Mingming Wang
Uni-PrevPredMap: Extending PrevPredMap to a Unified Framework of Prior-Informed Modeling for Online Vectorized HD Map Construction
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Safety constitutes a foundational imperative for autonomous driving systems, necessitating the maximal incorporation of accessible external prior information. This study establishes that temporal perception buffers and cost-efficient maps inherently form complementary prior sources for online vectorized high-definition (HD) map construction. We present Uni-PrevPredMap, a unified prior-informed framework that systematically integrates two synergistic information sources: previous predictions and simulated outdated HD maps. The framework introduces two core innovations: a tile-indexed 3D vectorized global map processor enabling efficient refreshment, storage, and retrieval of 3D vectorized priors; a tri-mode operational optimization paradigm ensuring consistency across non-prior, temporal-prior, and temporal-map-fusion-prior scenarios while mitigating reliance on idealized map fidelity assumptions. Uni-PrevPredMap achieves state-of-the-art performance in map-absent scenarios across established online vectorized HD map construction benchmarks. When provided with simulated outdated HD maps, the framework exhibits robust capabilities in error-resilient prior fusion, empirically confirming the synergistic complementarity between previous predictions and simulated outdated HD maps. Code will be available at https://github.com/pnnnnnnn/Uni-PrevPredMap.
PrevPredMap: Exploring Temporal Modeling with Previous Predictions for Online Vectorized HD Map Construction
Jul 24, 2024



Abstract:Temporal information is crucial for detecting occluded instances. Existing temporal representations have progressed from BEV or PV features to more compact query features. Compared to these aforementioned features, predictions offer the highest level of abstraction, providing explicit information. In the context of online vectorized HD map construction, this unique characteristic of predictions is potentially advantageous for long-term temporal modeling and the integration of map priors. This paper introduces PrevPredMap, a pioneering temporal modeling framework that leverages previous predictions for constructing online vectorized HD maps. We have meticulously crafted two essential modules for PrevPredMap: the previous-predictions-based query generator and the dynamic-position-query decoder. Specifically, the previous-predictions-based query generator is designed to separately encode different types of information from previous predictions, which are then effectively utilized by the dynamic-position-query decoder to generate current predictions. Furthermore, we have developed a dual-mode strategy to ensure PrevPredMap's robust performance across both single-frame and temporal modes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PrevPredMap achieves state-of-the-art performance on the nuScenes and Argoverse2 datasets. Code will be available at https://github.com/pnnnnnnn/PrevPredMap.
NeRF2Points: Large-Scale Point Cloud Generation From Street Views' Radiance Field Optimization
Apr 07, 2024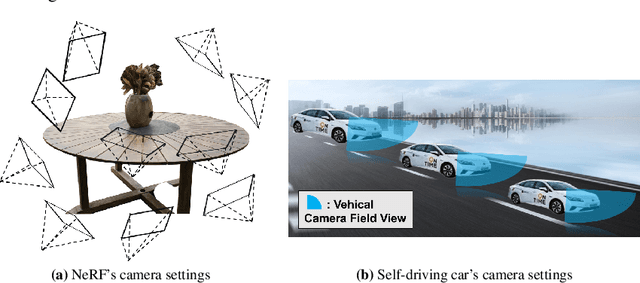
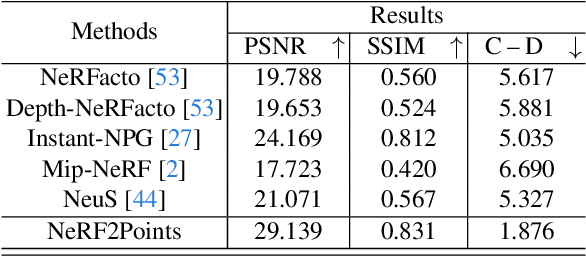
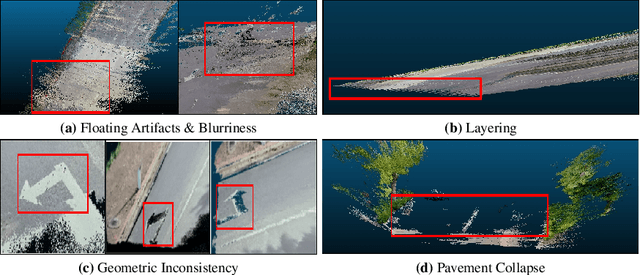
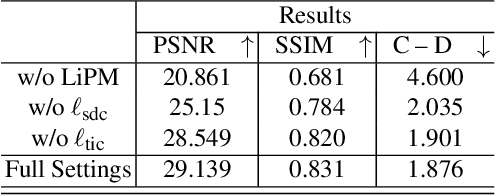
Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have emerged as a paradigm-shifting methodology for the photorealistic rendering of objects and environments, enabling the synthesis of novel viewpoints with remarkable fidelity. This is accomplished through the strategic utilization of object-centric camera poses characterized by significant inter-frame overlap. This paper explores a compelling, alternative utility of NeRF: the derivation of point clouds from aggregated urban landscape imagery. The transmutation of street-view data into point clouds is fraught with complexities, attributable to a nexus of interdependent variables. First, high-quality point cloud generation hinges on precise camera poses, yet many datasets suffer from inaccuracies in pose metadata. Also, the standard approach of NeRF is ill-suited for the distinct characteristics of street-view data from autonomous vehicles in vast, open settings. Autonomous vehicle cameras often record with limited overlap, leading to blurring, artifacts, and compromised pavement representation in NeRF-based point clouds. In this paper, we present NeRF2Points, a tailored NeRF variant for urban point cloud synthesis, notable for its high-quality output from RGB inputs alone. Our paper is supported by a bespoke, high-resolution 20-kilometer urban street dataset, designed for point cloud generation and evaluation. NeRF2Points adeptly navigates the inherent challenges of NeRF-based point cloud synthesis through the implementation of the following strategic innovations: (1) Integration of Weighted Iterative Geometric Optimization (WIGO) and Structure from Motion (SfM) for enhanced camera pose accuracy, elevating street-view data precision. (2) Layered Perception and Integrated Modeling (LPiM) is designed for distinct radiance field modeling in urban environments, resulting in coherent point cloud representations.
Multi-path Convolutional Neural Networks for Complex Image Classification
Jun 22, 2015



Abstract:Convolutional Neural Networks demonstrate high performance on ImageNet Large-Scale Visual Recognition Challenges contest. Nevertheless, the published results only show the overall performance for all image classes. There is no further analysis why certain images get worse results and how they could be improved. In this paper, we provide deep performance analysis based on different types of images and point out the weaknesses of convolutional neural networks through experiment. We design a novel multiple paths convolutional neural network, which feeds different versions of images into separated paths to learn more comprehensive features. This model has better presentation for image than the traditional single path model. We acquire better classification results on complex validation set on both top 1 and top 5 scores than the best ILSVRC 2013 classification model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge