Hongkun Yu
Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Wisconsin Madison, Madison, WI, USA
Incentivizing Agentic Reasoning in LLM Judges via Tool-Integrated Reinforcement Learning
Oct 27, 2025
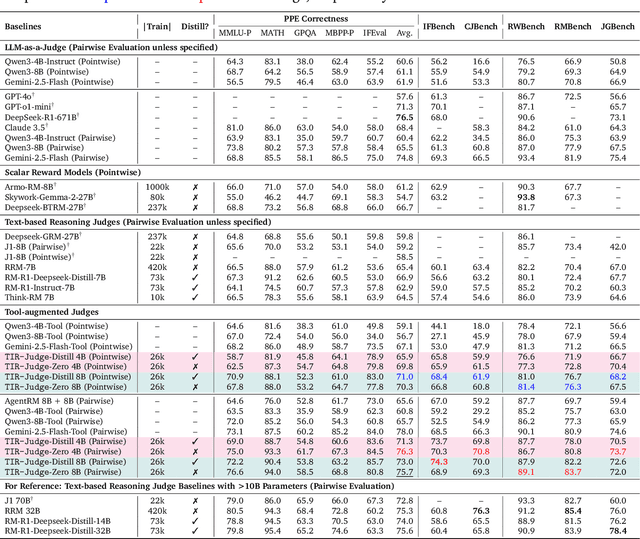
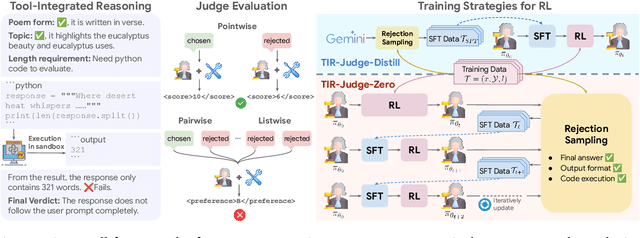
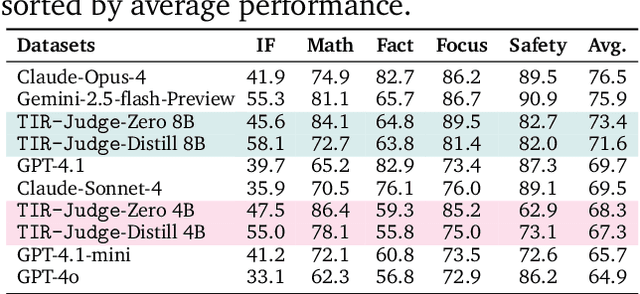
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are widely used as judges to evaluate response quality, providing a scalable alternative to human evaluation. However, most LLM judges operate solely on intrinsic text-based reasoning, limiting their ability to verify complex constraints or perform accurate computation. Motivated by the success of tool-integrated reasoning (TIR) in numerous tasks, we propose TIR-Judge, an end-to-end RL framework for training LLM judges that integrates a code executor for precise evaluation. TIR-Judge is built on three principles: (i) diverse training across verifiable and non-verifiable domains, (ii) flexible judgment formats (pointwise, pairwise, listwise), and (iii) iterative RL that bootstraps directly from the initial model without distillation. On seven public benchmarks, TIR-Judge surpasses strong reasoning-based judges by up to 6.4% (pointwise) and 7.7% (pairwise), and achieves listwise performance comparable to Claude-Opus-4 despite having only 8B parameters. Remarkably, TIR-Judge-Zero - trained entirely without distilled judge trajectories, matches the performance of distilled variants, demonstrating that tool-augmented judges can self-evolve through iterative reinforcement learning.
3D Nephrographic Image Synthesis in CT Urography with the Diffusion Model and Swin Transformer
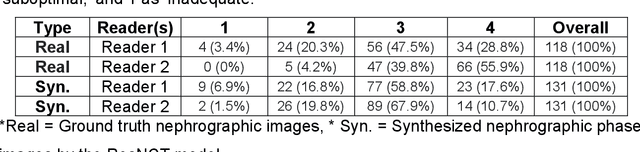
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Purpose: This study aims to develop and validate a method for synthesizing 3D nephrographic phase images in CT urography (CTU) examinations using a diffusion model integrated with a Swin Transformer-based deep learning approach. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study was approved by the local Institutional Review Board. A dataset comprising 327 patients who underwent three-phase CTU (mean $\pm$ SD age, 63 $\pm$ 15 years; 174 males, 153 females) was curated for deep learning model development. The three phases for each patient were aligned with an affine registration algorithm. A custom deep learning model coined dsSNICT (diffusion model with a Swin transformer for synthetic nephrographic phase images in CT) was developed and implemented to synthesize the nephrographic images. Performance was assessed using Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), Structural Similarity Index (SSIM), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), and Fr\'{e}chet Video Distance (FVD). Qualitative evaluation by two fellowship-trained abdominal radiologists was performed. Results: The synthetic nephrographic images generated by our proposed approach achieved high PSNR (26.3 $\pm$ 4.4 dB), SSIM (0.84 $\pm$ 0.069), MAE (12.74 $\pm$ 5.22 HU), and FVD (1323). Two radiologists provided average scores of 3.5 for real images and 3.4 for synthetic images (P-value = 0.5) on a Likert scale of 1-5, indicating that our synthetic images closely resemble real images. Conclusion: The proposed approach effectively synthesizes high-quality 3D nephrographic phase images. This model can be used to reduce radiation dose in CTU by 33.3\% without compromising image quality, which thereby enhances the safety and diagnostic utility of CT urography.
Conditioned Language Policy: A General Framework for Steerable Multi-Objective Finetuning
Jul 22, 2024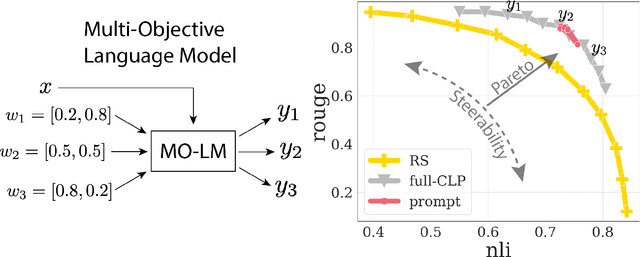
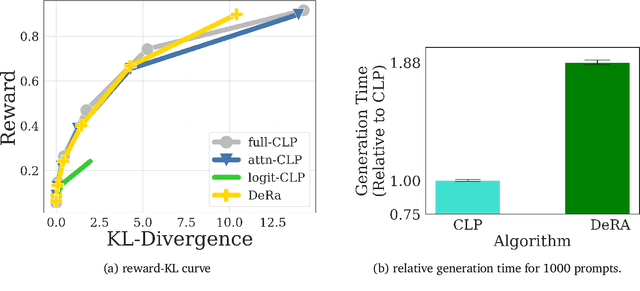
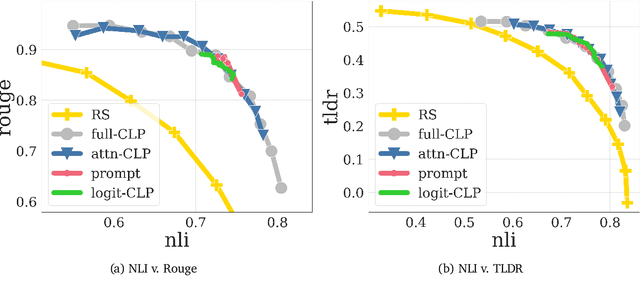
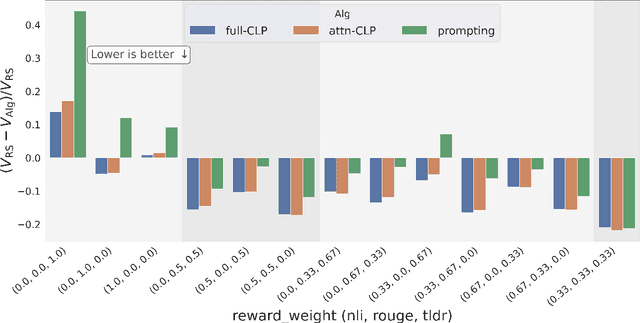
Abstract:Reward-based finetuning is crucial for aligning language policies with intended behaviors (e.g., creativity and safety). A key challenge here is to develop steerable language models that trade-off multiple (conflicting) objectives in a flexible and efficient manner. This paper presents Conditioned Language Policy (CLP), a general framework for finetuning language models on multiple objectives. Building on techniques from multi-task training and parameter-efficient finetuning, CLP can learn steerable models that effectively trade-off conflicting objectives at inference time. Notably, this does not require training or maintaining multiple models to achieve different trade-offs between the objectives. Through an extensive set of experiments and ablations, we show that the CLP framework learns steerable models that outperform and Pareto-dominate the current state-of-the-art approaches for multi-objective finetuning.
ResNCT: A Deep Learning Model for the Synthesis of Nephrographic Phase Images in CT Urography
May 07, 2024


Abstract:Purpose: To develop and evaluate a transformer-based deep learning model for the synthesis of nephrographic phase images in CT urography (CTU) examinations from the unenhanced and urographic phases. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study was approved by the local Institutional Review Board. A dataset of 119 patients (mean $\pm$ SD age, 65 $\pm$ 12 years; 75/44 males/females) with three-phase CT urography studies was curated for deep learning model development. The three phases for each patient were aligned with an affine registration algorithm. A custom model, coined Residual transformer model for Nephrographic phase CT image synthesis (ResNCT), was developed and implemented with paired inputs of non-contrast and urographic sets of images trained to produce the nephrographic phase images, that were compared with the corresponding ground truth nephrographic phase images. The synthesized images were evaluated with multiple performance metrics, including peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR), structural similarity index (SSIM), normalized cross correlation coefficient (NCC), mean absolute error (MAE), and root mean squared error (RMSE). Results: The ResNCT model successfully generated synthetic nephrographic images from non-contrast and urographic image inputs. With respect to ground truth nephrographic phase images, the images synthesized by the model achieved high PSNR (27.8 $\pm$ 2.7 dB), SSIM (0.88 $\pm$ 0.05), and NCC (0.98 $\pm$ 0.02), and low MAE (0.02 $\pm$ 0.005) and RMSE (0.042 $\pm$ 0.016). Conclusion: The ResNCT model synthesized nephrographic phase CT images with high similarity to ground truth images. The ResNCT model provides a means of eliminating the acquisition of the nephrographic phase with a resultant 33% reduction in radiation dose for CTU examinations.
Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:In this report, we present the latest model of the Gemini family, Gemini 1.5 Pro, a highly compute-efficient multimodal mixture-of-experts model capable of recalling and reasoning over fine-grained information from millions of tokens of context, including multiple long documents and hours of video and audio. Gemini 1.5 Pro achieves near-perfect recall on long-context retrieval tasks across modalities, improves the state-of-the-art in long-document QA, long-video QA and long-context ASR, and matches or surpasses Gemini 1.0 Ultra's state-of-the-art performance across a broad set of benchmarks. Studying the limits of Gemini 1.5 Pro's long-context ability, we find continued improvement in next-token prediction and near-perfect retrieval (>99%) up to at least 10M tokens, a generational leap over existing models such as Claude 2.1 (200k) and GPT-4 Turbo (128k). Finally, we highlight surprising new capabilities of large language models at the frontier; when given a grammar manual for Kalamang, a language with fewer than 200 speakers worldwide, the model learns to translate English to Kalamang at a similar level to a person who learned from the same content.
Multitask Multilingual Model Adaptation with Featurized Low-Rank Mixtures
Feb 27, 2024Abstract:Adapting pretrained large language models (LLMs) to various downstream tasks in tens or hundreds of human languages is computationally expensive. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) significantly reduces the adaptation cost, by tuning only a small amount of parameters. However, directly applying PEFT methods such as LoRA (Hu et al., 2022) on diverse dataset mixtures could lead to suboptimal performance due to limited parameter capacity and negative interference among different datasets. In this work, we propose Featurized Low-rank Mixtures (FLix), a novel PEFT method designed for effective multitask multilingual tuning. FLix associates each unique dataset feature, such as the dataset's language or task, with its own low-rank weight update parameters. By composing feature-specific parameters for each dataset, FLix can accommodate diverse dataset mixtures and generalize better to unseen datasets. Our experiments show that FLix leads to significant improvements over a variety of tasks for both supervised learning and zero-shot settings using different training data mixtures.
Multi-step Problem Solving Through a Verifier: An Empirical Analysis on Model-induced Process Supervision
Feb 05, 2024



Abstract:Process supervision, using a trained verifier to evaluate the intermediate steps generated by reasoner, has demonstrated significant improvements in multi-step problem solving. In this paper, to avoid expensive human annotation effort on the verifier training data, we introduce Model-induced Process Supervision (MiPS), a novel method for automating data curation. MiPS annotates an intermediate step by sampling completions of this solution through the reasoning model, and obtaining an accuracy defined as the proportion of correct completions. Errors in the reasoner would cause MiPS to underestimate the accuracy of intermediate steps, therefore, we suggest and empirically show that verification focusing on high predicted scores of the verifier shall be preferred over that of low predicted scores, contrary to prior work. Our approach significantly improves the performance of PaLM 2 on math and coding tasks (accuracy +0.67% on GSM8K, +4.16% on MATH, +0.92% on MBPP compared with an output supervision trained verifier). Additionally, our study demonstrates that the verifier exhibits strong generalization ability across different reasoning models.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Enable Language Models to Implicitly Learn Self-Improvement From Data
Oct 05, 2023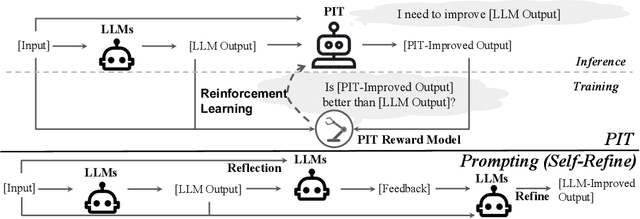
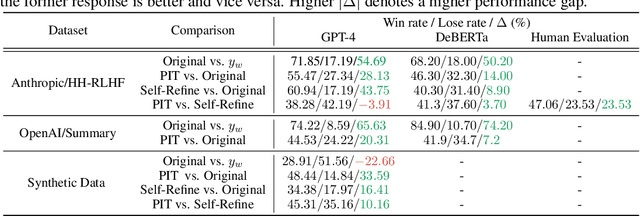
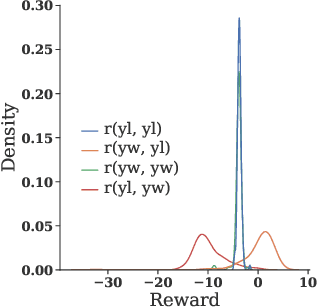
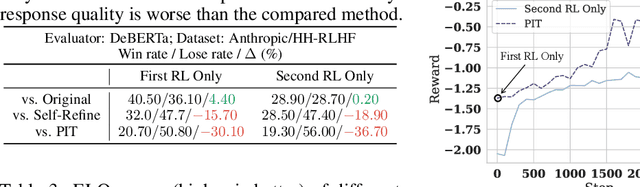
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in open-ended text generation tasks. However, the inherent open-ended nature of these tasks implies that there is always room for improvement in the quality of model responses. To address this challenge, various approaches have been proposed to enhance the performance of LLMs. There has been a growing focus on enabling LLMs to self-improve their response quality, thereby reducing the reliance on extensive human annotation efforts for collecting diverse and high-quality training data. Recently, prompting-based methods have been widely explored among self-improvement methods owing to their effectiveness, efficiency, and convenience. However, those methods usually require explicitly and thoroughly written rubrics as inputs to LLMs. It is expensive and challenging to manually derive and provide all necessary rubrics with a real-world complex goal for improvement (e.g., being more helpful and less harmful). To this end, we propose an ImPlicit Self-ImprovemenT (PIT) framework that implicitly learns the improvement goal from human preference data. PIT only requires preference data that are used to train reward models without extra human efforts. Specifically, we reformulate the training objective of reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) -- instead of maximizing response quality for a given input, we maximize the quality gap of the response conditioned on a reference response. In this way, PIT is implicitly trained with the improvement goal of better aligning with human preferences. Experiments on two real-world datasets and one synthetic dataset show that our method significantly outperforms prompting-based methods.
Flan-MoE: Scaling Instruction-Finetuned Language Models with Sparse Mixture of Experts
May 24, 2023Abstract:The explosive growth of language models and their applications have led to an increased demand for efficient and scalable methods. In this paper, we introduce Flan-MoE, a set of Instruction-Finetuned Sparse Mixture-of-Expert (MoE) models. We show that naively finetuning MoE models on a task-specific dataset (in other words, no instruction-finetuning) often yield worse performance compared to dense models of the same computational complexity. However, our Flan-MoE outperforms dense models under multiple experiment settings: instruction-finetuning only and instruction-finetuning followed by task-specific finetuning. This shows that instruction-finetuning is an essential stage for MoE models. Specifically, our largest model, Flan-MoE-32B, surpasses the performance of Flan-PaLM-62B on four benchmarks, while utilizing only one-third of the FLOPs. The success of Flan-MoE encourages rethinking the design of large-scale, high-performance language models, under the setting of task-agnostic learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge