Xiu Su
Do All Individual Layers Help? An Empirical Study of Task-Interfering Layers in Vision-Language Models
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Current VLMs have demonstrated capabilities across a wide range of multimodal tasks. Typically, in a pretrained VLM, all layers are engaged by default to make predictions on downstream tasks. We find that intervening on a single layer, such as by zeroing its parameters, can improve the performance on certain tasks, indicating that some layers hinder rather than help downstream tasks. We systematically investigate how individual layers influence different tasks via layer intervention. Specifically, we measure the change in performance relative to the base model after intervening on each layer and observe improvements when bypassing specific layers. This improvement can be generalizable across models and datasets, indicating the presence of Task-Interfering Layers that harm downstream tasks' performance. We introduce Task-Layer Interaction Vector, which quantifies the effect of intervening on each layer of a VLM given a task. These task-interfering layers exhibit task-specific sensitivity patterns: tasks requiring similar capabilities show consistent response trends under layer interventions, as evidenced by the high similarity in their task-layer interaction vectors. Inspired by these findings, we propose TaLo (Task-Adaptive Layer Knockout), a training-free, test-time adaptation method that dynamically identifies and bypasses the most interfering layer for a given task. Without parameter updates, TaLo improves performance across various models and datasets, including boosting Qwen-VL's accuracy on the Maps task in ScienceQA by up to 16.6%. Our work reveals an unexpected form of modularity in pretrained VLMs and provides a plug-and-play, training-free mechanism to unlock hidden capabilities at inference time. The source code will be publicly available.
APEX: A Decoupled Memory-based Explorer for Asynchronous Aerial Object Goal Navigation
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Aerial Object Goal Navigation, a challenging frontier in Embodied AI, requires an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) agent to autonomously explore, reason, and identify a specific target using only visual perception and language description. However, existing methods struggle with the memorization of complex spatial representations in aerial environments, reliable and interpretable action decision-making, and inefficient exploration and information gathering. To address these challenges, we introduce \textbf{APEX} (Aerial Parallel Explorer), a novel hierarchical agent designed for efficient exploration and target acquisition in complex aerial settings. APEX is built upon a modular, three-part architecture: 1) Dynamic Spatio-Semantic Mapping Memory, which leverages the zero-shot capability of a Vision-Language Model (VLM) to dynamically construct high-resolution 3D Attraction, Exploration, and Obstacle maps, serving as an interpretable memory mechanism. 2) Action Decision Module, trained with reinforcement learning, which translates this rich spatial understanding into a fine-grained and robust control policy. 3) Target Grounding Module, which employs an open-vocabulary detector to achieve definitive and generalizable target identification. All these components are integrated into a hierarchical, asynchronous, and parallel framework, effectively bypassing the VLM's inference latency and boosting the agent's proactivity in exploration. Extensive experiments show that APEX outperforms the previous state of the art by +4.2\% SR and +2.8\% SPL on challenging UAV-ON benchmarks, demonstrating its superior efficiency and the effectiveness of its hierarchical asynchronous design. Our source code is provided in \href{https://github.com/4amGodvzx/apex}{GitHub}
Inject Once Survive Later: Backdooring Vision-Language-Action Models to Persist Through Downstream Fine-tuning
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have become foundational to modern embodied AI systems. By integrating visual perception, language understanding, and action planning, they enable general-purpose task execution across diverse environments. Despite their importance, the security of VLA models remains underexplored -- particularly in the context of backdoor attacks, which pose realistic threats in physical-world deployments. While recent methods attempt to inject backdoors into VLA models, these backdoors are easily erased during downstream adaptation, as user-side fine-tuning with clean data significantly alters model parameters, rendering them impractical for real-world applications. To address these challenges, we propose INFUSE (INjection into Fine-tUne-inSensitive modulEs), the first backdoor attack framework for VLA base models that remains effective even with arbitrary user fine-tuning. INFUSE begins by analyzing parameter sensitivity across diverse fine-tuning scenarios to identify modules that remain largely unchanged -- the fine-tune-insensitive modules. It then injects backdoors into these stable modules while freezing the rest, ensuring malicious behavior persists after extensive user fine-tuning. Comprehensive experiments across multiple VLA architectures demonstrate INFUSE's effectiveness. After user-side fine-tuning, INFUSE maintains mean attack success rates of 91.0% on simulation environments and 79.8% on real-world robot tasks, substantially surpassing BadVLA (38.8% and 36.6%, respectively), while preserving clean-task performance comparable to standard models. These results uncover a critical threat: backdoors implanted before distribution can persist through fine-tuning and remain effective at deployment.
ConLA: Contrastive Latent Action Learning from Human Videos for Robotic Manipulation
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models achieve preliminary generalization through pretraining on large scale robot teleoperation datasets. However, acquiring datasets that comprehensively cover diverse tasks and environments is extremely costly and difficult to scale. In contrast, human demonstration videos offer a rich and scalable source of diverse scenes and manipulation behaviors, yet their lack of explicit action supervision hinders direct utilization. Prior work leverages VQ-VAE based frameworks to learn latent actions from human videos in an unsupervised manner. Nevertheless, since the training objective primarily focuses on reconstructing visual appearances rather than capturing inter-frame dynamics, the learned representations tend to rely on spurious visual cues, leading to shortcut learning and entangled latent representations that hinder transferability. To address this, we propose ConLA, an unsupervised pretraining framework for learning robotic policies from human videos. ConLA introduces a contrastive disentanglement mechanism that leverages action category priors and temporal cues to isolate motion dynamics from visual content, effectively mitigating shortcut learning. Extensive experiments show that ConLA achieves strong performance across diverse benchmarks. Notably, by pretraining solely on human videos, our method for the first time surpasses the performance obtained with real robot trajectory pretraining, highlighting its ability to extract pure and semantically consistent latent action representations for scalable robot learning.
Learning to Accelerate Vision-Language-Action Models through Adaptive Visual Token Caching
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have demonstrated remarkable generalization capabilities in robotic manipulation tasks, yet their substantial computational overhead remains a critical obstacle to real-world deployment. Improving inference efficiency is therefore essential for practical robotic applications. Existing acceleration methods often rely on heuristic or static strategies--such as rule-based token caching or pruning--that are decoupled from task objectives and fail to adapt to dynamic scene changes. In this work, we reformulate inference acceleration as a learnable policy optimization problem and propose a novel framework that integrates a dynamic, task-aware decision-making process directly into the VLA model. At its core are two lightweight, cooperative modules: a Cached Token Selector, which determines which tokens should be reused, and a Cache Ratio Predictor, which controls how many tokens to reuse. Training these modules is non-trivial due to their discrete decisions. We address this by adopting a differentiable relaxation that allows gradient-based end-to-end optimization. Extensive experiments on the LIBERO and SIMPLER benchmarks, as well as real-robot evaluations, show that our method achieves a 1.76x wall-clock inference speedup while simultaneously improving the average success rate by 1.9 percentage points (from 75.0% to 76.9%) on LIBERO and by 5.0 percentage points on real-world tasks, significantly outperforming existing baselines. This work highlights the potential of learning task-aware computational allocation policies, paving the way for VLA models that are both powerful and efficient.
LEGATO: Good Identity Unlearning Is Continuous
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Machine unlearning has become a crucial role in enabling generative models trained on large datasets to remove sensitive, private, or copyright-protected data. However, existing machine unlearning methods face three challenges in learning to forget identity of generative models: 1) inefficient, where identity erasure requires fine-tuning all the model's parameters; 2) limited controllability, where forgetting intensity cannot be controlled and explainability is lacking; 3) catastrophic collapse, where the model's retention capability undergoes drastic degradation as forgetting progresses. Forgetting has typically been handled through discrete and unstable updates, often requiring full-model fine-tuning and leading to catastrophic collapse. In this work, we argue that identity forgetting should be modeled as a continuous trajectory, and introduce LEGATO - Learn to ForgEt Identity in GenerAtive Models via Trajectory-consistent Neural Ordinary Differential Equations. LEGATO augments pre-trained generators with fine-tunable lightweight Neural ODE adapters, enabling smooth, controllable forgetting while keeping the original model weights frozen. This formulation allows forgetting intensity to be precisely modulated via ODE step size, offering interpretability and robustness. To further ensure stability, we introduce trajectory consistency constraints that explicitly prevent catastrophic collapse during unlearning. Extensive experiments across in-domain and out-of-domain identity unlearning benchmarks show that LEGATO achieves state-of-the-art forgetting performance, avoids catastrophic collapse and reduces fine-tuned parameters.
Calibrated Multimodal Representation Learning with Missing Modalities
Nov 15, 2025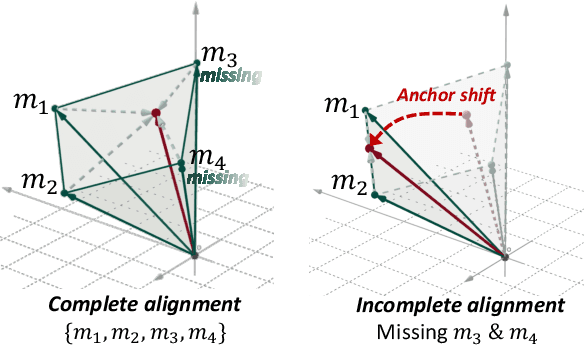
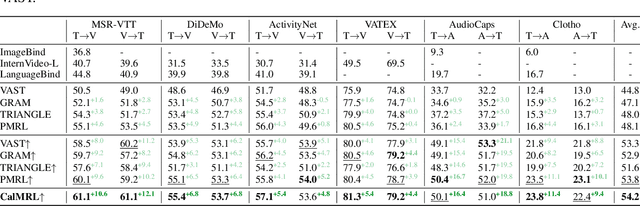
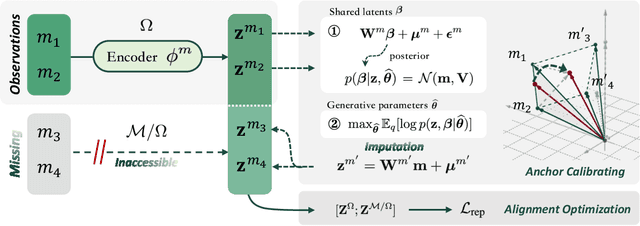
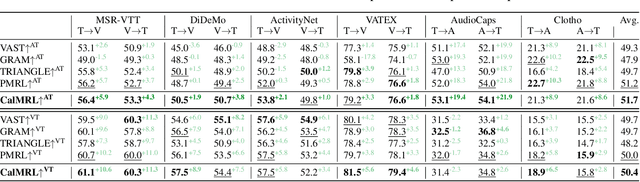
Abstract:Multimodal representation learning harmonizes distinct modalities by aligning them into a unified latent space. Recent research generalizes traditional cross-modal alignment to produce enhanced multimodal synergy but requires all modalities to be present for a common instance, making it challenging to utilize prevalent datasets with missing modalities. We provide theoretical insights into this issue from an anchor shift perspective. Observed modalities are aligned with a local anchor that deviates from the optimal one when all modalities are present, resulting in an inevitable shift. To address this, we propose CalMRL for multimodal representation learning to calibrate incomplete alignments caused by missing modalities. Specifically, CalMRL leverages the priors and the inherent connections among modalities to model the imputation for the missing ones at the representation level. To resolve the optimization dilemma, we employ a bi-step learning method with the closed-form solution of the posterior distribution of shared latents. We validate its mitigation of anchor shift and convergence with theoretical guidance. By equipping the calibrated alignment with the existing advanced method, we offer new flexibility to absorb data with missing modalities, which is originally unattainable. Extensive experiments and comprehensive analyses demonstrate the superiority of CalMRL. Our code, model checkpoints, and evaluation raw data will be publicly available.
DeCoP: Enhancing Self-Supervised Time Series Representation with Dependency Controlled Pre-training
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Modeling dynamic temporal dependencies is a critical challenge in time series pre-training, which evolve due to distribution shifts and multi-scale patterns. This temporal variability severely impairs the generalization of pre-trained models to downstream tasks. Existing frameworks fail to capture the complex interactions of short- and long-term dependencies, making them susceptible to spurious correlations that degrade generalization. To address these limitations, we propose DeCoP, a Dependency Controlled Pre-training framework that explicitly models dynamic, multi-scale dependencies by simulating evolving inter-patch dependencies. At the input level, DeCoP introduces Instance-wise Patch Normalization (IPN) to mitigate distributional shifts while preserving the unique characteristics of each patch, creating a robust foundation for representation learning. At the latent level, a hierarchical Dependency Controlled Learning (DCL) strategy explicitly models inter-patch dependencies across multiple temporal scales, with an Instance-level Contrastive Module (ICM) enhances global generalization by learning instance-discriminative representations from time-invariant positive pairs. DeCoP achieves state-of-the-art results on ten datasets with lower computing resources, improving MSE by 3% on ETTh1 over PatchTST using only 37% of the FLOPs.
ConCM: Consistency-Driven Calibration and Matching for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning (FSCIL) requires models to adapt to novel classes with limited supervision while preserving learned knowledge. Existing prospective learning-based space construction methods reserve space to accommodate novel classes. However, prototype deviation and structure fixity limit the expressiveness of the embedding space. In contrast to fixed space reservation, we explore the optimization of feature-structure dual consistency and propose a Consistency-driven Calibration and Matching Framework (ConCM) that systematically mitigate the knowledge conflict inherent in FSCIL. Specifically, inspired by hippocampal associative memory, we design a memory-aware prototype calibration that extracts generalized semantic attributes from base classes and reintegrates them into novel classes to enhance the conceptual center consistency of features. Further, we propose dynamic structure matching, which adaptively aligns the calibrated features to a session-specific optimal manifold space, ensuring cross-session structure consistency. Theoretical analysis shows that our method satisfies both geometric optimality and maximum matching, thereby overcoming the need for class-number priors. On large-scale FSCIL benchmarks including mini-ImageNet and CUB200, ConCM achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing current optimal method by 3.20% and 3.68% in harmonic accuracy of incremental sessions.
L-MTP: Leap Multi-Token Prediction Beyond Adjacent Context for Large Language Models
May 23, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved notable progress. Despite their success, next-token prediction (NTP), the dominant method for LLM training and inference, is constrained in both contextual coverage and inference efficiency due to its inherently sequential process. To overcome these challenges, we propose leap multi-token prediction~(L-MTP), an innovative token prediction method that extends the capabilities of multi-token prediction (MTP) by introducing a leap-based mechanism. Unlike conventional MTP, which generates multiple tokens at adjacent positions, L-MTP strategically skips over intermediate tokens, predicting non-sequential ones in a single forward pass. This structured leap not only enhances the model's ability to capture long-range dependencies but also enables a decoding strategy specially optimized for non-sequential leap token generation, effectively accelerating inference. We theoretically demonstrate the benefit of L-MTP in improving inference efficiency. Experiments across diverse benchmarks validate its merit in boosting both LLM performance and inference speed. The source code will be publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge