Andrew Strait
Towards Best Practices for Open Datasets for LLM Training
Jan 14, 2025Abstract:Many AI companies are training their large language models (LLMs) on data without the permission of the copyright owners. The permissibility of doing so varies by jurisdiction: in countries like the EU and Japan, this is allowed under certain restrictions, while in the United States, the legal landscape is more ambiguous. Regardless of the legal status, concerns from creative producers have led to several high-profile copyright lawsuits, and the threat of litigation is commonly cited as a reason for the recent trend towards minimizing the information shared about training datasets by both corporate and public interest actors. This trend in limiting data information causes harm by hindering transparency, accountability, and innovation in the broader ecosystem by denying researchers, auditors, and impacted individuals access to the information needed to understand AI models. While this could be mitigated by training language models on open access and public domain data, at the time of writing, there are no such models (trained at a meaningful scale) due to the substantial technical and sociological challenges in assembling the necessary corpus. These challenges include incomplete and unreliable metadata, the cost and complexity of digitizing physical records, and the diverse set of legal and technical skills required to ensure relevance and responsibility in a quickly changing landscape. Building towards a future where AI systems can be trained on openly licensed data that is responsibly curated and governed requires collaboration across legal, technical, and policy domains, along with investments in metadata standards, digitization, and fostering a culture of openness.
The Reality of AI and Biorisk
Dec 02, 2024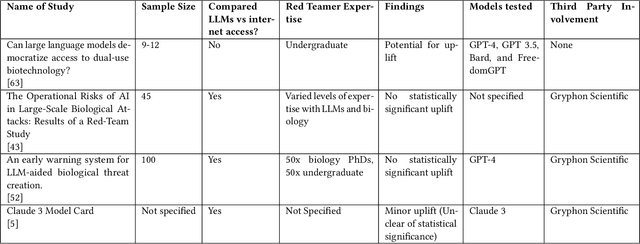
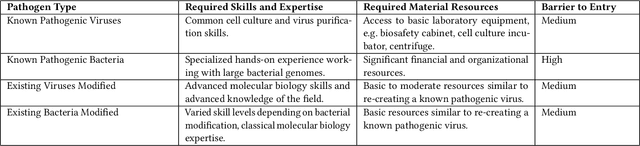
Abstract:To accurately and confidently answer the question 'could an AI model or system increase biorisk', it is necessary to have both a sound theoretical threat model for how AI models or systems could increase biorisk and a robust method for testing that threat model. This paper provides an analysis of existing available research surrounding two AI and biorisk threat models: 1) access to information and planning via large language models (LLMs), and 2) the use of AI-enabled biological tools (BTs) in synthesizing novel biological artifacts. We find that existing studies around AI-related biorisk are nascent, often speculative in nature, or limited in terms of their methodological maturity and transparency. The available literature suggests that current LLMs and BTs do not pose an immediate risk, and more work is needed to develop rigorous approaches to understanding how future models could increase biorisks. We end with recommendations about how empirical work can be expanded to more precisely target biorisk and ensure rigor and validity of findings.
Going public: the role of public participation approaches in commercial AI labs
Jun 16, 2023Abstract:In recent years, discussions of responsible AI practices have seen growing support for "participatory AI" approaches, intended to involve members of the public in the design and development of AI systems. Prior research has identified a lack of standardised methods or approaches for how to use participatory approaches in the AI development process. At present, there is a dearth of evidence on attitudes to and approaches for participation in the sites driving major AI developments: commercial AI labs. Through 12 semi-structured interviews with industry practitioners and subject-matter experts, this paper explores how commercial AI labs understand participatory AI approaches and the obstacles they have faced implementing these practices in the development of AI systems and research. We find that while interviewees view participation as a normative project that helps achieve "societally beneficial" AI systems, practitioners face numerous barriers to embedding participatory approaches in their companies: participation is expensive and resource intensive, it is "atomised" within companies, there is concern about exploitation, there is no incentive to be transparent about its adoption, and it is complicated by a lack of clear context. These barriers result in a piecemeal approach to participation that confers no decision-making power to participants and has little ongoing impact for AI labs. This papers contribution is to provide novel empirical research on the implementation of public participation in commercial AI labs, and shed light on the current challenges of using participatory approaches in this context.
Evaluating the Social Impact of Generative AI Systems in Systems and Society
Jun 12, 2023Abstract:Generative AI systems across modalities, ranging from text, image, audio, and video, have broad social impacts, but there exists no official standard for means of evaluating those impacts and which impacts should be evaluated. We move toward a standard approach in evaluating a generative AI system for any modality, in two overarching categories: what is able to be evaluated in a base system that has no predetermined application and what is able to be evaluated in society. We describe specific social impact categories and how to approach and conduct evaluations in the base technical system, then in people and society. Our framework for a base system defines seven categories of social impact: bias, stereotypes, and representational harms; cultural values and sensitive content; disparate performance; privacy and data protection; financial costs; environmental costs; and data and content moderation labor costs. Suggested methods for evaluation apply to all modalities and analyses of the limitations of existing evaluations serve as a starting point for necessary investment in future evaluations. We offer five overarching categories for what is able to be evaluated in society, each with their own subcategories: trustworthiness and autonomy; inequality, marginalization, and violence; concentration of authority; labor and creativity; and ecosystem and environment. Each subcategory includes recommendations for mitigating harm. We are concurrently crafting an evaluation repository for the AI research community to contribute existing evaluations along the given categories. This version will be updated following a CRAFT session at ACM FAccT 2023.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge