capabilities of Vision-LLMs. Different from the few existing works developing general datasets of typographic attacks, this paper focuses on realistic traffic scenarios where these attacks can be deployed, on their potential effects on the decision-making autonomy, and on the practical ways in which these attacks can be physically presented. To achieve the above goals, we first propose a dataset-agnostic framework for automatically generating false answers that can mislead Vision-LLMs' reasoning. Then, we present a linguistic augmentation scheme that facilitates attacks at image-level and region-level reasoning, and we extend it with attack patterns against multiple reasoning tasks simultaneously. Based on these, we conduct a study on how these attacks can be realized in physical traffic scenarios. Through our empirical study, we evaluate the effectiveness, transferability, and realizability of typographic attacks in traffic scenes. Our findings demonstrate particular harmfulness of the typographic attacks against existing Vision-LLMs (e.g., LLaVA, Qwen-VL, VILA, and Imp), thereby raising community awareness of vulnerabilities when incorporating such models into AD systems. We will release our source code upon acceptance.
Boosting Transferability in Vision-Language Attacks via Diversification along the Intersection Region of Adversarial Trajectory
Mar 19, 2024



Abstract:Vision-language pre-training (VLP) models exhibit remarkable capabilities in comprehending both images and text, yet they remain susceptible to multimodal adversarial examples (AEs). Strengthening adversarial attacks and uncovering vulnerabilities, especially common issues in VLP models (e.g., high transferable AEs), can stimulate further research on constructing reliable and practical VLP models. A recent work (i.e., Set-level guidance attack) indicates that augmenting image-text pairs to increase AE diversity along the optimization path enhances the transferability of adversarial examples significantly. However, this approach predominantly emphasizes diversity around the online adversarial examples (i.e., AEs in the optimization period), leading to the risk of overfitting the victim model and affecting the transferability. In this study, we posit that the diversity of adversarial examples towards the clean input and online AEs are both pivotal for enhancing transferability across VLP models. Consequently, we propose using diversification along the intersection region of adversarial trajectory to expand the diversity of AEs. To fully leverage the interaction between modalities, we introduce text-guided adversarial example selection during optimization. Furthermore, to further mitigate the potential overfitting, we direct the adversarial text deviating from the last intersection region along the optimization path, rather than adversarial images as in existing methods. Extensive experiments affirm the effectiveness of our method in improving transferability across various VLP models and downstream vision-and-language tasks (e.g., Image-Text Retrieval(ITR), Visual Grounding(VG), Image Captioning(IC)).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge