Awa Dieng
Understanding challenges to the interpretation of disaggregated evaluations of algorithmic fairness
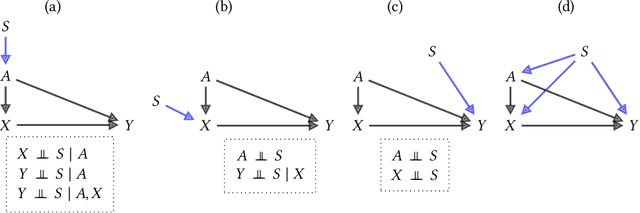
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Disaggregated evaluation across subgroups is critical for assessing the fairness of machine learning models, but its uncritical use can mislead practitioners. We show that equal performance across subgroups is an unreliable measure of fairness when data are representative of the relevant populations but reflective of real-world disparities. Furthermore, when data are not representative due to selection bias, both disaggregated evaluation and alternative approaches based on conditional independence testing may be invalid without explicit assumptions regarding the bias mechanism. We use causal graphical models to predict metric stability across subgroups under different data generating processes. Our framework suggests complementing disaggregated evaluations with explicit causal assumptions and analysis to control for confounding and distribution shift, including conditional independence testing and weighted performance estimation. These findings have broad implications for how practitioners design and interpret model assessments given the ubiquity of disaggregated evaluation.
Contextual Evaluation of Large Language Models for Classifying Tropical and Infectious Diseases
Sep 13, 2024Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) have shown promise for medical question answering, there is limited work focused on tropical and infectious disease-specific exploration. We build on an opensource tropical and infectious diseases (TRINDs) dataset, expanding it to include demographic and semantic clinical and consumer augmentations yielding 11000+ prompts. We evaluate LLM performance on these, comparing generalist and medical LLMs, as well as LLM outcomes to human experts. We demonstrate through systematic experimentation, the benefit of contextual information such as demographics, location, gender, risk factors for optimal LLM response. Finally we develop a prototype of TRINDs-LM, a research tool that provides a playground to navigate how context impacts LLM outputs for health.
A Toolbox for Surfacing Health Equity Harms and Biases in Large Language Models
Mar 18, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) hold immense promise to serve complex health information needs but also have the potential to introduce harm and exacerbate health disparities. Reliably evaluating equity-related model failures is a critical step toward developing systems that promote health equity. In this work, we present resources and methodologies for surfacing biases with potential to precipitate equity-related harms in long-form, LLM-generated answers to medical questions and then conduct an empirical case study with Med-PaLM 2, resulting in the largest human evaluation study in this area to date. Our contributions include a multifactorial framework for human assessment of LLM-generated answers for biases, and EquityMedQA, a collection of seven newly-released datasets comprising both manually-curated and LLM-generated questions enriched for adversarial queries. Both our human assessment framework and dataset design process are grounded in an iterative participatory approach and review of possible biases in Med-PaLM 2 answers to adversarial queries. Through our empirical study, we find that the use of a collection of datasets curated through a variety of methodologies, coupled with a thorough evaluation protocol that leverages multiple assessment rubric designs and diverse rater groups, surfaces biases that may be missed via narrower evaluation approaches. Our experience underscores the importance of using diverse assessment methodologies and involving raters of varying backgrounds and expertise. We emphasize that while our framework can identify specific forms of bias, it is not sufficient to holistically assess whether the deployment of an AI system promotes equitable health outcomes. We hope the broader community leverages and builds on these tools and methods towards realizing a shared goal of LLMs that promote accessible and equitable healthcare for all.
The Case for Globalizing Fairness: A Mixed Methods Study on Colonialism, AI, and Health in Africa
Mar 11, 2024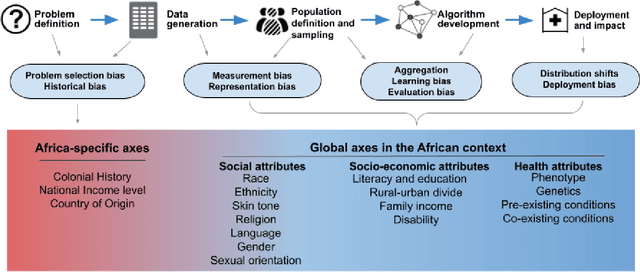
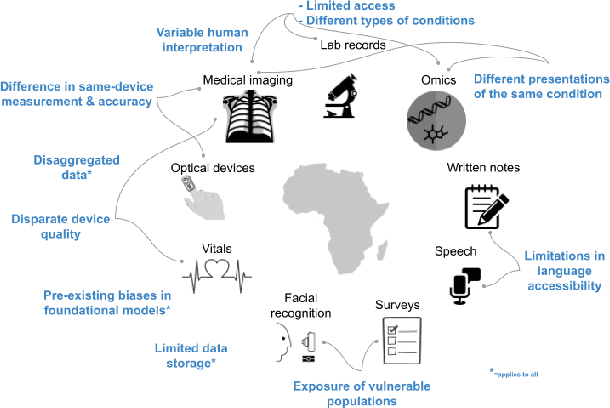
Abstract:With growing application of machine learning (ML) technologies in healthcare, there have been calls for developing techniques to understand and mitigate biases these systems may exhibit. Fair-ness considerations in the development of ML-based solutions for health have particular implications for Africa, which already faces inequitable power imbalances between the Global North and South.This paper seeks to explore fairness for global health, with Africa as a case study. We conduct a scoping review to propose axes of disparities for fairness consideration in the African context and delineate where they may come into play in different ML-enabled medical modalities. We then conduct qualitative research studies with 672 general population study participants and 28 experts inML, health, and policy focused on Africa to obtain corroborative evidence on the proposed axes of disparities. Our analysis focuses on colonialism as the attribute of interest and examines the interplay between artificial intelligence (AI), health, and colonialism. Among the pre-identified attributes, we found that colonial history, country of origin, and national income level were specific axes of disparities that participants believed would cause an AI system to be biased.However, there was also divergence of opinion between experts and general population participants. Whereas experts generally expressed a shared view about the relevance of colonial history for the development and implementation of AI technologies in Africa, the majority of the general population participants surveyed did not think there was a direct link between AI and colonialism. Based on these findings, we provide practical recommendations for developing fairness-aware ML solutions for health in Africa.
Globalizing Fairness Attributes in Machine Learning: A Case Study on Health in Africa
Apr 05, 2023

Abstract:With growing machine learning (ML) applications in healthcare, there have been calls for fairness in ML to understand and mitigate ethical concerns these systems may pose. Fairness has implications for global health in Africa, which already has inequitable power imbalances between the Global North and South. This paper seeks to explore fairness for global health, with Africa as a case study. We propose fairness attributes for consideration in the African context and delineate where they may come into play in different ML-enabled medical modalities. This work serves as a basis and call for action for furthering research into fairness in global health.
Maintaining fairness across distribution shift: do we have viable solutions for real-world applications?
Feb 02, 2022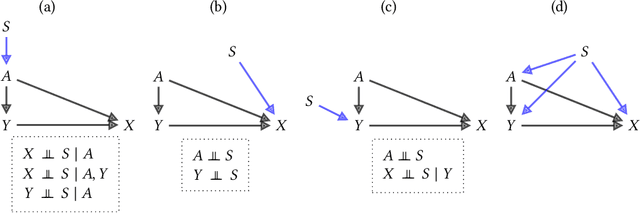
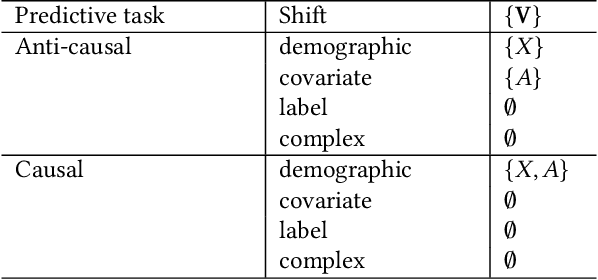
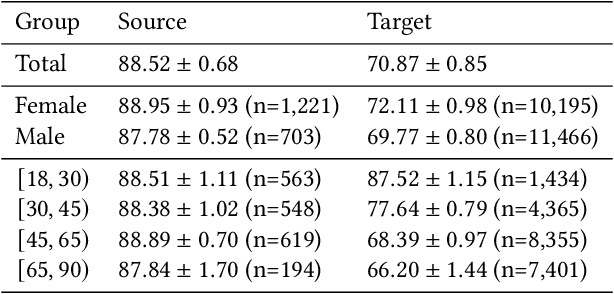
Abstract:Fairness and robustness are often considered as orthogonal dimensions when evaluating machine learning models. However, recent work has revealed interactions between fairness and robustness, showing that fairness properties are not necessarily maintained under distribution shift. In healthcare settings, this can result in e.g. a model that performs fairly according to a selected metric in "hospital A" showing unfairness when deployed in "hospital B". While a nascent field has emerged to develop provable fair and robust models, it typically relies on strong assumptions about the shift, limiting its impact for real-world applications. In this work, we explore the settings in which recently proposed mitigation strategies are applicable by referring to a causal framing. Using examples of predictive models in dermatology and electronic health records, we show that real-world applications are complex and often invalidate the assumptions of such methods. Our work hence highlights technical, practical, and engineering gaps that prevent the development of robustly fair machine learning models for real-world applications. Finally, we discuss potential remedies at each step of the machine learning pipeline.
Almost-Exact Matching with Replacement for Causal Inference
Nov 01, 2018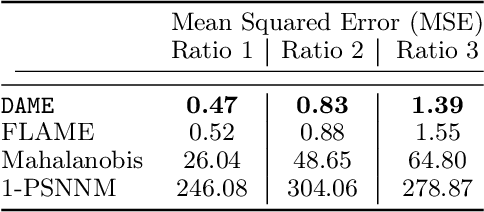
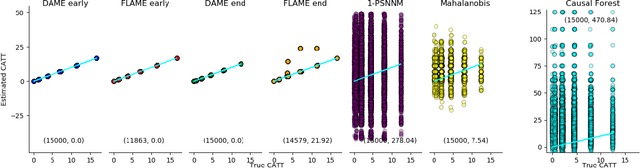
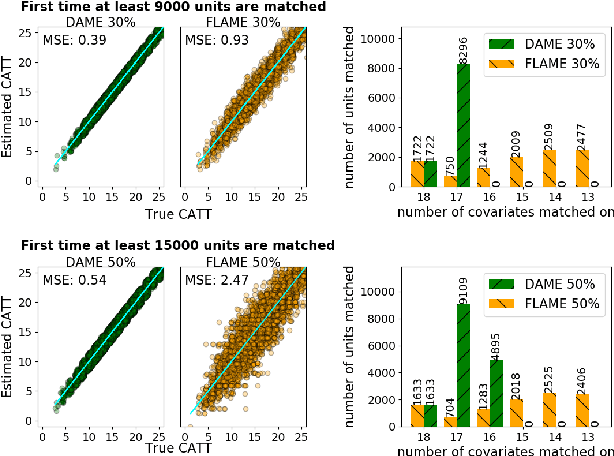

Abstract:We aim to create the highest possible quality of treatment-control matches for categorical data in the potential outcomes framework. Matching methods are heavily used in the social sciences due to their interpretability, but most matching methods do not pass basic sanity checks: they fail when irrelevant variables are introduced, and tend to be either computationally slow or produce low-quality matches. The method proposed in this work aims to match units on a weighted Hamming distance, taking into account the relative importance of the covariates; the algorithm aims to match units on as many relevant variables as possible. To do this, the algorithm creates a hierarchy of covariate combinations on which to match (similar to downward closure), in the process solving an optimization problem for each unit in order to construct the optimal matches. The algorithm uses a single dynamic program to solve all of the optimization problems simultaneously. Notable advantages of our method over existing matching procedures are its high-quality matches, versatility in handling different data distributions that may have irrelevant variables, and ability to handle missing data by matching on as many available covariates as possible.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge