Sayash Kapoor
The 2025 Foundation Model Transparency Index
Dec 11, 2025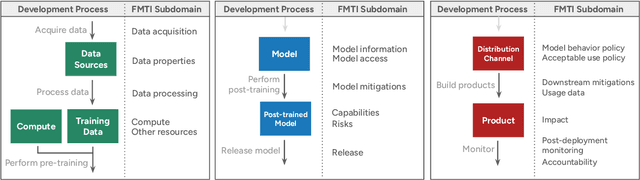
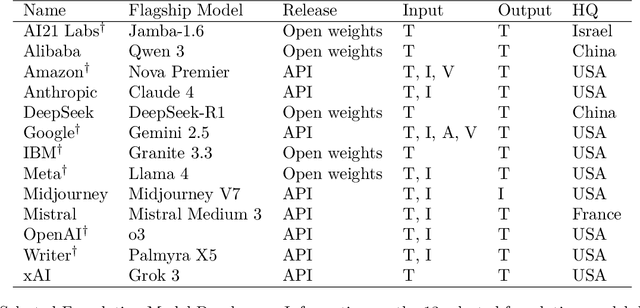
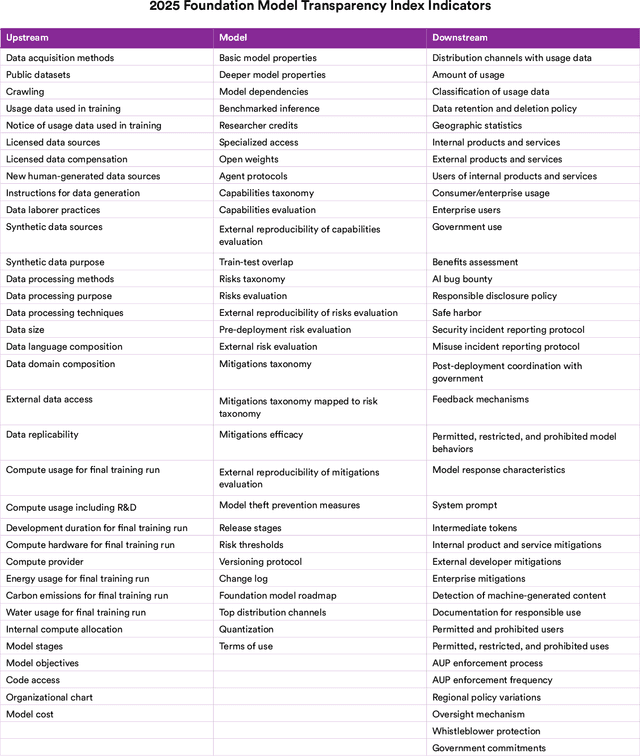
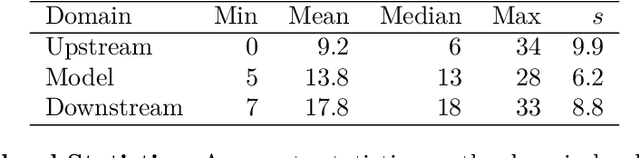
Abstract:Foundation model developers are among the world's most important companies. As these companies become increasingly consequential, how do their transparency practices evolve? The 2025 Foundation Model Transparency Index is the third edition of an annual effort to characterize and quantify the transparency of foundation model developers. The 2025 FMTI introduces new indicators related to data acquisition, usage data, and monitoring and evaluates companies like Alibaba, DeepSeek, and xAI for the first time. The 2024 FMTI reported that transparency was improving, but the 2025 FMTI finds this progress has deteriorated: the average score out of 100 fell from 58 in 2024 to 40 in 2025. Companies are most opaque about their training data and training compute as well as the post-deployment usage and impact of their flagship models. In spite of this general trend, IBM stands out as a positive outlier, scoring 95, in contrast to the lowest scorers, xAI and Midjourney, at just 14. The five members of the Frontier Model Forum we score end up in the middle of the Index: we posit that these companies avoid reputational harms from low scores but lack incentives to be transparency leaders. As policymakers around the world increasingly mandate certain types of transparency, this work reveals the current state of transparency for foundation model developers, how it may change given newly enacted policy, and where more aggressive policy interventions are necessary to address critical information deficits.
Establishing Best Practices for Building Rigorous Agentic Benchmarks
Jul 03, 2025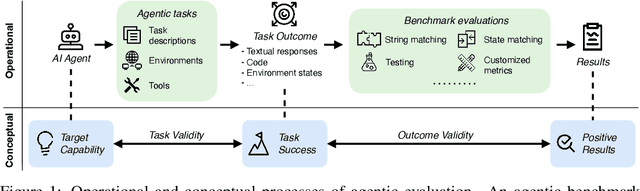
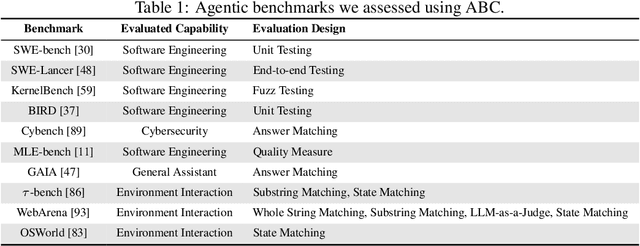
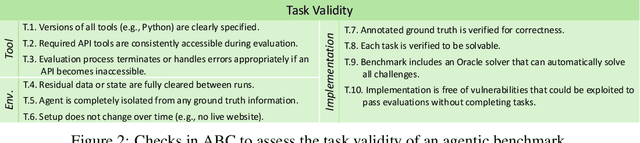
Abstract:Benchmarks are essential for quantitatively tracking progress in AI. As AI agents become increasingly capable, researchers and practitioners have introduced agentic benchmarks to evaluate agents on complex, real-world tasks. These benchmarks typically measure agent capabilities by evaluating task outcomes via specific reward designs. However, we show that many agentic benchmarks have issues task setup or reward design. For example, SWE-bench Verified uses insufficient test cases, while TAU-bench counts empty responses as successful. Such issues can lead to under- or overestimation agents' performance by up to 100% in relative terms. To make agentic evaluation rigorous, we introduce the Agentic Benchmark Checklist (ABC), a set of guidelines that we synthesized from our benchmark-building experience, a survey of best practices, and previously reported issues. When applied to CVE-Bench, a benchmark with a particularly complex evaluation design, ABC reduces the performance overestimation by 33%.
The Leaderboard Illusion
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Measuring progress is fundamental to the advancement of any scientific field. As benchmarks play an increasingly central role, they also grow more susceptible to distortion. Chatbot Arena has emerged as the go-to leaderboard for ranking the most capable AI systems. Yet, in this work we identify systematic issues that have resulted in a distorted playing field. We find that undisclosed private testing practices benefit a handful of providers who are able to test multiple variants before public release and retract scores if desired. We establish that the ability of these providers to choose the best score leads to biased Arena scores due to selective disclosure of performance results. At an extreme, we identify 27 private LLM variants tested by Meta in the lead-up to the Llama-4 release. We also establish that proprietary closed models are sampled at higher rates (number of battles) and have fewer models removed from the arena than open-weight and open-source alternatives. Both these policies lead to large data access asymmetries over time. Providers like Google and OpenAI have received an estimated 19.2% and 20.4% of all data on the arena, respectively. In contrast, a combined 83 open-weight models have only received an estimated 29.7% of the total data. We show that access to Chatbot Arena data yields substantial benefits; even limited additional data can result in relative performance gains of up to 112% on the arena distribution, based on our conservative estimates. Together, these dynamics result in overfitting to Arena-specific dynamics rather than general model quality. The Arena builds on the substantial efforts of both the organizers and an open community that maintains this valuable evaluation platform. We offer actionable recommendations to reform the Chatbot Arena's evaluation framework and promote fairer, more transparent benchmarking for the field
Toward an Evaluation Science for Generative AI Systems
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:There is an increasing imperative to anticipate and understand the performance and safety of generative AI systems in real-world deployment contexts. However, the current evaluation ecosystem is insufficient: Commonly used static benchmarks face validity challenges, and ad hoc case-by-case audits rarely scale. In this piece, we advocate for maturing an evaluation science for generative AI systems. While generative AI creates unique challenges for system safety engineering and measurement science, the field can draw valuable insights from the development of safety evaluation practices in other fields, including transportation, aerospace, and pharmaceutical engineering. In particular, we present three key lessons: Evaluation metrics must be applicable to real-world performance, metrics must be iteratively refined, and evaluation institutions and norms must be established. Applying these insights, we outline a concrete path toward a more rigorous approach for evaluating generative AI systems.
International AI Safety Report
Jan 29, 2025



Abstract:The first International AI Safety Report comprehensively synthesizes the current evidence on the capabilities, risks, and safety of advanced AI systems. The report was mandated by the nations attending the AI Safety Summit in Bletchley, UK. Thirty nations, the UN, the OECD, and the EU each nominated a representative to the report's Expert Advisory Panel. A total of 100 AI experts contributed, representing diverse perspectives and disciplines. Led by the report's Chair, these independent experts collectively had full discretion over the report's content.
The Reality of AI and Biorisk
Dec 02, 2024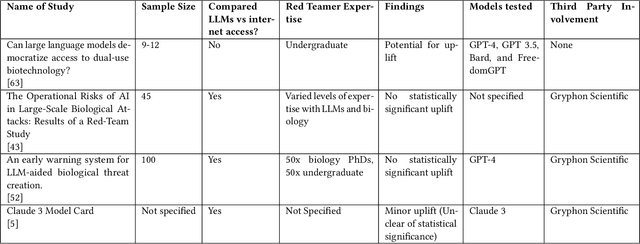
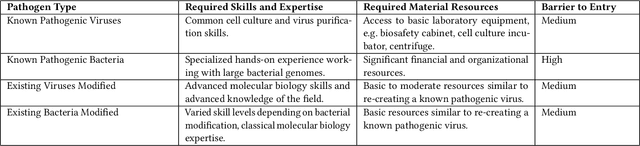
Abstract:To accurately and confidently answer the question 'could an AI model or system increase biorisk', it is necessary to have both a sound theoretical threat model for how AI models or systems could increase biorisk and a robust method for testing that threat model. This paper provides an analysis of existing available research surrounding two AI and biorisk threat models: 1) access to information and planning via large language models (LLMs), and 2) the use of AI-enabled biological tools (BTs) in synthesizing novel biological artifacts. We find that existing studies around AI-related biorisk are nascent, often speculative in nature, or limited in terms of their methodological maturity and transparency. The available literature suggests that current LLMs and BTs do not pose an immediate risk, and more work is needed to develop rigorous approaches to understanding how future models could increase biorisks. We end with recommendations about how empirical work can be expanded to more precisely target biorisk and ensure rigor and validity of findings.
Inference Scaling fLaws: The Limits of LLM Resampling with Imperfect Verifiers
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:Recent research has generated hope that inference scaling could allow weaker language models to match or exceed the accuracy of stronger models, such as by repeatedly sampling solutions to a coding problem until it passes unit tests. The central thesis of this paper is that there is no free lunch for inference scaling: indefinite accuracy improvement through resampling can only be realized if the "verifier" (in this case, a set of unit tests) is perfect. When the verifier is imperfect, as it almost always is in domains such as reasoning or coding (for example, unit tests have imperfect coverage), there is a nonzero probability of false positives: incorrect solutions that pass the verifier. Resampling cannot decrease this probability, so it imposes an upper bound to the accuracy of resampling-based inference scaling even with an infinite compute budget. We find that there is a very strong correlation between the model's single-sample accuracy (i.e. accuracy without unit tests) and its false positive rate on coding benchmarks HumanEval and MBPP, whose unit tests have limited coverage. Therefore, no amount of inference scaling of weaker models can enable them to match the single-sample accuracy of a sufficiently strong model (Fig. 1a). When we consider that false positives have a negative utility compared to abstaining from producing a solution, it bends the inference scaling curve further downward. Empirically, we find that the optimal number of samples can be less than 10 under realistic assumptions (Fig. 1b). Finally, we show that beyond accuracy, false positives may have other undesirable qualities, such as poor adherence to coding style conventions.
Inference Scaling $\scriptsize\mathtt{F}$Laws: The Limits of LLM Resampling with Imperfect Verifiers
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:Recent research has generated hope that inference scaling could allow weaker language models to match or exceed the accuracy of stronger models, such as by repeatedly sampling solutions to a coding problem until it passes unit tests. The central thesis of this paper is that there is no free lunch for inference scaling: indefinite accuracy improvement through resampling can only be realized if the "verifier" (in this case, a set of unit tests) is perfect. When the verifier is imperfect, as it almost always is in domains such as reasoning or coding (for example, unit tests have imperfect coverage), there is a nonzero probability of false positives: incorrect solutions that pass the verifier. Resampling cannot decrease this probability, so it imposes an upper bound to the accuracy of resampling-based inference scaling even with an infinite compute budget. We find that there is a very strong correlation between the model's single-sample accuracy (i.e. accuracy without unit tests) and its false positive rate on coding benchmarks HumanEval and MBPP, whose unit tests have limited coverage. Therefore, no amount of inference scaling of weaker models can enable them to match the single-sample accuracy of a sufficiently strong model (Fig. 1a). When we consider that false positives have a negative utility compared to abstaining from producing a solution, it bends the inference scaling curve further downward. Empirically, we find that the optimal number of samples can be less than 10 under realistic assumptions (Fig. 1b). Finally, we show that beyond accuracy, false positives may have other undesirable qualities, such as poor adherence to coding style conventions.
CORE-Bench: Fostering the Credibility of Published Research Through a Computational Reproducibility Agent Benchmark
Sep 17, 2024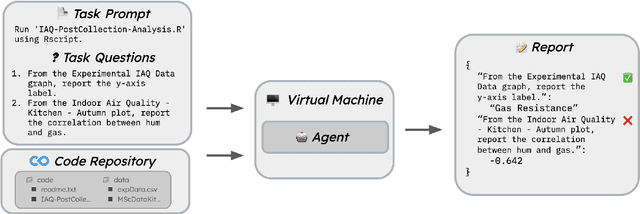
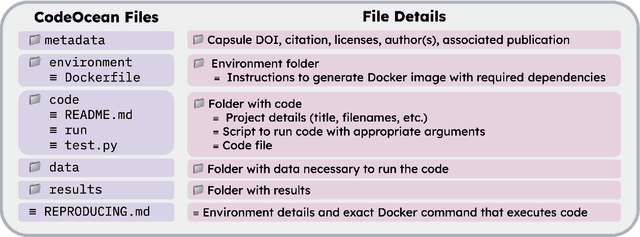
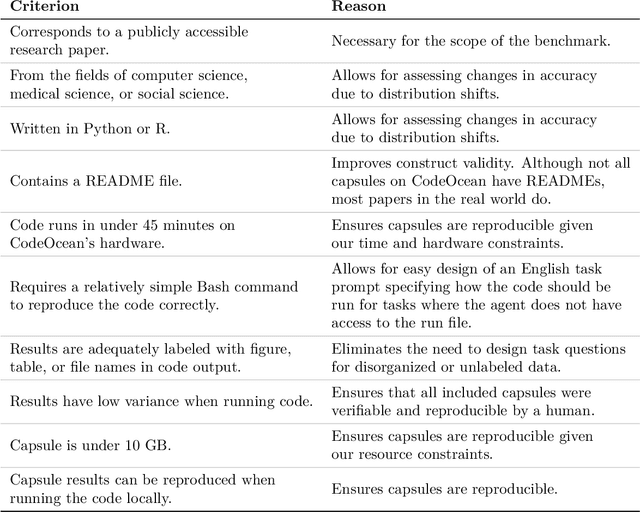
Abstract:AI agents have the potential to aid users on a variety of consequential tasks, including conducting scientific research. To spur the development of useful agents, we need benchmarks that are challenging, but more crucially, directly correspond to real-world tasks of interest. This paper introduces such a benchmark, designed to measure the accuracy of AI agents in tackling a crucial yet surprisingly challenging aspect of scientific research: computational reproducibility. This task, fundamental to the scientific process, involves reproducing the results of a study using the provided code and data. We introduce CORE-Bench (Computational Reproducibility Agent Benchmark), a benchmark consisting of 270 tasks based on 90 scientific papers across three disciplines (computer science, social science, and medicine). Tasks in CORE-Bench consist of three difficulty levels and include both language-only and vision-language tasks. We provide an evaluation system to measure the accuracy of agents in a fast and parallelizable way, saving days of evaluation time for each run compared to a sequential implementation. We evaluated two baseline agents: the general-purpose AutoGPT and a task-specific agent called CORE-Agent. We tested both variants using two underlying language models: GPT-4o and GPT-4o-mini. The best agent achieved an accuracy of 21% on the hardest task, showing the vast scope for improvement in automating routine scientific tasks. Having agents that can reproduce existing work is a necessary step towards building agents that can conduct novel research and could verify and improve the performance of other research agents. We hope that CORE-Bench can improve the state of reproducibility and spur the development of future research agents.
The Foundation Model Transparency Index v1.1: May 2024
Jul 17, 2024Abstract:Foundation models are increasingly consequential yet extremely opaque. To characterize the status quo, the Foundation Model Transparency Index was launched in October 2023 to measure the transparency of leading foundation model developers. The October 2023 Index (v1.0) assessed 10 major foundation model developers (e.g. OpenAI, Google) on 100 transparency indicators (e.g. does the developer disclose the wages it pays for data labor?). At the time, developers publicly disclosed very limited information with the average score being 37 out of 100. To understand how the status quo has changed, we conduct a follow-up study (v1.1) after 6 months: we score 14 developers against the same 100 indicators. While in v1.0 we searched for publicly available information, in v1.1 developers submit reports on the 100 transparency indicators, potentially including information that was not previously public. We find that developers now score 58 out of 100 on average, a 21 point improvement over v1.0. Much of this increase is driven by developers disclosing information during the v1.1 process: on average, developers disclosed information related to 16.6 indicators that was not previously public. We observe regions of sustained (i.e. across v1.0 and v1.1) and systemic (i.e. across most or all developers) opacity such as on copyright status, data access, data labor, and downstream impact. We publish transparency reports for each developer that consolidate information disclosures: these reports are based on the information disclosed to us via developers. Our findings demonstrate that transparency can be improved in this nascent ecosystem, the Foundation Model Transparency Index likely contributes to these improvements, and policymakers should consider interventions in areas where transparency has not improved.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge