Osamu Yoshie
Chart Specification: Structural Representations for Incentivizing VLM Reasoning in Chart-to-Code Generation
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have shown promise in generating plotting code from chart images, yet achieving structural fidelity remains challenging. Existing approaches largely rely on supervised fine-tuning, encouraging surface-level token imitation rather than faithful modeling of underlying chart structure, which often leads to hallucinated or semantically inconsistent outputs. We propose Chart Specification, a structured intermediate representation that shifts training from text imitation to semantically grounded supervision. Chart Specification filters syntactic noise to construct a structurally balanced training set and supports a Spec-Align Reward that provides fine-grained, verifiable feedback on structural correctness, enabling reinforcement learning to enforce consistent plotting logic. Experiments on three public benchmarks show that our method consistently outperforms prior approaches. With only 3K training samples, we achieve strong data efficiency, surpassing leading baselines by up to 61.7% on complex benchmarks, and scaling to 4K samples establishes new state-of-the-art results across all evaluated metrics. Overall, our results demonstrate that precise structural supervision offers an efficient pathway to high-fidelity chart-to-code generation. Code and dataset are available at: https://github.com/Mighten/chart-specification-paper
FluencyVE: Marrying Temporal-Aware Mamba with Bypass Attention for Video Editing
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Large-scale text-to-image diffusion models have achieved unprecedented success in image generation and editing. However, extending this success to video editing remains challenging. Recent video editing efforts have adapted pretrained text-to-image models by adding temporal attention mechanisms to handle video tasks. Unfortunately, these methods continue to suffer from temporal inconsistency issues and high computational overheads. In this study, we propose FluencyVE, which is a simple yet effective one-shot video editing approach. FluencyVE integrates the linear time-series module, Mamba, into a video editing model based on pretrained Stable Diffusion models, replacing the temporal attention layer. This enables global frame-level attention while reducing the computational costs. In addition, we employ low-rank approximation matrices to replace the query and key weight matrices in the causal attention, and use a weighted averaging technique during training to update the attention scores. This approach significantly preserves the generative power of the text-to-image model while effectively reducing the computational burden. Experiments and analyses demonstrate promising results in editing various attributes, subjects, and locations in real-world videos.
Multi-Attribute guided Thermal Face Image Translation based on Latent Diffusion Model
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Modern surveillance systems increasingly rely on multi-wavelength sensors and deep neural networks to recognize faces in infrared images captured at night. However, most facial recognition models are trained on visible light datasets, leading to substantial performance degradation on infrared inputs due to significant domain shifts. Early feature-based methods for infrared face recognition proved ineffective, prompting researchers to adopt generative approaches that convert infrared images into visible light images for improved recognition. This paradigm, known as Heterogeneous Face Recognition (HFR), faces challenges such as model and modality discrepancies, leading to distortion and feature loss in generated images. To address these limitations, this paper introduces a novel latent diffusion-based model designed to generate high-quality visible face images from thermal inputs while preserving critical identity features. A multi-attribute classifier is incorporated to extract key facial attributes from visible images, mitigating feature loss during infrared-to-visible image restoration. Additionally, we propose the Self-attn Mamba module, which enhances global modeling of cross-modal features and significantly improves inference speed. Experimental results on two benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of our approach, achieving state-of-the-art performance in both image quality and identity preservation.
DM$^3$Net: Dual-Camera Super-Resolution via Domain Modulation and Multi-scale Matching
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Dual-camera super-resolution is highly practical for smartphone photography that primarily super-resolve the wide-angle images using the telephoto image as a reference. In this paper, we propose DM$^3$Net, a novel dual-camera super-resolution network based on Domain Modulation and Multi-scale Matching. To bridge the domain gap between the high-resolution domain and the degraded domain, we learn two compressed global representations from image pairs corresponding to the two domains. To enable reliable transfer of high-frequency structural details from the reference image, we design a multi-scale matching module that conducts patch-level feature matching and retrieval across multiple receptive fields to improve matching accuracy and robustness. Moreover, we also introduce Key Pruning to achieve a significant reduction in memory usage and inference time with little model performance sacrificed. Experimental results on three real-world datasets demonstrate that our DM$^3$Net outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches.
PADriver: Towards Personalized Autonomous Driving
May 08, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose PADriver, a novel closed-loop framework for personalized autonomous driving (PAD). Built upon Multi-modal Large Language Model (MLLM), PADriver takes streaming frames and personalized textual prompts as inputs. It autoaggressively performs scene understanding, danger level estimation and action decision. The predicted danger level reflects the risk of the potential action and provides an explicit reference for the final action, which corresponds to the preset personalized prompt. Moreover, we construct a closed-loop benchmark named PAD-Highway based on Highway-Env simulator to comprehensively evaluate the decision performance under traffic rules. The dataset contains 250 hours videos with high-quality annotation to facilitate the development of PAD behavior analysis. Experimental results on the constructed benchmark show that PADriver outperforms state-of-the-art approaches on different evaluation metrics, and enables various driving modes.
R1-T1: Fully Incentivizing Translation Capability in LLMs via Reasoning Learning
Feb 27, 2025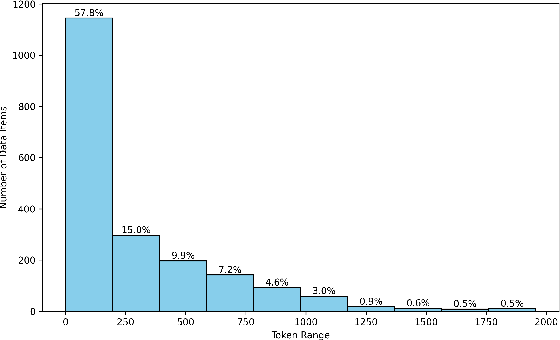
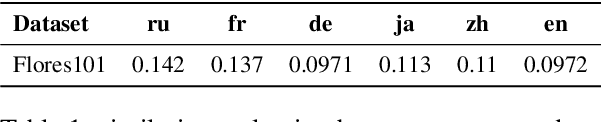
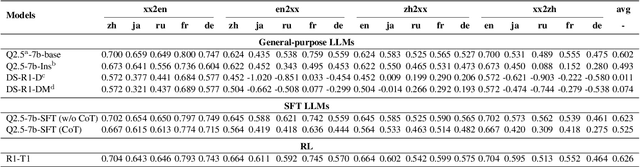
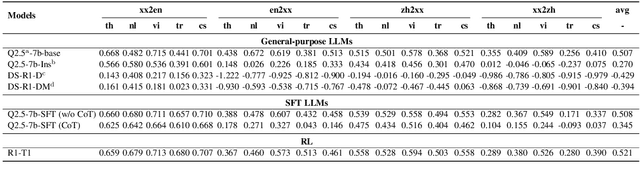
Abstract:Despite recent breakthroughs in reasoning-enhanced large language models (LLMs) like DeepSeek-R1, incorporating inference-time reasoning into machine translation (MT), where human translators naturally employ structured, multi-layered reasoning chain-of-thoughts (CoTs), is yet underexplored. Existing methods either design a fixed CoT tailored for a specific MT sub-task (e.g., literature translation), or rely on synthesizing CoTs unaligned with humans and supervised fine-tuning (SFT) prone to catastrophic forgetting, limiting their adaptability to diverse translation scenarios. This paper introduces R1-Translator (R1-T1), a novel framework to achieve inference-time reasoning for general MT via reinforcement learning (RL) with human-aligned CoTs comprising six common patterns. Our approach pioneers three innovations: (1) extending reasoning-based translation beyond MT sub-tasks to six languages and diverse tasks (e.g., legal/medical domain adaptation, idiom resolution); (2) formalizing six expert-curated CoT templates that mirror hybrid human strategies like context-aware paraphrasing and back translation; and (3) enabling self-evolving CoT discovery and anti-forgetting adaptation through RL with KL-constrained rewards. Experimental results indicate a steady translation performance improvement in 21 languages and 80 translation directions on Flores-101 test set, especially on the 15 languages unseen from training, with its general multilingual abilities preserved compared with plain SFT.
RoboMatrix: A Skill-centric Hierarchical Framework for Scalable Robot Task Planning and Execution in Open-World
Nov 29, 2024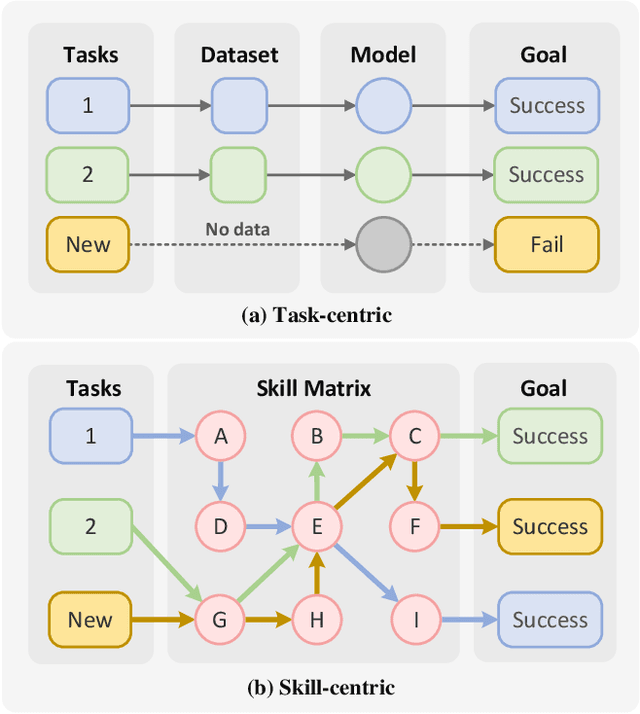

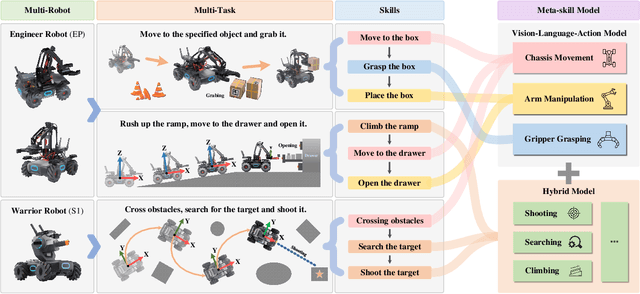

Abstract:Existing policy learning methods predominantly adopt the task-centric paradigm, necessitating the collection of task data in an end-to-end manner. Consequently, the learned policy tends to fail to tackle novel tasks. Moreover, it is hard to localize the errors for a complex task with multiple stages due to end-to-end learning. To address these challenges, we propose RoboMatrix, a skill-centric and hierarchical framework for scalable task planning and execution. We first introduce a novel skill-centric paradigm that extracts the common meta-skills from different complex tasks. This allows for the capture of embodied demonstrations through a kill-centric approach, enabling the completion of open-world tasks by combining learned meta-skills. To fully leverage meta-skills, we further develop a hierarchical framework that decouples complex robot tasks into three interconnected layers: (1) a high-level modular scheduling layer; (2) a middle-level skill layer; and (3) a low-level hardware layer. Experimental results illustrate that our skill-centric and hierarchical framework achieves remarkable generalization performance across novel objects, scenes, tasks, and embodiments. This framework offers a novel solution for robot task planning and execution in open-world scenarios. Our software and hardware are available at https://github.com/WayneMao/RoboMatrix.
What Do You Want? User-centric Prompt Generation for Text-to-image Synthesis via Multi-turn Guidance
Aug 23, 2024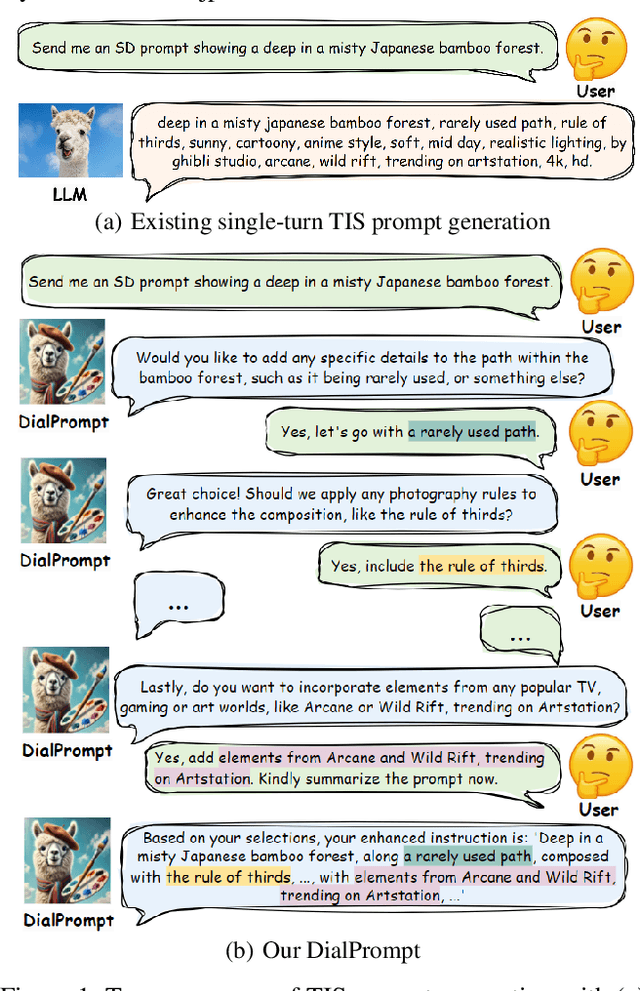
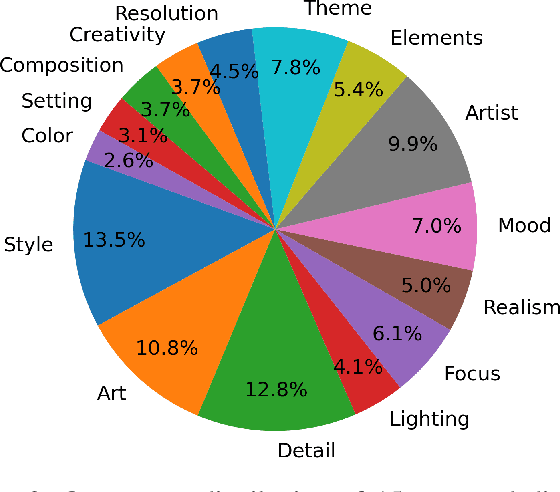
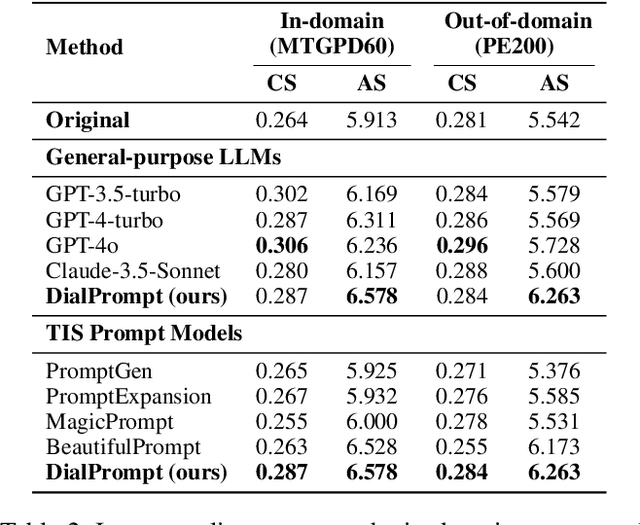
Abstract:The emergence of text-to-image synthesis (TIS) models has significantly influenced digital image creation by producing high-quality visuals from written descriptions. Yet these models heavily rely on the quality and specificity of textual prompts, posing a challenge for novice users who may not be familiar with TIS-model-preferred prompt writing. Existing solutions relieve this via automatic model-preferred prompt generation from user queries. However, this single-turn manner suffers from limited user-centricity in terms of result interpretability and user interactivity. To address these issues, we propose DialPrompt, a multi-turn dialogue-based TIS prompt generation model that emphasises user-centricity. DialPrompt is designed to follow a multi-turn guidance workflow, where in each round of dialogue the model queries user with their preferences on possible optimization dimensions before generating the final TIS prompt. To achieve this, we mined 15 essential dimensions for high-quality prompts from advanced users and curated a multi-turn dataset. Through training on this dataset, DialPrompt can improve interpretability by allowing users to understand the correlation between specific phrases and image attributes. Additionally, it enables greater user control and engagement in the prompt generation process, leading to more personalized and visually satisfying outputs. Experiments indicate that DialPrompt achieves a competitive result in the quality of synthesized images, outperforming existing prompt engineering approaches by 5.7%. Furthermore, in our user evaluation, DialPrompt outperforms existing approaches by 46.5% in user-centricity score and is rated 7.9/10 by 19 human reviewers.
MM-Instruct: Generated Visual Instructions for Large Multimodal Model Alignment
Jun 28, 2024
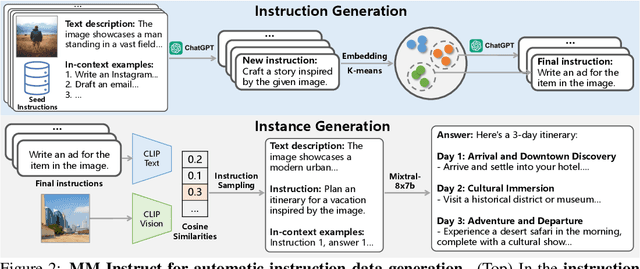


Abstract:This paper introduces MM-Instruct, a large-scale dataset of diverse and high-quality visual instruction data designed to enhance the instruction-following capabilities of large multimodal models (LMMs). While existing visual instruction datasets often focus on question-answering, they struggle to generalize to broader application scenarios such as creative writing, summarization, or image analysis. To address these limitations, we propose a novel approach to constructing MM-Instruct that leverages the strong instruction-following capabilities of existing LLMs to generate novel visual instruction data from large-scale but conventional image captioning datasets. MM-Instruct first leverages ChatGPT to automatically generate diverse instructions from a small set of seed instructions through augmenting and summarization. It then matches these instructions with images and uses an open-sourced large language model (LLM) to generate coherent answers to the instruction-image pairs. The LLM is grounded by the detailed text descriptions of images in the whole answer generation process to guarantee the alignment of the instruction data. Moreover, we introduce a benchmark based on the generated instruction data to evaluate the instruction-following capabilities of existing LMMs. We demonstrate the effectiveness of MM-Instruct by training a LLaVA-1.5 model on the generated data, denoted as LLaVA-Instruct, which exhibits significant improvements in instruction-following capabilities compared to LLaVA-1.5 models. The MM-Instruct dataset, benchmark, and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/jihaonew/MM-Instruct.
BreakGPT: A Large Language Model with Multi-stage Structure for Financial Breakout Detection
Feb 12, 2024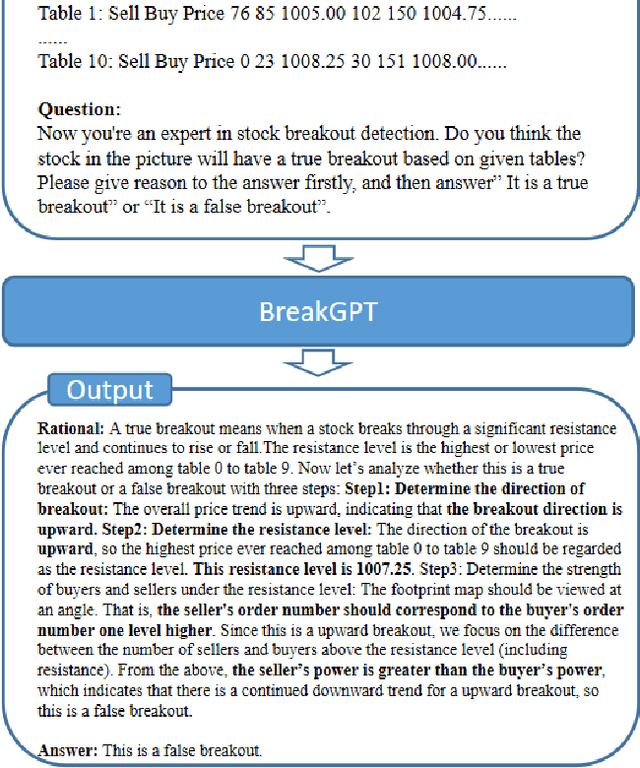
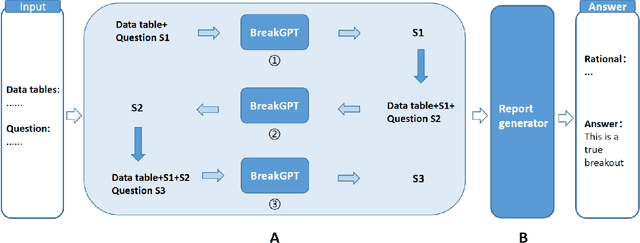
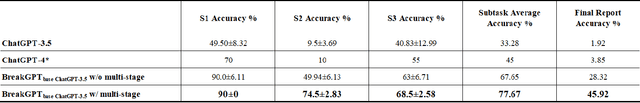

Abstract:Trading range breakout (TRB) is a key method in the technical analysis of financial trading, widely employed by traders in financial markets such as stocks, futures, and foreign exchange. However, distinguishing between true and false breakout and providing the correct rationale cause significant challenges to investors. Recently, large language models have achieved success in various downstream applications, but their effectiveness in the domain of financial breakout detection has been subpar. The reason is that the unique data and specific knowledge are required in breakout detection. To address these issues, we introduce BreakGPT, the first large language model for financial breakout detection. Furthermore, we have developed a novel framework for large language models, namely multi-stage structure, effectively reducing mistakes in downstream applications. Experimental results indicate that compared to GPT-3.5, BreakGPT improves the accuracy of answers and rational by 44%, with the multi-stage structure contributing 17.6% to the improvement. Additionally, it outperforms ChatGPT-4 by 42.07%. Our Code is publicly available: https://github.com/Neviim96/BreakGPT
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge