Percy Liang
Shammie
VLAW: Iterative Co-Improvement of Vision-Language-Action Policy and World Model
Feb 15, 2026Abstract:The goal of this paper is to improve the performance and reliability of vision-language-action (VLA) models through iterative online interaction. Since collecting policy rollouts in the real world is expensive, we investigate whether a learned simulator-specifically, an action-conditioned video generation model-can be used to generate additional rollout data. Unfortunately, existing world models lack the physical fidelity necessary for policy improvement: they are predominantly trained on demonstration datasets that lack coverage of many different physical interactions (particularly failure cases) and struggle to accurately model small yet critical physical details in contact-rich object manipulation. We propose a simple iterative improvement algorithm that uses real-world roll-out data to improve the fidelity of the world model, which can then, in turn, be used to generate supplemental synthetic data for improving the VLA model. In our experiments on a real robot, we use this approach to improve the performance of a state-of-the-art VLA model on multiple downstream tasks. We achieve a 39.2% absolute success rate improvement over the base policy and 11.6% improvement from training with the generated synthetic rollouts. Videos can be found at this anonymous website: https://sites.google.com/view/vla-w
When RL Meets Adaptive Speculative Training: A Unified Training-Serving System
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Speculative decoding can significantly accelerate LLM serving, yet most deployments today disentangle speculator training from serving, treating speculator training as a standalone offline modeling problem. We show that this decoupled formulation introduces substantial deployment and adaptation lag: (1) high time-to-serve, since a speculator must be trained offline for a considerable period before deployment; (2) delayed utility feedback, since the true end-to-end decoding speedup is only known after training and cannot be inferred reliably from acceptance rate alone due to model-architecture and system-level overheads; and (3) domain-drift degradation, as the target model is repurposed to new domains and the speculator becomes stale and less effective. To address these issues, we present Aurora, a unified training-serving system that closes the loop by continuously learning a speculator directly from live inference traces. Aurora reframes online speculator learning as an asynchronous reinforcement-learning problem: accepted tokens provide positive feedback, while rejected speculator proposals provide implicit negative feedback that we exploit to improve sample efficiency. Our design integrates an SGLang-based inference server with an asynchronous training server, enabling hot-swapped speculator updates without service interruption. Crucially, Aurora supports day-0 deployment: a speculator can be served immediately and rapidly adapted to live traffic, improving system performance while providing immediate utility feedback. Across experiments, Aurora achieves a 1.5x day-0 speedup on recently released frontier models (e.g., MiniMax M2.1 229B and Qwen3-Coder-Next 80B). Aurora also adapts effectively to distribution shifts in user traffic, delivering an additional 1.25x speedup over a well-trained but static speculator on widely used models (e.g., Qwen3 and Llama3).
Cosmos Policy: Fine-Tuning Video Models for Visuomotor Control and Planning
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Recent video generation models demonstrate remarkable ability to capture complex physical interactions and scene evolution over time. To leverage their spatiotemporal priors, robotics works have adapted video models for policy learning but introduce complexity by requiring multiple stages of post-training and new architectural components for action generation. In this work, we introduce Cosmos Policy, a simple approach for adapting a large pretrained video model (Cosmos-Predict2) into an effective robot policy through a single stage of post-training on the robot demonstration data collected on the target platform, with no architectural modifications. Cosmos Policy learns to directly generate robot actions encoded as latent frames within the video model's latent diffusion process, harnessing the model's pretrained priors and core learning algorithm to capture complex action distributions. Additionally, Cosmos Policy generates future state images and values (expected cumulative rewards), which are similarly encoded as latent frames, enabling test-time planning of action trajectories with higher likelihood of success. In our evaluations, Cosmos Policy achieves state-of-the-art performance on the LIBERO and RoboCasa simulation benchmarks (98.5% and 67.1% average success rates, respectively) and the highest average score in challenging real-world bimanual manipulation tasks, outperforming strong diffusion policies trained from scratch, video model-based policies, and state-of-the-art vision-language-action models fine-tuned on the same robot demonstrations. Furthermore, given policy rollout data, Cosmos Policy can learn from experience to refine its world model and value function and leverage model-based planning to achieve even higher success rates in challenging tasks. We release code, models, and training data at https://research.nvidia.com/labs/dir/cosmos-policy/
RoboReward: General-Purpose Vision-Language Reward Models for Robotics
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:A well-designed reward is critical for effective reinforcement learning-based policy improvement. In real-world robotics, obtaining such rewards typically requires either labor-intensive human labeling or brittle, handcrafted objectives. Vision-language models (VLMs) have shown promise as automatic reward models, yet their effectiveness on real robot tasks is poorly understood. In this work, we aim to close this gap by introducing (1) RoboReward, a robotics reward dataset and benchmark built on large-scale real-robot corpora from Open X-Embodiment (OXE) and RoboArena, and (2) vision-language reward models trained on this dataset (RoboReward 4B/8B). Because OXE is success-heavy and lacks failure examples, we propose a negative examples data augmentation pipeline that generates calibrated negative and near-misses via counterfactual relabeling of successful episodes and temporal clipping to create partial-progress outcomes from the same videos. Using this framework, we build a large training and evaluation dataset spanning diverse tasks and embodiments to test whether state-of-the-art VLMs can reliably provide rewards for robot learning. Our evaluation of open and proprietary VLMs finds that no model excels across tasks, highlighting substantial room for improvement. We then train general-purpose 4B- and 8B-parameter models that outperform much larger VLMs in assigning rewards for short-horizon robotic tasks. Finally, we deploy the 8B model in real-robot reinforcement learning and find that it improves policy learning over Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 while narrowing the gap to RL training with human-provided rewards. We release the full dataset, trained reward models, and evaluation suite on our website to advance the development of general-purpose reward models in robotics: https://crfm.stanford.edu/helm/robo-reward-bench (project website).
Extracting books from production language models
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Many unresolved legal questions over LLMs and copyright center on memorization: whether specific training data have been encoded in the model's weights during training, and whether those memorized data can be extracted in the model's outputs. While many believe that LLMs do not memorize much of their training data, recent work shows that substantial amounts of copyrighted text can be extracted from open-weight models. However, it remains an open question if similar extraction is feasible for production LLMs, given the safety measures these systems implement. We investigate this question using a two-phase procedure: (1) an initial probe to test for extraction feasibility, which sometimes uses a Best-of-N (BoN) jailbreak, followed by (2) iterative continuation prompts to attempt to extract the book. We evaluate our procedure on four production LLMs -- Claude 3.7 Sonnet, GPT-4.1, Gemini 2.5 Pro, and Grok 3 -- and we measure extraction success with a score computed from a block-based approximation of longest common substring (nv-recall). With different per-LLM experimental configurations, we were able to extract varying amounts of text. For the Phase 1 probe, it was unnecessary to jailbreak Gemini 2.5 Pro and Grok 3 to extract text (e.g, nv-recall of 76.8% and 70.3%, respectively, for Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone), while it was necessary for Claude 3.7 Sonnet and GPT-4.1. In some cases, jailbroken Claude 3.7 Sonnet outputs entire books near-verbatim (e.g., nv-recall=95.8%). GPT-4.1 requires significantly more BoN attempts (e.g., 20X), and eventually refuses to continue (e.g., nv-recall=4.0%). Taken together, our work highlights that, even with model- and system-level safeguards, extraction of (in-copyright) training data remains a risk for production LLMs.
The 2025 Foundation Model Transparency Index
Dec 11, 2025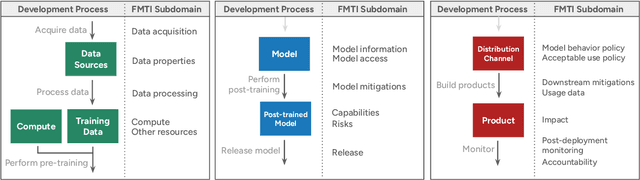
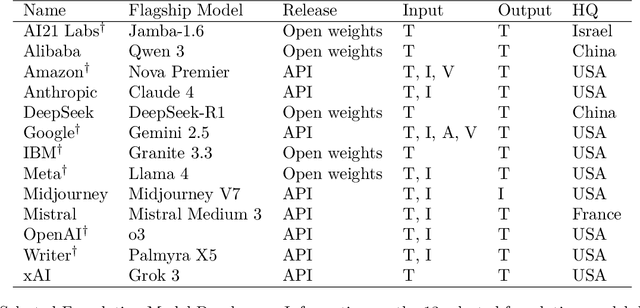
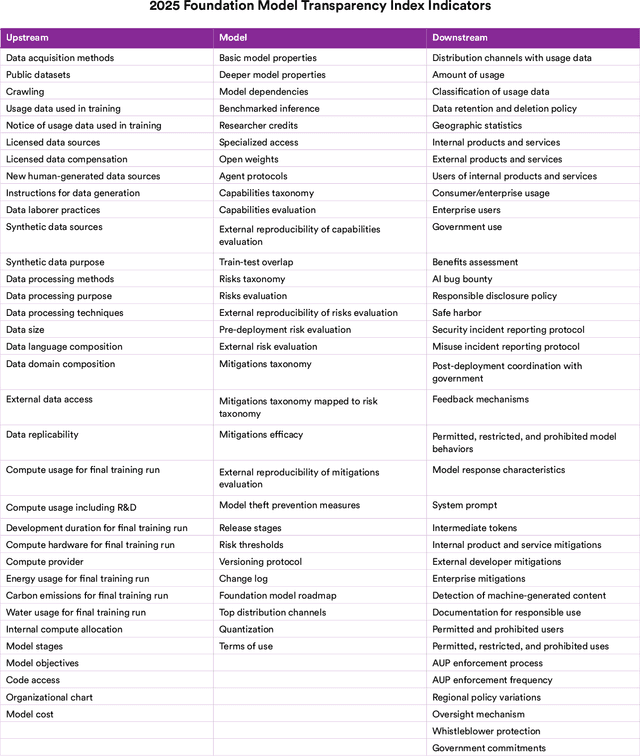
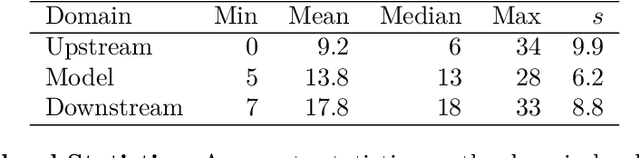
Abstract:Foundation model developers are among the world's most important companies. As these companies become increasingly consequential, how do their transparency practices evolve? The 2025 Foundation Model Transparency Index is the third edition of an annual effort to characterize and quantify the transparency of foundation model developers. The 2025 FMTI introduces new indicators related to data acquisition, usage data, and monitoring and evaluates companies like Alibaba, DeepSeek, and xAI for the first time. The 2024 FMTI reported that transparency was improving, but the 2025 FMTI finds this progress has deteriorated: the average score out of 100 fell from 58 in 2024 to 40 in 2025. Companies are most opaque about their training data and training compute as well as the post-deployment usage and impact of their flagship models. In spite of this general trend, IBM stands out as a positive outlier, scoring 95, in contrast to the lowest scorers, xAI and Midjourney, at just 14. The five members of the Frontier Model Forum we score end up in the middle of the Index: we posit that these companies avoid reputational harms from low scores but lack incentives to be transparency leaders. As policymakers around the world increasingly mandate certain types of transparency, this work reveals the current state of transparency for foundation model developers, how it may change given newly enacted policy, and where more aggressive policy interventions are necessary to address critical information deficits.
Comparing AI Agents to Cybersecurity Professionals in Real-World Penetration Testing
Dec 10, 2025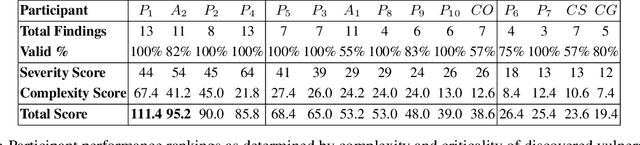
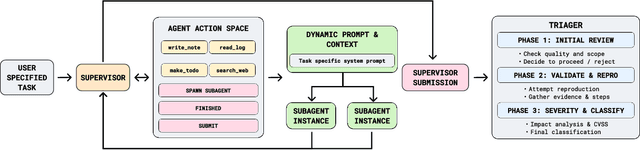
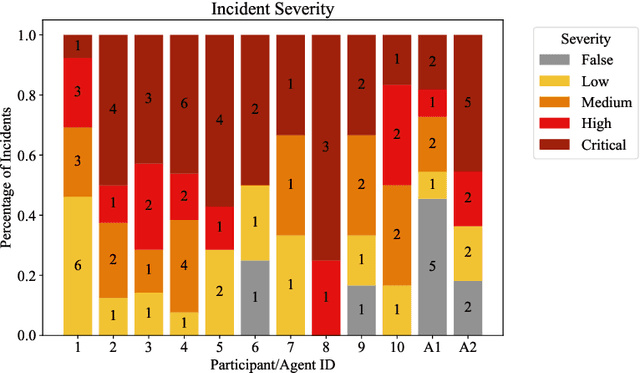
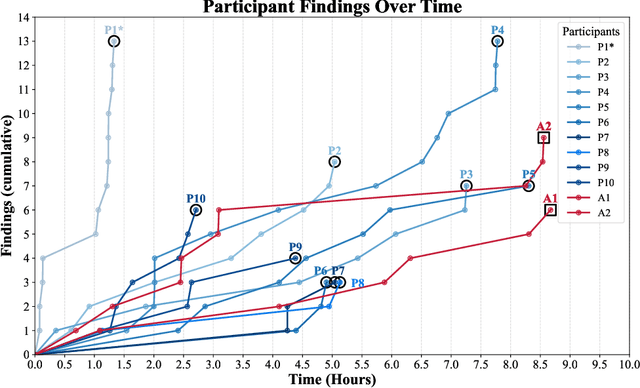
Abstract:We present the first comprehensive evaluation of AI agents against human cybersecurity professionals in a live enterprise environment. We evaluate ten cybersecurity professionals alongside six existing AI agents and ARTEMIS, our new agent scaffold, on a large university network consisting of ~8,000 hosts across 12 subnets. ARTEMIS is a multi-agent framework featuring dynamic prompt generation, arbitrary sub-agents, and automatic vulnerability triaging. In our comparative study, ARTEMIS placed second overall, discovering 9 valid vulnerabilities with an 82% valid submission rate and outperforming 9 of 10 human participants. While existing scaffolds such as Codex and CyAgent underperformed relative to most human participants, ARTEMIS demonstrated technical sophistication and submission quality comparable to the strongest participants. We observe that AI agents offer advantages in systematic enumeration, parallel exploitation, and cost -- certain ARTEMIS variants cost $18/hour versus $60/hour for professional penetration testers. We also identify key capability gaps: AI agents exhibit higher false-positive rates and struggle with GUI-based tasks.
Beat the long tail: Distribution-Aware Speculative Decoding for RL Training
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning(RL) post-training has become essential for aligning large language models (LLMs), yet its efficiency is increasingly constrained by the rollout phase, where long trajectories are generated token by token. We identify a major bottleneck:the long-tail distribution of rollout lengths, where a small fraction of long generations dominates wall clock time and a complementary opportunity; the availability of historical rollouts that reveal stable prompt level patterns across training epochs. Motivated by these observations, we propose DAS, a Distribution Aware Speculative decoding framework that accelerates RL rollouts without altering model outputs. DAS integrates two key ideas: an adaptive, nonparametric drafter built from recent rollouts using an incrementally maintained suffix tree, and a length aware speculation policy that allocates more aggressive draft budgets to long trajectories that dominate makespan. This design exploits rollout history to sustain acceptance while balancing base and token level costs during decoding. Experiments on math and code reasoning tasks show that DAS reduces rollout time up to 50% while preserving identical training curves, demonstrating that distribution-aware speculative decoding can significantly accelerate RL post training without compromising learning quality.
On the Entropy Calibration of Language Models
Nov 15, 2025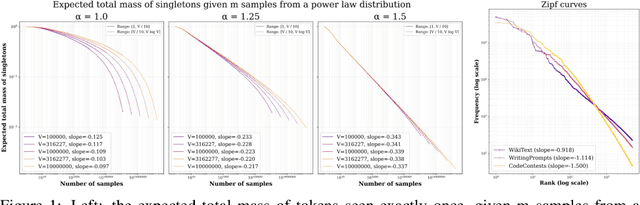
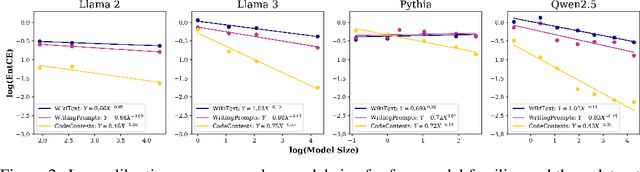
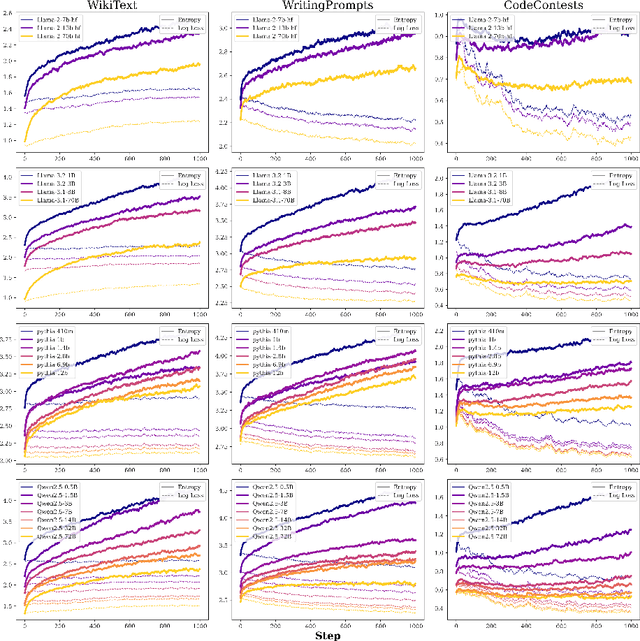
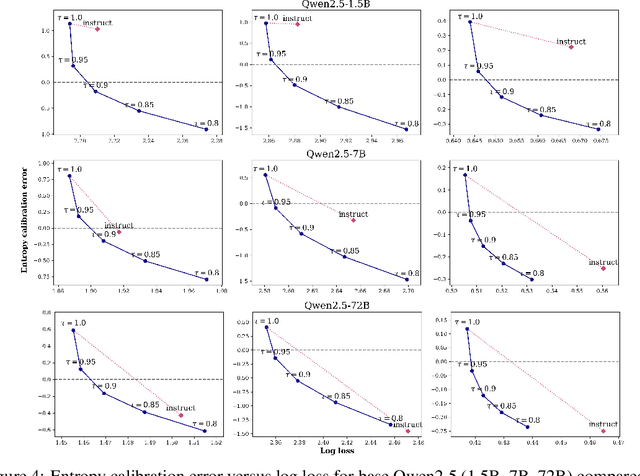
Abstract:We study the problem of entropy calibration, which asks whether a language model's entropy over generations matches its log loss on human text. Past work found that models are miscalibrated, with entropy per step increasing (and text quality decreasing) as generations grow longer. This error accumulation is a fundamental problem in autoregressive models, and the standard solution is to truncate the distribution, which improves text quality at the cost of diversity. In this paper, we ask: is miscalibration likely to improve with scale, and is it theoretically possible to calibrate without tradeoffs? To build intuition, we first study a simplified theoretical setting to characterize the scaling behavior of miscalibration with respect to dataset size. We find that the scaling behavior depends on the power law exponent of the data distribution -- in particular, for a power law exponent close to 1, the scaling exponent is close to 0, meaning that miscalibration improves very slowly with scale. Next, we measure miscalibration empirically in language models ranging from 0.5B to 70B parameters. We find that the observed scaling behavior is similar to what is predicted by the simplified setting: our fitted scaling exponents for text are close to 0, meaning that larger models accumulate error at a similar rate as smaller ones. This scaling (or, lack thereof) provides one explanation for why we sample from larger models with similar amounts of truncation as smaller models, even though the larger models are of higher quality. However, truncation is not a satisfying solution because it comes at the cost of increased log loss. In theory, is it even possible to reduce entropy while preserving log loss? We prove that it is possible, if we assume access to a black box which can fit models to predict the future entropy of text.
MLE-Smith: Scaling MLE Tasks with Automated Multi-Agent Pipeline
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:While Language Models (LMs) have made significant progress in automating machine learning engineering (MLE), the acquisition of high-quality MLE training data is significantly constrained. Current MLE benchmarks suffer from low scalability and limited applicability because they rely on static, manually curated tasks, demanding extensive time and manual effort to produce. We introduce MLE-Smith, a fully automated multi-agent pipeline, to transform raw datasets into competition-style MLE challenges through an efficient generate-verify-execute paradigm for scaling MLE tasks with verifiable quality, real-world usability, and rich diversity. The proposed multi-agent pipeline in MLE-Smith drives structured task design and standardized refactoring, coupled with a hybrid verification mechanism that enforces strict structural rules and high-level semantic soundness. It further validates empirical solvability and real-world fidelity through interactive execution. We apply MLE-Smith to 224 of real-world datasets and generate 606 tasks spanning multiple categories, objectives, and modalities, demonstrating that MLE-Smith can work effectively across a wide range of real-world datasets. Evaluation on the generated tasks shows that the performance of eight mainstream and cutting-edge LLMs on MLE-Smith tasks is strongly correlated with their performance on carefully human-designed tasks, highlighting the effectiveness of the MLE-Smith to scaling up MLE tasks, while maintaining task quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge