COPILOT: Human Collision Prediction and Localization from Multi-view Egocentric Videos
Paper and Code
Oct 04, 2022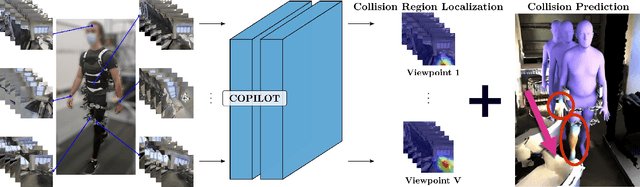
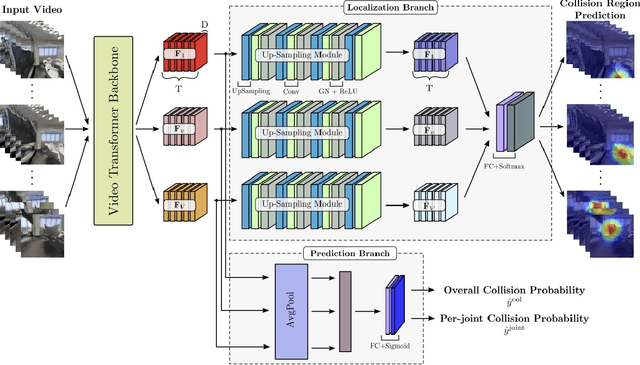
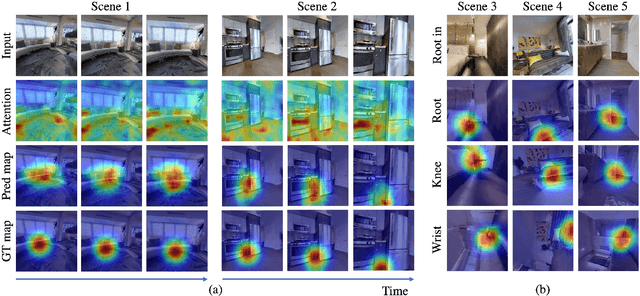
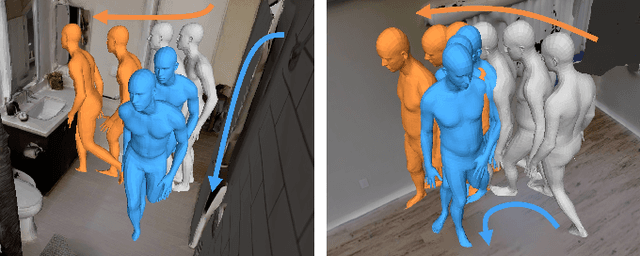
To produce safe human motions, assistive wearable exoskeletons must be equipped with a perception system that enables anticipating potential collisions from egocentric observations. However, previous approaches to exoskeleton perception greatly simplify the problem to specific types of environments, limiting their scalability. In this paper, we propose the challenging and novel problem of predicting human-scene collisions for diverse environments from multi-view egocentric RGB videos captured from an exoskeleton. By classifying which body joints will collide with the environment and predicting a collision region heatmap that localizes potential collisions in the environment, we aim to develop an exoskeleton perception system that generalizes to complex real-world scenes and provides actionable outputs for downstream control. We propose COPILOT, a video transformer-based model that performs both collision prediction and localization simultaneously, leveraging multi-view video inputs via a proposed joint space-time-viewpoint attention operation. To train and evaluate the model, we build a synthetic data generation framework to simulate virtual humans moving in photo-realistic 3D environments. This framework is then used to establish a dataset consisting of 8.6M egocentric RGBD frames to enable future work on the problem. Extensive experiments suggest that our model achieves promising performance and generalizes to unseen scenes as well as real world. We apply COPILOT to a downstream collision avoidance task, and successfully reduce collision cases by 29% on unseen scenes using a simple closed-loop control algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge