Chang Shu
All Roads Lead to Rome: Graph-Based Confidence Estimation for Large Language Model Reasoning
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Confidence estimation is essential for the reliable deployment of large language models (LLMs). Existing methods are primarily designed for factual QA tasks and often fail to generalize to reasoning tasks. To address this gap, we propose a set of training-free, graph-based confidence estimation methods tailored to reasoning tasks. Our approach models reasoning paths as directed graphs and estimates confidence by exploiting graph properties such as centrality, path convergence, and path weighting. Experiments with two LLMs on three reasoning datasets demonstrate improved confidence estimation and enhanced performance on two downstream tasks.
StableMotion: Training Motion Cleanup Models with Unpaired Corrupted Data
May 06, 2025
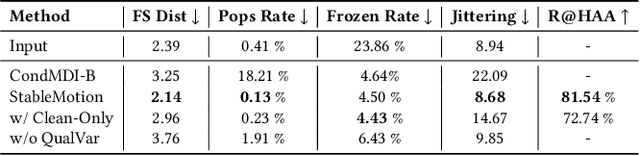
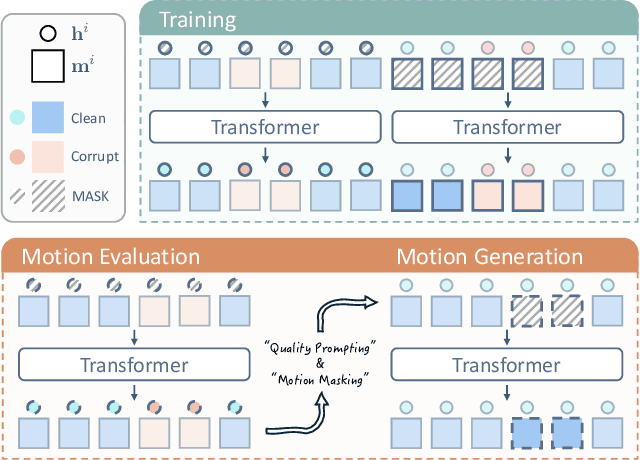
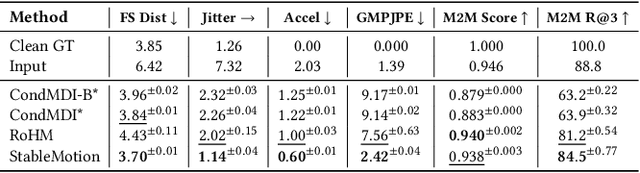
Abstract:Motion capture (mocap) data often exhibits visually jarring artifacts due to inaccurate sensors and post-processing. Cleaning this corrupted data can require substantial manual effort from human experts, which can be a costly and time-consuming process. Previous data-driven motion cleanup methods offer the promise of automating this cleanup process, but often require in-domain paired corrupted-to-clean training data. Constructing such paired datasets requires access to high-quality, relatively artifact-free motion clips, which often necessitates laborious manual cleanup. In this work, we present StableMotion, a simple yet effective method for training motion cleanup models directly from unpaired corrupted datasets that need cleanup. The core component of our method is the introduction of motion quality indicators, which can be easily annotated through manual labeling or heuristic algorithms and enable training of quality-aware motion generation models on raw motion data with mixed quality. At test time, the model can be prompted to generate high-quality motions using the quality indicators. Our method can be implemented through a simple diffusion-based framework, leading to a unified motion generate-discriminate model, which can be used to both identify and fix corrupted frames. We demonstrate that our proposed method is effective for training motion cleanup models on raw mocap data in production scenarios by applying StableMotion to SoccerMocap, a 245-hour soccer mocap dataset containing real-world motion artifacts. The trained model effectively corrects a wide range of motion artifacts, reducing motion pops and frozen frames by 68% and 81%, respectively. See https://youtu.be/3Y7MMAH02B4 for more results.
PLV-IEKF: Consistent Visual-Inertial Odometry using Points, Lines, and Vanishing Points
Nov 08, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we propose an Invariant Extended Kalman Filter (IEKF) based Visual-Inertial Odometry (VIO) using multiple features in man-made environments. Conventional EKF-based VIO usually suffers from system inconsistency and angular drift that naturally occurs in feature-based methods. However, in man-made environments, notable structural regularities, such as lines and vanishing points, offer valuable cues for localization. To exploit these structural features effectively and maintain system consistency, we design a right invariant filter-based VIO scheme incorporating point, line, and vanishing point features. We demonstrate that the conventional additive error definition for point features can also preserve system consistency like the invariant error definition by proving a mathematically equivalent measurement model. And a similar conclusion is established for line features. Additionally, we conduct an invariant filter-based observability analysis proving that vanishing point measurement maintains unobservable directions naturally. Both simulation and real-world tests are conducted to validate our methods' pose accuracy and consistency. The experimental results validate the competitive performance of our method, highlighting its ability to deliver accurate and consistent pose estimation in man-made environments.
POSQA: Probe the World Models of LLMs with Size Comparisons
Oct 20, 2023



Abstract:Embodied language comprehension emphasizes that language understanding is not solely a matter of mental processing in the brain but also involves interactions with the physical and social environment. With the explosive growth of Large Language Models (LLMs) and their already ubiquitous presence in our daily lives, it is becoming increasingly necessary to verify their real-world understanding. Inspired by cognitive theories, we propose POSQA: a Physical Object Size Question Answering dataset with simple size comparison questions to examine the extremity and analyze the potential mechanisms of the embodied comprehension of the latest LLMs. We show that even the largest LLMs today perform poorly under the zero-shot setting. We then push their limits with advanced prompting techniques and external knowledge augmentation. Furthermore, we investigate whether their real-world comprehension primarily derives from contextual information or internal weights and analyse the impact of prompt formats and report bias of different objects. Our results show that real-world understanding that LLMs shaped from textual data can be vulnerable to deception and confusion by the surface form of prompts, which makes it less aligned with human behaviours.
FireAct: Toward Language Agent Fine-tuning
Oct 09, 2023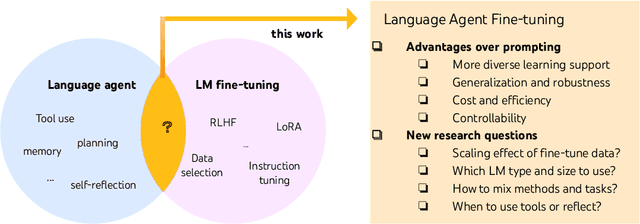
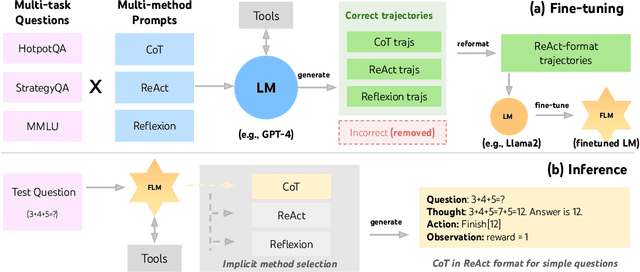

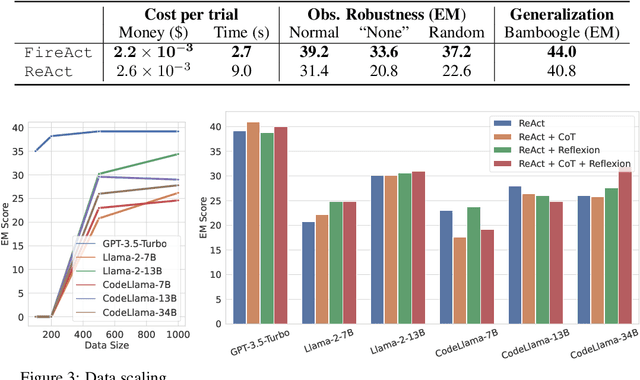
Abstract:Recent efforts have augmented language models (LMs) with external tools or environments, leading to the development of language agents that can reason and act. However, most of these agents rely on few-shot prompting techniques with off-the-shelf LMs. In this paper, we investigate and argue for the overlooked direction of fine-tuning LMs to obtain language agents. Using a setup of question answering (QA) with a Google search API, we explore a variety of base LMs, prompting methods, fine-tuning data, and QA tasks, and find language agents are consistently improved after fine-tuning their backbone LMs. For example, fine-tuning Llama2-7B with 500 agent trajectories generated by GPT-4 leads to a 77% HotpotQA performance increase. Furthermore, we propose FireAct, a novel approach to fine-tuning LMs with trajectories from multiple tasks and prompting methods, and show having more diverse fine-tuning data can further improve agents. Along with other findings regarding scaling effects, robustness, generalization, efficiency and cost, our work establishes comprehensive benefits of fine-tuning LMs for agents, and provides an initial set of experimental designs, insights, as well as open questions toward language agent fine-tuning.
Duet: efficient and scalable hybriD neUral rElation undersTanding
Jul 28, 2023Abstract:Learned cardinality estimation methods have achieved high precision compared to traditional methods. Among learned methods, query-driven approaches face the data and workload drift problem for a long time. Although both query-driven and hybrid methods are proposed to avoid this problem, even the state-of-the-art of them suffer from high training and estimation costs, limited scalability, instability, and long-tailed distribution problem on high cardinality and high-dimensional tables, which seriously affects the practical application of learned cardinality estimators. In this paper, we prove that most of these problems are directly caused by the widely used progressive sampling. We solve this problem by introducing predicates information into the autoregressive model and propose Duet, a stable, efficient, and scalable hybrid method to estimate cardinality directly without sampling or any non-differentiable process, which can not only reduces the inference complexity from O(n) to O(1) compared to Naru and UAE but also achieve higher accuracy on high cardinality and high-dimensional tables. Experimental results show that Duet can achieve all the design goals above and be much more practical and even has a lower inference cost on CPU than that of most learned methods on GPU.
Do LLMs Understand Social Knowledge? Evaluating the Sociability of Large Language Models with SocKET Benchmark
May 24, 2023



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been shown to perform well at a variety of syntactic, discourse, and reasoning tasks. While LLMs are increasingly deployed in many forms including conversational agents that interact with humans, we lack a grounded benchmark to measure how well LLMs understand \textit{social} language. Here, we introduce a new theory-driven benchmark, SocKET, that contains 58 NLP tasks testing social knowledge which we group into five categories: humor & sarcasm, offensiveness, sentiment & emotion, and trustworthiness. In tests on the benchmark, we demonstrate that current models attain only moderate performance but reveal significant potential for task transfer among different types and categories of tasks, which were predicted from theory. Through zero-shot evaluations, we show that pretrained models already possess some innate but limited capabilities of social language understanding and training on one category of tasks can improve zero-shot testing on others. Our benchmark provides a systematic way to analyze model performance on an important dimension of language and points to clear room for improvement to build more socially-aware LLMs. The associated resources are released at https://github.com/minjechoi/SOCKET.
Pre-trained Language Models as Re-Annotators
May 11, 2022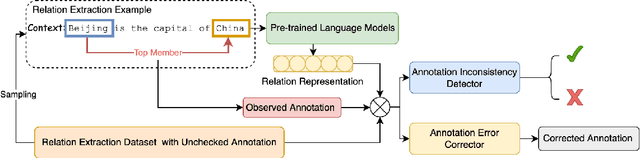

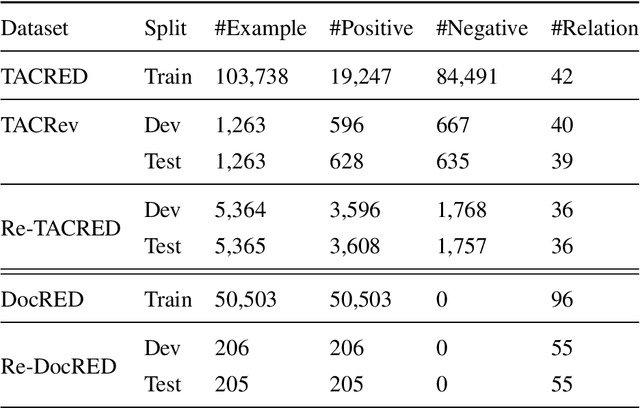
Abstract:Annotation noise is widespread in datasets, but manually revising a flawed corpus is time-consuming and error-prone. Hence, given the prior knowledge in Pre-trained Language Models and the expected uniformity across all annotations, we attempt to reduce annotation noise in the corpus through two tasks automatically: (1) Annotation Inconsistency Detection that indicates the credibility of annotations, and (2) Annotation Error Correction that rectifies the abnormal annotations. We investigate how to acquire semantic sensitive annotation representations from Pre-trained Language Models, expecting to embed the examples with identical annotations to the mutually adjacent positions even without fine-tuning. We proposed a novel credibility score to reveal the likelihood of annotation inconsistencies based on the neighbouring consistency. Then, we fine-tune the Pre-trained Language Models based classifier with cross-validation for annotation correction. The annotation corrector is further elaborated with two approaches: (1) soft labelling by Kernel Density Estimation and (2) a novel distant-peer contrastive loss. We study the re-annotation in relation extraction and create a new manually revised dataset, Re-DocRED, for evaluating document-level re-annotation. The proposed credibility scores show promising agreement with human revisions, achieving a Binary F1 of 93.4 and 72.5 in detecting inconsistencies on TACRED and DocRED respectively. Moreover, the neighbour-aware classifiers based on distant-peer contrastive learning and uncertain labels achieve Macro F1 up to 66.2 and 57.8 in correcting annotations on TACRED and DocRED respectively. These improvements are not merely theoretical: Rather, automatically denoised training sets demonstrate up to 3.6% performance improvement for state-of-the-art relation extraction models.
SideRT: A Real-time Pure Transformer Architecture for Single Image Depth Estimation
Apr 29, 2022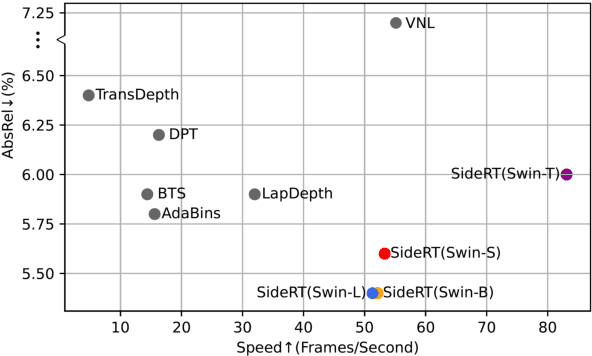
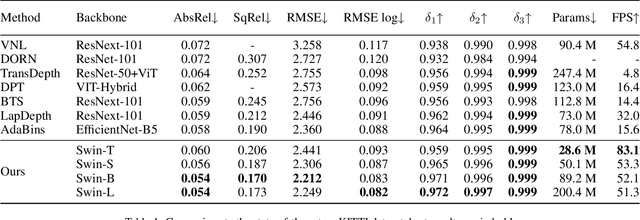
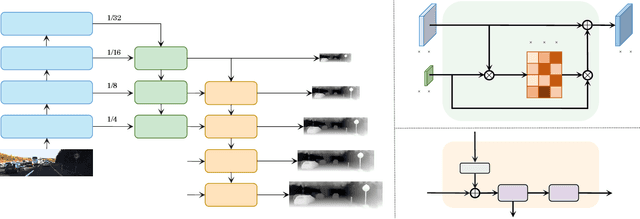
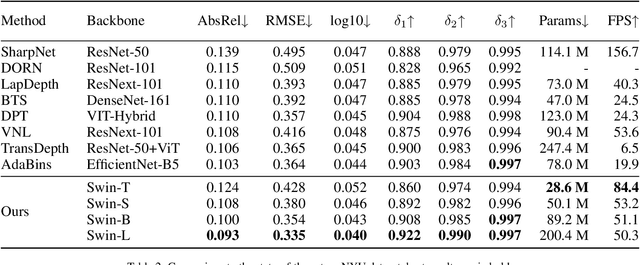
Abstract:Since context modeling is critical for estimating depth from a single image, researchers put tremendous effort into obtaining global context. Many global manipulations are designed for traditional CNN-based architectures to overcome the locality of convolutions. Attention mechanisms or transformers originally designed for capturing long-range dependencies might be a better choice, but usually complicates architectures and could lead to a decrease in inference speed. In this work, we propose a pure transformer architecture called SideRT that can attain excellent predictions in real-time. In order to capture better global context, Cross-Scale Attention (CSA) and Multi-Scale Refinement (MSR) modules are designed to work collaboratively to fuse features of different scales efficiently. CSA modules focus on fusing features of high semantic similarities, while MSR modules aim to fuse features at corresponding positions. These two modules contain a few learnable parameters without convolutions, based on which a lightweight yet effective model is built. This architecture achieves state-of-the-art performances in real-time (51.3 FPS) and becomes much faster with a reasonable performance drop on a smaller backbone Swin-T (83.1 FPS). Furthermore, its performance surpasses the previous state-of-the-art by a large margin, improving AbsRel metric 6.9% on KITTI and 9.7% on NYU. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to show that transformer-based networks can attain state-of-the-art performance in real-time in the single image depth estimation field. Code will be made available soon.
Deep Multi-Branch Aggregation Network for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation in Street Scenes
Mar 08, 2022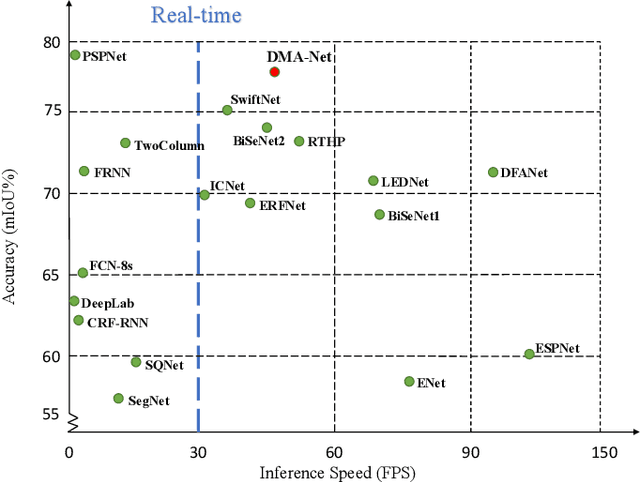

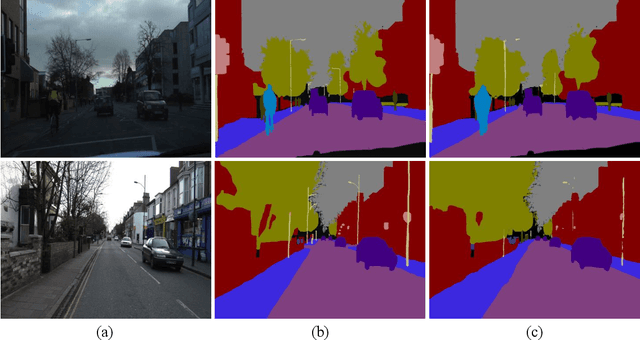
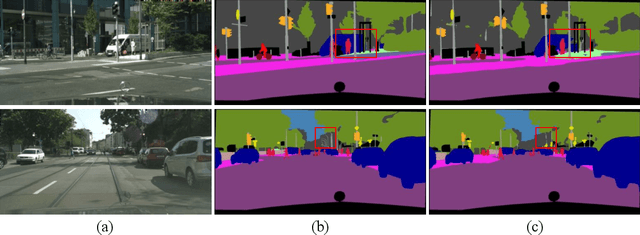
Abstract:Real-time semantic segmentation, which aims to achieve high segmentation accuracy at real-time inference speed, has received substantial attention over the past few years. However, many state-of-the-art real-time semantic segmentation methods tend to sacrifice some spatial details or contextual information for fast inference, thus leading to degradation in segmentation quality. In this paper, we propose a novel Deep Multi-branch Aggregation Network (called DMA-Net) based on the encoder-decoder structure to perform real-time semantic segmentation in street scenes. Specifically, we first adopt ResNet-18 as the encoder to efficiently generate various levels of feature maps from different stages of convolutions. Then, we develop a Multi-branch Aggregation Network (MAN) as the decoder to effectively aggregate different levels of feature maps and capture the multi-scale information. In MAN, a lattice enhanced residual block is designed to enhance feature representations of the network by taking advantage of the lattice structure. Meanwhile, a feature transformation block is introduced to explicitly transform the feature map from the neighboring branch before feature aggregation. Moreover, a global context block is used to exploit the global contextual information. These key components are tightly combined and jointly optimized in a unified network. Extensive experimental results on the challenging Cityscapes and CamVid datasets demonstrate that our proposed DMA-Net respectively obtains 77.0% and 73.6% mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) at the inference speed of 46.7 FPS and 119.8 FPS by only using a single NVIDIA GTX 1080Ti GPU. This shows that DMA-Net provides a good tradeoff between segmentation quality and speed for semantic segmentation in street scenes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge