Rory Sayres
A Toolbox for Surfacing Health Equity Harms and Biases in Large Language Models
Mar 18, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) hold immense promise to serve complex health information needs but also have the potential to introduce harm and exacerbate health disparities. Reliably evaluating equity-related model failures is a critical step toward developing systems that promote health equity. In this work, we present resources and methodologies for surfacing biases with potential to precipitate equity-related harms in long-form, LLM-generated answers to medical questions and then conduct an empirical case study with Med-PaLM 2, resulting in the largest human evaluation study in this area to date. Our contributions include a multifactorial framework for human assessment of LLM-generated answers for biases, and EquityMedQA, a collection of seven newly-released datasets comprising both manually-curated and LLM-generated questions enriched for adversarial queries. Both our human assessment framework and dataset design process are grounded in an iterative participatory approach and review of possible biases in Med-PaLM 2 answers to adversarial queries. Through our empirical study, we find that the use of a collection of datasets curated through a variety of methodologies, coupled with a thorough evaluation protocol that leverages multiple assessment rubric designs and diverse rater groups, surfaces biases that may be missed via narrower evaluation approaches. Our experience underscores the importance of using diverse assessment methodologies and involving raters of varying backgrounds and expertise. We emphasize that while our framework can identify specific forms of bias, it is not sufficient to holistically assess whether the deployment of an AI system promotes equitable health outcomes. We hope the broader community leverages and builds on these tools and methods towards realizing a shared goal of LLMs that promote accessible and equitable healthcare for all.
Closing the AI generalization gap by adjusting for dermatology condition distribution differences across clinical settings
Feb 23, 2024Abstract:Recently, there has been great progress in the ability of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to classify dermatological conditions from clinical photographs. However, little is known about the robustness of these algorithms in real-world settings where several factors can lead to a loss of generalizability. Understanding and overcoming these limitations will permit the development of generalizable AI that can aid in the diagnosis of skin conditions across a variety of clinical settings. In this retrospective study, we demonstrate that differences in skin condition distribution, rather than in demographics or image capture mode are the main source of errors when an AI algorithm is evaluated on data from a previously unseen source. We demonstrate a series of steps to close this generalization gap, requiring progressively more information about the new source, ranging from the condition distribution to training data enriched for data less frequently seen during training. Our results also suggest comparable performance from end-to-end fine tuning versus fine tuning solely the classification layer on top of a frozen embedding model. Our approach can inform the adaptation of AI algorithms to new settings, based on the information and resources available.
Towards Expert-Level Medical Question Answering with Large Language Models
May 16, 2023



Abstract:Recent artificial intelligence (AI) systems have reached milestones in "grand challenges" ranging from Go to protein-folding. The capability to retrieve medical knowledge, reason over it, and answer medical questions comparably to physicians has long been viewed as one such grand challenge. Large language models (LLMs) have catalyzed significant progress in medical question answering; Med-PaLM was the first model to exceed a "passing" score in US Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) style questions with a score of 67.2% on the MedQA dataset. However, this and other prior work suggested significant room for improvement, especially when models' answers were compared to clinicians' answers. Here we present Med-PaLM 2, which bridges these gaps by leveraging a combination of base LLM improvements (PaLM 2), medical domain finetuning, and prompting strategies including a novel ensemble refinement approach. Med-PaLM 2 scored up to 86.5% on the MedQA dataset, improving upon Med-PaLM by over 19% and setting a new state-of-the-art. We also observed performance approaching or exceeding state-of-the-art across MedMCQA, PubMedQA, and MMLU clinical topics datasets. We performed detailed human evaluations on long-form questions along multiple axes relevant to clinical applications. In pairwise comparative ranking of 1066 consumer medical questions, physicians preferred Med-PaLM 2 answers to those produced by physicians on eight of nine axes pertaining to clinical utility (p < 0.001). We also observed significant improvements compared to Med-PaLM on every evaluation axis (p < 0.001) on newly introduced datasets of 240 long-form "adversarial" questions to probe LLM limitations. While further studies are necessary to validate the efficacy of these models in real-world settings, these results highlight rapid progress towards physician-level performance in medical question answering.
Underspecification Presents Challenges for Credibility in Modern Machine Learning
Nov 06, 2020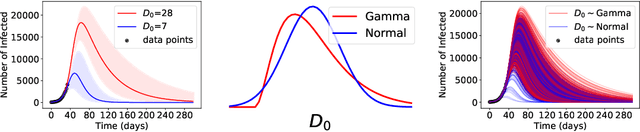


Abstract:ML models often exhibit unexpectedly poor behavior when they are deployed in real-world domains. We identify underspecification as a key reason for these failures. An ML pipeline is underspecified when it can return many predictors with equivalently strong held-out performance in the training domain. Underspecification is common in modern ML pipelines, such as those based on deep learning. Predictors returned by underspecified pipelines are often treated as equivalent based on their training domain performance, but we show here that such predictors can behave very differently in deployment domains. This ambiguity can lead to instability and poor model behavior in practice, and is a distinct failure mode from previously identified issues arising from structural mismatch between training and deployment domains. We show that this problem appears in a wide variety of practical ML pipelines, using examples from computer vision, medical imaging, natural language processing, clinical risk prediction based on electronic health records, and medical genomics. Our results show the need to explicitly account for underspecification in modeling pipelines that are intended for real-world deployment in any domain.
Improving Medical Annotation Quality to Decrease Labeling Burden Using Stratified Noisy Cross-Validation
Sep 22, 2020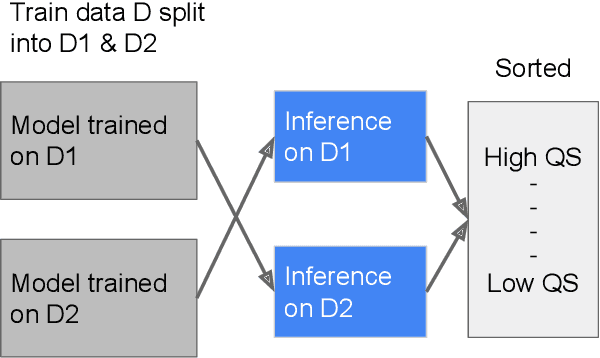

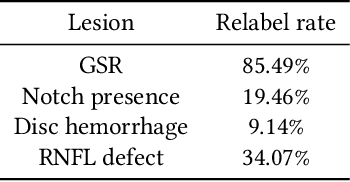
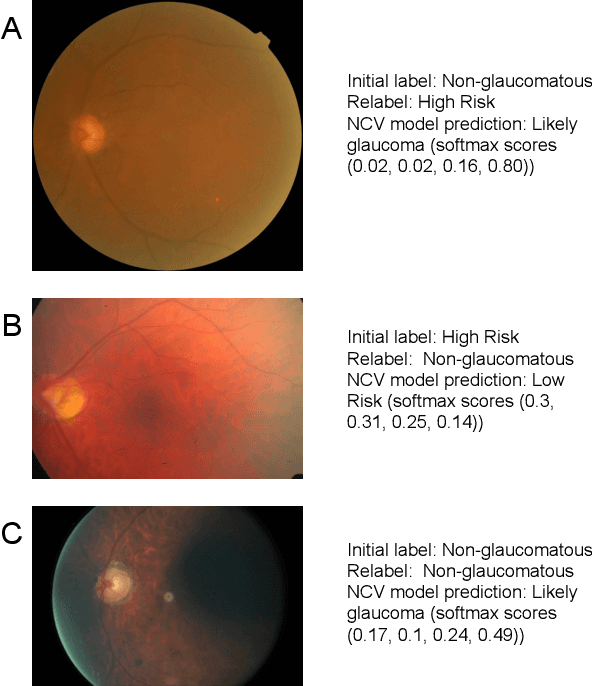
Abstract:As machine learning has become increasingly applied to medical imaging data, noise in training labels has emerged as an important challenge. Variability in diagnosis of medical images is well established; in addition, variability in training and attention to task among medical labelers may exacerbate this issue. Methods for identifying and mitigating the impact of low quality labels have been studied, but are not well characterized in medical imaging tasks. For instance, Noisy Cross-Validation splits the training data into halves, and has been shown to identify low-quality labels in computer vision tasks; but it has not been applied to medical imaging tasks specifically. In this work we introduce Stratified Noisy Cross-Validation (SNCV), an extension of noisy cross validation. SNCV can provide estimates of confidence in model predictions by assigning a quality score to each example; stratify labels to handle class imbalance; and identify likely low-quality labels to analyze the causes. We assess performance of SNCV on diagnosis of glaucoma suspect risk from retinal fundus photographs, a clinically important yet nuanced labeling task. Using training data from a previously-published deep learning model, we compute a continuous quality score (QS) for each training example. We relabel 1,277 low-QS examples using a trained glaucoma specialist; the new labels agree with the SNCV prediction over the initial label >85% of the time, indicating that low-QS examples mostly reflect labeler errors. We then quantify the impact of training with only high-QS labels, showing that strong model performance may be obtained with many fewer examples. By applying the method to randomly sub-sampled training dataset, we show that our method can reduce labelling burden by approximately 50% while achieving model performance non-inferior to using the full dataset on multiple held-out test sets.
Deep Learning to Assess Glaucoma Risk and Associated Features in Fundus Images
Dec 21, 2018
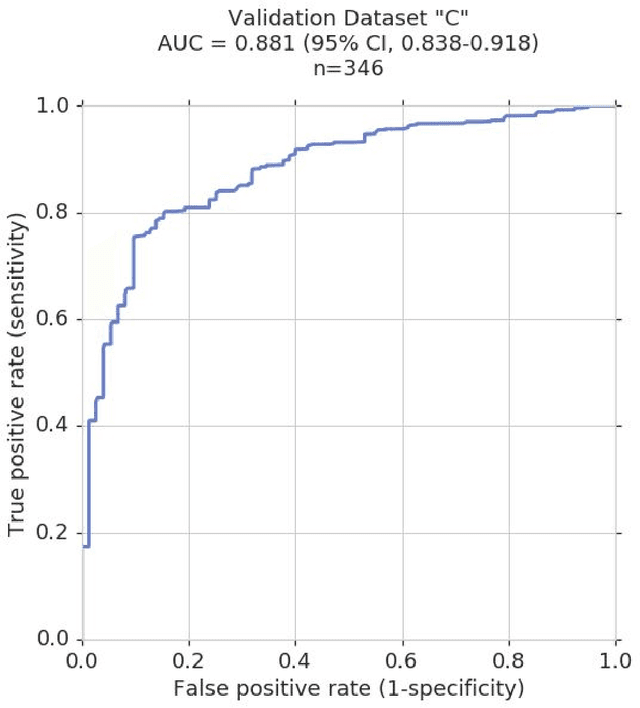
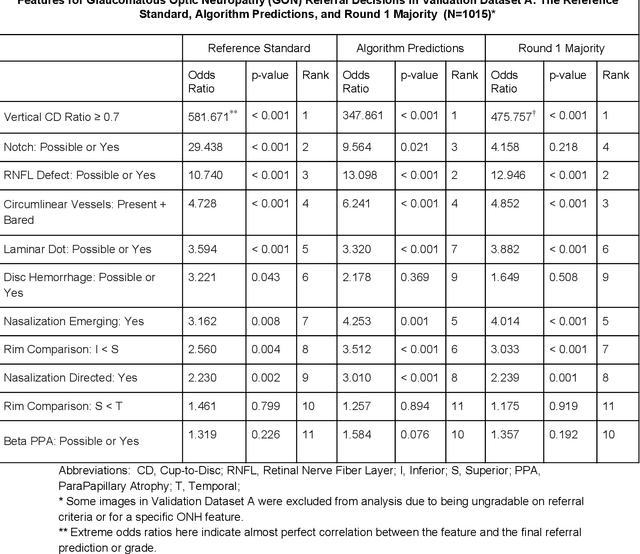
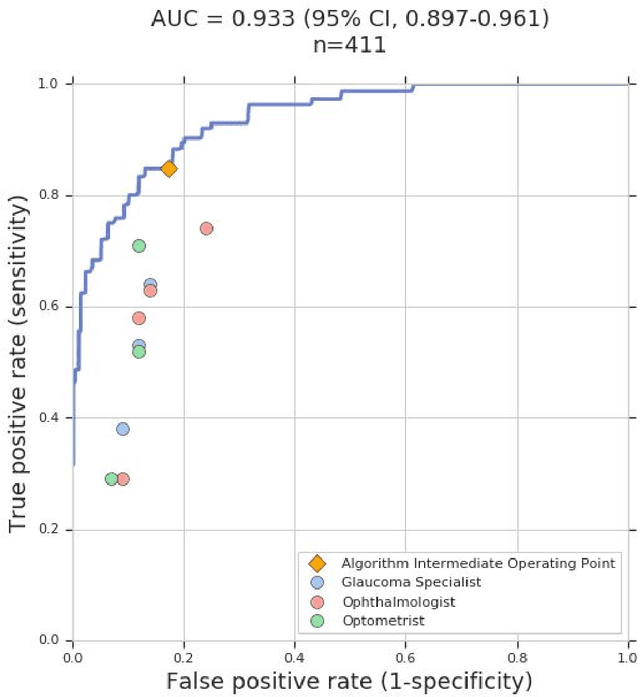
Abstract:Glaucoma is the leading cause of preventable, irreversible blindness world-wide. The disease can remain asymptomatic until severe, and an estimated 50%-90% of people with glaucoma remain undiagnosed. Thus, glaucoma screening is recommended for early detection and treatment. A cost-effective tool to detect glaucoma could expand healthcare access to a much larger patient population, but such a tool is currently unavailable. We trained a deep learning (DL) algorithm using a retrospective dataset of 58,033 images, assessed for gradability, glaucomatous optic nerve head (ONH) features, and referable glaucoma risk. The resultant algorithm was validated using 2 separate datasets. For referable glaucoma risk, the algorithm had an AUC of 0.940 (95%CI, 0.922-0.955) in validation dataset "A" (1,205 images, 1 image/patient; 19% referable where images were adjudicated by panels of fellowship-trained glaucoma specialists) and 0.858 (95% CI, 0.836-0.878) in validation dataset "B" (17,593 images from 9,643 patients; 9.2% referable where images were from the Atlanta Veterans Affairs Eye Clinic diabetic teleretinal screening program using clinical referral decisions as the reference standard). Additionally, we found that the presence of vertical cup-to-disc ratio >= 0.7, neuroretinal rim notching, retinal nerve fiber layer defect, and bared circumlinear vessels contributed most to referable glaucoma risk assessment by both glaucoma specialists and the algorithm. Algorithm AUCs ranged between 0.608-0.977 for glaucomatous ONH features. The DL algorithm was significantly more sensitive than 6 of 10 graders, including 2 of 3 glaucoma specialists, with comparable or higher specificity relative to all graders. A DL algorithm trained on fundus images alone can detect referable glaucoma risk with higher sensitivity and comparable specificity to eye care providers.
Deep Learning vs. Human Graders for Classifying Severity Levels of Diabetic Retinopathy in a Real-World Nationwide Screening Program
Oct 18, 2018
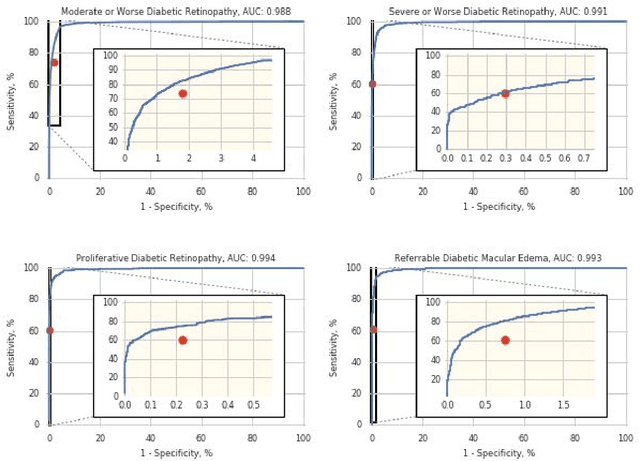
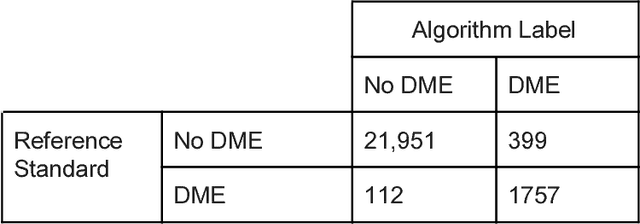
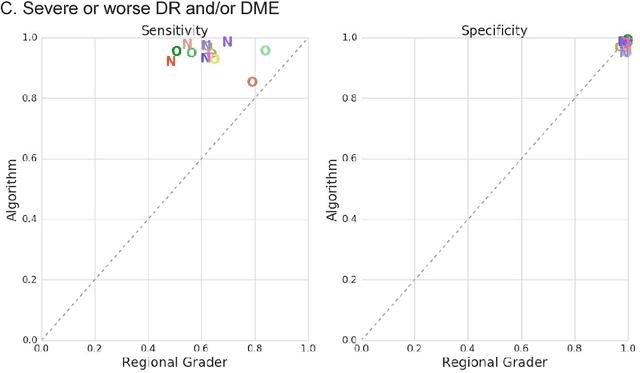
Abstract:Deep learning algorithms have been used to detect diabetic retinopathy (DR) with specialist-level accuracy. This study aims to validate one such algorithm on a large-scale clinical population, and compare the algorithm performance with that of human graders. 25,326 gradable retinal images of patients with diabetes from the community-based, nation-wide screening program of DR in Thailand were analyzed for DR severity and referable diabetic macular edema (DME). Grades adjudicated by a panel of international retinal specialists served as the reference standard. Across different severity levels of DR for determining referable disease, deep learning significantly reduced the false negative rate (by 23%) at the cost of slightly higher false positive rates (2%). Deep learning algorithms may serve as a valuable tool for DR screening.
Direct Uncertainty Prediction for Medical Second Opinions
Sep 13, 2018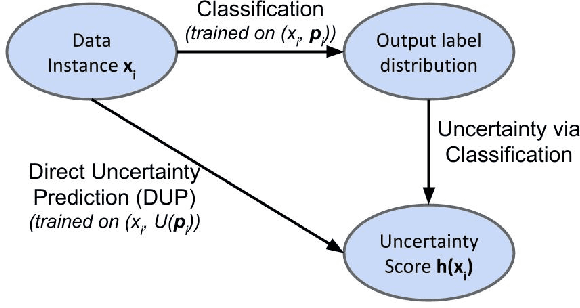
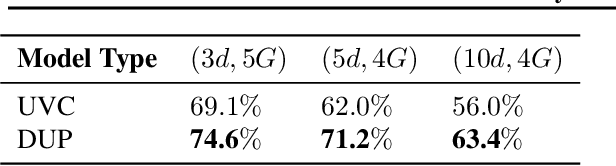
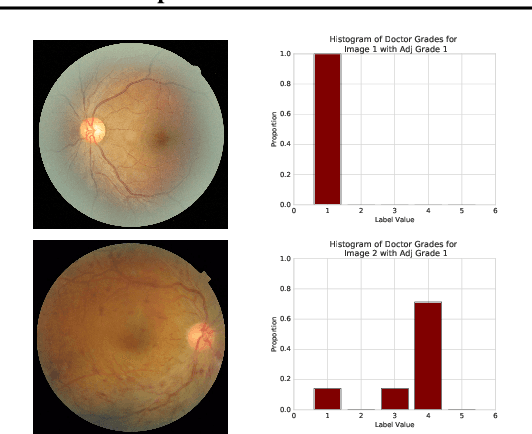

Abstract:A persistent challenge in the practice of medicine (and machine learning) is the disagreement of highly trained human experts on data instances, such as patient image scans. We study the application of machine learning to predict which instances are likely to give rise to maximal expert disagreement. As necessitated by this, we develop predictors on datasets with noisy and scarce labels. Our central methodological finding is that direct prediction of a scalar uncertainty score performs better than the two-step process of (i) training a classifier (ii) using the classifier outputs to derive an uncertainty score. This is seen in both a synthetic setting whose parameters we can control, and a paradigmatic healthcare application involving multiple labels by medical domain experts. We evaluate these direct uncertainty models on a gold standard adjudicated set, where they accurately predict when an individual expert will disagree with an unknown ground truth. We explore the consequences for using these predictors to identify the need for a medical second opinion and a machine learning data curation application.
Interpretability Beyond Feature Attribution: Quantitative Testing with Concept Activation Vectors (TCAV)
Jun 07, 2018



Abstract:The interpretation of deep learning models is a challenge due to their size, complexity, and often opaque internal state. In addition, many systems, such as image classifiers, operate on low-level features rather than high-level concepts. To address these challenges, we introduce Concept Activation Vectors (CAVs), which provide an interpretation of a neural net's internal state in terms of human-friendly concepts. The key idea is to view the high-dimensional internal state of a neural net as an aid, not an obstacle. We show how to use CAVs as part of a technique, Testing with CAVs (TCAV), that uses directional derivatives to quantify the degree to which a user-defined concept is important to a classification result--for example, how sensitive a prediction of "zebra" is to the presence of stripes. Using the domain of image classification as a testing ground, we describe how CAVs may be used to explore hypotheses and generate insights for a standard image classification network as well as a medical application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge