Nicola De Cao
Learning to Plan and Generate Text with Citations
Apr 04, 2024Abstract:The increasing demand for the deployment of LLMs in information-seeking scenarios has spurred efforts in creating verifiable systems, which generate responses to queries along with supporting evidence. In this paper, we explore the attribution capabilities of plan-based models which have been recently shown to improve the faithfulness, grounding, and controllability of generated text. We conceptualize plans as a sequence of questions which serve as blueprints of the generated content and its organization. We propose two attribution models that utilize different variants of blueprints, an abstractive model where questions are generated from scratch, and an extractive model where questions are copied from the input. Experiments on long-form question-answering show that planning consistently improves attribution quality. Moreover, the citations generated by blueprint models are more accurate compared to those obtained from LLM-based pipelines lacking a planning component.
Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:In this report, we present the latest model of the Gemini family, Gemini 1.5 Pro, a highly compute-efficient multimodal mixture-of-experts model capable of recalling and reasoning over fine-grained information from millions of tokens of context, including multiple long documents and hours of video and audio. Gemini 1.5 Pro achieves near-perfect recall on long-context retrieval tasks across modalities, improves the state-of-the-art in long-document QA, long-video QA and long-context ASR, and matches or surpasses Gemini 1.0 Ultra's state-of-the-art performance across a broad set of benchmarks. Studying the limits of Gemini 1.5 Pro's long-context ability, we find continued improvement in next-token prediction and near-perfect retrieval (>99%) up to at least 10M tokens, a generational leap over existing models such as Claude 2.1 (200k) and GPT-4 Turbo (128k). Finally, we highlight surprising new capabilities of large language models at the frontier; when given a grammar manual for Kalamang, a language with fewer than 200 speakers worldwide, the model learns to translate English to Kalamang at a similar level to a person who learned from the same content.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Querying Large Language Models with SQL
Apr 02, 2023



Abstract:In many use-cases, information is stored in text but not available in structured data. However, extracting data from natural language text to precisely fit a schema, and thus enable querying, is a challenging task. With the rise of pre-trained Large Language Models (LLMs), there is now an effective solution to store and use information extracted from massive corpora of text documents. Thus, we envision the use of SQL queries to cover a broad range of data that is not captured by traditional databases by tapping the information in LLMs. To ground this vision, we present Galois, a prototype based on a traditional database architecture, but with new physical operators for querying the underlying LLM. The main idea is to execute some operators of the the query plan with prompts that retrieve data from the LLM. For a large class of SQL queries, querying LLMs returns well structured relations, with encouraging qualitative results. Preliminary experimental results make pre-trained LLMs a promising addition to the field of database systems, introducing a new direction for hybrid query processing. However, we pinpoint several research challenges that must be addressed to build a DBMS that exploits LLMs. While some of these challenges necessitate integrating concepts from the NLP literature, others offer novel research avenues for the DB community.
GenIE: Generative Information Extraction
Dec 15, 2021



Abstract:Structured and grounded representation of text is typically formalized by closed information extraction, the problem of extracting an exhaustive set of (subject, relation, object) triplets that are consistent with a predefined set of entities and relations from a knowledge base schema. Most existing works are pipelines prone to error accumulation, and all approaches are only applicable to unrealistically small numbers of entities and relations. We introduce GenIE (generative information extraction), the first end-to-end autoregressive formulation of closed information extraction. GenIE naturally exploits the language knowledge from the pre-trained transformer by autoregressively generating relations and entities in textual form. Thanks to a new bi-level constrained generation strategy, only triplets consistent with the predefined knowledge base schema are produced. Our experiments show that GenIE is state-of-the-art on closed information extraction, generalizes from fewer training data points than baselines, and scales to a previously unmanageable number of entities and relations. With this work, closed information extraction becomes practical in realistic scenarios, providing new opportunities for downstream tasks. Finally, this work paves the way towards a unified end-to-end approach to the core tasks of information extraction. Code and models available at https://github.com/epfl-dlab/GenIE.
Sparse Interventions in Language Models with Differentiable Masking
Dec 13, 2021



Abstract:There has been a lot of interest in understanding what information is captured by hidden representations of language models (LMs). Typically, interpretation methods i) do not guarantee that the model actually uses the encoded information, and ii) do not discover small subsets of neurons responsible for a considered phenomenon. Inspired by causal mediation analysis, we propose a method that discovers within a neural LM a small subset of neurons responsible for a particular linguistic phenomenon, i.e., subsets causing a change in the corresponding token emission probabilities. We use a differentiable relaxation to approximately search through the combinatorial space. An $L_0$ regularization term ensures that the search converges to discrete and sparse solutions. We apply our method to analyze subject-verb number agreement and gender bias detection in LSTMs. We observe that it is fast and finds better solutions than the alternative (REINFORCE). Our experiments confirm that each of these phenomenons is mediated through a small subset of neurons that do not play any other discernible role.
Highly Parallel Autoregressive Entity Linking with Discriminative Correction
Sep 08, 2021



Abstract:Generative approaches have been recently shown to be effective for both Entity Disambiguation and Entity Linking (i.e., joint mention detection and disambiguation). However, the previously proposed autoregressive formulation for EL suffers from i) high computational cost due to a complex (deep) decoder, ii) non-parallelizable decoding that scales with the source sequence length, and iii) the need for training on a large amount of data. In this work, we propose a very efficient approach that parallelizes autoregressive linking across all potential mentions and relies on a shallow and efficient decoder. Moreover, we augment the generative objective with an extra discriminative component, i.e., a correction term which lets us directly optimize the generator's ranking. When taken together, these techniques tackle all the above issues: our model is >70 times faster and more accurate than the previous generative method, outperforming state-of-the-art approaches on the standard English dataset AIDA-CoNLL. Source code available at https://github.com/nicola-decao/efficient-autoregressive-EL
Editing Factual Knowledge in Language Models
Apr 16, 2021



Abstract:The factual knowledge acquired during pretraining and stored in the parameters of Language Models (LM) can be useful in downstream tasks (e.g., question answering or textual inference). However, some facts can be incorrectly induced or become obsolete over time. We present KnowledgeEditor, a method that can be used to edit this knowledge and, thus, fix 'bugs' or unexpected predictions without the need for expensive re-training or fine-tuning. Besides being computationally efficient, KnowledgeEditor does not require any modifications in LM pre-training (e.g., the use of meta-learning). In our approach, we train a hyper-network with constrained optimization to modify a fact without affecting the rest of the knowledge; the trained hyper-network is then used to predict the weight update at test time. We show KnowledgeEditor's efficacy with two popular architectures and knowledge-intensive tasks: i) a BERT model fine-tuned for fact-checking, and ii) a sequence-to-sequence BART model for question answering. With our method, changing a prediction on the specific wording of a query tends to result in a consistent change in predictions also for its paraphrases. We show that this can be further encouraged by exploiting (e.g., automatically-generated) paraphrases during training. Interestingly, our hyper-network can be regarded as a 'probe' revealing which components of a model need to be changed to manipulate factual knowledge; our analysis shows that the updates tend to be concentrated on a small subset of components. Code at https://github.com/nicola-decao/KnowledgeEditor
Multilingual Autoregressive Entity Linking
Mar 23, 2021



Abstract:We present mGENRE, a sequence-to-sequence system for the Multilingual Entity Linking (MEL) problem -- the task of resolving language-specific mentions to a multilingual Knowledge Base (KB). For a mention in a given language, mGENRE predicts the name of the target entity left-to-right, token-by-token in an autoregressive fashion. The autoregressive formulation allows us to effectively cross-encode mention string and entity names to capture more interactions than the standard dot product between mention and entity vectors. It also enables fast search within a large KB even for mentions that do not appear in mention tables and with no need for large-scale vector indices. While prior MEL works use a single representation for each entity, we match against entity names of as many languages as possible, which allows exploiting language connections between source input and target name. Moreover, in a zero-shot setting on languages with no training data at all, mGENRE treats the target language as a latent variable that is marginalized at prediction time. This leads to over 50% improvements in average accuracy. We show the efficacy of our approach through extensive evaluation including experiments on three popular MEL benchmarks where mGENRE establishes new state-of-the-art results. Code and pre-trained models at https://github.com/facebookresearch/GENRE.
NeurIPS 2020 EfficientQA Competition: Systems, Analyses and Lessons Learned
Jan 01, 2021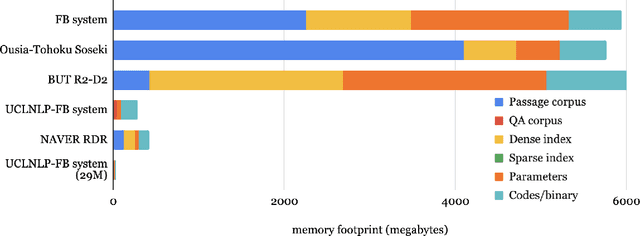
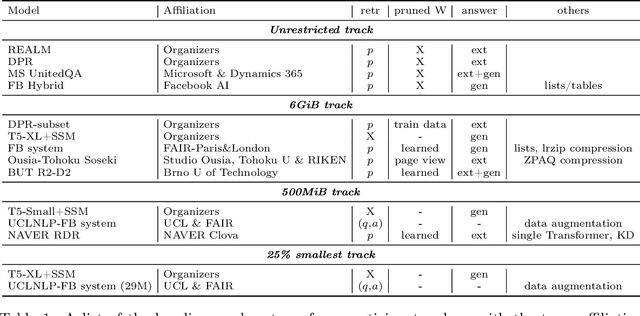
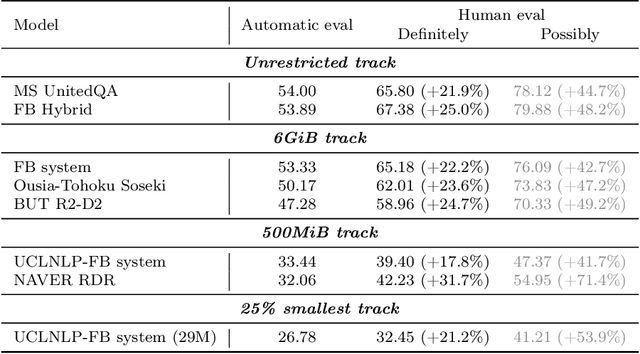
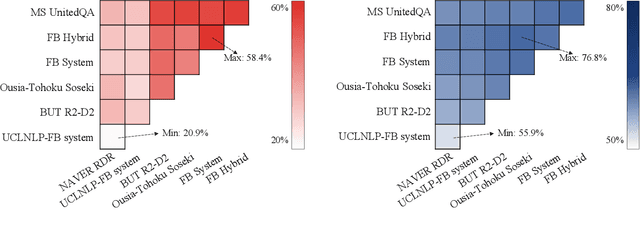
Abstract:We review the EfficientQA competition from NeurIPS 2020. The competition focused on open-domain question answering (QA), where systems take natural language questions as input and return natural language answers. The aim of the competition was to build systems that can predict correct answers while also satisfying strict on-disk memory budgets. These memory budgets were designed to encourage contestants to explore the trade-off between storing large, redundant, retrieval corpora or the parameters of large learned models. In this report, we describe the motivation and organization of the competition, review the best submissions, and analyze system predictions to inform a discussion of evaluation for open-domain QA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge