Dustin Tran
Dima
Gemma 3 Technical Report
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:We introduce Gemma 3, a multimodal addition to the Gemma family of lightweight open models, ranging in scale from 1 to 27 billion parameters. This version introduces vision understanding abilities, a wider coverage of languages and longer context - at least 128K tokens. We also change the architecture of the model to reduce the KV-cache memory that tends to explode with long context. This is achieved by increasing the ratio of local to global attention layers, and keeping the span on local attention short. The Gemma 3 models are trained with distillation and achieve superior performance to Gemma 2 for both pre-trained and instruction finetuned versions. In particular, our novel post-training recipe significantly improves the math, chat, instruction-following and multilingual abilities, making Gemma3-4B-IT competitive with Gemma2-27B-IT and Gemma3-27B-IT comparable to Gemini-1.5-Pro across benchmarks. We release all our models to the community.
Long-form factuality in large language models
Apr 03, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often generate content that contains factual errors when responding to fact-seeking prompts on open-ended topics. To benchmark a model's long-form factuality in open domains, we first use GPT-4 to generate LongFact, a prompt set comprising thousands of questions spanning 38 topics. We then propose that LLM agents can be used as automated evaluators for long-form factuality through a method which we call Search-Augmented Factuality Evaluator (SAFE). SAFE utilizes an LLM to break down a long-form response into a set of individual facts and to evaluate the accuracy of each fact using a multi-step reasoning process comprising sending search queries to Google Search and determining whether a fact is supported by the search results. Furthermore, we propose extending F1 score as an aggregated metric for long-form factuality. To do so, we balance the percentage of supported facts in a response (precision) with the percentage of provided facts relative to a hyperparameter representing a user's preferred response length (recall). Empirically, we demonstrate that LLM agents can outperform crowdsourced human annotators - on a set of ~16k individual facts, SAFE agrees with crowdsourced human annotators 72% of the time, and on a random subset of 100 disagreement cases, SAFE wins 76% of the time. At the same time, SAFE is more than 20 times cheaper than human annotators. We also benchmark thirteen language models on LongFact across four model families (Gemini, GPT, Claude, and PaLM-2), finding that larger language models generally achieve better long-form factuality. LongFact, SAFE, and all experimental code are available at https://github.com/google-deepmind/long-form-factuality.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Larger language models do in-context learning differently
Mar 08, 2023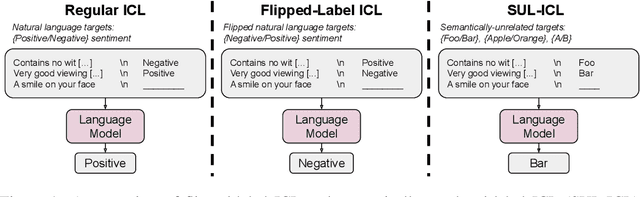



Abstract:We study how in-context learning (ICL) in language models is affected by semantic priors versus input-label mappings. We investigate two setups-ICL with flipped labels and ICL with semantically-unrelated labels-across various model families (GPT-3, InstructGPT, Codex, PaLM, and Flan-PaLM). First, experiments on ICL with flipped labels show that overriding semantic priors is an emergent ability of model scale. While small language models ignore flipped labels presented in-context and thus rely primarily on semantic priors from pretraining, large models can override semantic priors when presented with in-context exemplars that contradict priors, despite the stronger semantic priors that larger models may hold. We next study semantically-unrelated label ICL (SUL-ICL), in which labels are semantically unrelated to their inputs (e.g., foo/bar instead of negative/positive), thereby forcing language models to learn the input-label mappings shown in in-context exemplars in order to perform the task. The ability to do SUL-ICL also emerges primarily with scale, and large-enough language models can even perform linear classification in a SUL-ICL setting. Finally, we evaluate instruction-tuned models and find that instruction tuning strengthens both the use of semantic priors and the capacity to learn input-label mappings, but more of the former.
A Simple Zero-shot Prompt Weighting Technique to Improve Prompt Ensembling in Text-Image Models
Feb 13, 2023



Abstract:Contrastively trained text-image models have the remarkable ability to perform zero-shot classification, that is, classifying previously unseen images into categories that the model has never been explicitly trained to identify. However, these zero-shot classifiers need prompt engineering to achieve high accuracy. Prompt engineering typically requires hand-crafting a set of prompts for individual downstream tasks. In this work, we aim to automate this prompt engineering and improve zero-shot accuracy through prompt ensembling. In particular, we ask "Given a large pool of prompts, can we automatically score the prompts and ensemble those that are most suitable for a particular downstream dataset, without needing access to labeled validation data?". We demonstrate that this is possible. In doing so, we identify several pathologies in a naive prompt scoring method where the score can be easily overconfident due to biases in pre-training and test data, and we propose a novel prompt scoring method that corrects for the biases. Using our proposed scoring method to create a weighted average prompt ensemble, our method outperforms equal average ensemble, as well as hand-crafted prompts, on ImageNet, 4 of its variants, and 11 fine-grained classification benchmarks, all while being fully automatic, optimization-free, and not requiring access to labeled validation data.
Scaling Vision Transformers to 22 Billion Parameters
Feb 10, 2023



Abstract:The scaling of Transformers has driven breakthrough capabilities for language models. At present, the largest large language models (LLMs) contain upwards of 100B parameters. Vision Transformers (ViT) have introduced the same architecture to image and video modelling, but these have not yet been successfully scaled to nearly the same degree; the largest dense ViT contains 4B parameters (Chen et al., 2022). We present a recipe for highly efficient and stable training of a 22B-parameter ViT (ViT-22B) and perform a wide variety of experiments on the resulting model. When evaluated on downstream tasks (often with a lightweight linear model on frozen features), ViT-22B demonstrates increasing performance with scale. We further observe other interesting benefits of scale, including an improved tradeoff between fairness and performance, state-of-the-art alignment to human visual perception in terms of shape/texture bias, and improved robustness. ViT-22B demonstrates the potential for "LLM-like" scaling in vision, and provides key steps towards getting there.
Benchmarking Bayesian Deep Learning on Diabetic Retinopathy Detection Tasks
Nov 23, 2022Abstract:Bayesian deep learning seeks to equip deep neural networks with the ability to precisely quantify their predictive uncertainty, and has promised to make deep learning more reliable for safety-critical real-world applications. Yet, existing Bayesian deep learning methods fall short of this promise; new methods continue to be evaluated on unrealistic test beds that do not reflect the complexities of downstream real-world tasks that would benefit most from reliable uncertainty quantification. We propose the RETINA Benchmark, a set of real-world tasks that accurately reflect such complexities and are designed to assess the reliability of predictive models in safety-critical scenarios. Specifically, we curate two publicly available datasets of high-resolution human retina images exhibiting varying degrees of diabetic retinopathy, a medical condition that can lead to blindness, and use them to design a suite of automated diagnosis tasks that require reliable predictive uncertainty quantification. We use these tasks to benchmark well-established and state-of-the-art Bayesian deep learning methods on task-specific evaluation metrics. We provide an easy-to-use codebase for fast and easy benchmarking following reproducibility and software design principles. We provide implementations of all methods included in the benchmark as well as results computed over 100 TPU days, 20 GPU days, 400 hyperparameter configurations, and evaluation on at least 6 random seeds each.
Plex: Towards Reliability using Pretrained Large Model Extensions
Jul 15, 2022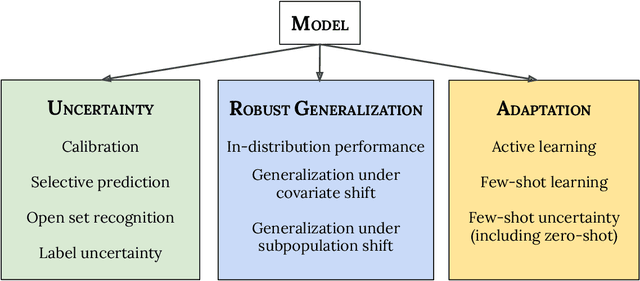

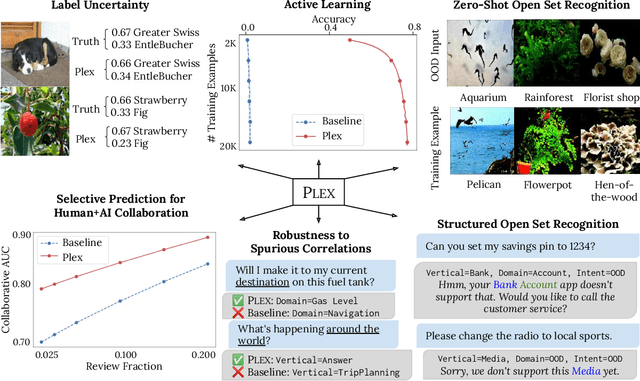

Abstract:A recent trend in artificial intelligence is the use of pretrained models for language and vision tasks, which have achieved extraordinary performance but also puzzling failures. Probing these models' abilities in diverse ways is therefore critical to the field. In this paper, we explore the reliability of models, where we define a reliable model as one that not only achieves strong predictive performance but also performs well consistently over many decision-making tasks involving uncertainty (e.g., selective prediction, open set recognition), robust generalization (e.g., accuracy and proper scoring rules such as log-likelihood on in- and out-of-distribution datasets), and adaptation (e.g., active learning, few-shot uncertainty). We devise 10 types of tasks over 40 datasets in order to evaluate different aspects of reliability on both vision and language domains. To improve reliability, we developed ViT-Plex and T5-Plex, pretrained large model extensions for vision and language modalities, respectively. Plex greatly improves the state-of-the-art across reliability tasks, and simplifies the traditional protocol as it improves the out-of-the-box performance and does not require designing scores or tuning the model for each task. We demonstrate scaling effects over model sizes up to 1B parameters and pretraining dataset sizes up to 4B examples. We also demonstrate Plex's capabilities on challenging tasks including zero-shot open set recognition, active learning, and uncertainty in conversational language understanding.
A Simple Approach to Improve Single-Model Deep Uncertainty via Distance-Awareness
May 01, 2022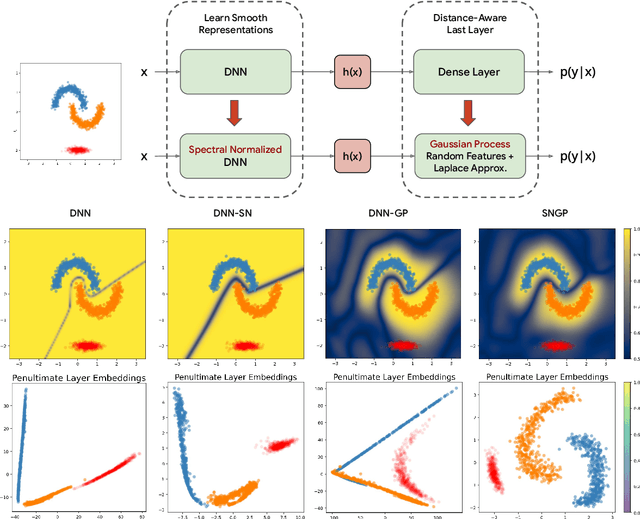
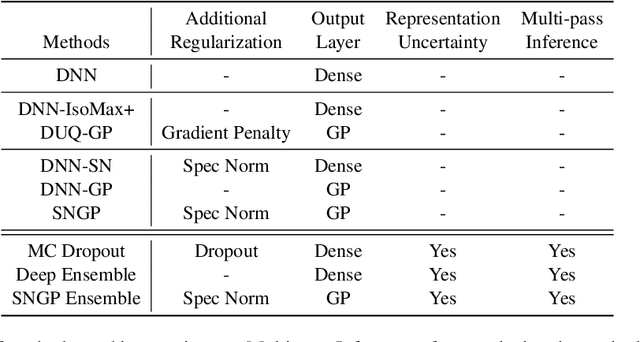
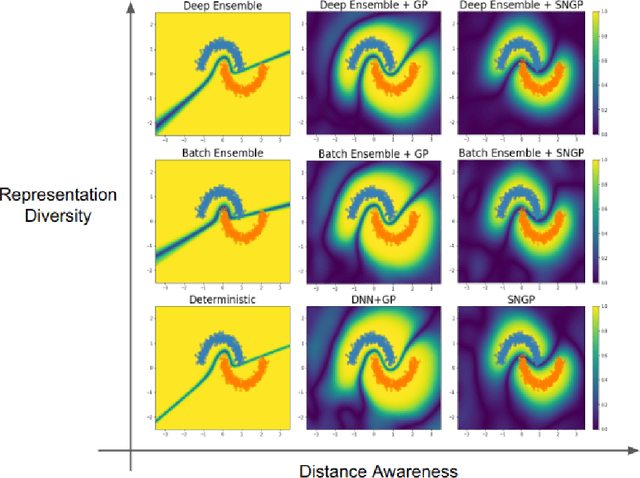
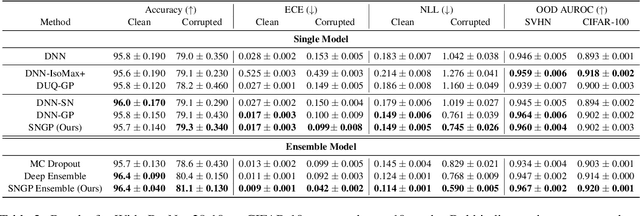
Abstract:Accurate uncertainty quantification is a major challenge in deep learning, as neural networks can make overconfident errors and assign high confidence predictions to out-of-distribution (OOD) inputs. The most popular approaches to estimate predictive uncertainty in deep learning are methods that combine predictions from multiple neural networks, such as Bayesian neural networks (BNNs) and deep ensembles. However their practicality in real-time, industrial-scale applications are limited due to the high memory and computational cost. Furthermore, ensembles and BNNs do not necessarily fix all the issues with the underlying member networks. In this work, we study principled approaches to improve uncertainty property of a single network, based on a single, deterministic representation. By formalizing the uncertainty quantification as a minimax learning problem, we first identify distance awareness, i.e., the model's ability to quantify the distance of a testing example from the training data, as a necessary condition for a DNN to achieve high-quality (i.e., minimax optimal) uncertainty estimation. We then propose Spectral-normalized Neural Gaussian Process (SNGP), a simple method that improves the distance-awareness ability of modern DNNs with two simple changes: (1) applying spectral normalization to hidden weights to enforce bi-Lipschitz smoothness in representations and (2) replacing the last output layer with a Gaussian process layer. On a suite of vision and language understanding benchmarks, SNGP outperforms other single-model approaches in prediction, calibration and out-of-domain detection. Furthermore, SNGP provides complementary benefits to popular techniques such as deep ensembles and data augmentation, making it a simple and scalable building block for probabilistic deep learning. Code is open-sourced at https://github.com/google/uncertainty-baselines
Sparse MoEs meet Efficient Ensembles
Oct 07, 2021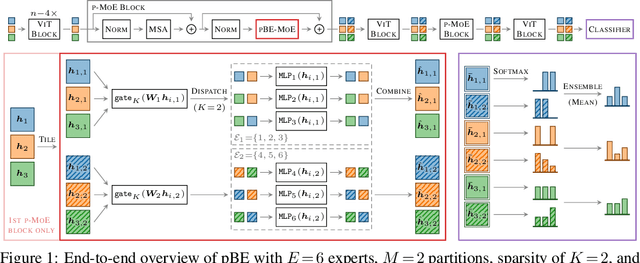

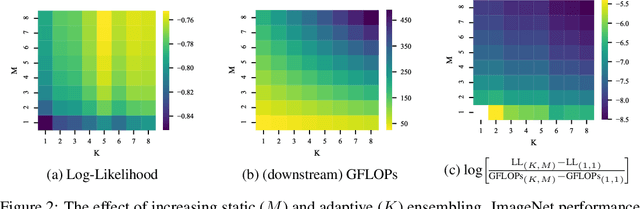
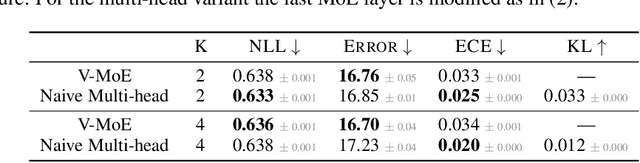
Abstract:Machine learning models based on the aggregated outputs of submodels, either at the activation or prediction levels, lead to strong performance. We study the interplay of two popular classes of such models: ensembles of neural networks and sparse mixture of experts (sparse MoEs). First, we show that these two approaches have complementary features whose combination is beneficial. Then, we present partitioned batch ensembles, an efficient ensemble of sparse MoEs that takes the best of both classes of models. Extensive experiments on fine-tuned vision transformers demonstrate the accuracy, log-likelihood, few-shot learning, robustness, and uncertainty calibration improvements of our approach over several challenging baselines. Partitioned batch ensembles not only scale to models with up to 2.7B parameters, but also provide larger performance gains for larger models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge