Sheng Cheng
UniDrive-WM: Unified Understanding, Planning and Generation World Model For Autonomous Driving
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:World models have become central to autonomous driving, where accurate scene understanding and future prediction are crucial for safe control. Recent work has explored using vision-language models (VLMs) for planning, yet existing approaches typically treat perception, prediction, and planning as separate modules. We propose UniDrive-WM, a unified VLM-based world model that jointly performs driving-scene understanding, trajectory planning, and trajectory-conditioned future image generation within a single architecture. UniDrive-WM's trajectory planner predicts a future trajectory, which conditions a VLM-based image generator to produce plausible future frames. These predictions provide additional supervisory signals that enhance scene understanding and iteratively refine trajectory generation. We further compare discrete and continuous output representations for future image prediction, analyzing their influence on downstream driving performance. Experiments on the challenging Bench2Drive benchmark show that UniDrive-WM produces high-fidelity future images and improves planning performance by 5.9% in L2 trajectory error and 9.2% in collision rate over the previous best method. These results demonstrate the advantages of tightly integrating VLM-driven reasoning, planning, and generative world modeling for autonomous driving. The project page is available at https://unidrive-wm.github.io/UniDrive-WM .
LOOPRAG: Enhancing Loop Transformation Optimization with Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models
Dec 12, 2025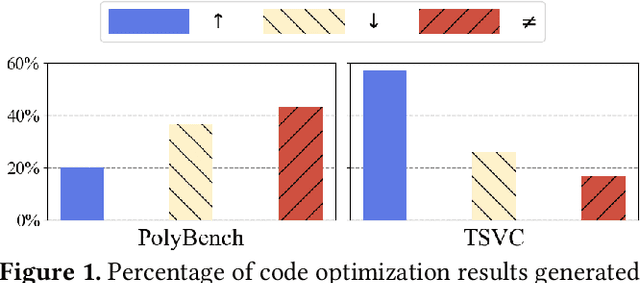
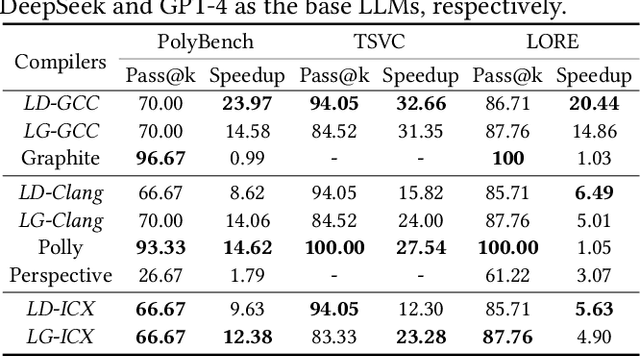
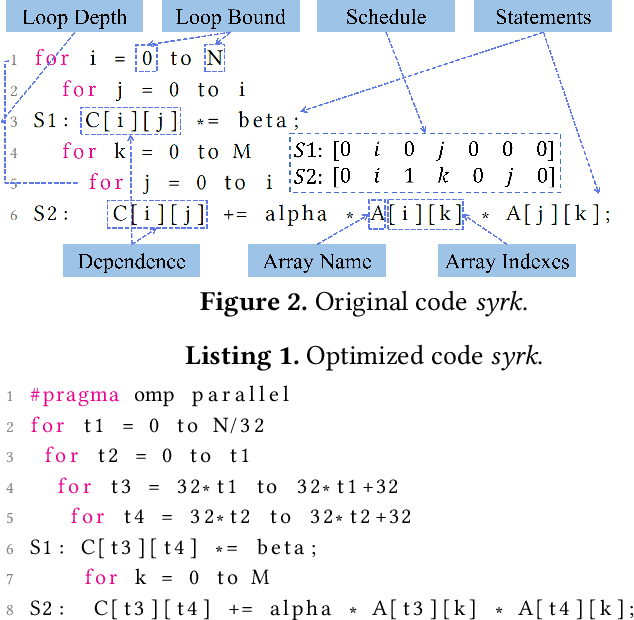
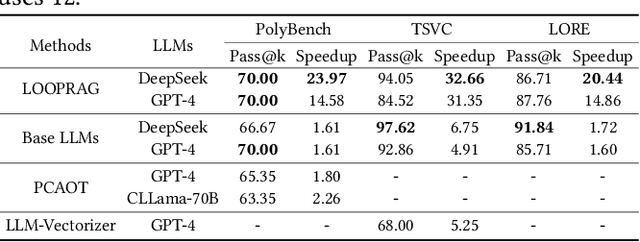
Abstract:Loop transformations are semantics-preserving optimization techniques, widely used to maximize objectives such as parallelism. Despite decades of research, applying the optimal composition of loop transformations remains challenging due to inherent complexities, including cost modeling for optimization objectives. Recent studies have explored the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) for code optimization. However, our key observation is that LLMs often struggle with effective loop transformation optimization, frequently leading to errors or suboptimal optimization, thereby missing opportunities for performance improvements. To bridge this gap, we propose LOOPRAG, a novel retrieval-augmented generation framework designed to guide LLMs in performing effective loop optimization on Static Control Part. We introduce a parameter-driven method to harness loop properties, which trigger various loop transformations, and generate diverse yet legal example codes serving as a demonstration source. To effectively obtain the most informative demonstrations, we propose a loop-aware algorithm based on loop features, which balances similarity and diversity for code retrieval. To enhance correct and efficient code generation, we introduce a feedback-based iterative mechanism that incorporates compilation, testing and performance results as feedback to guide LLMs. Each optimized code undergoes mutation, coverage and differential testing for equivalence checking. We evaluate LOOPRAG on PolyBench, TSVC and LORE benchmark suites, and compare it against compilers (GCC-Graphite, Clang-Polly, Perspective and ICX) and representative LLMs (DeepSeek and GPT-4). The results demonstrate average speedups over base compilers of up to 11.20$\times$, 14.34$\times$, and 9.29$\times$ for PolyBench, TSVC, and LORE, respectively, and speedups over base LLMs of up to 11.97$\times$, 5.61$\times$, and 11.59$\times$.
PerfTracker: Online Performance Troubleshooting for Large-scale Model Training in Production
Jun 12, 2025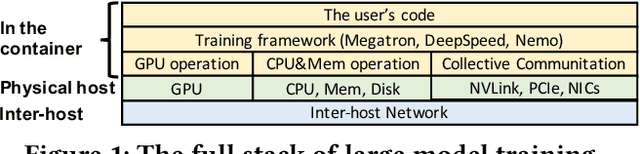



Abstract:Troubleshooting performance problems of large model training (LMT) is immensely challenging, due to unprecedented scales of modern GPU clusters, the complexity of software-hardware interactions, and the data intensity of the training process. Existing troubleshooting approaches designed for traditional distributed systems or datacenter networks fall short and can hardly apply to real-world training systems. In this paper, we present PerfTracker, the first online troubleshooting system utilizing fine-grained profiling, to diagnose performance issues of large-scale model training in production. PerfTracker can diagnose performance issues rooted in both hardware (e.g., GPUs and their interconnects) and software (e.g., Python functions and GPU operations). It scales to LMT on modern GPU clusters. PerfTracker effectively summarizes runtime behavior patterns of fine-grained LMT functions via online profiling, and leverages differential observability to localize the root cause with minimal production impact. PerfTracker has been deployed as a production service for large-scale GPU clusters of O(10, 000) GPUs (product homepage https://help.aliyun.com/zh/pai/user-guide/perftracker-online-performance-analysis-diagnostic-tool). It has been used to diagnose a variety of difficult performance issues.
DiffCoTune: Differentiable Co-Tuning for Cross-domain Robot Control
May 29, 2025



Abstract:The deployment of robot controllers is hindered by modeling discrepancies due to necessary simplifications for computational tractability or inaccuracies in data-generating simulators. Such discrepancies typically require ad-hoc tuning to meet the desired performance, thereby ensuring successful transfer to a target domain. We propose a framework for automated, gradient-based tuning to enhance performance in the deployment domain by leveraging differentiable simulators. Our method collects rollouts in an iterative manner to co-tune the simulator and controller parameters, enabling systematic transfer within a few trials in the deployment domain. Specifically, we formulate multi-step objectives for tuning and employ alternating optimization to effectively adapt the controller to the deployment domain. The scalability of our framework is demonstrated by co-tuning model-based and learning-based controllers of arbitrary complexity for tasks ranging from low-dimensional cart-pole stabilization to high-dimensional quadruped and biped tracking, showing performance improvements across different deployment domains.
BEVDiffuser: Plug-and-Play Diffusion Model for BEV Denoising with Ground-Truth Guidance
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Bird's-eye-view (BEV) representations play a crucial role in autonomous driving tasks. Despite recent advancements in BEV generation, inherent noise, stemming from sensor limitations and the learning process, remains largely unaddressed, resulting in suboptimal BEV representations that adversely impact the performance of downstream tasks. To address this, we propose BEVDiffuser, a novel diffusion model that effectively denoises BEV feature maps using the ground-truth object layout as guidance. BEVDiffuser can be operated in a plug-and-play manner during training time to enhance existing BEV models without requiring any architectural modifications. Extensive experiments on the challenging nuScenes dataset demonstrate BEVDiffuser's exceptional denoising and generation capabilities, which enable significant enhancement to existing BEV models, as evidenced by notable improvements of 12.3\% in mAP and 10.1\% in NDS achieved for 3D object detection without introducing additional computational complexity. Moreover, substantial improvements in long-tail object detection and under challenging weather and lighting conditions further validate BEVDiffuser's effectiveness in denoising and enhancing BEV representations.
Task-Parameter Nexus: Task-Specific Parameter Learning for Model-Based Control
Dec 17, 2024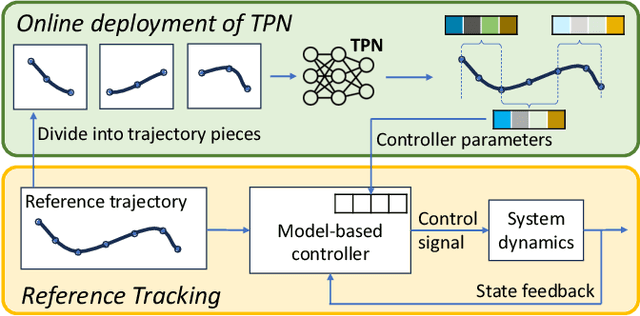
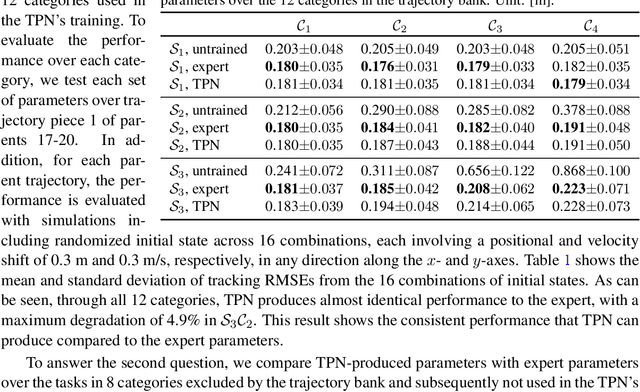
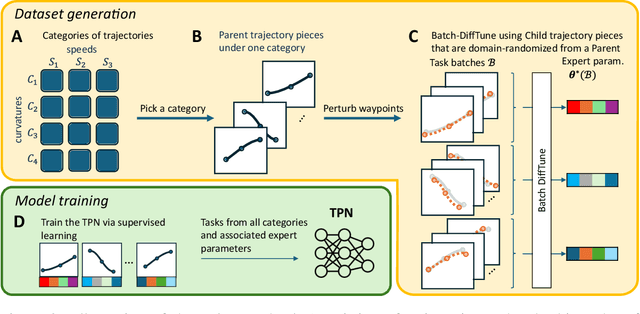
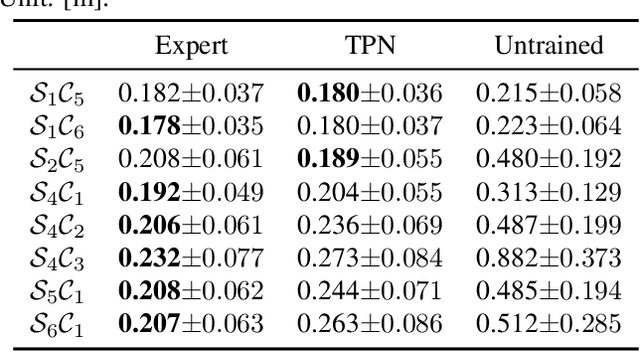
Abstract:This paper presents the Task-Parameter Nexus (TPN), a learning-based approach for online determination of the (near-)optimal control parameters of model-based controllers (MBCs) for tracking tasks. In TPN, a deep neural network is introduced to predict the control parameters for any given tracking task at runtime, especially when optimal parameters for new tasks are not immediately available. To train this network, we constructed a trajectory bank with various speeds and curvatures that represent different motion characteristics. Then, for each trajectory in the bank, we auto-tune the optimal control parameters offline and use them as the corresponding ground truth. With this dataset, the TPN is trained by supervised learning. We evaluated the TPN on the quadrotor platform. In simulation experiments, it is shown that the TPN can predict near-optimal control parameters for a spectrum of tracking tasks, demonstrating its robust generalization capabilities to unseen tasks.
Precision or Recall? An Analysis of Image Captions for Training Text-to-Image Generation Model
Nov 07, 2024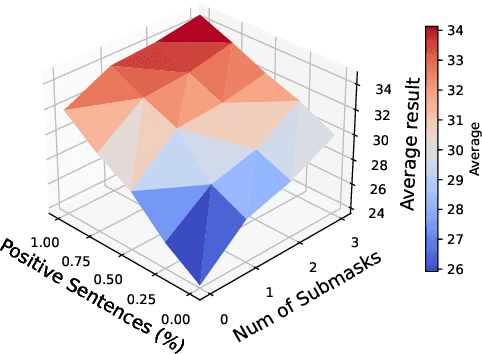
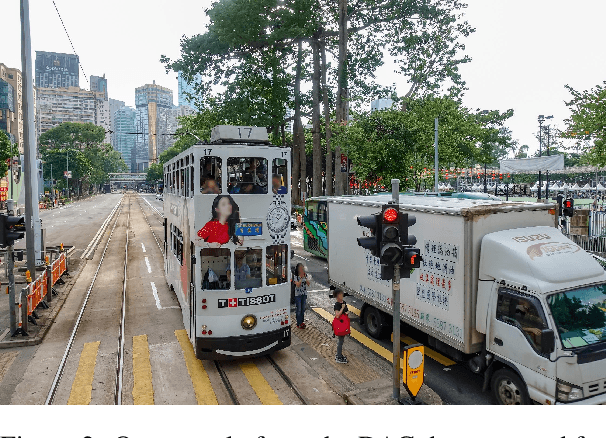
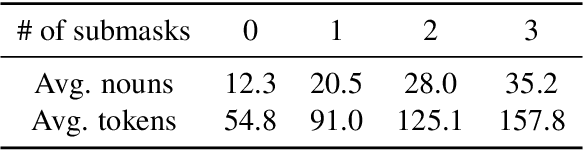
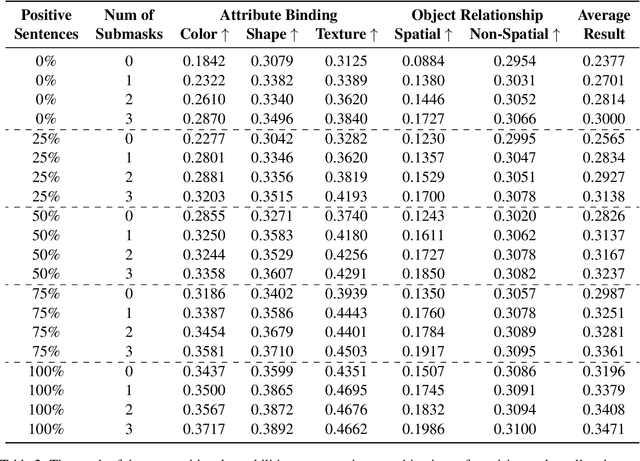

Abstract:Despite advancements in text-to-image models, generating images that precisely align with textual descriptions remains challenging due to misalignment in training data. In this paper, we analyze the critical role of caption precision and recall in text-to-image model training. Our analysis of human-annotated captions shows that both precision and recall are important for text-image alignment, but precision has a more significant impact. Leveraging these insights, we utilize Large Vision Language Models to generate synthetic captions for training. Models trained with these synthetic captions show similar behavior to those trained on human-annotated captions, underscores the potential for synthetic data in text-to-image training.
TripletCLIP: Improving Compositional Reasoning of CLIP via Synthetic Vision-Language Negatives
Nov 04, 2024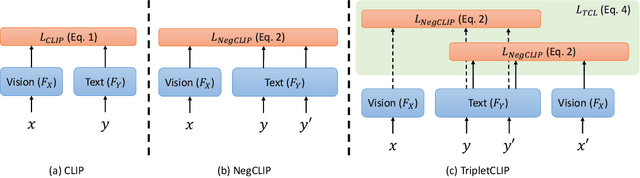
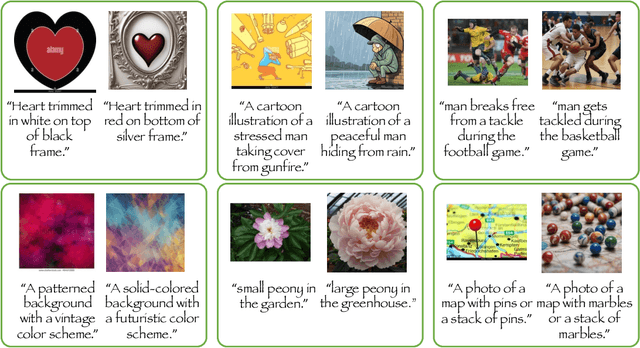
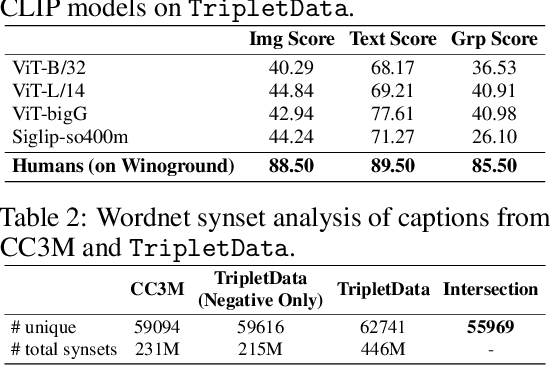

Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) models maximize the mutual information between text and visual modalities to learn representations. This makes the nature of the training data a significant factor in the efficacy of CLIP for downstream tasks. However, the lack of compositional diversity in contemporary image-text datasets limits the compositional reasoning ability of CLIP. We show that generating ``hard'' negative captions via in-context learning and synthesizing corresponding negative images with text-to-image generators offers a solution. We introduce a novel contrastive pre-training strategy that leverages these hard negative captions and images in an alternating fashion to train CLIP. We demonstrate that our method, named TripletCLIP, when applied to existing datasets such as CC3M and CC12M, enhances the compositional capabilities of CLIP, resulting in an absolute improvement of over 9% on the SugarCrepe benchmark on an equal computational budget, as well as improvements in zero-shot image classification and image retrieval. Our code, models, and data are available at: https://tripletclip.github.io
Bridging Context Gaps: Leveraging Coreference Resolution for Long Contextual Understanding
Oct 02, 2024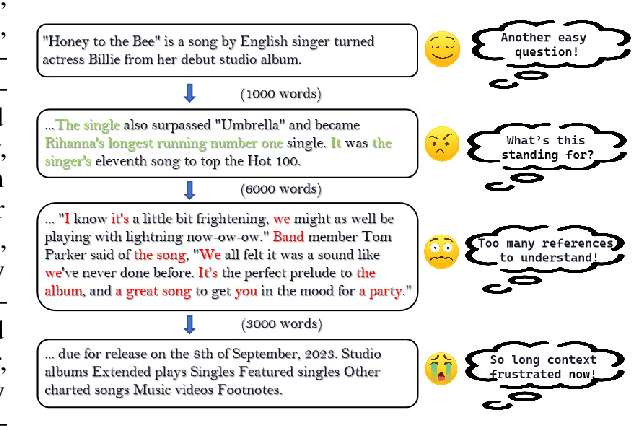
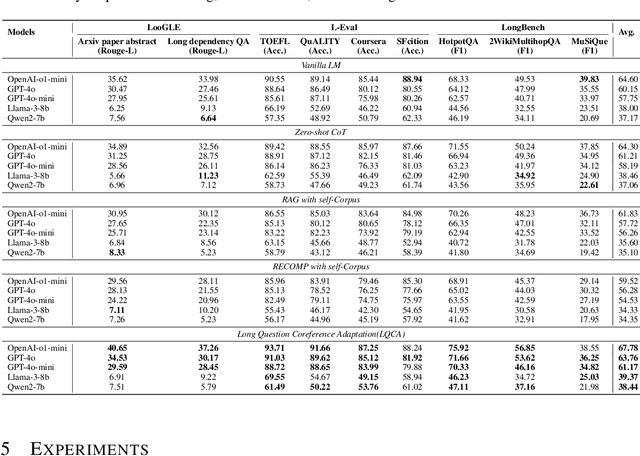
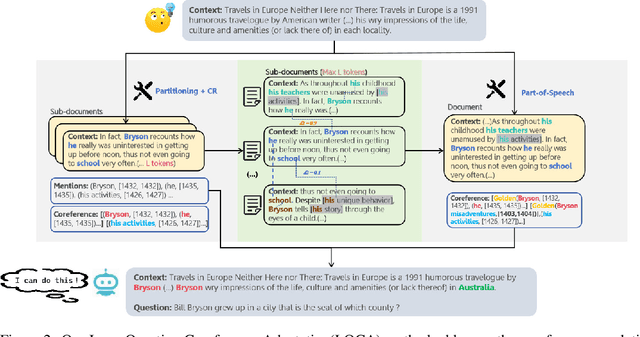
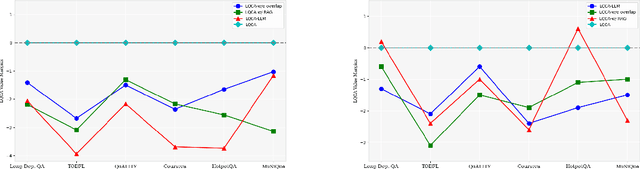
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities in natural language processing; however, they still face difficulties when tasked with understanding lengthy contexts and executing effective question answering. These challenges often arise due to the complexity and ambiguity present in longer texts. To enhance the performance of LLMs in such scenarios, we introduce the Long Question Coreference Adaptation (LQCA) method. This innovative framework focuses on coreference resolution tailored to long contexts, allowing the model to identify and manage references effectively. The LQCA method encompasses four key steps: resolving coreferences within sub-documents, computing the distances between mentions, defining a representative mention for coreference, and answering questions through mention replacement. By processing information systematically, the framework provides easier-to-handle partitions for LLMs, promoting better understanding. Experimental evaluations on a range of LLMs and datasets have yielded positive results, with a notable improvements on OpenAI-o1-mini and GPT-4o models, highlighting the effectiveness of leveraging coreference resolution to bridge context gaps in question answering.
Latent Space Energy-based Neural ODEs
Sep 05, 2024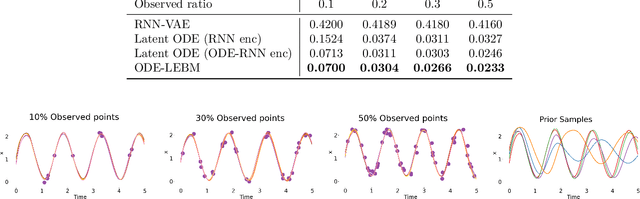
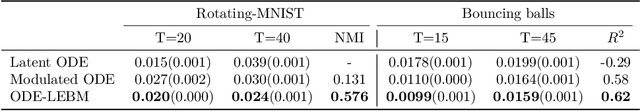
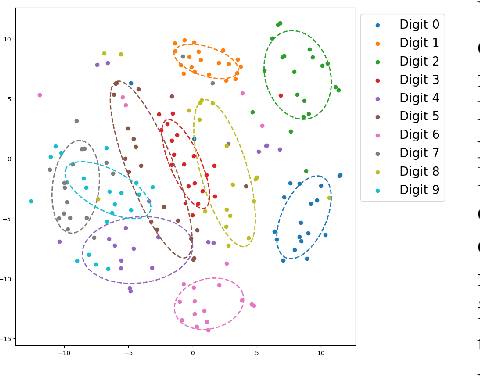
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel family of deep dynamical models designed to represent continuous-time sequence data. This family of models generates each data point in the time series by a neural emission model, which is a non-linear transformation of a latent state vector. The trajectory of the latent states is implicitly described by a neural ordinary differential equation (ODE), with the initial state following an informative prior distribution parameterized by an energy-based model. Furthermore, we can extend this model to disentangle dynamic states from underlying static factors of variation, represented as time-invariant variables in the latent space. We train the model using maximum likelihood estimation with Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) in an end-to-end manner, without requiring additional assisting components such as an inference network. Our experiments on oscillating systems, videos and real-world state sequences (MuJoCo) illustrate that ODEs with the learnable energy-based prior outperform existing counterparts, and can generalize to new dynamic parameterization, enabling long-horizon predictions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge