Sanmi Koyejo
Stanford University
Latent Adversarial Regularization for Offline Preference Optimization
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Learning from human feedback typically relies on preference optimization that constrains policy updates through token-level regularization. However, preference optimization for language models is particularly challenging because token-space similarity does not imply semantic or behavioral similarity. To address this challenge, we leverage latent-space regularization for language model preference optimization. We introduce GANPO, which achieves latent-space regularization by penalizing divergence between the internal representations of a policy model and a reference model. Given that latent representations are not associated with explicit probability densities, we adopt an adversarial approach inspired by GANs to minimize latent-space divergence. We integrate GANPO as a regularizer into existing offline preference optimization objectives. Experiments across multiple model architectures and tasks show consistent improvements from latent-space regularization. Further, by comparing GANPO-induced inferential biases with those from token-level regularization, we find that GANPO provides more robust structural feedback under distributional shift and noise while maintaining comparable downstream performance with minor computational overhead.
Neural Nonmyopic Bayesian Optimization in Dynamic Cost Settings
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Bayesian optimization (BO) is a common framework for optimizing black-box functions, yet most existing methods assume static query costs and rely on myopic acquisition strategies. We introduce LookaHES, a nonmyopic BO framework designed for dynamic, history-dependent cost environments, where evaluation costs vary with prior actions, such as travel distance in spatial tasks or edit distance in sequence design. LookaHES combines a multi-step variant of $H$-Entropy Search with pathwise sampling and neural policy optimization, enabling long-horizon planning beyond twenty steps without the exponential complexity of existing nonmyopic methods. The key innovation is the integration of neural policies, including large language models, to effectively navigate structured, combinatorial action spaces such as protein sequences. These policies amortize lookahead planning and can be integrated with domain-specific constraints during rollout. Empirically, LookaHES outperforms strong myopic and nonmyopic baselines across nine synthetic benchmarks from two to eight dimensions and two real-world tasks: geospatial optimization using NASA night-light imagery and protein sequence design with constrained token-level edits. In short, LookaHES provides a general, scalable, and cost-aware solution for robust long-horizon optimization in complex decision spaces, which makes it a useful tool for researchers in machine learning, statistics, and applied domains. Our implementation is available at https://github.com/sangttruong/nonmyopia.
Quantifying the Effect of Test Set Contamination on Generative Evaluations
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:As frontier AI systems are pretrained on web-scale data, test set contamination has become a critical concern for accurately assessing their capabilities. While research has thoroughly investigated the impact of test set contamination on discriminative evaluations like multiple-choice question-answering, comparatively little research has studied the impact of test set contamination on generative evaluations. In this work, we quantitatively assess the effect of test set contamination on generative evaluations through the language model lifecycle. We pretrain language models on mixtures of web data and the MATH benchmark, sweeping model sizes and number of test set replicas contaminating the pretraining corpus; performance improves with contamination and model size. Using scaling laws, we make a surprising discovery: including even a single test set replica enables models to achieve lower loss than the irreducible error of training on the uncontaminated corpus. We then study further training: overtraining with fresh data reduces the effects of contamination, whereas supervised finetuning on the training set can either increase or decrease performance on test data, depending on the amount of pretraining contamination. Finally, at inference, we identify factors that modulate memorization: high sampling temperatures mitigate contamination effects, and longer solutions are exponentially more difficult to memorize than shorter ones, presenting a contrast with discriminative evaluations, where solutions are only a few tokens in length. By characterizing how generation and memorization interact, we highlight a new layer of complexity for trustworthy evaluation of AI systems.
Extracting books from production language models
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Many unresolved legal questions over LLMs and copyright center on memorization: whether specific training data have been encoded in the model's weights during training, and whether those memorized data can be extracted in the model's outputs. While many believe that LLMs do not memorize much of their training data, recent work shows that substantial amounts of copyrighted text can be extracted from open-weight models. However, it remains an open question if similar extraction is feasible for production LLMs, given the safety measures these systems implement. We investigate this question using a two-phase procedure: (1) an initial probe to test for extraction feasibility, which sometimes uses a Best-of-N (BoN) jailbreak, followed by (2) iterative continuation prompts to attempt to extract the book. We evaluate our procedure on four production LLMs -- Claude 3.7 Sonnet, GPT-4.1, Gemini 2.5 Pro, and Grok 3 -- and we measure extraction success with a score computed from a block-based approximation of longest common substring (nv-recall). With different per-LLM experimental configurations, we were able to extract varying amounts of text. For the Phase 1 probe, it was unnecessary to jailbreak Gemini 2.5 Pro and Grok 3 to extract text (e.g, nv-recall of 76.8% and 70.3%, respectively, for Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone), while it was necessary for Claude 3.7 Sonnet and GPT-4.1. In some cases, jailbroken Claude 3.7 Sonnet outputs entire books near-verbatim (e.g., nv-recall=95.8%). GPT-4.1 requires significantly more BoN attempts (e.g., 20X), and eventually refuses to continue (e.g., nv-recall=4.0%). Taken together, our work highlights that, even with model- and system-level safeguards, extraction of (in-copyright) training data remains a risk for production LLMs.
End-to-End Test-Time Training for Long Context
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:We formulate long-context language modeling as a problem in continual learning rather than architecture design. Under this formulation, we only use a standard architecture -- a Transformer with sliding-window attention. However, our model continues learning at test time via next-token prediction on the given context, compressing the context it reads into its weights. In addition, we improve the model's initialization for learning at test time via meta-learning at training time. Overall, our method, a form of Test-Time Training (TTT), is End-to-End (E2E) both at test time (via next-token prediction) and training time (via meta-learning), in contrast to previous forms. We conduct extensive experiments with a focus on scaling properties. In particular, for 3B models trained with 164B tokens, our method (TTT-E2E) scales with context length in the same way as Transformer with full attention, while others, such as Mamba 2 and Gated DeltaNet, do not. However, similar to RNNs, TTT-E2E has constant inference latency regardless of context length, making it 2.7 times faster than full attention for 128K context. Our code is publicly available.
CURE: Cultural Understanding and Reasoning Evaluation - A Framework for "Thick" Culture Alignment Evaluation in LLMs
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in culturally diverse environments, yet existing evaluations of cultural competence remain limited. Existing methods focus on de-contextualized correctness or forced-choice judgments, overlooking the need for cultural understanding and reasoning required for appropriate responses. To address this gap, we introduce a set of benchmarks that, instead of directly probing abstract norms or isolated statements, present models with realistic situational contexts that require culturally grounded reasoning. In addition to the standard Exact Match metric, we introduce four complementary metrics (Coverage, Specificity, Connotation, and Coherence) to capture different dimensions of model's response quality. Empirical analysis across frontier models reveals that thin evaluation systematically overestimates cultural competence and produces unstable assessments with high variance. In contrast, thick evaluation exposes differences in reasoning depth, reduces variance, and provides more stable, interpretable signals of cultural understanding.
Who Evaluates AI's Social Impacts? Mapping Coverage and Gaps in First and Third Party Evaluations
Nov 06, 2025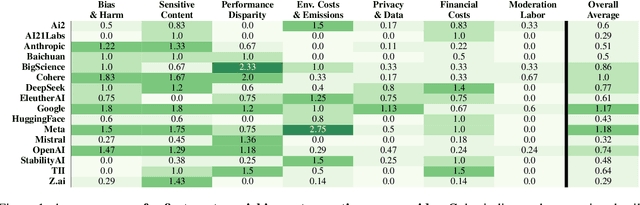
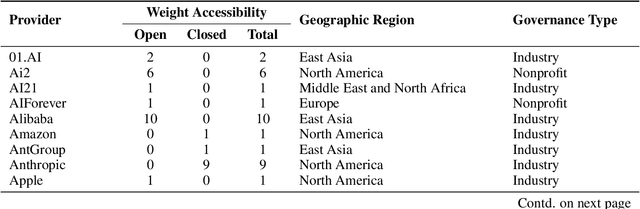
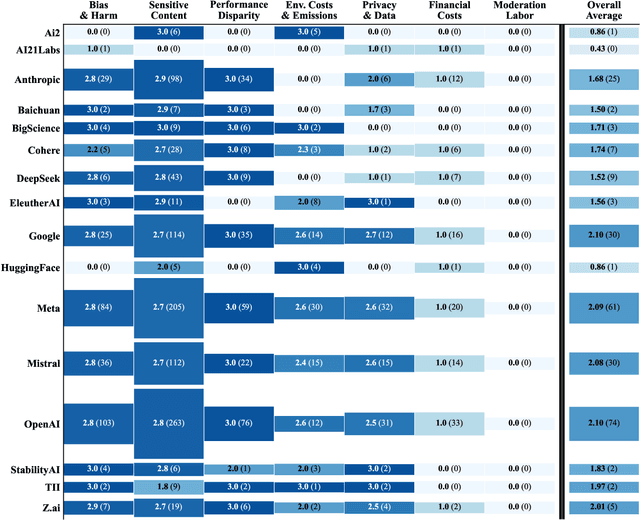
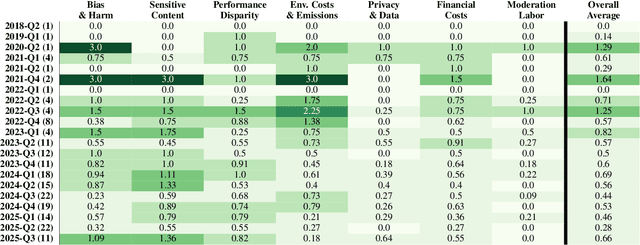
Abstract:Foundation models are increasingly central to high-stakes AI systems, and governance frameworks now depend on evaluations to assess their risks and capabilities. Although general capability evaluations are widespread, social impact assessments covering bias, fairness, privacy, environmental costs, and labor practices remain uneven across the AI ecosystem. To characterize this landscape, we conduct the first comprehensive analysis of both first-party and third-party social impact evaluation reporting across a wide range of model developers. Our study examines 186 first-party release reports and 183 post-release evaluation sources, and complements this quantitative analysis with interviews of model developers. We find a clear division of evaluation labor: first-party reporting is sparse, often superficial, and has declined over time in key areas such as environmental impact and bias, while third-party evaluators including academic researchers, nonprofits, and independent organizations provide broader and more rigorous coverage of bias, harmful content, and performance disparities. However, this complementarity has limits. Only model developers can authoritatively report on data provenance, content moderation labor, financial costs, and training infrastructure, yet interviews reveal that these disclosures are often deprioritized unless tied to product adoption or regulatory compliance. Our findings indicate that current evaluation practices leave major gaps in assessing AI's societal impacts, highlighting the urgent need for policies that promote developer transparency, strengthen independent evaluation ecosystems, and create shared infrastructure to aggregate and compare third-party evaluations in a consistent and accessible way.
Understanding Adversarial Transfer: Why Representation-Space Attacks Fail Where Data-Space Attacks Succeed
Oct 01, 2025



Abstract:The field of adversarial robustness has long established that adversarial examples can successfully transfer between image classifiers and that text jailbreaks can successfully transfer between language models (LMs). However, a pair of recent studies reported being unable to successfully transfer image jailbreaks between vision-language models (VLMs). To explain this striking difference, we propose a fundamental distinction regarding the transferability of attacks against machine learning models: attacks in the input data-space can transfer, whereas attacks in model representation space do not, at least not without geometric alignment of representations. We then provide theoretical and empirical evidence of this hypothesis in four different settings. First, we mathematically prove this distinction in a simple setting where two networks compute the same input-output map but via different representations. Second, we construct representation-space attacks against image classifiers that are as successful as well-known data-space attacks, but fail to transfer. Third, we construct representation-space attacks against LMs that successfully jailbreak the attacked models but again fail to transfer. Fourth, we construct data-space attacks against VLMs that successfully transfer to new VLMs, and we show that representation space attacks \emph{can} transfer when VLMs' latent geometries are sufficiently aligned in post-projector space. Our work reveals that adversarial transfer is not an inherent property of all attacks but contingent on their operational domain - the shared data-space versus models' unique representation spaces - a critical insight for building more robust models.
UQ: Assessing Language Models on Unsolved Questions
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Benchmarks shape progress in AI research. A useful benchmark should be both difficult and realistic: questions should challenge frontier models while also reflecting real-world usage. Yet, current paradigms face a difficulty-realism tension: exam-style benchmarks are often made artificially difficult with limited real-world value, while benchmarks based on real user interaction often skew toward easy, high-frequency problems. In this work, we explore a radically different paradigm: assessing models on unsolved questions. Rather than a static benchmark scored once, we curate unsolved questions and evaluate models asynchronously over time with validator-assisted screening and community verification. We introduce UQ, a testbed of 500 challenging, diverse questions sourced from Stack Exchange, spanning topics from CS theory and math to sci-fi and history, probing capabilities including reasoning, factuality, and browsing. UQ is difficult and realistic by construction: unsolved questions are often hard and naturally arise when humans seek answers, thus solving them yields direct real-world value. Our contributions are threefold: (1) UQ-Dataset and its collection pipeline combining rule-based filters, LLM judges, and human review to ensure question quality (e.g., well-defined and difficult); (2) UQ-Validators, compound validation strategies that leverage the generator-validator gap to provide evaluation signals and pre-screen candidate solutions for human review; and (3) UQ-Platform, an open platform where experts collectively verify questions and solutions. The top model passes UQ-validation on only 15% of questions, and preliminary human verification has already identified correct answers among those that passed. UQ charts a path for evaluating frontier models on real-world, open-ended challenges, where success pushes the frontier of human knowledge. We release UQ at https://uq.stanford.edu.
Algorithmic Fairness amid Social Determinants: Reflection, Characterization, and Approach
Aug 10, 2025



Abstract:Social determinants are variables that, while not directly pertaining to any specific individual, capture key aspects of contexts and environments that have direct causal influences on certain attributes of an individual. Previous algorithmic fairness literature has primarily focused on sensitive attributes, often overlooking the role of social determinants. Our paper addresses this gap by introducing formal and quantitative rigor into a space that has been shaped largely by qualitative proposals regarding the use of social determinants. To demonstrate theoretical perspectives and practical applicability, we examine a concrete setting of college admissions, using region as a proxy for social determinants. Our approach leverages a region-based analysis with Gamma distribution parameterization to model how social determinants impact individual outcomes. Despite its simplicity, our method quantitatively recovers findings that resonate with nuanced insights in previous qualitative debates, that are often missed by existing algorithmic fairness approaches. Our findings suggest that mitigation strategies centering solely around sensitive attributes may introduce new structural injustice when addressing existing discrimination. Considering both sensitive attributes and social determinants facilitates a more comprehensive explication of benefits and burdens experienced by individuals from diverse demographic backgrounds as well as contextual environments, which is essential for understanding and achieving fairness effectively and transparently.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge