Michelle Phung
Closing the AI generalization gap by adjusting for dermatology condition distribution differences across clinical settings
Feb 23, 2024Abstract:Recently, there has been great progress in the ability of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to classify dermatological conditions from clinical photographs. However, little is known about the robustness of these algorithms in real-world settings where several factors can lead to a loss of generalizability. Understanding and overcoming these limitations will permit the development of generalizable AI that can aid in the diagnosis of skin conditions across a variety of clinical settings. In this retrospective study, we demonstrate that differences in skin condition distribution, rather than in demographics or image capture mode are the main source of errors when an AI algorithm is evaluated on data from a previously unseen source. We demonstrate a series of steps to close this generalization gap, requiring progressively more information about the new source, ranging from the condition distribution to training data enriched for data less frequently seen during training. Our results also suggest comparable performance from end-to-end fine tuning versus fine tuning solely the classification layer on top of a frozen embedding model. Our approach can inform the adaptation of AI algorithms to new settings, based on the information and resources available.
Development and Clinical Evaluation of an AI Support Tool for Improving Telemedicine Photo Quality
Sep 12, 2022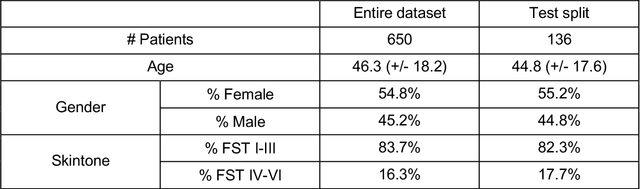
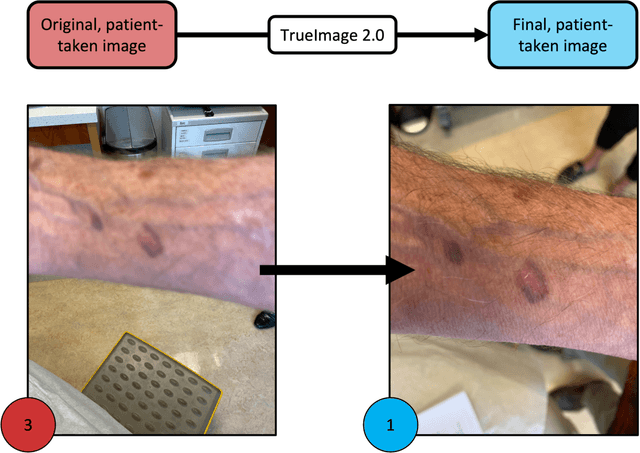
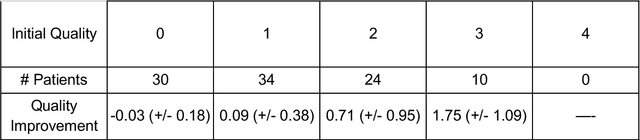
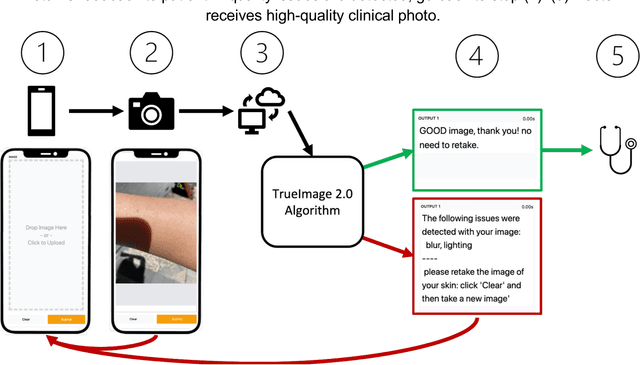
Abstract:Telemedicine utilization was accelerated during the COVID-19 pandemic, and skin conditions were a common use case. However, the quality of photographs sent by patients remains a major limitation. To address this issue, we developed TrueImage 2.0, an artificial intelligence (AI) model for assessing patient photo quality for telemedicine and providing real-time feedback to patients for photo quality improvement. TrueImage 2.0 was trained on 1700 telemedicine images annotated by clinicians for photo quality. On a retrospective dataset of 357 telemedicine images, TrueImage 2.0 effectively identified poor quality images (Receiver operator curve area under the curve (ROC-AUC) =0.78) and the reason for poor quality (Blurry ROC-AUC=0.84, Lighting issues ROC-AUC=0.70). The performance is consistent across age, gender, and skin tone. Next, we assessed whether patient-TrueImage 2.0 interaction led to an improvement in submitted photo quality through a prospective clinical pilot study with 98 patients. TrueImage 2.0 reduced the number of patients with a poor-quality image by 68.0%.
Disparities in Dermatology AI Performance on a Diverse, Curated Clinical Image Set
Mar 15, 2022Abstract:Access to dermatological care is a major issue, with an estimated 3 billion people lacking access to care globally. Artificial intelligence (AI) may aid in triaging skin diseases. However, most AI models have not been rigorously assessed on images of diverse skin tones or uncommon diseases. To ascertain potential biases in algorithm performance in this context, we curated the Diverse Dermatology Images (DDI) dataset-the first publicly available, expertly curated, and pathologically confirmed image dataset with diverse skin tones. Using this dataset of 656 images, we show that state-of-the-art dermatology AI models perform substantially worse on DDI, with receiver operator curve area under the curve (ROC-AUC) dropping by 27-36 percent compared to the models' original test results. All the models performed worse on dark skin tones and uncommon diseases, which are represented in the DDI dataset. Additionally, we find that dermatologists, who typically provide visual labels for AI training and test datasets, also perform worse on images of dark skin tones and uncommon diseases compared to ground truth biopsy annotations. Finally, fine-tuning AI models on the well-characterized and diverse DDI images closed the performance gap between light and dark skin tones. Moreover, algorithms fine-tuned on diverse skin tones outperformed dermatologists on identifying malignancy on images of dark skin tones. Our findings identify important weaknesses and biases in dermatology AI that need to be addressed to ensure reliable application to diverse patients and diseases.
Disparities in Dermatology AI: Assessments Using Diverse Clinical Images
Nov 15, 2021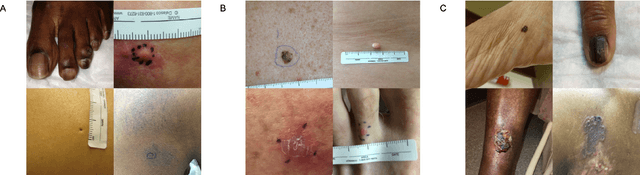
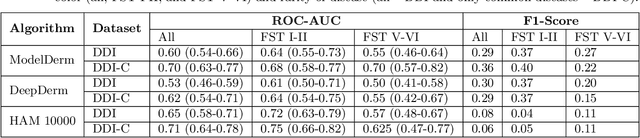
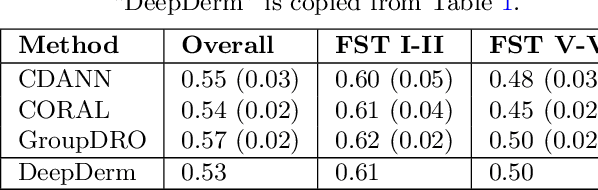
Abstract:More than 3 billion people lack access to care for skin disease. AI diagnostic tools may aid in early skin cancer detection; however most models have not been assessed on images of diverse skin tones or uncommon diseases. To address this, we curated the Diverse Dermatology Images (DDI) dataset - the first publicly available, pathologically confirmed images featuring diverse skin tones. We show that state-of-the-art dermatology AI models perform substantially worse on DDI, with ROC-AUC dropping 29-40 percent compared to the models' original results. We find that dark skin tones and uncommon diseases, which are well represented in the DDI dataset, lead to performance drop-offs. Additionally, we show that state-of-the-art robust training methods cannot correct for these biases without diverse training data. Our findings identify important weaknesses and biases in dermatology AI that need to be addressed to ensure reliable application to diverse patients and across all disease.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge