Junjie Sun
IntTravel: A Real-World Dataset and Generative Framework for Integrated Multi-Task Travel Recommendation
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Next Point of Interest (POI) recommendation is essential for modern mobility and location-based services. To provide a smooth user experience, models must understand several components of a journey holistically: "when to depart", "how to travel", "where to go", and "what needs arise via the route". However, current research is limited by fragmented datasets that focus merely on next POI recommendation ("where to go"), neglecting the departure time, travel mode, and situational requirements along the journey. Furthermore, the limited scale of these datasets impedes accurate evaluation of performance. To bridge this gap, we introduce IntTravel, the first large-scale public dataset for integrated travel recommendation, including 4.1 billion interactions from 163 million users with 7.3 million POIs. Built upon this dataset, we introduce an end-to-end, decoder-only generative framework for multi-task recommendation. It incorporates information preservation, selection, and factorization to balance task collaboration with specialized differentiation, yielding substantial performance gains. The framework's generalizability is highlighted by its state-of-the-art performance across both IntTravel dataset and an additional non-travel benchmark. IntTravel has been successfully deployed on Amap serving hundreds of millions of users, leading to a 1.09% increase in CTR. IntTravel is available at https://github.com/AMAP-ML/IntTravel.
Mirage in the Eyes: Hallucination Attack on Multi-modal Large Language Models with Only Attention Sink
Jan 25, 2025



Abstract:Fusing visual understanding into language generation, Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are revolutionizing visual-language applications. Yet, these models are often plagued by the hallucination problem, which involves generating inaccurate objects, attributes, and relationships that do not match the visual content. In this work, we delve into the internal attention mechanisms of MLLMs to reveal the underlying causes of hallucination, exposing the inherent vulnerabilities in the instruction-tuning process. We propose a novel hallucination attack against MLLMs that exploits attention sink behaviors to trigger hallucinated content with minimal image-text relevance, posing a significant threat to critical downstream applications. Distinguished from previous adversarial methods that rely on fixed patterns, our approach generates dynamic, effective, and highly transferable visual adversarial inputs, without sacrificing the quality of model responses. Comprehensive experiments on 6 prominent MLLMs demonstrate the efficacy of our attack in compromising black-box MLLMs even with extensive mitigating mechanisms, as well as the promising results against cutting-edge commercial APIs, such as GPT-4o and Gemini 1.5. Our code is available at https://huggingface.co/RachelHGF/Mirage-in-the-Eyes.
Navigate Beyond Shortcuts: Debiased Learning through the Lens of Neural Collapse
May 09, 2024



Abstract:Recent studies have noted an intriguing phenomenon termed Neural Collapse, that is, when the neural networks establish the right correlation between feature spaces and the training targets, their last-layer features, together with the classifier weights, will collapse into a stable and symmetric structure. In this paper, we extend the investigation of Neural Collapse to the biased datasets with imbalanced attributes. We observe that models will easily fall into the pitfall of shortcut learning and form a biased, non-collapsed feature space at the early period of training, which is hard to reverse and limits the generalization capability. To tackle the root cause of biased classification, we follow the recent inspiration of prime training, and propose an avoid-shortcut learning framework without additional training complexity. With well-designed shortcut primes based on Neural Collapse structure, the models are encouraged to skip the pursuit of simple shortcuts and naturally capture the intrinsic correlations. Experimental results demonstrate that our method induces better convergence properties during training, and achieves state-of-the-art generalization performance on both synthetic and real-world biased datasets.
BELT: Old-School Backdoor Attacks can Evade the State-of-the-Art Defense with Backdoor Exclusivity Lifting
Dec 08, 2023



Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) are susceptible to backdoor attacks, where malicious functionality is embedded to allow attackers to trigger incorrect classifications. Old-school backdoor attacks use strong trigger features that can easily be learned by victim models. Despite robustness against input variation, the robustness however increases the likelihood of unintentional trigger activations. This leaves traces to existing defenses, which find approximate replacements for the original triggers that can activate the backdoor without being identical to the original trigger via, e.g., reverse engineering and sample overlay. In this paper, we propose and investigate a new characteristic of backdoor attacks, namely, backdoor exclusivity, which measures the ability of backdoor triggers to remain effective in the presence of input variation. Building upon the concept of backdoor exclusivity, we propose Backdoor Exclusivity LifTing (BELT), a novel technique which suppresses the association between the backdoor and fuzzy triggers to enhance backdoor exclusivity for defense evasion. Extensive evaluation on three popular backdoor benchmarks validate, our approach substantially enhances the stealthiness of four old-school backdoor attacks, which, after backdoor exclusivity lifting, is able to evade six state-of-the-art backdoor countermeasures, at almost no cost of the attack success rate and normal utility. For example, one of the earliest backdoor attacks BadNet, enhanced by BELT, evades most of the state-of-the-art defenses including ABS and MOTH which would otherwise recognize the backdoored model.
A Simple Meta-learning Paradigm for Zero-shot Intent Classification with Mixture Attention Mechanism
Jun 05, 2022


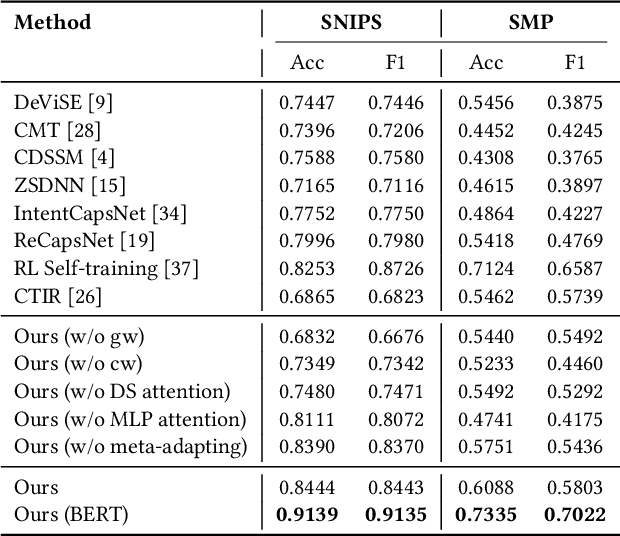
Abstract:Zero-shot intent classification is a vital and challenging task in dialogue systems, which aims to deal with numerous fast-emerging unacquainted intents without annotated training data. To obtain more satisfactory performance, the crucial points lie in two aspects: extracting better utterance features and strengthening the model generalization ability. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective meta-learning paradigm for zero-shot intent classification. To learn better semantic representations for utterances, we introduce a new mixture attention mechanism, which encodes the pertinent word occurrence patterns by leveraging the distributional signature attention and multi-layer perceptron attention simultaneously. To strengthen the transfer ability of the model from seen classes to unseen classes, we reformulate zero-shot intent classification with a meta-learning strategy, which trains the model by simulating multiple zero-shot classification tasks on seen categories, and promotes the model generalization ability with a meta-adapting procedure on mimic unseen categories. Extensive experiments on two real-world dialogue datasets in different languages show that our model outperforms other strong baselines on both standard and generalized zero-shot intent classification tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge