Meghan G. Lubner
Department of Radiology, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine & Public Health, Madison, WI, USA
Opportunistic Promptable Segmentation: Leveraging Routine Radiological Annotations to Guide 3D CT Lesion Segmentation
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:The development of machine learning models for CT imaging depends on the availability of large, high-quality, and diverse annotated datasets. Although large volumes of CT images and reports are readily available in clinical picture archiving and communication systems (PACS), 3D segmentations of critical findings are costly to obtain, typically requiring extensive manual annotation by radiologists. On the other hand, it is common for radiologists to provide limited annotations of findings during routine reads, such as line measurements and arrows, that are often stored in PACS as GSPS objects. We posit that these sparse annotations can be extracted along with CT volumes and converted into 3D segmentations using promptable segmentation models, a paradigm we term Opportunistic Promptable Segmentation. To enable this paradigm, we propose SAM2CT, the first promptable segmentation model designed to convert radiologist annotations into 3D segmentations in CT volumes. SAM2CT builds upon SAM2 by extending the prompt encoder to support arrow and line inputs and by introducing Memory-Conditioned Memories (MCM), a memory encoding strategy tailored to 3D medical volumes. On public lesion segmentation benchmarks, SAM2CT outperforms existing promptable segmentation models and similarly trained baselines, achieving Dice similarity coefficients of 0.649 for arrow prompts and 0.757 for line prompts. Applying the model to pre-existing GSPS annotations from a clinical PACS (N = 60), SAM2CT generates 3D segmentations that are clinically acceptable or require only minor adjustments in 87% of cases, as scored by radiologists. Additionally, SAM2CT demonstrates strong zero-shot performance on select Emergency Department findings. These results suggest that large-scale mining of historical GSPS annotations represents a promising and scalable approach for generating 3D CT segmentation datasets.
3D Nephrographic Image Synthesis in CT Urography with the Diffusion Model and Swin Transformer
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Purpose: This study aims to develop and validate a method for synthesizing 3D nephrographic phase images in CT urography (CTU) examinations using a diffusion model integrated with a Swin Transformer-based deep learning approach. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study was approved by the local Institutional Review Board. A dataset comprising 327 patients who underwent three-phase CTU (mean $\pm$ SD age, 63 $\pm$ 15 years; 174 males, 153 females) was curated for deep learning model development. The three phases for each patient were aligned with an affine registration algorithm. A custom deep learning model coined dsSNICT (diffusion model with a Swin transformer for synthetic nephrographic phase images in CT) was developed and implemented to synthesize the nephrographic images. Performance was assessed using Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), Structural Similarity Index (SSIM), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), and Fr\'{e}chet Video Distance (FVD). Qualitative evaluation by two fellowship-trained abdominal radiologists was performed. Results: The synthetic nephrographic images generated by our proposed approach achieved high PSNR (26.3 $\pm$ 4.4 dB), SSIM (0.84 $\pm$ 0.069), MAE (12.74 $\pm$ 5.22 HU), and FVD (1323). Two radiologists provided average scores of 3.5 for real images and 3.4 for synthetic images (P-value = 0.5) on a Likert scale of 1-5, indicating that our synthetic images closely resemble real images. Conclusion: The proposed approach effectively synthesizes high-quality 3D nephrographic phase images. This model can be used to reduce radiation dose in CTU by 33.3\% without compromising image quality, which thereby enhances the safety and diagnostic utility of CT urography.
ResNCT: A Deep Learning Model for the Synthesis of Nephrographic Phase Images in CT Urography
May 07, 2024


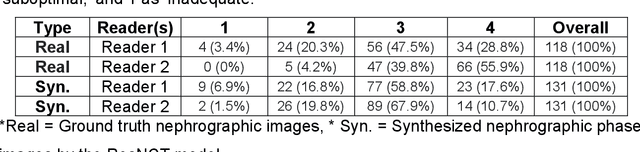
Abstract:Purpose: To develop and evaluate a transformer-based deep learning model for the synthesis of nephrographic phase images in CT urography (CTU) examinations from the unenhanced and urographic phases. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study was approved by the local Institutional Review Board. A dataset of 119 patients (mean $\pm$ SD age, 65 $\pm$ 12 years; 75/44 males/females) with three-phase CT urography studies was curated for deep learning model development. The three phases for each patient were aligned with an affine registration algorithm. A custom model, coined Residual transformer model for Nephrographic phase CT image synthesis (ResNCT), was developed and implemented with paired inputs of non-contrast and urographic sets of images trained to produce the nephrographic phase images, that were compared with the corresponding ground truth nephrographic phase images. The synthesized images were evaluated with multiple performance metrics, including peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR), structural similarity index (SSIM), normalized cross correlation coefficient (NCC), mean absolute error (MAE), and root mean squared error (RMSE). Results: The ResNCT model successfully generated synthetic nephrographic images from non-contrast and urographic image inputs. With respect to ground truth nephrographic phase images, the images synthesized by the model achieved high PSNR (27.8 $\pm$ 2.7 dB), SSIM (0.88 $\pm$ 0.05), and NCC (0.98 $\pm$ 0.02), and low MAE (0.02 $\pm$ 0.005) and RMSE (0.042 $\pm$ 0.016). Conclusion: The ResNCT model synthesized nephrographic phase CT images with high similarity to ground truth images. The ResNCT model provides a means of eliminating the acquisition of the nephrographic phase with a resultant 33% reduction in radiation dose for CTU examinations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge