CurveCloudNet: Processing Point Clouds with 1D Structure
Paper and Code
Mar 21, 2023


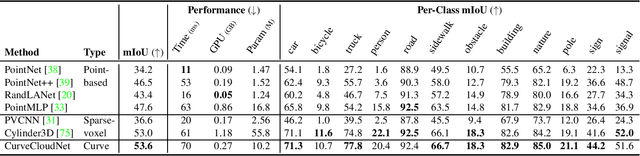
Modern depth sensors such as LiDAR operate by sweeping laser-beams across the scene, resulting in a point cloud with notable 1D curve-like structures. In this work, we introduce a new point cloud processing scheme and backbone, called CurveCloudNet, which takes advantage of the curve-like structure inherent to these sensors. While existing backbones discard the rich 1D traversal patterns and rely on Euclidean operations, CurveCloudNet parameterizes the point cloud as a collection of polylines (dubbed a "curve cloud"), establishing a local surface-aware ordering on the points. Our method applies curve-specific operations to process the curve cloud, including a symmetric 1D convolution, a ball grouping for merging points along curves, and an efficient 1D farthest point sampling algorithm on curves. By combining these curve operations with existing point-based operations, CurveCloudNet is an efficient, scalable, and accurate backbone with low GPU memory requirements. Evaluations on the ShapeNet, Kortx, Audi Driving, and nuScenes datasets demonstrate that CurveCloudNet outperforms both point-based and sparse-voxel backbones in various segmentation settings, notably scaling better to large scenes than point-based alternatives while exhibiting better single object performance than sparse-voxel alternatives.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge