Stephen R. Pfohl
Understanding challenges to the interpretation of disaggregated evaluations of algorithmic fairness
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Disaggregated evaluation across subgroups is critical for assessing the fairness of machine learning models, but its uncritical use can mislead practitioners. We show that equal performance across subgroups is an unreliable measure of fairness when data are representative of the relevant populations but reflective of real-world disparities. Furthermore, when data are not representative due to selection bias, both disaggregated evaluation and alternative approaches based on conditional independence testing may be invalid without explicit assumptions regarding the bias mechanism. We use causal graphical models to predict metric stability across subgroups under different data generating processes. Our framework suggests complementing disaggregated evaluations with explicit causal assumptions and analysis to control for confounding and distribution shift, including conditional independence testing and weighted performance estimation. These findings have broad implications for how practitioners design and interpret model assessments given the ubiquity of disaggregated evaluation.
A Toolbox for Surfacing Health Equity Harms and Biases in Large Language Models
Mar 18, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) hold immense promise to serve complex health information needs but also have the potential to introduce harm and exacerbate health disparities. Reliably evaluating equity-related model failures is a critical step toward developing systems that promote health equity. In this work, we present resources and methodologies for surfacing biases with potential to precipitate equity-related harms in long-form, LLM-generated answers to medical questions and then conduct an empirical case study with Med-PaLM 2, resulting in the largest human evaluation study in this area to date. Our contributions include a multifactorial framework for human assessment of LLM-generated answers for biases, and EquityMedQA, a collection of seven newly-released datasets comprising both manually-curated and LLM-generated questions enriched for adversarial queries. Both our human assessment framework and dataset design process are grounded in an iterative participatory approach and review of possible biases in Med-PaLM 2 answers to adversarial queries. Through our empirical study, we find that the use of a collection of datasets curated through a variety of methodologies, coupled with a thorough evaluation protocol that leverages multiple assessment rubric designs and diverse rater groups, surfaces biases that may be missed via narrower evaluation approaches. Our experience underscores the importance of using diverse assessment methodologies and involving raters of varying backgrounds and expertise. We emphasize that while our framework can identify specific forms of bias, it is not sufficient to holistically assess whether the deployment of an AI system promotes equitable health outcomes. We hope the broader community leverages and builds on these tools and methods towards realizing a shared goal of LLMs that promote accessible and equitable healthcare for all.
Proxy Methods for Domain Adaptation
Mar 12, 2024Abstract:We study the problem of domain adaptation under distribution shift, where the shift is due to a change in the distribution of an unobserved, latent variable that confounds both the covariates and the labels. In this setting, neither the covariate shift nor the label shift assumptions apply. Our approach to adaptation employs proximal causal learning, a technique for estimating causal effects in settings where proxies of unobserved confounders are available. We demonstrate that proxy variables allow for adaptation to distribution shift without explicitly recovering or modeling latent variables. We consider two settings, (i) Concept Bottleneck: an additional ''concept'' variable is observed that mediates the relationship between the covariates and labels; (ii) Multi-domain: training data from multiple source domains is available, where each source domain exhibits a different distribution over the latent confounder. We develop a two-stage kernel estimation approach to adapt to complex distribution shifts in both settings. In our experiments, we show that our approach outperforms other methods, notably those which explicitly recover the latent confounder.
Adapting to Latent Subgroup Shifts via Concepts and Proxies
Dec 21, 2022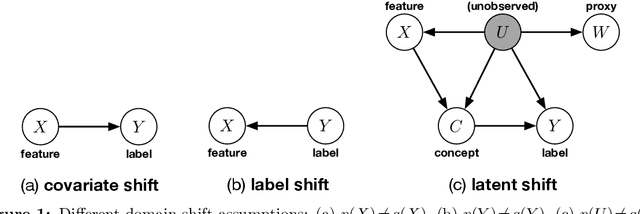
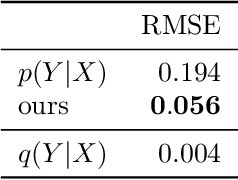
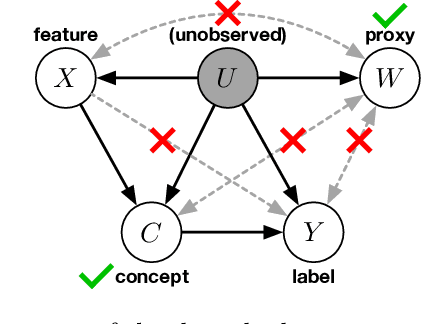
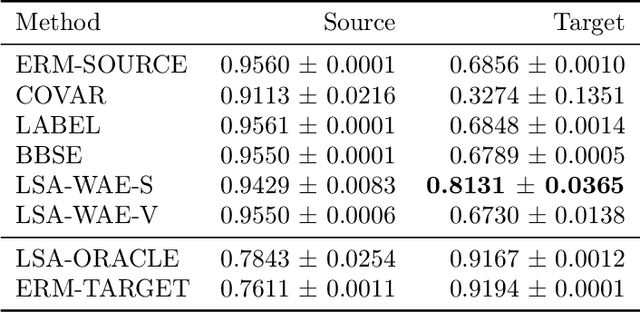
Abstract:We address the problem of unsupervised domain adaptation when the source domain differs from the target domain because of a shift in the distribution of a latent subgroup. When this subgroup confounds all observed data, neither covariate shift nor label shift assumptions apply. We show that the optimal target predictor can be non-parametrically identified with the help of concept and proxy variables available only in the source domain, and unlabeled data from the target. The identification results are constructive, immediately suggesting an algorithm for estimating the optimal predictor in the target. For continuous observations, when this algorithm becomes impractical, we propose a latent variable model specific to the data generation process at hand. We show how the approach degrades as the size of the shift changes, and verify that it outperforms both covariate and label shift adjustment.
Net benefit, calibration, threshold selection, and training objectives for algorithmic fairness in healthcare
Feb 03, 2022


Abstract:A growing body of work uses the paradigm of algorithmic fairness to frame the development of techniques to anticipate and proactively mitigate the introduction or exacerbation of health inequities that may follow from the use of model-guided decision-making. We evaluate the interplay between measures of model performance, fairness, and the expected utility of decision-making to offer practical recommendations for the operationalization of algorithmic fairness principles for the development and evaluation of predictive models in healthcare. We conduct an empirical case-study via development of models to estimate the ten-year risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease to inform statin initiation in accordance with clinical practice guidelines. We demonstrate that approaches that incorporate fairness considerations into the model training objective typically do not improve model performance or confer greater net benefit for any of the studied patient populations compared to the use of standard learning paradigms followed by threshold selection concordant with patient preferences, evidence of intervention effectiveness, and model calibration. These results hold when the measured outcomes are not subject to differential measurement error across patient populations and threshold selection is unconstrained, regardless of whether differences in model performance metrics, such as in true and false positive error rates, are present. In closing, we argue for focusing model development efforts on developing calibrated models that predict outcomes well for all patient populations while emphasizing that such efforts are complementary to transparent reporting, participatory design, and reasoning about the impact of model-informed interventions in context.
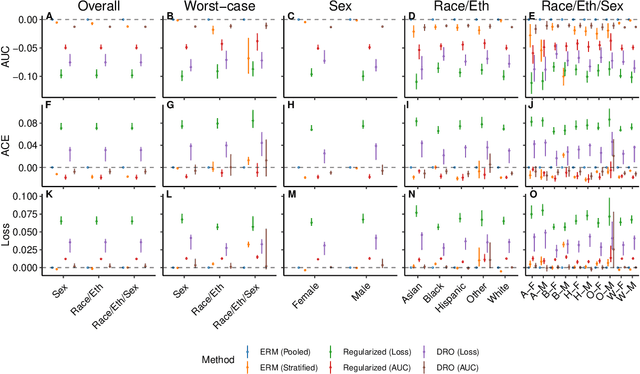
A comparison of approaches to improve worst-case predictive model performance over patient subpopulations
Aug 27, 2021



Abstract:Predictive models for clinical outcomes that are accurate on average in a patient population may underperform drastically for some subpopulations, potentially introducing or reinforcing inequities in care access and quality. Model training approaches that aim to maximize worst-case model performance across subpopulations, such as distributionally robust optimization (DRO), attempt to address this problem without introducing additional harms. We conduct a large-scale empirical study of DRO and several variations of standard learning procedures to identify approaches for model development and selection that consistently improve disaggregated and worst-case performance over subpopulations compared to standard approaches for learning predictive models from electronic health records data. In the course of our evaluation, we introduce an extension to DRO approaches that allows for specification of the metric used to assess worst-case performance. We conduct the analysis for models that predict in-hospital mortality, prolonged length of stay, and 30-day readmission for inpatient admissions, and predict in-hospital mortality using intensive care data. We find that, with relatively few exceptions, no approach performs better, for each patient subpopulation examined, than standard learning procedures using the entire training dataset. These results imply that when it is of interest to improve model performance for patient subpopulations beyond what can be achieved with standard practices, it may be necessary to do so via techniques that implicitly or explicitly increase the effective sample size.
An Empirical Characterization of Fair Machine Learning For Clinical Risk Prediction
Jul 20, 2020



Abstract:The use of machine learning to guide clinical decision making has the potential to worsen existing health disparities. Several recent works frame the problem as that of algorithmic fairness, a framework that has attracted considerable attention and criticism. However, the appropriateness of this framework is unclear due to both ethical as well as technical considerations, the latter of which include trade-offs between measures of fairness and model performance that are not well-understood for predictive models of clinical outcomes. To inform the ongoing debate, we conduct an empirical study to characterize the impact of penalizing group fairness violations on an array of measures of model performance and group fairness. We repeat the analyses across multiple observational healthcare databases, clinical outcomes, and sensitive attributes. We find that procedures that penalize differences between the distributions of predictions across groups induce nearly-universal degradation of multiple performance metrics within groups. On examining the secondary impact of these procedures, we observe heterogeneity of the effect of these procedures on measures of fairness in calibration and ranking across experimental conditions. Beyond the reported trade-offs, we emphasize that analyses of algorithmic fairness in healthcare lack the contextual grounding and causal awareness necessary to reason about the mechanisms that lead to health disparities, as well as about the potential of algorithmic fairness methods to counteract those mechanisms. In light of these limitations, we encourage researchers building predictive models for clinical use to step outside the algorithmic fairness frame and engage critically with the broader sociotechnical context surrounding the use of machine learning in healthcare.
Language Models Are An Effective Patient Representation Learning Technique For Electronic Health Record Data
Jan 06, 2020



Abstract:Widespread adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) has fueled development of clinical outcome models using machine learning. However, patient EHR data are complex, and how to optimally represent them is an open question. This complexity, along with often small training set sizes available to train these clinical outcome models, are two core challenges for training high quality models. In this paper, we demonstrate that learning generic representations from the data of all the patients in the EHR enables better performing prediction models for clinical outcomes, allowing for these challenges to be overcome. We adapt common representation learning techniques used in other domains and find that representations inspired by language models enable a 3.5% mean improvement in AUROC on five clinical outcomes compared to standard baselines, with the average improvement rising to 19% when only a small number of patients are available for training a prediction model for a given clinical outcome.
Federated and Differentially Private Learning for Electronic Health Records
Nov 13, 2019

Abstract:The use of collaborative and decentralized machine learning techniques such as federated learning have the potential to enable the development and deployment of clinical risk predictions models in low-resource settings without requiring sensitive data be shared or stored in a central repository. This process necessitates communication of model weights or updates between collaborating entities, but it is unclear to what extent patient privacy is compromised as a result. To gain insight into this question, we study the efficacy of centralized versus federated learning in both private and non-private settings. The clinical prediction tasks we consider are the prediction of prolonged length of stay and in-hospital mortality across thirty one hospitals in the eICU Collaborative Research Database. We find that while it is straightforward to apply differentially private stochastic gradient descent to achieve strong privacy bounds when training in a centralized setting, it is considerably more difficult to do so in the federated setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge