Davis Rempe
GENMO: A GENeralist Model for Human MOtion
May 02, 2025



Abstract:Human motion modeling traditionally separates motion generation and estimation into distinct tasks with specialized models. Motion generation models focus on creating diverse, realistic motions from inputs like text, audio, or keyframes, while motion estimation models aim to reconstruct accurate motion trajectories from observations like videos. Despite sharing underlying representations of temporal dynamics and kinematics, this separation limits knowledge transfer between tasks and requires maintaining separate models. We present GENMO, a unified Generalist Model for Human Motion that bridges motion estimation and generation in a single framework. Our key insight is to reformulate motion estimation as constrained motion generation, where the output motion must precisely satisfy observed conditioning signals. Leveraging the synergy between regression and diffusion, GENMO achieves accurate global motion estimation while enabling diverse motion generation. We also introduce an estimation-guided training objective that exploits in-the-wild videos with 2D annotations and text descriptions to enhance generative diversity. Furthermore, our novel architecture handles variable-length motions and mixed multimodal conditions (text, audio, video) at different time intervals, offering flexible control. This unified approach creates synergistic benefits: generative priors improve estimated motions under challenging conditions like occlusions, while diverse video data enhances generation capabilities. Extensive experiments demonstrate GENMO's effectiveness as a generalist framework that successfully handles multiple human motion tasks within a single model.
COIN: Control-Inpainting Diffusion Prior for Human and Camera Motion Estimation
Aug 29, 2024



Abstract:Estimating global human motion from moving cameras is challenging due to the entanglement of human and camera motions. To mitigate the ambiguity, existing methods leverage learned human motion priors, which however often result in oversmoothed motions with misaligned 2D projections. To tackle this problem, we propose COIN, a control-inpainting motion diffusion prior that enables fine-grained control to disentangle human and camera motions. Although pre-trained motion diffusion models encode rich motion priors, we find it non-trivial to leverage such knowledge to guide global motion estimation from RGB videos. COIN introduces a novel control-inpainting score distillation sampling method to ensure well-aligned, consistent, and high-quality motion from the diffusion prior within a joint optimization framework. Furthermore, we introduce a new human-scene relation loss to alleviate the scale ambiguity by enforcing consistency among the humans, camera, and scene. Experiments on three challenging benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of COIN, which outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of global human motion estimation and camera motion estimation. As an illustrative example, COIN outperforms the state-of-the-art method by 33% in world joint position error (W-MPJPE) on the RICH dataset.
Generating Human Interaction Motions in Scenes with Text Control
Apr 16, 2024Abstract:We present TeSMo, a method for text-controlled scene-aware motion generation based on denoising diffusion models. Previous text-to-motion methods focus on characters in isolation without considering scenes due to the limited availability of datasets that include motion, text descriptions, and interactive scenes. Our approach begins with pre-training a scene-agnostic text-to-motion diffusion model, emphasizing goal-reaching constraints on large-scale motion-capture datasets. We then enhance this model with a scene-aware component, fine-tuned using data augmented with detailed scene information, including ground plane and object shapes. To facilitate training, we embed annotated navigation and interaction motions within scenes. The proposed method produces realistic and diverse human-object interactions, such as navigation and sitting, in different scenes with various object shapes, orientations, initial body positions, and poses. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach surpasses prior techniques in terms of the plausibility of human-scene interactions, as well as the realism and variety of the generated motions. Code will be released upon publication of this work at https://research.nvidia.com/labs/toronto-ai/tesmo.
Multi-Track Timeline Control for Text-Driven 3D Human Motion Generation
Jan 16, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in generative modeling have led to promising progress on synthesizing 3D human motion from text, with methods that can generate character animations from short prompts and specified durations. However, using a single text prompt as input lacks the fine-grained control needed by animators, such as composing multiple actions and defining precise durations for parts of the motion. To address this, we introduce the new problem of timeline control for text-driven motion synthesis, which provides an intuitive, yet fine-grained, input interface for users. Instead of a single prompt, users can specify a multi-track timeline of multiple prompts organized in temporal intervals that may overlap. This enables specifying the exact timings of each action and composing multiple actions in sequence or at overlapping intervals. To generate composite animations from a multi-track timeline, we propose a new test-time denoising method. This method can be integrated with any pre-trained motion diffusion model to synthesize realistic motions that accurately reflect the timeline. At every step of denoising, our method processes each timeline interval (text prompt) individually, subsequently aggregating the predictions with consideration for the specific body parts engaged in each action. Experimental comparisons and ablations validate that our method produces realistic motions that respect the semantics and timing of given text prompts. Our code and models are publicly available at https://mathis.petrovich.fr/stmc.
NIFTY: Neural Object Interaction Fields for Guided Human Motion Synthesis
Jul 14, 2023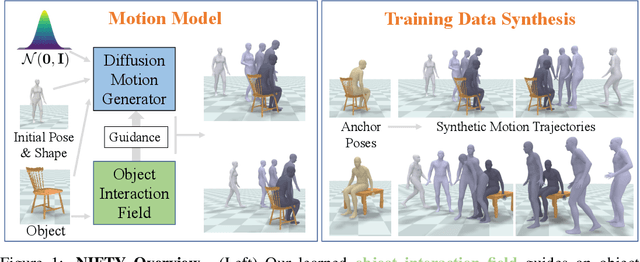

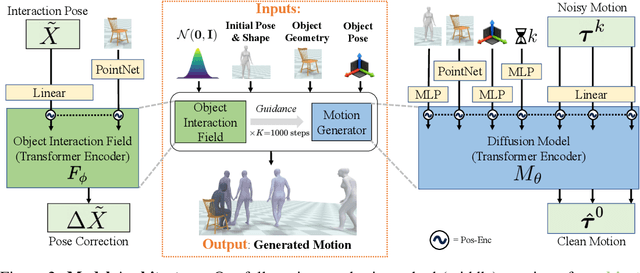
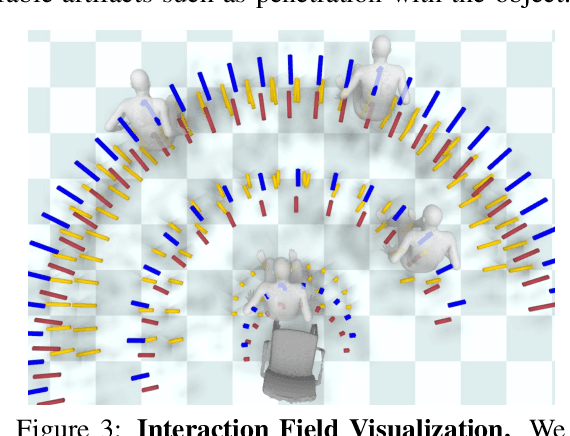
Abstract:We address the problem of generating realistic 3D motions of humans interacting with objects in a scene. Our key idea is to create a neural interaction field attached to a specific object, which outputs the distance to the valid interaction manifold given a human pose as input. This interaction field guides the sampling of an object-conditioned human motion diffusion model, so as to encourage plausible contacts and affordance semantics. To support interactions with scarcely available data, we propose an automated synthetic data pipeline. For this, we seed a pre-trained motion model, which has priors for the basics of human movement, with interaction-specific anchor poses extracted from limited motion capture data. Using our guided diffusion model trained on generated synthetic data, we synthesize realistic motions for sitting and lifting with several objects, outperforming alternative approaches in terms of motion quality and successful action completion. We call our framework NIFTY: Neural Interaction Fields for Trajectory sYnthesis.
Language-Guided Traffic Simulation via Scene-Level Diffusion
Jun 10, 2023Abstract:Realistic and controllable traffic simulation is a core capability that is necessary to accelerate autonomous vehicle (AV) development. However, current approaches for controlling learning-based traffic models require significant domain expertise and are difficult for practitioners to use. To remedy this, we present CTG++, a scene-level conditional diffusion model that can be guided by language instructions. Developing this requires tackling two challenges: the need for a realistic and controllable traffic model backbone, and an effective method to interface with a traffic model using language. To address these challenges, we first propose a scene-level diffusion model equipped with a spatio-temporal transformer backbone, which generates realistic and controllable traffic. We then harness a large language model (LLM) to convert a user's query into a loss function, guiding the diffusion model towards query-compliant generation. Through comprehensive evaluation, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method in generating realistic, query-compliant traffic simulations.
Trace and Pace: Controllable Pedestrian Animation via Guided Trajectory Diffusion
Apr 04, 2023



Abstract:We introduce a method for generating realistic pedestrian trajectories and full-body animations that can be controlled to meet user-defined goals. We draw on recent advances in guided diffusion modeling to achieve test-time controllability of trajectories, which is normally only associated with rule-based systems. Our guided diffusion model allows users to constrain trajectories through target waypoints, speed, and specified social groups while accounting for the surrounding environment context. This trajectory diffusion model is integrated with a novel physics-based humanoid controller to form a closed-loop, full-body pedestrian animation system capable of placing large crowds in a simulated environment with varying terrains. We further propose utilizing the value function learned during RL training of the animation controller to guide diffusion to produce trajectories better suited for particular scenarios such as collision avoidance and traversing uneven terrain. Video results are available on the project page at https://nv-tlabs.github.io/trace-pace .
CurveCloudNet: Processing Point Clouds with 1D Structure
Mar 21, 2023


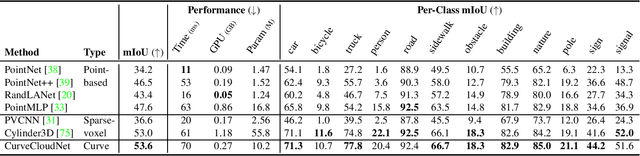
Abstract:Modern depth sensors such as LiDAR operate by sweeping laser-beams across the scene, resulting in a point cloud with notable 1D curve-like structures. In this work, we introduce a new point cloud processing scheme and backbone, called CurveCloudNet, which takes advantage of the curve-like structure inherent to these sensors. While existing backbones discard the rich 1D traversal patterns and rely on Euclidean operations, CurveCloudNet parameterizes the point cloud as a collection of polylines (dubbed a "curve cloud"), establishing a local surface-aware ordering on the points. Our method applies curve-specific operations to process the curve cloud, including a symmetric 1D convolution, a ball grouping for merging points along curves, and an efficient 1D farthest point sampling algorithm on curves. By combining these curve operations with existing point-based operations, CurveCloudNet is an efficient, scalable, and accurate backbone with low GPU memory requirements. Evaluations on the ShapeNet, Kortx, Audi Driving, and nuScenes datasets demonstrate that CurveCloudNet outperforms both point-based and sparse-voxel backbones in various segmentation settings, notably scaling better to large scenes than point-based alternatives while exhibiting better single object performance than sparse-voxel alternatives.
Guided Conditional Diffusion for Controllable Traffic Simulation
Oct 31, 2022Abstract:Controllable and realistic traffic simulation is critical for developing and verifying autonomous vehicles. Typical heuristic-based traffic models offer flexible control to make vehicles follow specific trajectories and traffic rules. On the other hand, data-driven approaches generate realistic and human-like behaviors, improving transfer from simulated to real-world traffic. However, to the best of our knowledge, no traffic model offers both controllability and realism. In this work, we develop a conditional diffusion model for controllable traffic generation (CTG) that allows users to control desired properties of trajectories at test time (e.g., reach a goal or follow a speed limit) while maintaining realism and physical feasibility through enforced dynamics. The key technical idea is to leverage recent advances from diffusion modeling and differentiable logic to guide generated trajectories to meet rules defined using signal temporal logic (STL). We further extend guidance to multi-agent settings and enable interaction-based rules like collision avoidance. CTG is extensively evaluated on the nuScenes dataset for diverse and composite rules, demonstrating improvement over strong baselines in terms of the controllability-realism tradeoff.
COPILOT: Human Collision Prediction and Localization from Multi-view Egocentric Videos
Oct 04, 2022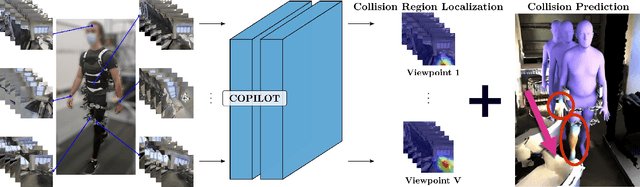
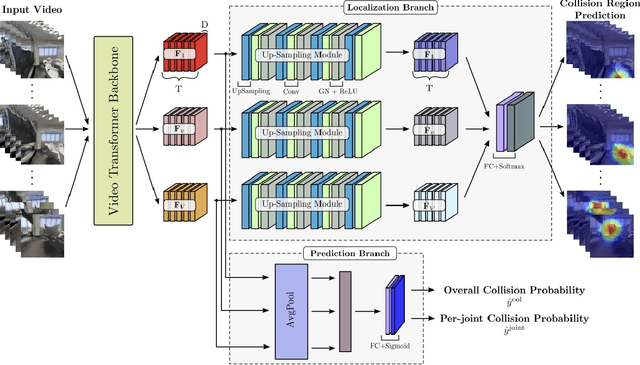
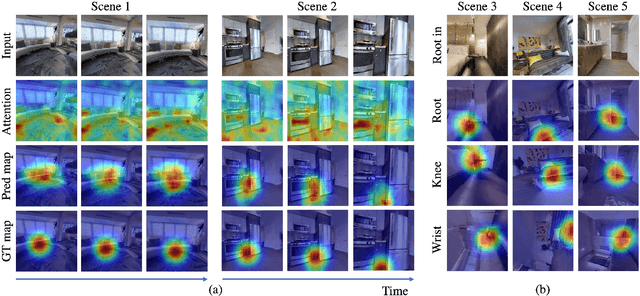
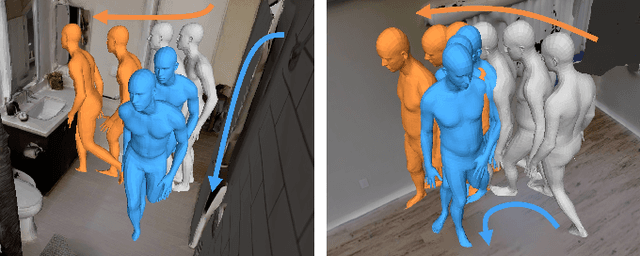
Abstract:To produce safe human motions, assistive wearable exoskeletons must be equipped with a perception system that enables anticipating potential collisions from egocentric observations. However, previous approaches to exoskeleton perception greatly simplify the problem to specific types of environments, limiting their scalability. In this paper, we propose the challenging and novel problem of predicting human-scene collisions for diverse environments from multi-view egocentric RGB videos captured from an exoskeleton. By classifying which body joints will collide with the environment and predicting a collision region heatmap that localizes potential collisions in the environment, we aim to develop an exoskeleton perception system that generalizes to complex real-world scenes and provides actionable outputs for downstream control. We propose COPILOT, a video transformer-based model that performs both collision prediction and localization simultaneously, leveraging multi-view video inputs via a proposed joint space-time-viewpoint attention operation. To train and evaluate the model, we build a synthetic data generation framework to simulate virtual humans moving in photo-realistic 3D environments. This framework is then used to establish a dataset consisting of 8.6M egocentric RGBD frames to enable future work on the problem. Extensive experiments suggest that our model achieves promising performance and generalizes to unseen scenes as well as real world. We apply COPILOT to a downstream collision avoidance task, and successfully reduce collision cases by 29% on unseen scenes using a simple closed-loop control algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge